Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Health Assessment
Uploaded by
athenaethereal9201Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Health Assessment
Uploaded by
athenaethereal9201Copyright:
Available Formats
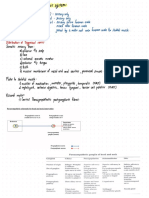
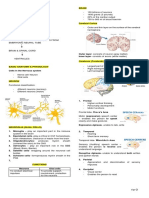
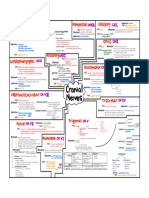
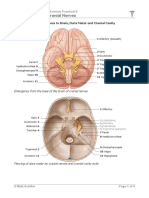
CRANIAL NERVE vestibulocochlear -
Hearing and balance CN VIII
General Function:sensory
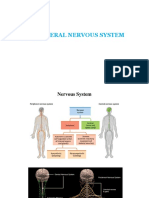
12 pairs. Originate or terminate in the brain
synapse with the brain. Majority ofthe cranial nerve Glossopharyngeal Sensory:Taste
-
and Touch to back oftongue;
Synapse with the brainstem Motor pharyngeal
to muscles;parasymphatetic to salivary gland
General Function:Sensory, Motor, parasympathetic CNIX
Bulb
vagus sensory to pharynx, larynx, and viscera;motor to palate
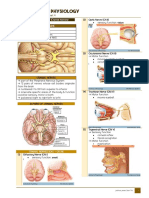
Olfactory
pharynxand larynx, parasympathetic to viscera ofthorax CNX
Optic nerve and abdomen General function:Sensory, Motor, Parasympathetic
Oculomotor nerve
Trochlear nerve
Accessory -
Motor oft wo and
neck upper back muscles
General Function:Motor. CNXII
Spinal Accessory Nerve-CNX
primarily innervate the head and neck except For CNX
Functions:1. Sensory
2. MOtOr
3. Parasympathetic. Involuntary actions
sequence:
Olfactory. Optic, oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal. Abducens,
Facial. Acoustic/ vestibulocochlear, Glossopharyngeal vagus
On Old Obando Tower Top A Filipino Army Guards
Villages And HOUSES
Functions:Some say Marry Money But My Brother says
Big Business Makes Money (Sensory. Both, Motor)
Olfactory Nerve-sensory Impulses to smell (Sensory) CNI
Optic Nerve-sensory Impulses to vision (sensory) CNII
Oculomotor -
Four OFSIX
Motor to extrinsic eye muscle and upper
eyelld:parasympathetic constricts pupil, thickens lens
CN III
Genetic function:Motor, parasympathetic
Trochlear -
Motor to one extrinsic eye muscle
General Function:Motor CN IV
oculomotor. Trochlear. Abducens mustwork
together
x
Trigeminal. Sensory to face and teeth, motor to muscles of
mastifactory General function:Sensory,Motor CNV
Abducens -
Motor to one extrinsic eye muscle
CN VI
General Function:Motor
Facial Sensory:taste;Motor to Muscles OFFacial expression:
-
parasympathetic to salivary and tear glands CN UII
General Function:Sensury, Motor, Parasympathetic
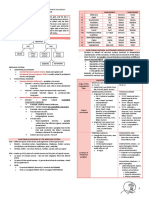
Neurologic Assessment Observe For General Behavior
cranial Nerve Acting Normally on his age, sex, occupation.
Dressed neatly, slovenly, or appropriately for age and occasion
Optic Nerve:Visual Acuity, visual confrontation test. Fundoscopy
Hyperactivity, quiet, catatonic
oculomotor Nerve. Trochlear Nerve. Abducens Nerve:Pupils,
palpebral, Fissures, extraocular Muscles Observe For Speech and Talk
Irigeminal Nerve:Corneal Reflex. Facial sensation, Muscles OF Flow of speech
Mastication Excessively talkative
Auditory Nerve:Gross Hearing, Weber's and Rinne Test ·Anxious. Forced, scared, Halting
Glossopharyngeal Nerve:Phonation, swallowing/coughing Observe For Mood
Facial expression and display emotions
of
vagus Nerve:
Gag Reflex, palatal Elevation
Spinal Accessory Nerve:Sternocleldomastoid and content ofthought
trapezius Muscles Do reach conversational
you goals when you ask questions
illusions, auditory, or visual Hallucinations, delusions, paranola
Hypoglossal:Tongue protrusion, articulation
level ofconsciousness Attention Span
A Function ofAlertness and FOCUS
consciousness:The awareness of the person, self-awareness, as
"
well of his
Ask the patient to spell the word "World" "cat
as awareness surroundings.
