Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1.1b The Function of The CPU (13) - OCR J277
1.1.1b The Function of The CPU (13) - OCR J277
Uploaded by
emona.mockuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1.1b The Function of The CPU (13) - OCR J277
1.1.1b The Function of The CPU (13) - OCR J277
Uploaded by
emona.mockuCopyright:
Available Formats
ComputerScienceUK.
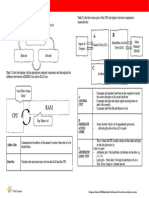
com Fold Line OCR J277 Flashcards - CSUK:Teacher
Q A
The CPU (central processing unit) is a small
What is the CPU? computer component which is responsible for
the processing of data and instructions.
Q A
CPUs are often known as ‘the ‘Brain’ of the
What are CPUs often known as?
Computer’.
Q A
The job of the CPU is to ‘Fetch’, ‘Decode’ and
What is the job of a CPU? ‘Execute’ instructions.
In other words, ‘process data’.
Q A
Processing means things like:
Searching
What examples are there of processing data? Sorting
Calculating
Decision Making
Q A
When you open a program, all the data
When you open a program, where is its
needed for the program to run is loaded onto
instructions and data loaded?
the RAM
Q A
The CPU will fetch data/instructions from the RAM.
What happens during the ‘Fetch’ stage of the To do this it will call the address of the next item via
fetch-decode-execute cycle? the address bus.
The data/instructions are then sent back to the
CPU via the data bus.
Q A
The decode stage is where the CPU makes
What happens during the ‘Decode’ stage of
sense of the instructions and prepares for the
the fetch-decode-execute cycle?
next stage.
Q A
The execute stage is where the data
What happens during the ‘Execute’ stage of processing takes place.
the fetch-decode-execute cycle?
Instructions are carried out on the data.
Computer Science UK – 1.1 The Function of the CPU 1
ComputerScienceUK.com Fold Line OCR J277 Flashcards - CSUK:Teacher
Q A
The CPU consists of:
What are the three main areas that together - Control Unit
form the CPU architecture? - Immediate Access Store (cache)
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Q A
1. Managing and monitoring hardware ensuring
Name 3 jobs that the control unit will carry data goes to the correct hardware.
out. 2. Managing and monitoring input / output signals,
ensuring they are dealt with correctly.
3. Managing the Fetch – Decode -Execute cycle.
Q A
The RAM is far slower at delivering data than the ALU
(arithmetic and logic unit) is at processing it. The IAS (cache) is
What is the purpose of the IAS? far faster at delivering the data than the RAM. The IAS,
therefore, will accept sets of instructions from the RAM so that it
(Immediate Access Store) can supply the ALU at the same speed as the CPU can process.
This means the CPU can work at top speed (not having to wait
for deliveries of data from the RAM).
Q A
The ALU is where the CPU actually carries out the
What is the purpose of the ALU? maths and logic on the data (it processes it). It has
an arithmetic part (where it performs calculations on
(Arithmetic & Logic Unit) the data) and it has a logic part (where it deals with
logical operators such as true/false/equal to etc).
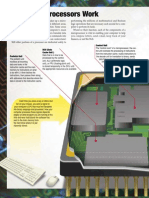
Q A 1. An input device (e.g. keyboard) sends data/instructions to
the CPU. The Control Unit receives these data/instructions.
2. The Control Unit sends this data/instruction into main
Describe the journey of an instruction as it memory (RAM) to be used later.
3. When the time is right, the data will be transferred from
makes its way to through the CPU. main memory into cache (IAS)
4. The data will then be sent to the ALU for processing
5. The control unit will send the processed data back, for
example, to an output device such as a screen or monitor,
or back into main memory for later use.
