Professional Documents
Culture Documents
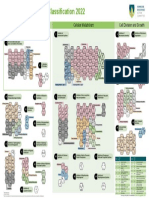
Clasificación Mecanismos de Acción de Insecticidas - 2024
Uploaded by
Pedro RodríguezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clasificación Mecanismos de Acción de Insecticidas - 2024
Uploaded by
Pedro RodríguezCopyright:
Available Formats
Key to Targeted Group 1: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors Group 2: GABA-gated chloride Group 21: M itochondrial com plex I electron
Group 2: GABA-gated chloride Group 21: M itochondrial com plex I electron transport inhibitors Group 22: Voltage-dependent
Physiology (Only representatives actives of the groups are shown) channel antagonists sodium channel blockers
22A
1A 2A Cyclodiene Organochlorines Indoxacarb
Nerve & Oxadiazines
Muscle Carbamates
Rotenone
Pyrimidifen
Growth & O
O Fenazaquin
Development
O
Carbofuran
N S
Methomyl
N
21B
Pyridaben Rotenone
Chlordane Endosulfan Tolfenpyrad
Respiration
Carbosulfan 22B
2B Phenylpyrazoles (Fiproles) 21A METI acaricides and
Insecticide Resistance Action Committee
O S
Semicarbazones Metaflumizone
Midgut P Fenpyroximate Tebufenpyrad insecticides
O S
S
Protein
Mode of Action Classification
Acephate Phorate
Suppressor Group 23: Inhibitors of acetyl-CoA carboxylase Group 24: M itochondrial
1B
Fipronil com plex IV electron transport
Unknown or Organophosphates Ethiprole AlP
Non-specific Chlorpyrifos inhibitors
Aluminium
Group 9: Chordotonal Group 10: M ite growth inhibitors
phosphide PH3 CN-
Spiromesifen Spirotetramat
Group 3: Sodium channel m odulators (Only representative actives of group 3A are shown) organ TRPV channel m odulators affecting CHS1
Phosphine Cyanide
Ca3P2 Zn3P2 salts
Spiropidion
Spirodiclofen
Calcium Zinc
Etoxazole
phosphide 24A phosphide 24B Cyanides
Pymetrozine Diflovidazin 23 Tetronic & Tetramic acid derivatives Spidoxamat Phosphides
10B
Bifenthrin Esfenvalerate Permethrin 9B Pyridine Afidopyropen Etoxazole
DDT azomethine Pyrifluquinazon 10A Hexythiazox
derivatives Clofentezine Group 25: M itochondrial com plex Group 28: Ryanodine Group 29: Chordotonal
lambda- 9D Pyropenes Clofentezine,
Deltamethrin Diflovidazin,Hexythiazox II electron transport inhibitors receptor m odulators organ nicotinam idase
cyhalothrin
3A inhibitors
Methoxychlor 25A beta-Ketonitrile
Pyrethroids N
alpha- Pyrethrins
CN N
derivatives Chlorantraniliprole R=Cl
cypermethrin Etofenprox Tefluthrin 3B DDT, Group 11: M icrobial disruptors of insect m idgut m em branes Cyantraniliprole R=CN
O
Methoxychlor O
Includes transgenic crops expressing Bacillus thuringiensis Bacillus thuringiensis and the O O
S
toxins (however, specific guidance for resistance management insecticidal proteins produced Bacillus sphaericus
Cyenopyrafen I HN
Cyclaniliprole
Group 4: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of transgenic crops is not based on rotation of modes of action) B.t. israelensis, B.t. aitzawai,
O
O Flubendiamide
B.t. kurstaki, B.t. tenebrionis F 3C
(nAChR) com petitive m odulators
HN
O
Rotation between certain specific B.t. microbial products NC CF3
Flonicamid
may provide resistance management benefits for some O Pyflubumide F
CF3
pests. Consult product-specific recommendations. 11A Bacillus thuringiensis 11B Bacillus sphaericus O
O
25B Carboxanilides 29 Flonicamid
Nicotine Flupyradifurone Cyflumetofen 28 Diamides
Sulfoxaflor Tetraniliprole
4B Nicotine 4C Sulfoximines 4D Butenolides Group 12: Inhibitors of m itochondrial ATP synthase
Dinotefuran
O
Group 30: GABA-gated Group 31: Group 32: Nicotinic
S O
O O
N N Sn
Sn O
O
S
O S Cl chloride channel allosteric Baculoviruses Acetylcholine receptor
4F Pyridylidenes
Sn
H H
N
O
m odulators (nAChR) allosteric
