Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Ergonomics
Introduction To Ergonomics
Uploaded by
ed21b049Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Ergonomics
Introduction To Ergonomics
Uploaded by
ed21b049Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Biomechanics Tutorials
Venkatesh Balasubramanian, Ph.D.
Rehabilitation Bioengineering Group
Department of Engineering Design
IIT Madras, Chennai 600036
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
2
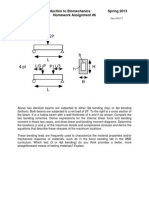
Problem 1:
Shoe has rubber sole. The coefficient of static friction for rubber on
concrete surface is 0.60. The left leg of a person makes an angle of 45 deg
with the floor. A force of 15 lb is acting on the left foot. Determine the
frictional force due to the left foot on the floor.
W = 5 lb
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
3
Problem 2:
An arm is held by two cables: one in the shoulder and the other one in the wrist.
Determine the tension of each cable and the support reactions if a force of 10 lb
is applied to the elbow. D E
10 lb
10 in 9 in
A B C
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
4
Problem 3:
When the hand is holding the 25 N stone, the Hemerus H, assumed to be
smooth, exerts normal forces Fc and Fa on the radius C and ulna A,
respectively, as shown in the figure. If the smallest cross – sectional area
of the ligament at B is 190 mm2 , determine the greatest average tensile
stress to which it is subjected.
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
5
Problem 4:
For the 70 Kg man whose upper limb is shown below, what is the moment
of inertia of:
a) The forearm, for an axis located at the elbow?
b) For forearm + hand, for an axis located at the centre of mass?
Hint:
We can use anthropometric data BY Winter (1979,15). The moment of inertia formula is
I = m*k2, where k is the radius of gyration and m is the segment mass.
Winter’s table:
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
6
Problem 5:
Patient weighs 175 lb. The center of gravity of his thigh lies 8.5 in
above the knee joint, a and that of the leg and foot 8 in. below it.
Where does the center of gravity of the entire lower limb lie in
relation to the knee joint?
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
7
Problem 1:
Calculate the reaction at the elbow when the person holds a metal ball with
mass 3 kg. The forearm’s length is 30 cm. The weight of the forearm is 5 N.
w
15 cm
30 cm
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
8
Problem 2:
A forearm holding a weight is presented in this diagram. There R is the reaction
force at the elbow, B is the muscle force for the biceps, G is the weight of the
forearm and W is the weight in the hand. Let W=20 N and G= 15 N. The forearm
is in equilibrium. Find the muscle force for the biceps B and the reaction force R.
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
9
Problem 3:
Three muscles are the major contributors to flexing the forearm; the biceps,
the brachioradialis, and the brachialis. Determine the force in the biceps
muscle, the joint force reaction, and the joint moment at the elbow for an
individual holding a 10 kg mass with its forearm 90º of flexion. The force in
the brachialis muscle is 5 N and in the brachioradialis is 3.6 N.
The following anatomical data is given by the
author:
Length of forearm and hand: 0.5 m
Mass of forearm and hand: 2 kg
Distance from muscle intersection to elbow:
Biceps: 4 cm
Beachialis: 3.5 cm
Brachioradialis: 20 cm
Angle of muscle at 90 º flexion
Biceps: 80.3º
Beachialis: 68.7º
Brachioradialis: 23º
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
10
Problem 4:
In an athletics event, two persons are pulling a rope. Determine the
internal forces of the member ABC at the point H and the member BCD
at the point I, if the force applied by the two men is 95 N and the mass
of each arm is 3 Kg. The weight of the rope is not considered.
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
11
Problem 5:
A person is eating his lunch and while this action occur the superior teeth
are keeping in contact with the under teeth. If the coefficient of kinetic
friction is 0.20 and the normal force between the teeth is 5 N, estimate the
kinetic friction force.
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
12
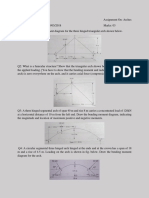
Problem 6:
Consider a woman extending her knee against resistance provided by a
physiotherapist. The mass of the leg (shank + foot) is 5 Kg, located at the center
of mass shown, and 12 mm anterior to the joint. The physiotherapist force of 250
N is applied perpendicular to the leg at a distance of 150 mm from the joint, at an
angle of 8º to horizontal as shown. The quadriceps muscle has a moment arm =
25 mm (applied via the patella tendon at 15º from vertical). What is the
quadriceps muscle force and what is the knee joint (tibio-femoral) force for
equilibrium?
