Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microscope
Uploaded by
k75544863Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microscope
Uploaded by
k75544863Copyright:
Available Formats
This document is sponsored by
Better your dreams
The Science Foundation college Kiwanga-Namanve,
Uganda East Africa
Senior one to Senior six,
+256 776 802709, +256 753 802709
Dr. Bbosa Science
Based on sciences, Best for Sciences
Obtain free notes, tests, making guides from: digitalteachers.co.ug
Microscope
Objectives
The learners should be able to
a. Explain the functioning principles of a light and electron microscope
b. Prepare temporary mounts of cell and tissue slides
c. Use simple stains in studying cell and tissues
d. Identify different plant tissues using different laboratory stains
e. Determine cell size
f. Draw and label the different type of epithelial tissues.
Definition
A microscope is an instrument that focuses light.
Types of microscopes
There are two types
Light microscope
A beam of light through the specimen is focused by glass lenses.
Electron microscope
A beam of electron through the specimen is focused by electromagnetic field.
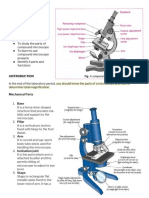
Parts of light microscope Eye piece
Course adjusting knob
Turret
Fine adjusting knob
Objective lens
Arm
Stage
Mirror
Base
Function of parts of microscope
Eye piece: magnifies the image of the specimen
Course adjusting knob: focuses the image of the specimen
Fine adjusting knob: fine tune the focus of the specimen
Turret: rotates and changes the objective lenses
Objective lenses: magnify specimens
Stage: is where the specimen is placed
Mirror: reflects light through the specimen
Preparation of specimen for microscopic observation
- A section of the specimen is to be observed must be very thin to allow light through.
- Stains may help to see parts of specimen clearly.
Comparing light and electron microscope
Light microscope Electron microscope
Advantages disadvantages
- cheap to purchase and operate Very expensive to purchase and operate
- small and potable Very large
- preparation of materials is simple, quick and - preparation of material require skill and is
cheap lengthy
Disadvantage Advantage
- low magnification (x200) - high magnification (x 5000)
- the depth of field is restricted - depth of the field is bigger
Magnification = Size of drawing
Size of specimen
Magnification using s microscope
To determine the total magnification of an image viewed through a microscope, multiply the power of the
eyepiece or ocular lens by the power of the objective lens. If the magnification power of the ocular lens is 10x
and that of the objective lens is 4x, total magnification is 40x.
Resolving power of microscope
Is the ability of a microscope to distinguish fine detail.
++++Exercise
Objective type questions
1. 2012/1/4 The actual diameter of a cell organelle which measures 0.4mm at a
magnification of x400 is
A. 0.01µm
B. 0.1 µm
C. 1.0 µm
D. 0.001 µm
2. 2009/1/13 The resolving power of a microscope it the
A. Ability of the microscope to distinguish fine detail.
B. Clarity of the image formed by the microscope
C. Number of times the image is magnified by the objective lens
D. The power of the microscope to focus very small objects.
3. 2004/1/3 What is the actual length of animal cell that appear 4mm long when viewed
through a magnification of x400?
A. 0.1 µm
B. 1.6 µm
C. 10 µm
D. 100 µm
4. The actual diameter of a cell organelle which measure 0.4 mm at a magnification of x400
A. 0.01
B.
C.
D.
4. The answer is C
𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑟𝑔𝑎𝑛𝑒𝑙𝑙𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑚𝑖𝑐𝑟𝑜𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑝𝑒 (𝑑1 )
Magnification of organelle = 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑟𝑔𝑎𝑛𝑒𝑙𝑙𝑒 (𝑑0 )
Magnification = x 400
Now
d1 : = 0.4mm = 400µm
d0 = ?