Acetamiprid N
Nitenpyram Cl Cl Cl
Cydia pomonella GV
O
Diafenthiuron N
Fenbutatin
m odulators site II
Fenmezoditiaz Azocyclotin oxide Tetradifon
N CF3
Propargite Thaumatotibia
12A Sn
leucotreta GV Anticarsia
Imidacloprid Thiamethoxam
N
Diafenthiuron
OH
12B 12C Propargite gemmatalis MNPV GS-omega/kappa
Cyhexatin
12D Tetradifon Isocycloseram HXTX-Hv1a
Cl N
Organotin miticides Broflanilide
peptide
Triflumezopyrim Helicoverpa
Flupyrimin armigera NPV
Clothianidin
4A
Thiacloprid
Neonicotinoids Group 13: Uncouplers of oxidative phos- Group 14: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) 30 Meta-diamides Fluxametamide 31 Granuloviruses
4E Mesoionics Dicloromezotiaz 32 GS-omega/kappa
phorylation via disruption of proton gradient channel blockers & Isoxazolines & Nucleopolyhedroviruses
HXTX-Hv1a peptide
Br S
O
Group 33: Calcium -
CN
O
S
S Group 34: M itochondrial Group 35: RNA Group 36: Chordotonal
Group 5: Nicotinic Group 6: Glutam ate-gated chloride channel (GluCl)
F3C
N
S
N
S
activated potassium com plex III electron interference m ediated organ m odulators –
Spinetoram acetylcholine receptor allosteric m odulators OH N
S
S
O NH2 SO 3Na
channel (KCa2) transport inhibitors – Qi target suppressors undefined target site
Abamectin R1 = major component R2 = Ethyl O Cl
O O S
major component R = H, 5,6 single
minor component R = CH3, 5,6 double (nAChR) allosteric minor component R2 = Methyl
13
O2N
Sulfluramid S
m odulators site I HO
O
Chlorfenapyr Bensultap
S NH 2
Thiocyclam
S
m odulators site
O O
Pyrroles, N
H Cl
N SO3Na
Spinosad Dinitrophenols, NO2
14 Nereistoxin
O
Thiosultap-
H O
O O
Sulfluramid Cartap
major component R = H
minor component R = CH3 Emamectin
H
N
Lepimectin O
H
R DNOC analogues sodium O O
O N
O hydrochloride O N
benzoate R1 = Ledprona
N
H O O N
O O O O N
OH H F3C
O
O
H
R
Milbemectin O N N
O O
O
OH H
H
Acynonapyr Flometoquin Dimpropyridaz
5 Spinosyns OH
Group 15: Inhibitors of chitin Group 16: Inhibitors of chitin Group 18: Ecdysone receptor
6 Avermectins & Milbemycins O
H
major component R = Ethyl
minor component R = Methyl
biosynthesis affecting CHS1 biosynthesis, type 1 agonists
OH
(Only representative 33 Acynonapyr 34 Flometoquin 35 Ledprona 36 Dimpropyridaz
actives of group are
Group 7: Juvenile horm one shown)
Hydroprene R1 = ethyl, R2 = H
receptor m odulators UN: Unknown or uncertain UNF Fungal agents
Methoprene R1 = isopropyl, R2 – OCH3
7A Juvenile m ode of action Akanthomyces muscarius Ve6
Diflubenzuron Chromafenozide
hormone O Beauveria bassiana strains
7B 7C Buprofezin O N O
Metarhizium brunneum strain F52,
analogues Pyriproxyfen
16 Buprofezin
Kinoprene R1 = propargyl, R2 = H Fenoxycarb Cl
Paecilomyces fumosoroseus
Fenoxycarb Pyriproxyfen O
Apopka strain 97 Burkholderia spp,
Flufenoxuron Bromopropylate O
Wolbachia pipientis (Zap)
Group 17: Moulting disruptors, Azadirachtin Benzoximate
UNB Bacterial
Group 8: M iscellaneous non-specific (m ulti-site) Dipteran
Halofenozide agents (non-Bt)
inhibitors Lufenuron
N S
Cl Cl Oxazosulfyl
OH
O UNM Non-specific
Methoxyfenozide N S
Diatomaceous earth
Methyl
8A Alkyl Na2B4O7·10H2O Novaluron CCl3
m echanical and
bromide Cryolite Dazomet Mineral oil
halides Chinomethionat Dicofol physical disruptors
Borax Tartar emetic Cyromazine
8E Teflubenzuron Tebufenozide
15 Benzoylureas 17 Cyromazine 18 Diacylhydrazines Chenopodium ambrosioides
8D Borates Tartar emetic Cl
S
Cl
O O Mancozeb Benzpyrimoxan near ambrosioides UNE Botanical essence
N
extract
CaSX
Cl O Cl CF3
8C 8F Methyl isothiocyanate including synthetic,
8B Sulfuryl Fatty acid monoesters with
fluoride Fluorides generators Metam