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
13
Thank You !!!
VB – Tutorials, ED3010, July-Nov, 2017
You might also like
- Student Exploration: Muscles and BonesDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Muscles and Bonesabdullah farhanNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument7 pagesFinal ExamrileyNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Bones GizmoDocument9 pagesMuscles and Bones GizmoCharles VollmersNo ratings yet
- Muscles Bones SeDocument7 pagesMuscles Bones SeErupt DawnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Part 2Document21 pagesChapter 1 - Part 2Yanendra SahNo ratings yet
- BME 102 HW 6 SolutionsDocument14 pagesBME 102 HW 6 SolutionsAlexNo ratings yet
- AU Design GuideDocument74 pagesAU Design GuideShin JoonHoNo ratings yet
- A Person Is Performing Slow Arm Curls With A 10-Kg Weight As - QuizletDocument5 pagesA Person Is Performing Slow Arm Curls With A 10-Kg Weight As - Quizlet刘洋No ratings yet
- Offline Homework 6 PDFDocument6 pagesOffline Homework 6 PDFLola Skenzie OladinniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document29 pagesLecture 4علي رضاNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution - 2: Three Continuous Beam Worked ExamplesDocument10 pagesMoment Distribution - 2: Three Continuous Beam Worked Examples형표 김No ratings yet
- HookesLawAPhetLab 1Document8 pagesHookesLawAPhetLab 1arg456No ratings yet
- H 14 May 04 SolutionDocument47 pagesH 14 May 04 SolutionAnonymous 83o62cNo ratings yet
- Joint Structure and Function 5th Edition Levangie Test BankDocument10 pagesJoint Structure and Function 5th Edition Levangie Test Bankkylewyattptdxcgywsa100% (16)
- Muscles Bones SEDocument8 pagesMuscles Bones SEETYMONo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Kevin Farina - Gizmos MusclesBonesSE 2021Document7 pagesKami Export - Kevin Farina - Gizmos MusclesBonesSE 2021Kevin FarinaNo ratings yet
- Physics 104: Health TrackDocument12 pagesPhysics 104: Health TrackAnas SaadNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On The Activity and The Challenge: G Has The Same Value, About 10 M/sDocument1 pageReflecting On The Activity and The Challenge: G Has The Same Value, About 10 M/sReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Tibia Bone AnalysisDocument14 pagesTibia Bone AnalysisVasudev BansalNo ratings yet
- Note 2 - Introduction To Statics and Dynamics in BiomaterialsDocument47 pagesNote 2 - Introduction To Statics and Dynamics in Biomaterialschibuzorosinachi21No ratings yet
- Week 7 - Day 2Document3 pagesWeek 7 - Day 2CARL JUSTINE LADRANo ratings yet
- Physics of Martial ArtsDocument23 pagesPhysics of Martial ArtsJohn Jill T. VillamorNo ratings yet
- Bioguide-Musclemodel 0Document9 pagesBioguide-Musclemodel 0tonybony585960No ratings yet
- Force and Motion Quiz Presentation Colorful IllustratedDocument19 pagesForce and Motion Quiz Presentation Colorful IllustratedEdrose WycocoNo ratings yet
- Science: Force and Motion Law of AccelerationDocument11 pagesScience: Force and Motion Law of AccelerationPaolo AimanNo ratings yet
- O-New Bobath Concept Approach in Adolescent With Traumatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage (Tich) : A Case StudyDocument6 pagesO-New Bobath Concept Approach in Adolescent With Traumatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage (Tich) : A Case StudyRobiatul AdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Pex 02 07Document6 pagesPex 02 07Tasha Magee100% (1)
- Analytical Study of The Tibia Bone Under Static Load Using Finite Element MethodDocument5 pagesAnalytical Study of The Tibia Bone Under Static Load Using Finite Element MethodIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Emg Movimientos de TricepsDocument38 pagesEmg Movimientos de TricepsVictor LopezNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Learning Guide Name: InstructionsDocument17 pagesUnit 5 Learning Guide Name: Instructionsnatalie manNo ratings yet