400
400 = 𝑑0
400
d0 = = 1µm
400
do = 400
Note that
1mm = 1 x 10-3m
You might also like
- Microscopy Lab 3Document8 pagesMicroscopy Lab 3AhmadNo ratings yet
- Title Allocated Marks Marks: 15 SEPTEMBER 2015Document18 pagesTitle Allocated Marks Marks: 15 SEPTEMBER 2015AisyahNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 EDITED #1Document8 pagesExperiment 1 EDITED #1Ronel MendozaNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument6 pagesMicrosKlenn OrtezaNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPEFelisa Pauline VallarNo ratings yet
- (07Q2W1) MicroscopeDocument44 pages(07Q2W1) MicroscopeAldwinC EspirituNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MicrosDocument11 pagesUnit 1 MicrosDharviNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report BIO122Document12 pagesLaboratory Report BIO122Arissa Syamina100% (1)
- Biology Report (Experiment 2)Document2 pagesBiology Report (Experiment 2)djash92100% (1)
- B1.1 MicroscopesDocument25 pagesB1.1 MicroscopesReef SalterNo ratings yet
- 2018 Microscopy Review 0 PDFDocument12 pages2018 Microscopy Review 0 PDFFelipe Andrés Jorquera100% (1)
- The MicrosopeDocument16 pagesThe MicrosopeMarc Andreo MalalaNo ratings yet
- Using The Microscope: Introductory PracticalDocument11 pagesUsing The Microscope: Introductory Practicalalex zhangNo ratings yet
- Stick The Starter in Your Book and See If You Can Label The Microscope and Answer The Question About MagnifcationDocument19 pagesStick The Starter in Your Book and See If You Can Label The Microscope and Answer The Question About MagnifcationMelody RbayNo ratings yet
- Intruduction and MicroscopesDocument25 pagesIntruduction and Microscopesgangstar9vegasNo ratings yet
- The Microscope and Its Use: Lab ReportDocument4 pagesThe Microscope and Its Use: Lab ReportArbab GillNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1.2 Cell and Microscope - Dr. DomingoDocument8 pagesAnatomy 1.2 Cell and Microscope - Dr. DomingoChristiel John MagtibayNo ratings yet
- E290 Zool11 LaboratoryExerciseNo.1Document4 pagesE290 Zool11 LaboratoryExerciseNo.1Ruth DiangNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab ACTIVITY 1Document6 pagesAnaphy Lab ACTIVITY 1Anonymous giverNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes PDFDocument76 pagesPractical Notes PDFJocund QuNo ratings yet
- Microscopes, Cell Organelles and Cellular OrganizationDocument14 pagesMicroscopes, Cell Organelles and Cellular OrganizationMighty Warrior GSRNo ratings yet
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaNo ratings yet
- 1 MicrosDocument7 pages1 MicrosJachelle KateNo ratings yet
- Principles of MicrosDocument22 pagesPrinciples of MicrosJue LeiNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument3 pagesParts of A Microscopeazaanhasnat345No ratings yet
- Bio-Pr0cess Training HandoutDocument11 pagesBio-Pr0cess Training HandoutKaname KuranNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadDocument48 pagesCell Structure 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- MB Lab ReportDocument7 pagesMB Lab ReportJhoanna Rein DuzonNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleDocument13 pagesExp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Practice Microscope TestDocument4 pagesPractice Microscope Testapi-305603050No ratings yet
- Biology Lab Report #1Document7 pagesBiology Lab Report #1Evernim OmpacanNo ratings yet
- Ge17 Parts of MicroscopeDocument6 pagesGe17 Parts of MicroscopeNICOLE MAE ELEAZARNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Document4 pagesBacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Eloisa LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Microscope: M1U1: The Compound MicroscopeDocument6 pagesMicroscope: M1U1: The Compound MicroscopeYvonne Nerio BadorNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument4 pagesMICROSCOPEJeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- Lab Bio411 As2011bDocument28 pagesLab Bio411 As2011bNURUL AIHAN AHMAD HILMINo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportFatima Shiera BarraquiasNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: The Microscope: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesActivity 2: The Microscope: ObjectivesKhim BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Biology Combined Knowledge OrganiserDocument30 pagesBiology Combined Knowledge OrganiserHumna RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Laboratory Activity #1A: Table 1.1 Parts of A Microscope and Its FunctionsDocument7 pagesLaboratory Report Laboratory Activity #1A: Table 1.1 Parts of A Microscope and Its FunctionsRGems PHNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Lab Microscopes and CellsDocument7 pagesAnswer Key Lab Microscopes and CellslvigilNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - MicrosDocument8 pagesLab 1 - MicrosQuino AmarelaNo ratings yet
- Biology Report1Document7 pagesBiology Report1Hatice Sena YenigünNo ratings yet
- Jeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFDocument3 pagesJeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFJeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Presentation NotesDocument27 pagesMicroscopy Presentation NotesSaid HassanNo ratings yet