Group 19: Octopam ine Group 20: M itochondrial com plex III electron transport inhibitors – Qo site (Lime sulfur) glycerol or propanediol extracts and
Chloropicrin Chloropicrin Pyridalyl Sulfurs Neem oil
receptor agonists unrefined oils
O
Hydramethylnon O
CF3 O
F 3C O O HN NH
Use of Groups: Use of Sub-Groups:
HN
Poster Notes:
O
N
N O O
N N
H O
• Alternations, sequences or rotations of compounds between • Sub-groups represent distinct structural classes which are O
O N O
• Sub-group 3B: DDT is no longer used in agriculture and therefore this is only applicable for the control of
MoA groups reduce selection for target site resistance. believed to have the same mode of action. insect vectors of human disease, such as mosquitoes, because of a lack of alternatives.
• Applications are arranged into MoA spray windows defined • Sub-groups provide differentiation between compounds that may 19 CF 3
Acequinocyl Fluacrypyrim Bifenazate
• Sub-group10A: Hexythiazox is grouped with Clofentezine because they exhibit cross-resistance even
Amitraz Amitraz
by crop growth stage and pest biology. Several sprays of a bind at the same target site but are structurally different enough though they are structurally distinct. Diflovidazin has been added to this group because it is a close
20A Hydramethylnon 20B Acequinocyl 20C Fluacrypyrim 20D Bifenazate analogue of Clofentezine and is expected to have the same mode of action.
compound may be possible within each spray window, but that risk of metabolic cross-resistance is lower than for close
chemical analogs. • Group 20: While there is strong evidence that Bifenazate acts on the Qo site of Mitochondrial Complex III
successive generations of a pest should not be treated with
compounds from the same MoA group. Local expert advice • Cross-resistance potential between sub-groups is higher than and some Bifenazate resistance mutations confer cross-resistance to Acequinocyl, the sites of action of
Disclaimer: While CropLife International and IRAC make every effort to present accurate and reliable information, they do not Fluacrypyrim and Hydramethylnon have not been determined.
on spray windows and timings should always be followed. between groups, so rotation between sub-groups should be guarantee the accuracy, completeness, efficacy, timeliness, or correct sequencing of such information. Inclusion of active ingredients • Groups 26 & 27 are unassigned
• Groups in the classification whose members do not act at a considered only when there are no alternatives, and only if cross- on the IRAC Code Lists is based on scientific evaluation of their modes of action; it does not provide any kind of testimonial for the use • In some cases, only representative actives are shown.
common target site are exempt from the proscription against resistance does not exist, following consultation with local expert of a product or a judgment on efficacy. CropLife International and IRAC are not responsible for, and expressly disclaim all liability for, • Because of documented cross-resistance between dicofol, bromopropylate and abamectin, these active
rotation within the group (Group 8, 13 and all UN groups: UN, advice. These exceptions are not sustainable, and alternative damages of any kind arising out of use, reference to, or reliance on information provided. Listing of chemical classes or modes of ingredients should not be rotated after each other in an IRM program
UNB, UNE, UNF, UNM, UNP & UNV). options should be sought. action must not be interpreted as approval for use of a compound in a given country. Prior to implementation, each user must
Internal
determine the current registration status in the country of use and strictly adhere to the uses and instructions approved in that country.
