Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SFC ProcessChart English
SFC ProcessChart English
Uploaded by
Hichem OunisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SFC ProcessChart English
SFC ProcessChart English
Uploaded by
Hichem OunisCopyright:
Available Formats
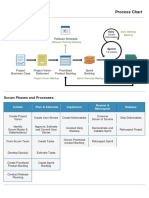
Process Chart
Scrum Flow
Daily
Create Daily Standup
Release Schedule Deliverables Meeting
Release Planning Session
Sprint
1-6 weeks
Project Project Vision Prioritized Sprint Accepted
Business Case Statement Product Backlog Backlog Deliverables
Project Vision Sprint Planning Meeting Sprint Review Meeting
Meeting Retrospect Meeting
Début du cycle
Scrum Phases and Processes
Review &
Initiate Plan & Estimate Implement Release
Retrospect
Create Project Create User Stories Create Deliverables Demonstrate and Ship Deliverables
Vision Validate Sprint
Identify Estimate User Conduct Daily Retrospect Sprint Retrospect Project
Scrum Master & Stories Standup
Stakeholder(s)
Form Scrum Team Commit User Groom Prioritized
Stories Product Backlog
Develop Epics Identify Tasks
Create Prioritized Estimate Tasks
Product Backlog
Conduct Release Create Sprint
Planning Backlog
© 2021 VMEdu, Inc. V4
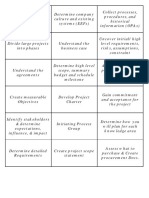
SCRUM ON A PAGE
SCRUM PRINCIPLES ROLES ARTIFACTS MEETINGS
Empirical Process Control CORE: Project Vision Statement Project Vision Meeting
Scrum prescribes making decisions Explains the business need the Stakeholders meet to identify the
based on observation and Product Owner project is intended to meet and business context, business requirements,
experimentation rather than detailed should focus on the problem rather and stakeholder expectations in order to
upfront planning. • Defines the Project Vision and Release than the solution. develop an effective Project Vision
Schedule as the “Voice of the Customer” Statement.
• Defines customer requirements in the form
Prioritized Product Backlog
1
Self-organization of Epics/User Stories and clarifies these 2 Release Planning Meeting
Scrum believes that today’s workers requirements for team members 3
A prioritized list of requirements that, The purpose of this meeting it to develop
4
have much more knowledge to offer • Prioritizes items on the Product Backlog when turned into potentially shippable a Release Plan which defines when
than just their technical expertise and according to business value product functionality, will deliver the various sets of usable functionality or
that they deliver greater value when • Provides Acceptance/Done Criteria and Project Vision. Owned by the Product products will be delivered to the customer.
self-organized. inspects deliverable(s) to validate them Owner.
Sprint Planning Meeting
Collaboration Scrum Master Sprint Goal
The primary output of this meeting is the
In Scrum, product development is a • Ensures that Scrum processes are correctly Proposed by the Product Owner and Sprint Backlog. Task Planning and
shared value-creation process that followed by all Scrum Core Team members, accepted by the team, it is a one Task Estimation are accomplished during
needs all the stakeholders working and including the Product Owner sentence aim for the current Sprint. Sprint Planning. Time-boxed to 8 hours
interacting together to deliver the for a 1 month Sprint.
greatest value. • Ensures that an ideal project environment
exists for the Scrum Team to successfully
complete Sprints
Sprint Backlog
Daily Standup Meeting
3
2
A list of items the Scrum Team commits 1
Value-based Prioritization • Oversees Release Planning Sessions and
to execute in the upcoming Sprint.
convenes other meetings Short, daily meeting time-boxed to
Delivering the greatest value in the Any risk mitigating activities are also 15 minutes. Each Scrum Team member
• Acts as a servant-leader that helps motivate
shortest amount of time requires included as tasks in the Sprint Backlog. answers the following three questions:
and coach the team
prioritization and selection of what
• What have I done since the last meeting?
could be done from what should be
done. Scrum Team Impediment Log • What do I plan to do before the next me
Impediments or obstacles encountered • What impediments or obstacles (if any)
• Typically a small team of 6-10 members with am I currently facing?