Q A
Q A
Q A
Computer Science UK – 1.1 The Function of the CPU 2
You might also like
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 1.1 WorkbookDocument8 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 1.1 WorkbookMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Common Computer Problems and SolutionsDocument61 pagesCommon Computer Problems and SolutionsAmieAnneMacedonioTanguinNo ratings yet
- Case Version 6.5 Service ManualDocument276 pagesCase Version 6.5 Service ManualFauza Aryagus80% (5)
- 1.3.1a Networks and Topologies (LANs)Document25 pages1.3.1a Networks and Topologies (LANs)emona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.4.2 The Fetch-Execute Cycle PDFDocument7 pages1.4.2 The Fetch-Execute Cycle PDFtalentNo ratings yet
- PastPapers Harony P4 AR 2022Document409 pagesPastPapers Harony P4 AR 2022Mjstc YTNo ratings yet
- Image ProcessingDocument31 pagesImage ProcessingN180988 MANGARAJU THARUN KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1a CSUK Aianna Raps - Function of The CPU - OCRDocument1 page1.1.1a CSUK Aianna Raps - Function of The CPU - OCRemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - CSS PresentationDocument40 pagesGroup 1 - CSS PresentationlagurashannelleNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Workbook FinishedDocument8 pages1.1 Workbook Finished19subedarzNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1b The Function of The CPU - Answers - BrainQuestDocument1 page1.1.1b The Function of The CPU - Answers - BrainQuestemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- Computer - Archito - Lecture 2Document21 pagesComputer - Archito - Lecture 2Dennis YartelNo ratings yet
- Sec 1.3.2 Computer Architecture & Fetch Execute Cycle: Computer Science 2210 With Majid TahirDocument9 pagesSec 1.3.2 Computer Architecture & Fetch Execute Cycle: Computer Science 2210 With Majid TahirFiyazul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Fetch Cycle Questions2323Document4 pagesFetch Cycle Questions2323Emilia KullutweNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1a Architecture of The CPU - OCR GCSEDocument16 pages1.1.1a Architecture of The CPU - OCR GCSEemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2: The Computer System HardwareDocument17 pagesUNIT 2: The Computer System HardwareRussel RosagaranNo ratings yet
- (Computer Definitions & Basics) Lecture # 01 By: Khurram Bajwa Lecturer. Department of CS & ITDocument29 pages(Computer Definitions & Basics) Lecture # 01 By: Khurram Bajwa Lecturer. Department of CS & ITScorpioPlaysNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation PDFDocument32 pagesPowerPoint Presentation PDFkaloNo ratings yet
- Processing DeviceDocument4 pagesProcessing DeviceKundai ChiwesheNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument24 pagesComputer ArchitectureInsaf ACHOURNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document9 pagesGroup 1chandani jainNo ratings yet
- Instruction Cycle in Computer Architecture - Naukri Code 360Document9 pagesInstruction Cycle in Computer Architecture - Naukri Code 360samwelkiprotich420No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 (2) Comp Science IgcseDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 (2) Comp Science Igcseamartya k singhNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Comp Arch Quick RevisionDocument4 pages3.1 Comp Arch Quick RevisionayeshaNo ratings yet
- Notes TemplateDocument4 pagesNotes TemplateJoe PalmerNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 The Function of The CPUDocument6 pages1.1.1 The Function of The CPUaisha akhlaqNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument15 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- Adrian Tyler - Senior Thesis Rough DraftDocument17 pagesAdrian Tyler - Senior Thesis Rough Draftapi-748077790No ratings yet
- OrganizedDocument189 pagesOrganized20sirohiuNo ratings yet
- ٣محاضرات أساسيات نضام الحاسوبDocument10 pages٣محاضرات أساسيات نضام الحاسوبmuazalamri2006No ratings yet
- Comp SciiDocument94 pagesComp Sciiumar568No ratings yet
- 7 ProcessorDocument5 pages7 ProcessorMuhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Green Teal Futuristic Technology PresentationDocument29 pagesGreen Teal Futuristic Technology Presentationquoctuanisme0610No ratings yet
- Hardware (CH#3)Document6 pagesHardware (CH#3)itslilyjulesssNo ratings yet
- 01 134202 073 8023281785 26112020 081952pmDocument4 pages01 134202 073 8023281785 26112020 081952pmBisma QamarNo ratings yet
- Week 5 (New)Document66 pagesWeek 5 (New)api-3824692No ratings yet
- Instruction Set ArchitectureDocument7 pagesInstruction Set ArchitectureKuzo TribeNo ratings yet
- Class Activity 9 (S60529)Document5 pagesClass Activity 9 (S60529)narienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Architecture - Languages - Operating - SystemsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 - Architecture - Languages - Operating - SystemsMOG FBUINo ratings yet