IRAC document protected by © Copyright 2024. Poster/Classification Version Edition 11.1, January 2024. Visit www.irac-online.org
You might also like
- Chemistry - Periodic Table - Advanced PDFDocument2 pagesChemistry - Periodic Table - Advanced PDFCA_Ken86% (7)
- BattleTech BattleMaster Blueprint RevDocument1 pageBattleTech BattleMaster Blueprint RevSantiago de la Esperanza100% (1)
- BattleTech BattleMaster Blueprint RevDocument1 pageBattleTech BattleMaster Blueprint RevMenthro100% (1)
- Gigabyte Ga-b250m-Ds3h Rev. 1.0 (PDF Boardview)Document2 pagesGigabyte Ga-b250m-Ds3h Rev. 1.0 (PDF Boardview)AlbertNo ratings yet
- Elephant - Biology, Medicine and SurgeryDocument596 pagesElephant - Biology, Medicine and Surgerymada_superhero100% (2)
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: MathNo ratings yet
- Tabla Periódica de Los Elementos QuímicosDocument2 pagesTabla Periódica de Los Elementos QuímicosGael Josue Vega100% (1)
- Single Line Diagram Adw C Blri Ka DWG 001 - SLD - r04Document1 pageSingle Line Diagram Adw C Blri Ka DWG 001 - SLD - r04Design and Estimation DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- H61M-S2P Rev.3.0 BV PDFDocument1 pageH61M-S2P Rev.3.0 BV PDFLester RodriguezNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-S2P Rev.2.1 BoardviewDocument1 pageGA-H61M-S2P Rev.2.1 Boardviewnishatiwari8285% (13)
- Microbiology and Parasitology Exam ReviewDocument157 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology Exam ReviewJhasmin SalipotNo ratings yet
- How To Choose Your SCENAR DeviceDocument49 pagesHow To Choose Your SCENAR DeviceJohn100% (1)
- Foraminifera and Its ApplicationsDocument23 pagesForaminifera and Its ApplicationsAzhar UddinNo ratings yet
- Environmental PsychologyDocument5 pagesEnvironmental PsychologyKarthi Keyan VeeraNo ratings yet
- Explaining Cancer - Finding Order in Disorder CH 2Document44 pagesExplaining Cancer - Finding Order in Disorder CH 2Jon DevriesNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte GA H61M S2PV.r2.2 BoardviewDocument1 pageGigabyte GA H61M S2PV.r2.2 Boardviewsỹ QuốcNo ratings yet
- DBT BET Question Paper 2009 With Answer KeyDocument22 pagesDBT BET Question Paper 2009 With Answer KeyAbhay Kumar100% (3)
- Adenocarcinoma PulmonarDocument75 pagesAdenocarcinoma PulmonarLigia Micaela García XitamulNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster 2020v2Document1 pageFrac Moa Poster 2020v2NGUYỄN HỮU THÀNHNo ratings yet
- Captura de Tela 2023-03-21 À(s) 7.09.54 PMDocument1 pageCaptura de Tela 2023-03-21 À(s) 7.09.54 PMGroff DiegoNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte Ga-H110m-H-Ddr3-1.0 (PDF Boardview)Document2 pagesGigabyte Ga-H110m-H-Ddr3-1.0 (PDF Boardview)RicardoNo ratings yet
- Model Building Guide: BiochemistryDocument14 pagesModel Building Guide: BiochemistryDaniyar TemirovNo ratings yet
- Cec2 Cec6 Cec9 Cec1 R - USB30 TypecDocument2 pagesCec2 Cec6 Cec9 Cec1 R - USB30 TypecAndy Díaz MorenoNo ratings yet
- Afs Gigabyte Ga-H110m-S2h-Ddr3-1.0 (PDF Boardview)Document2 pagesAfs Gigabyte Ga-H110m-S2h-Ddr3-1.0 (PDF Boardview)Евгений КуценкоNo ratings yet
- FRAC Classification On Mode of Action 2018 (WWW - Frac.info)Document1 pageFRAC Classification On Mode of Action 2018 (WWW - Frac.info)Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte Ga-H110m-S2v-Ddr3 Rev. 1.0 1.01 (PDF Boardview)Document3 pagesGigabyte Ga-H110m-S2v-Ddr3 Rev. 1.0 1.01 (PDF Boardview)juan luis san miguelNo ratings yet