Time-boxing by the team should be formally recorded
no further sub-division of teams
by the Scrum Master in an Impediment
Time is treated as a limiting constraint • Cross-functional and self-organizing, the Log.
and time-boxing is used as the rhythm Scrum Team enjoys complete autonomy Sprint Review Meeting
to which all stakeholders work and during a Sprint
The Scrum Team presents the completed
contribute. • Members are generalists across domains and Product Increment Sprint deliverables to the Product Owner
specialists in at least on area
• Responsibility of the work lies with the
$ The potentially shippable deliverable who either accepts or rejects them based
Iterative Development of the team at the end of each Sprint on the defined Acceptance and Done
whole team that satisfies the Acceptance and Criteria. Time-boxed to 4 hours for a 1
The customer may not always be able to Done Criteria. month Sprint.
define very concrete requirements.
The iterative model is more flexible in NON-CORE ROLE: Retrospect Sprint Meeting
accommodating changing requirements.
Team members discuss what went well
Stakeholders during the previous Sprint and what did
• Customers not go well, the goal being to learn and
• Users make improvements in the Sprints to
follow. Time-boxed to 4 hours for a 1
• Sponsors
month Sprint.
Vendors
Scrum Guidance Body
© 2021 VMEdu, Inc. v4
You might also like
- Biology 150 Student Lab Manual 2010Document46 pagesBiology 150 Student Lab Manual 2010Athena Wars0% (1)
- How Buy Sunglasses EbookDocument39 pagesHow Buy Sunglasses EbookSahrul RamadanNo ratings yet
- Agile Project Management: Scrum for BeginnersFrom EverandAgile Project Management: Scrum for BeginnersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- ERP Rollout and Merger - Demerger ProcessDocument15 pagesERP Rollout and Merger - Demerger ProcessDanesh ThangarajNo ratings yet
- Agile Scrum Methodology-Final - SastryDocument34 pagesAgile Scrum Methodology-Final - Sastrybotlasai6846No ratings yet
- Ritas Process Chart Game CardsDocument7 pagesRitas Process Chart Game Cards04ParthPurandareNo ratings yet
- Scrum One PagerDocument2 pagesScrum One Pagertapera_mangeziNo ratings yet
- 8J Magnets and Magnetism Multiple Choice TestDocument4 pages8J Magnets and Magnetism Multiple Choice Testapi-369814693% (15)
- Imprest Funds & ReplenishmentsDocument38 pagesImprest Funds & ReplenishmentsraghavNo ratings yet
- Agile Release CriteriaDocument36 pagesAgile Release Criterianeovik82No ratings yet
- SMC Process ChartDocument2 pagesSMC Process ChartnurtureNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document26 pagesSession 3Anuj KhannaNo ratings yet
- 4 ERP Implementation ApproachDocument47 pages4 ERP Implementation ApproachSherine PaulNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Teacher Made Module Quarter 4 Week 6Document2 pagesScience 9 Teacher Made Module Quarter 4 Week 6Ricky Peñaroyo VentozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson and Demo PlanDocument74 pagesLesson and Demo PlanVikasNo ratings yet
- Scrum Process Chart 1.1Document2 pagesScrum Process Chart 1.1Zameer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Agile Software Development ScrumDocument50 pagesAgile Software Development ScrumKevin Yudistira100% (2)
- Reflective Thinking and Reflective PracticeDocument134 pagesReflective Thinking and Reflective PracticeShiferawuNo ratings yet
- Process Chart (PM Roadmap)Document8 pagesProcess Chart (PM Roadmap)asif 4926No ratings yet
- Session 4Document21 pagesSession 4Anuj KhannaNo ratings yet
- Agile Hybrid Scrum Approach Methodology TemplatesDocument18 pagesAgile Hybrid Scrum Approach Methodology TemplatesAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Delivery Agile Framework TrainingDocument43 pagesDelivery Agile Framework TrainingMuhammad Kashif100% (2)
- Activities On - Blue Print-RealizationDocument4 pagesActivities On - Blue Print-RealizationRama Krishna Vemulapalli100% (1)