- The Von Neumann ConceptDocument8 pagesThe Von Neumann ConcepthannietatyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Systemunit PDFDocument42 pagesLecture 5 - Systemunit PDFankNo ratings yet
- How Microprocessors Work: Control Unit DCU (Data Cache Unit) Prefetch UnitDocument2 pagesHow Microprocessors Work: Control Unit DCU (Data Cache Unit) Prefetch UnitAhmad FairuzNo ratings yet
- The Fetch-Decode-Execute CycleDocument1 pageThe Fetch-Decode-Execute CyclePrima Patricia PiguingNo ratings yet
- CSE Practice SolutionsDocument52 pagesCSE Practice Solutionskhasin306No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Central Processing UnitDocument43 pagesChapter 4 - Central Processing UnitmuhammadirfanabdulhadiNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument12 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE ch-1Document38 pagesCOMPUTER ARCHITECTURE ch-1Tolera TamiruNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Notes (Software & Hardware)Document16 pagesComputer Science Notes (Software & Hardware)Muhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 CaoDocument71 pagesUnit-1 CaoKishoreK BNo ratings yet
- L-3 (A Top-Level View of Computer)Document62 pagesL-3 (A Top-Level View of Computer)jubairahmed1678No ratings yet
- GCSE OCR 1.1 The Purpose of The CPU - The Fetch-Execute CycleDocument20 pagesGCSE OCR 1.1 The Purpose of The CPU - The Fetch-Execute CycleMichael O’LearyNo ratings yet
- Module1 Part BDocument25 pagesModule1 Part BSai SileshNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Architecture: Instructor Engr. Zeeshan RazaDocument33 pagesComputer Organization & Architecture: Instructor Engr. Zeeshan RazaRana Gulraiz HassanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document11 pagesAssignment 7ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- ALevel Computer Science KODocument24 pagesALevel Computer Science KOTadiambaNo ratings yet
- I CT Lecture 01 Computer Definitions and Basics Compatibility Mode PDFDocument29 pagesI CT Lecture 01 Computer Definitions and Basics Compatibility Mode PDFAsadNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Digital Circuit Arithmetic Bitwise Logical Integer Binary Numbers Central Processing UnitDocument1 pageDigital Electronics Digital Circuit Arithmetic Bitwise Logical Integer Binary Numbers Central Processing UnitPatuan TampuolonNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument31 pagesComputer ScienceOkay NopeNo ratings yet
- Abrar Ali Os 1Document8 pagesAbrar Ali Os 1abrar aliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - The ProcessorDocument4 pagesUnit 3 - The ProcessorAndreea CraescuNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Based Systems: Lecture No 03 Introduction To Von Neumann ArchitectureDocument32 pagesMicroprocessor Based Systems: Lecture No 03 Introduction To Von Neumann ArchitectureMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- IICT Lecture # 01 Computer Definitions and BasicsDocument34 pagesIICT Lecture # 01 Computer Definitions and BasicsRajab AliNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer For EPFO Part 10Document113 pagesBasics of Computer For EPFO Part 10Himanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Diab Computer 3Document41 pagesDiab Computer 3RadNo ratings yet
- 1.5.1 Operating Systems - BrainQuestDocument2 pages1.5.1 Operating Systems - BrainQuestemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- UCSER Worksheet 1 File Management AnswersDocument2 pagesUCSER Worksheet 1 File Management Answersemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1 Types of Operating System - WORKBOOKDocument5 pages1.2.1 Types of Operating System - WORKBOOKemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.5.1 Operating Systems - Answers - BrainQuestDocument1 page1.5.1 Operating Systems - Answers - BrainQuestemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.8b Issues and Legislation ANSWERSDocument1 page1.8b Issues and Legislation ANSWERSemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Issues and LegislationDocument13 pages1.8 Issues and Legislationemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- Ethical, Legal, Cultural and Environmental Concerns - GCSEDocument29 pagesEthical, Legal, Cultural and Environmental Concerns - GCSEemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1a GCSE Lesson Retrieval Practice (Assessments) Answers - Function of The CPU (OCR)Document3 pages1.1.1a GCSE Lesson Retrieval Practice (Assessments) Answers - Function of The CPU (OCR)emona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1 Operating Systems SLIDESDocument35 pages1.2.1 Operating Systems SLIDESemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1 Operating Systems CLASSWORKDocument9 pages1.2.1 Operating Systems CLASSWORKemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.2.3 Translators and Compilation - StudentDocument27 pages1.2.3 Translators and Compilation - Studentemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.2 Wired, WiFi and Protocols (34) - OCR J277Document5 pages1.3.2 Wired, WiFi and Protocols (34) - OCR J277emona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.2 Wired and Wireless Networks, Protocols and Layers - Workbook OCR GCSE ANSWERSDocument1 page1.3.2 Wired and Wireless Networks, Protocols and Layers - Workbook OCR GCSE ANSWERSemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1a Architecture of The CPU - Workbook OCR GCSE ANSWERSDocument1 page1.1.1a Architecture of The CPU - Workbook OCR GCSE ANSWERSemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To TKinter - Windows, Labels, Entry Boxes, Buttons and Text BoxesDocument21 pages01 Introduction To TKinter - Windows, Labels, Entry Boxes, Buttons and Text Boxesemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1a GCSE Lesson Retrieval Practice (Assessments) - Function of The CPU (OCR)Document2 pages1.1.1a GCSE Lesson Retrieval Practice (Assessments) - Function of The CPU (OCR)emona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.2 Wires, WiFi and Protocols - Answers - BrainQuestDocument1 page1.3.2 Wires, WiFi and Protocols - Answers - BrainQuestemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1a LANs Brainquest ANSWERSDocument1 page1.3.1a LANs Brainquest ANSWERSemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1b WANs Brainquest ANSWERSDocument1 page1.3.1b WANs Brainquest ANSWERSemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.2 Lesson Retrieval Practice ANSWERSDocument2 pages1.3.2 Lesson Retrieval Practice ANSWERSemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1b WANs BrainquestDocument1 page1.3.1b WANs Brainquestemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1a LANs FlashcardsDocument3 pages1.3.1a LANs Flashcardsemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- A197a A198a A199aDocument24 pagesA197a A198a A199aKalipNo ratings yet
- Nforce4m-A1 0Document86 pagesNforce4m-A1 0Meyra SazukeyNo ratings yet
- Microprosser 8085Document15 pagesMicroprosser 8085saigdv1978No ratings yet
- VT07-B23A - Datasheet - 20220824Document2 pagesVT07-B23A - Datasheet - 20220824TRANG LINDANo ratings yet
- Acer Aspire 4740 - 4745 - 5745G Compal LA-5681P NAL90 - NALG0 Rev1.0 SchematicDocument61 pagesAcer Aspire 4740 - 4745 - 5745G Compal LA-5681P NAL90 - NALG0 Rev1.0 SchematicholinsunNo ratings yet
- HP OpenVMS Programming Concepts ManualDocument526 pagesHP OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manualbilalahmedq87No ratings yet
- AMD Networking Solutions On Zen-Based Processors - For CustomersDocument35 pagesAMD Networking Solutions On Zen-Based Processors - For CustomersFamily LinNo ratings yet
- 15 6 Inch RK3288 Android Tablet Support POE From HOPESTAR ElinaDocument1 page15 6 Inch RK3288 Android Tablet Support POE From HOPESTAR ElinaAnut TangkijvorachaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Types of ComputerDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - Types of ComputerHazel Mae EbaritaNo ratings yet
- Book Intro To Information TechnologyDocument44 pagesBook Intro To Information TechnologymuheFace100% (1)
- Computer Link Ethernet DriverDocument30 pagesComputer Link Ethernet DriverCristian CanazaNo ratings yet
- Products: Nuc7I3Bnk, Nuc7I3Bnh, Nuc7I5Bnk, Nuc7I5Bnh, NUC7i7BNHDocument17 pagesProducts: Nuc7I3Bnk, Nuc7I3Bnh, Nuc7I5Bnk, Nuc7I5Bnh, NUC7i7BNHcaminante992997No ratings yet
- Goldstar Prime2 IsaLDocument4 pagesGoldstar Prime2 IsaLDenes MarschalkoNo ratings yet
- Design A Trustzone-Enalble Soc Using The Xilinx Vivado Cad ToolDocument28 pagesDesign A Trustzone-Enalble Soc Using The Xilinx Vivado Cad ToolNguyen Van ToanNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Release Management: User's Guide Release 12.2Document198 pagesOracle® Release Management: User's Guide Release 12.2yadavdevenderNo ratings yet
- PythoncanDocument3 pagesPythoncanMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Pentasonic Corporation Surveillance & Security SystemDocument2 pagesPentasonic Corporation Surveillance & Security SystemearvngNo ratings yet
- Offboard Storage Guide: Ibm Security QradarDocument54 pagesOffboard Storage Guide: Ibm Security Qradarmohamed saadNo ratings yet
- BR 600 BrochureDocument2 pagesBR 600 BrochureTassieAnnNo ratings yet
- Dheeraj ResumeDocument2 pagesDheeraj ResumePrince KhanNo ratings yet
- Banquet Hall Booking System SynopsisDocument3 pagesBanquet Hall Booking System SynopsisSudipta33% (3)
- 2 IP-20G Introduction v1Document21 pages2 IP-20G Introduction v1IvanNo ratings yet
- DM00035129 - STM32F41xxxDocument156 pagesDM00035129 - STM32F41xxxbatrung2906No ratings yet
- Intel® Server System SR1600URR: Tested Memory and Hardware ListDocument28 pagesIntel® Server System SR1600URR: Tested Memory and Hardware ListHal DeNo ratings yet
- Mic ProjectDocument12 pagesMic Projectsarthakjoshi012No ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument3 pagesTypes of ComputersJohn Philip MalonesNo ratings yet