- The High-Bar and Low-Bar Back-Squats A Biomechanical AnalysisDocument55 pagesThe High-Bar and Low-Bar Back-Squats A Biomechanical AnalysisAlvaro Sánchez SolanaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Static Equilibrium - Solution RevisedDocument6 pagesTutorial 3 - Static Equilibrium - Solution RevisedSlim ShaddysNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in MomentumDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Momentumanalyn hosenillaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in MomentumDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in MomentumBryanJAbulocNo ratings yet
- Team Sports Pe Finals Quizes and Exam PDF FreeDocument32 pagesTeam Sports Pe Finals Quizes and Exam PDF FreeJOSHUA JOSHUANo ratings yet
- ΔΙΚΕΦΑΛΟΣ ΜΗΡΙΑΙΟΣ ACE - HamstringsStudyDocument4 pagesΔΙΚΕΦΑΛΟΣ ΜΗΡΙΑΙΟΣ ACE - HamstringsStudydeepblue9700No ratings yet
- 2121 Trial Final Exam SignedDocument4 pages2121 Trial Final Exam SignedNguyễn Lưu TrườngNo ratings yet
- A - Forces On The Body - Chapter 1Document8 pagesA - Forces On The Body - Chapter 1Balqees MohammedNo ratings yet
- Effect of Bone Shaft Geometry in Its BendingDocument32 pagesEffect of Bone Shaft Geometry in Its BendingShailendra Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 09 - Rotational DynamicsDocument23 pagesCh. 09 - Rotational Dynamicssthembisosthera992No ratings yet
- Homework3 14Document2 pagesHomework3 14anteljohnNo ratings yet
- Am5010 Biomechanics Assignment1-2017Document10 pagesAm5010 Biomechanics Assignment1-2017SivaranjaniNo ratings yet
- Statics SPDocument67 pagesStatics SPDianne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Gizmo Muscles and BonesDocument7 pagesGizmo Muscles and BonesColeson BaehrNo ratings yet
- 27 - Jpts 2015 284Document3 pages27 - Jpts 2015 2849661jackNo ratings yet
- PHY Lab ManualDocument57 pagesPHY Lab ManualswathiNo ratings yet
- Olave Natascha Roies ARCH3B Strength of Materials MidTerm ExamDocument4 pagesOlave Natascha Roies ARCH3B Strength of Materials MidTerm ExamJherick Sandoval TagudinNo ratings yet
- Weekly QuestionsDocument6 pagesWeekly QuestionsLungsodaan NhsNo ratings yet
- School of Health Sciences Bachelor of Occupational Therapy: Biomechanics & Kinesiology (BOCT 1103) Assignment 1Document4 pagesSchool of Health Sciences Bachelor of Occupational Therapy: Biomechanics & Kinesiology (BOCT 1103) Assignment 1thevatnaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Advantage With Pulleys: Free Body DiagramsDocument3 pagesMechanical Advantage With Pulleys: Free Body DiagramsgameraviNo ratings yet
- LungDocument8 pagesLungapi-267335639No ratings yet
- Gizmo - Muscles and BonesDocument7 pagesGizmo - Muscles and BonesMayaNo ratings yet
- Grades 1-12 Daily Lesson LogDocument4 pagesGrades 1-12 Daily Lesson LogPaul GloriaNo ratings yet
- Muscles Bones SEDocument5 pagesMuscles Bones SESalma Mohammad MashaelNo ratings yet
- Terra Rosa E-Magazine Issue 9, December 2011Document42 pagesTerra Rosa E-Magazine Issue 9, December 2011Terra Rosa100% (1)
- Physics Equilibrium QueDocument3 pagesPhysics Equilibrium QueLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- SCGYM 7 3 2015 Article5Document11 pagesSCGYM 7 3 2015 Article5DiegoNo ratings yet
- Physics of The SkeletonDocument12 pagesPhysics of The Skeletonmus321gamilNo ratings yet
- How To Bench: The Definitive Guide: Photo by Adam Palmer, 9for9 MediaDocument94 pagesHow To Bench: The Definitive Guide: Photo by Adam Palmer, 9for9 MediaVicente Gonzalo MarinNo ratings yet
- MRI of the Upper Extremity: Elbow, Wrist, and HandFrom EverandMRI of the Upper Extremity: Elbow, Wrist, and HandBethany U. CasagrandaNo ratings yet
- Magnetostatics PDFDocument63 pagesMagnetostatics PDFShashank KrrishnaNo ratings yet