- Delivery PlanDocument2 pagesDelivery PlanSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document30 pagesSession 2Anuj KhannaNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Vs ScrumDocument24 pagesPMBOK Vs Scrummilee_yuNo ratings yet
- B1AIP30 - Kickoff Meeting TemplateDocument45 pagesB1AIP30 - Kickoff Meeting TemplateArwin Somo100% (1)
- Steelwedge Rapid Implementation MethodologyDocument13 pagesSteelwedge Rapid Implementation MethodologyNarayan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Makato and The Cowrie Shell Demo LPDocument8 pagesMakato and The Cowrie Shell Demo LPLanie Sanchez EvarolaNo ratings yet
- Scrum Process ChartDocument2 pagesScrum Process ChartSenetor Brian BakariNo ratings yet
- Procesos SCRUMDocument2 pagesProcesos SCRUMRoseNo ratings yet
- Scrum Flow: Process ChartDocument2 pagesScrum Flow: Process ChartArley Fernando GallegoNo ratings yet
- Shubham Assignment PDFDocument10 pagesShubham Assignment PDFlnlNo ratings yet
- 9 IDC New Product Development SimplifiedDocument18 pages9 IDC New Product Development SimplifiedY SAHITHNo ratings yet
- You Exec - Agile Project Management CompleteDocument15 pagesYou Exec - Agile Project Management CompleteanmNo ratings yet
- Scrum Coach Reference March 2024Document82 pagesScrum Coach Reference March 2024Nour El-hoda M. El-GzarNo ratings yet
- Webinar Use Cases and User Stories For Agile RequirementsDocument42 pagesWebinar Use Cases and User Stories For Agile Requirementsmuhammad yusufNo ratings yet
- Lean & Agile: Enterprise FrameworksDocument36 pagesLean & Agile: Enterprise FrameworksDr. Sanaz TehraniNo ratings yet
- Scrum and Agile Software Development Reading::, by Deemer/Benefield/Larman/VoddeDocument31 pagesScrum and Agile Software Development Reading::, by Deemer/Benefield/Larman/VoddesastrybvssrsNo ratings yet
- One Key: Group 4 - Product StrategyDocument22 pagesOne Key: Group 4 - Product StrategyNidhi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Scrum: by Hubert SmitsDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Scrum: by Hubert SmitsvekramNo ratings yet
- Managing Projects Using Oracle Project Management (PJT) & SpreadsheetsDocument19 pagesManaging Projects Using Oracle Project Management (PJT) & SpreadsheetsMichelle TanNo ratings yet
- Quick Scrum PresentationDocument10 pagesQuick Scrum PresentationRugved BhiseNo ratings yet
- Scrum PresentationDocument10 pagesScrum PresentationRugved BhiseNo ratings yet
- Scrum Presentation SPM CVDocument12 pagesScrum Presentation SPM CVPetronela VieruNo ratings yet
- Agile MethodologyDocument25 pagesAgile MethodologynorfaliaNo ratings yet
- Focused MaxA AE VADocument72 pagesFocused MaxA AE VANeeraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Agile Lec With ASB WatermarkDocument91 pagesAgile Lec With ASB Watermarkhirdesh aroraNo ratings yet
- MC SP Module 08 - Supply Planning Tools and ReportingDocument33 pagesMC SP Module 08 - Supply Planning Tools and Reportingsamah sNo ratings yet
- Pastel Watercolor Painted PowerPoint TemplateDocument40 pagesPastel Watercolor Painted PowerPoint TemplateMohamedDhiaElHak SASSINo ratings yet
- ScrumDocument21 pagesScrumapi-3803419No ratings yet
- GL CreationDocument38 pagesGL CreationMK YNo ratings yet
- Learn The Truth About "Agile" Versus "Waterfall": Learn How To Get The Best of Both WorldsDocument13 pagesLearn The Truth About "Agile" Versus "Waterfall": Learn How To Get The Best of Both WorldsMónica AraújoNo ratings yet
- Agile ArtefactsDocument41 pagesAgile ArtefactsFrau CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Scrum and DevOps - 2023-2024Document65 pagesLecture 3 - Scrum and DevOps - 2023-2024guilhermematosn1No ratings yet
- Rita ProcessesDocument7 pagesRita ProcesseshasanNo ratings yet
- VITA Project Management Class: AgendaDocument47 pagesVITA Project Management Class: AgendaNaqi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Task 2: Conference Schedule Project: Greenwichcollege - Edu.auDocument7 pagesTask 2: Conference Schedule Project: Greenwichcollege - Edu.auLei ShenNo ratings yet