- DNA Repair Pathways PosterDocument1 pageDNA Repair Pathways Posterdyk2100% (1)
- Bitmap H61M-S2PV - REV 2.2Document1 pageBitmap H61M-S2PV - REV 2.2leminhtrildb100% (1)
- 24 A 220 VCA/VCCDocument2 pages24 A 220 VCA/VCCfsahmedNo ratings yet
- Drug Compatibility WangthongDocument3 pagesDrug Compatibility WangthongKanokpol AphichoNo ratings yet
- HRAC MOA Poster January 6 2022Document1 pageHRAC MOA Poster January 6 2022Francisco EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster March FRACDocument1 pageFrac Moa Poster March FRACEliana Garcia ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster FungicidasDocument1 pageFrac Moa Poster Fungicidaskelvin horna guiopNo ratings yet
- Tcon/Power Block/Gamma: Multi DC/DC T-Con ConnectorDocument1 pageTcon/Power Block/Gamma: Multi DC/DC T-Con ConnectorPaulinho MenezesNo ratings yet
- AF S1 SW-1 MaxDocument1 pageAF S1 SW-1 MaxTosikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic MapDocument2 pagesMetabolic Mappablo.s4672No ratings yet
- Bitmaps H110M-DS2-DDR3-1.0Document2 pagesBitmaps H110M-DS2-DDR3-1.0Rin 193No ratings yet
- Placa Mae LGA1151 v2Document2 pagesPlaca Mae LGA1151 v2paranozjpcNo ratings yet
- Cec6 Cec9 Cec2 Cec1: Daec2 Daec3 Daec4Document2 pagesCec6 Cec9 Cec2 Cec1: Daec2 Daec3 Daec4rick martinsNo ratings yet
- Ga H81M DS2 2.1 BVDocument1 pageGa H81M DS2 2.1 BVbao giaNo ratings yet
- Trompeterias EscoreDocument27 pagesTrompeterias Escoremao santacruzNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster 2021Document1 pageFrac Moa Poster 2021Raul Ernesto Meza CabreraNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster 2022Document1 pageFrac Moa Poster 2022Fernanda Amaral FariaNo ratings yet
- GA H61M S2PV Rev.2.1 BitmapDocument1 pageGA H61M S2PV Rev.2.1 Bitmapsỹ QuốcNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-S1-R2.1 BoardviewDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-S1-R2.1 BoardviewJuliano Estevam80% (10)
- GA-H61M-S1-R2.1 ( Ăî Í ) BipmacDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-S1-R2.1 ( Ăî Í ) Bipmacsỹ QuốcNo ratings yet
- H61M DS2 Rev.4.0 BitmapDocument2 pagesH61M DS2 Rev.4.0 BitmapHoàng Quốc Trung100% (2)
- Skyworth 3t03 Chassis - Tmpa8803, strg6653, La7840, La428 sch-47977 PDFDocument1 pageSkyworth 3t03 Chassis - Tmpa8803, strg6653, La7840, La428 sch-47977 PDFManuel CruzNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Notes IBDocument1 pageCell Respiration Notes IBlaeticia schmiesNo ratings yet
- GA-Z170X-UD3-1.0 位置图Document2 pagesGA-Z170X-UD3-1.0 位置图謝紳泳No ratings yet
- LV Room Cable Tray ScheduleDocument1 pageLV Room Cable Tray ScheduleOmer SharifNo ratings yet
- GA-Z170-HD3-1.01 BVDocument2 pagesGA-Z170-HD3-1.01 BVbats2008.bsNo ratings yet
- KB - Ms - Usb: Paec1Document1 pageKB - Ms - Usb: Paec1Adi copycenterNo ratings yet
- Sistem Sumatera Bagian Utara: Single Line DiagramDocument1 pageSistem Sumatera Bagian Utara: Single Line DiagramDaniel VerjuandNo ratings yet
- 1 454Document1 page1 454elrudo11No ratings yet
- Apéndice C - Cortocircuito Trifásico Año 2019Document25 pagesApéndice C - Cortocircuito Trifásico Año 2019Daniel ValerioNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - Bipmapsỹ QuốcNo ratings yet