- Microscopically DetailsDocument6 pagesMicroscopically DetailsAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 MicroscopeDocument5 pagesExercise 1 MicroscopeNicole Bondad GapazNo ratings yet
- The Lens EquationDocument22 pagesThe Lens EquationCedie SanchezNo ratings yet
- 2096 Light MicrosDocument49 pages2096 Light MicrosSaad Zafar AwanNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroscopeDocument34 pages1 MicroscopeBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document7 pagesLab Report 2aqilNo ratings yet
- The Cell The Microscope?Document18 pagesThe Cell The Microscope?Dan LimNo ratings yet
- MD 2Y2-1B Laboratory Group 1 Week 1 Laboratory ActivityDocument5 pagesMD 2Y2-1B Laboratory Group 1 Week 1 Laboratory ActivityAlea LinksNo ratings yet
- Biology Day 1Document4 pagesBiology Day 1Kapil DhamaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report General Biology (s1) - MicrosDocument11 pagesLab Report General Biology (s1) - MicrosNurul ZahidahNo ratings yet
- 4 Micros PDFDocument6 pages4 Micros PDFNuraini OchadahNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT BIO 1 (Latest)Document7 pagesLAB REPORT BIO 1 (Latest)mwddahtarmiziNo ratings yet
- Act 2 Bot LabDocument3 pagesAct 2 Bot LabAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- NSG20 Exercise 2Document8 pagesNSG20 Exercise 2NANAMI BOLIGOR SUZUKINo ratings yet
- Practical CS ProcessingDocument483 pagesPractical CS ProcessinganAMUstudent100% (2)
- Volleyball Unit PlanDocument4 pagesVolleyball Unit Planapi-214597204No ratings yet
- Trend in Agricultural ProductivityDocument1 pageTrend in Agricultural ProductivityGiaNo ratings yet
- The Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFDocument5 pagesThe Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- DTS Nozzles R3Document2 pagesDTS Nozzles R3meilia teknikNo ratings yet
- m07srt Lesson KmarlinkDocument3 pagesm07srt Lesson Kmarlinkapi-515106812No ratings yet
- Musk Founded Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, or Spacex, in 2002 With TheDocument4 pagesMusk Founded Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, or Spacex, in 2002 With TheLauren Harris0% (1)
- The Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaDocument15 pagesThe Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaAasvogel Felodese Carnivora64% (14)
- MSS SP 69pdfDocument18 pagesMSS SP 69pdfLaura CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Family History Timeline Rubric HonorsDocument1 pageFamily History Timeline Rubric Honorsapi-291510568No ratings yet
- PD750-01 Engine Data Sheet 12-29-20Document4 pagesPD750-01 Engine Data Sheet 12-29-20Service Brags & Hayes, Inc.No ratings yet
- Essential Study SkillsDocument86 pagesEssential Study SkillsFady NgunyuNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument627 pagesMachine DesignlucarNo ratings yet
- Munchies BrochureDocument28 pagesMunchies BrochureIbrahim Diaz LazoNo ratings yet
- SRM 7 EHP 4 Release Notes PDFDocument18 pagesSRM 7 EHP 4 Release Notes PDFMOHAMMED SHEHBAAZNo ratings yet
- L&T Motor CatalogDocument24 pagesL&T Motor CatalogSanjeev DhariwalNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric-Material Based Energy Harvesting Device.Document29 pagesPiezoelectric-Material Based Energy Harvesting Device.jobert100% (1)
- Al Multaqaa Presentation v2Document22 pagesAl Multaqaa Presentation v2Hasaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- EHR StandardsIndia - August 2013-32630521Document54 pagesEHR StandardsIndia - August 2013-32630521kartiksinhNo ratings yet
- Supermini200 (Hi-Res Book) Brochure en Ver1 00Document4 pagesSupermini200 (Hi-Res Book) Brochure en Ver1 00PauloValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- International Rice Research Newsletter Vol12 No.4Document67 pagesInternational Rice Research Newsletter Vol12 No.4ccquintosNo ratings yet
- Buy Wholesale China Popular Outdoor Football Boot For Teenagers Casual High Quality Soccer Shoes FG Ag Graffiti Style & FootballDocument1 pageBuy Wholesale China Popular Outdoor Football Boot For Teenagers Casual High Quality Soccer Shoes FG Ag Graffiti Style & Footballjcdc9chh8dNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper DementiaDocument1 pageReaction Paper DementiaElla MejiaNo ratings yet
- KirbyDocument3 pagesKirbyNorhassanah UtosabuayanNo ratings yet
- CV Old NicDocument4 pagesCV Old NicTensonNo ratings yet
- QLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataDocument242 pagesQLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataRohit Jain100% (1)
- CR-805 Retransfer PrinterDocument2 pagesCR-805 Retransfer PrinterBolivio FelizNo ratings yet
- No Experience ResumeDocument2 pagesNo Experience ResumeNatalia PantojaNo ratings yet
- Sorting Algorithms in Fortran: Dr. Ugur GUVENDocument10 pagesSorting Algorithms in Fortran: Dr. Ugur GUVENDHWANIT MISENo ratings yet
- Police Cranston School Committee Member Stole PTO FundsDocument1 pagePolice Cranston School Committee Member Stole PTO FundsashaydelineNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)