- Lean and Agile SAPDocument45 pagesLean and Agile SAPPhil Johnson100% (1)
- Lean and Agile SAP: September 28, 2015Document44 pagesLean and Agile SAP: September 28, 2015NHS REDDYNo ratings yet
- Team CharterDocument3 pagesTeam Charterlamthunguyen001No ratings yet
- Scrum SummaryDocument2 pagesScrum SummaryEnda MolloyNo ratings yet
- How I See The Role of Product Management Working in A Scrum Product Development EnvironmentDocument22 pagesHow I See The Role of Product Management Working in A Scrum Product Development EnvironmentCagalhaoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Scrum. The Agile Manifesto A Statement of ValuesDocument23 pagesAn Introduction To Scrum. The Agile Manifesto A Statement of Valuesjames kimemiaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Project 2013 (MSP) - WBDocument29 pagesMicrosoft Project 2013 (MSP) - WBSundararajan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Thesis StatementDocument12 pagesLesson 4 Thesis StatementJoanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Geography p2 Memo Nov 2019 EnglishDocument12 pagesGeography p2 Memo Nov 2019 EnglishSamkele SibiyaNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes (Eapp) Week 5 and 6Document4 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes (Eapp) Week 5 and 6John MontenegroNo ratings yet
- CPS Assignment 2 PDFDocument5 pagesCPS Assignment 2 PDFMuhd IqbalNo ratings yet
- Geometry Unit 1 PlanDocument5 pagesGeometry Unit 1 Planapi-377800175No ratings yet
- Cleaning and Disinfection:: VehiclesDocument2 pagesCleaning and Disinfection:: VehiclesEugene Mark DollolasaNo ratings yet
- Mini Pupillage Cover LetterDocument7 pagesMini Pupillage Cover Letterfspvwrzh100% (1)
- EN60034 2 1 (2014) e - CodifiedDocument9 pagesEN60034 2 1 (2014) e - Codifiedbay hiçkimseNo ratings yet
- 1S9A30 25-2-10 AVyQS-en PDFDocument156 pages1S9A30 25-2-10 AVyQS-en PDFTaufik Hidayat KurniansyahNo ratings yet
- Estimating Population ProportionLength of Confidence Interval, and Sample Size LPDocument4 pagesEstimating Population ProportionLength of Confidence Interval, and Sample Size LPdeswejusNo ratings yet
- BS Islamic Studies (World Religions)Document112 pagesBS Islamic Studies (World Religions)Hussan BanoNo ratings yet
- APA Citation Guide - Normativa AcadémicaDocument13 pagesAPA Citation Guide - Normativa AcadémicaKaterin CantareroNo ratings yet
- Final CaseDocument98 pagesFinal CaseArpeet NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Scientific Writing and Peer Review Assignment 3 RubricDocument4 pagesScientific Writing and Peer Review Assignment 3 RubricKainatNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Exam With TosDocument6 pagesScience 4 Exam With TosroseNo ratings yet
- B. EstimationDocument16 pagesB. EstimationAyon SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5-6Document2 pagesTutorial 5-6nick thompsonNo ratings yet
- EG Actuator Tester Models 8909-041 and 8909-059: Product Manual 55021 (Revision F, 10/2021)Document28 pagesEG Actuator Tester Models 8909-041 and 8909-059: Product Manual 55021 (Revision F, 10/2021)MussardNo ratings yet
- Retno Fajar Satiti, M.PD.: Marlins English TestDocument21 pagesRetno Fajar Satiti, M.PD.: Marlins English TestretnoNo ratings yet
- Alaska COVID Monthly UpdateDocument17 pagesAlaska COVID Monthly UpdateAlaska's News SourceNo ratings yet
- Dhea Savitri Erwayani: Educational HistoryDocument1 pageDhea Savitri Erwayani: Educational Historydhea savitriNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Chapter 1: General Concept of Stress and Strain: Matzaini KDocument7 pagesTutorial 1 Chapter 1: General Concept of Stress and Strain: Matzaini Kha haNo ratings yet
- Test Report On The California Bearing Ratio AASHTO T 193 - 99Document1 pageTest Report On The California Bearing Ratio AASHTO T 193 - 99Dominto MicoNo ratings yet