- Andreason Pipette - AviralDocument7 pagesAndreason Pipette - AviralsaurabhNo ratings yet
- High-Temperature Deformation Behavior and Processing Map of The As Cast Inconel 625 AlloyDocument9 pagesHigh-Temperature Deformation Behavior and Processing Map of The As Cast Inconel 625 Alloy鄭勝元No ratings yet
- 729 Simplified Model of Heat Loss in A Coffee Cup PDFDocument4 pages729 Simplified Model of Heat Loss in A Coffee Cup PDFAdamSultansyahNo ratings yet
- A Micromechanical Muscle Model For Determining TheDocument14 pagesA Micromechanical Muscle Model For Determining TheMazinNo ratings yet
- Sakurai 1.17Document11 pagesSakurai 1.17uberpawsNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 (Singularity Functions & Statitically Indeterminate Beams) 2Document50 pagesTopic 2 (Singularity Functions & Statitically Indeterminate Beams) 2DiShanNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Lrbs in Opensees 3d Basis With Heating of Lead CoreDocument8 pagesModeling of Lrbs in Opensees 3d Basis With Heating of Lead Coreümit özkanNo ratings yet
- Vibrations of Shells and PlatesDocument586 pagesVibrations of Shells and PlatesAres ZhaoNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate TorqueDocument6 pagesHow To Calculate TorqueAiza Caboles100% (1)
- 5.6 The Curl of A Vector FieldDocument1 page5.6 The Curl of A Vector FieldRubensVilhenaFonsecaNo ratings yet
- Gasesous State PuuchoDocument78 pagesGasesous State PuuchoNdbbdh bdbdbNo ratings yet
- Assignment On ArchesDocument2 pagesAssignment On ArchesbharatNo ratings yet
- Full Test-2 PDFDocument23 pagesFull Test-2 PDFrajeshNo ratings yet
- 10.1201 9781003323020-147 ChapterpdfDocument8 pages10.1201 9781003323020-147 ChapterpdfFarjallah Al-AssãadNo ratings yet
- 4 Vector Slide PDFDocument27 pages4 Vector Slide PDFNasibhaNo ratings yet
- Ballistic Performance of Unidirectional Glass Fiber Laminated Composite Plate Under Normal and Oblique ImpactDocument8 pagesBallistic Performance of Unidirectional Glass Fiber Laminated Composite Plate Under Normal and Oblique ImpactVeeturiVarunNo ratings yet
- Agenda: - Basic Logic Gates - Quantum Bit (Qubit) - Quantum Gates & CircuitsDocument42 pagesAgenda: - Basic Logic Gates - Quantum Bit (Qubit) - Quantum Gates & CircuitsAkshay BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Experimental Stress Analysis Two Marks With AnswersDocument24 pagesExperimental Stress Analysis Two Marks With Answersmatrixrajiv34100% (2)
- Exp 2 Thin-Thick Cylinders Analysis (Revised July 2010)Document9 pagesExp 2 Thin-Thick Cylinders Analysis (Revised July 2010)azraiezakiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus DDITDocument80 pagesDetailed Syllabus DDITKafaNo ratings yet
- Ecological Psychology: To Cite This Article: Mayo Martínez-Kahn & León Martínez-Castilla (2010) : The FourthDocument21 pagesEcological Psychology: To Cite This Article: Mayo Martínez-Kahn & León Martínez-Castilla (2010) : The Fourthramkeshmit_413125668No ratings yet
- Air-Quality TechnologyDocument12 pagesAir-Quality TechnologyMurli RamchandranNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws - Dahil Sa Covid19 ACTIVITIESDocument5 pagesGas Laws - Dahil Sa Covid19 ACTIVITIESCharmee EsnaraNo ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019Document3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019Mayur PKNo ratings yet
- 04 Potential ModelsDocument15 pages04 Potential ModelsSam PicassoNo ratings yet
- KCS - CTDocument8 pagesKCS - CTakıle neseNo ratings yet
- M07 - Separation EquipmentDocument48 pagesM07 - Separation Equipmenthoghost123100% (2)
- Exploring Forging Load in Closed-Die Forging: D. Sheth, Santanu Das, A. Chatterjee and A. BhattacharyaDocument6 pagesExploring Forging Load in Closed-Die Forging: D. Sheth, Santanu Das, A. Chatterjee and A. BhattacharyaIlham TanamasNo ratings yet