- Bipmap GA-H61M-DS2.3.0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesBipmap GA-H61M-DS2.3.0 - BipmapANH TUANNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapANH TUANNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - Bipmapsỹ QuốcNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapANH TUANNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapTranVinhNo ratings yet
- Bipmap GA-H61M-DS2.3.0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesBipmap GA-H61M-DS2.3.0 - BipmapANH TUANNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapDocument2 pagesGA-H61M-DS2 3 0 - BipmapTranVinhNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte Ga-h61m-Ds2 Rev. 3.0 (PDF Boardview)Document3 pagesGigabyte Ga-h61m-Ds2 Rev. 3.0 (PDF Boardview)tkphanNo ratings yet
- Biochem 313 Prac 5Document8 pagesBiochem 313 Prac 5Anonymous G8WVOfRqV100% (2)
- Environmental Biotech UsesDocument40 pagesEnvironmental Biotech Usesalfi alfathanaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Diagnostico Equipos Sysmex Akralab.Document56 pagesCatalogo Diagnostico Equipos Sysmex Akralab.Liudmila MazaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetic Studies in Bad Obstetric History (Boh) and Infertility-A Retrospective Study Froma Stand-Alone LaboratoryDocument7 pagesCytogenetic Studies in Bad Obstetric History (Boh) and Infertility-A Retrospective Study Froma Stand-Alone LaboratoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- SuturepatternsDocument8 pagesSuturepatternsSunil MohanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Blue Eye TechnologyDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Blue Eye Technologyafdtvuzih100% (1)
- Anatomy MataDocument9 pagesAnatomy MataputriNo ratings yet
- Diversity IndexDocument13 pagesDiversity IndexAditi Patil100% (2)
- Sugar and Blood 2Document19 pagesSugar and Blood 2shaira ubaldeNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood Pressure Disorders in Diabetes MellitusDocument467 pages1 Blood Pressure Disorders in Diabetes MellitusPaola alvarezNo ratings yet
- Dhikav - Neuropsychopharmacology - CH 3Document13 pagesDhikav - Neuropsychopharmacology - CH 3anurag kumarNo ratings yet
- 10th Science II SemiENG QueBank MSCERTDocument48 pages10th Science II SemiENG QueBank MSCERTuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- Loeffler 1986Document11 pagesLoeffler 1986Dicson Sánchez AbadNo ratings yet
- Ijp 17 5 Albrektsson 7Document8 pagesIjp 17 5 Albrektsson 7Ziad RabieNo ratings yet
- FPPS 127 Exer1Document7 pagesFPPS 127 Exer1Chiaw Yuen LooNo ratings yet
- Rh Blood Group System ExplainedDocument10 pagesRh Blood Group System ExplainedAarzoo SikarwarNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of JelloDocument5 pagesThe Chemistry of Jelloapi-242679288No ratings yet
- Pomar-Types of Carbonate Platforms A Genetic Approach-ShortDocument4 pagesPomar-Types of Carbonate Platforms A Genetic Approach-ShortTora Man ChashmdarrahamNo ratings yet
- DNHE-1 Dec 2013Document8 pagesDNHE-1 Dec 2013Nikita GuptaNo ratings yet
- General BotanyDocument329 pagesGeneral BotanyHernaly FernandezNo ratings yet
- 3.IRR of RA 8485 As Amended by RA 10631Document63 pages3.IRR of RA 8485 As Amended by RA 10631ptdwnhroNo ratings yet
- UoN UnderGrad StudySkills 2011Document184 pagesUoN UnderGrad StudySkills 2011Bi AnhNo ratings yet