Arousal:wakefullness. Mediated anatomically by ascending Orientation
reticular (ARAS), diencephalon and the Ask the three spheres (Time, place, and person)
activating system
thalamus.
Memory
Awareness:Anatomically the cerebral hemispheres. Mediated by Immediate recall:ask patient to remember
in
Following words
a Functioning cerebral cortex. like "ball""Flag""Tree""Mangga"
short term recall:Ask the patient to recall the 3 words you
Alert. State ofnormality previously asked to Remember
lethargic -
Open eyes, answers questions. Falls back to sleep RecentMemory:"What did you have for breakfast or
"
lunch today
Obtunded -
Open eyes to loud voice, responds slowly to confusion
unwave ofthe environment
Remote Memory:Who is your Grade"teacher?
state between wakefulness, and stupor can be aroused by less
vigorous stimulation than stuporous patients.
stupor:sleep-like state. Able to arouse the patient using vigorous
stimulation. Patient is still able to make purposeful responses.
Comatose. May not be aroused by vigorous stimuli but can
perform reflexive motor movements. No awareness
U se
*
Glasgow Coma Scale For clients who are at Risk For
Rapid deterioration of the nervous system
CN1:OIFactory Astereognosia
close eyes then SIFF and Identify aromatic substances Refers to the inability to recognize the form and Import of
Objects by touch
CN 11:OPTIC
Stereognosis:Close eyes, Identify the object place in their
visual acuity (test one eye at a time)
hand. Repeat the Process on the other hand
Ask the client to Read
Graphesthesia: Close eye, identify the number or letter you
Visual Field / visual Confrontation Test will write with the back of a pen on their palm
Testing
Finger agnosla:Identify each finger ofhis hand
CN III:OCULOMOTOR
Assess directions ofgaze by asking client to Follow moving APrAXIA
objects
inability to execute a previously learned skilled movementwhich is
Pupillary light Reflex and consensual light Reflex not due to sensory or motor dysfunction
Ideamotor apraxia:Give the patient a pen or Comb and
CNIV and VI: Trochlear and Abducens
ask him on how to use it.
Assess directions ofgaze by asking client to Follow moving
objects Dressing aproxia: DIFFICulty in the orientation ofarticles of
Clothing with reference to the body
CNV: Trigeminal constructional apraxia:draw intersecting pentagons. Ask the
Corneal LightReflex Patient to copy exactly as it is. All 10 must be present
angles
TM) Opening the mouth against resistance
·Assess light touch and pain sensation across the Face Aphasia
CN VII:Facial
loss ofthe ability to use language or words due to a
cerebral pathology
Raise eyebrows. Frown or wrinkle Forehead
speaking: Give a picture with a story. Ask him to tell you on
Smile. Close mouth, PUFFCheecks
what is going on in the picture.
can Identify salty and sweet tastes on Front of tongue
Naming:show the patient a wrist watch and ask him/her what
he calls it. Repeat using a pen or key
ON VIII:ACOUSTC
Repitation:Ask the Patientto Repeat "Do IFs, ands, or buts
"
Gross hearing
Weber's Test, Rinne Test and Schwabach's test Writting, Comprehension, Reading
CN IX. X, XI
Observe speech, articulation, tone volume, quality of voice
Observe IFthere are any drooling saliva
of
Ask him to swallow or cough
Test For palatal elevation and gag reflex
CNX1: Accessory
·Sternocleldomastoid muscle
Trapezius Muscle
You might also like
- Cranial Nerves TableDocument2 pagesCranial Nerves TableKim Ocampo RojasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document5 pagesLecture 11bibifamelaganieNo ratings yet
- 1cranial NervesDocument62 pages1cranial Nervesmyka brilliant cristobalNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusDocument5 pagesParasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusChristine NathaliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology With PhatophysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With PhatophysiologyJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- Ainstem IIDocument39 pagesAinstem IINishanth LakshmanNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Assessment: Rhenier S. Ilado RNDocument106 pagesNeurologic Assessment: Rhenier S. Ilado RNJyra Mae TaganasNo ratings yet
- Ferraris Ana213 Week4labsheetDocument32 pagesFerraris Ana213 Week4labsheetZoe FormosoNo ratings yet
- Physiology U-5 Autonomous NSDocument98 pagesPhysiology U-5 Autonomous NSsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesakexisNo ratings yet
- Must KnowDocument10 pagesMust KnowahmadsatamahbobaNo ratings yet
- List of Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesList of Cranial NervesKay Lumpas Cruda100% (1)
- STUDENT IndividualWorksheet Week4CNBSDocument30 pagesSTUDENT IndividualWorksheet Week4CNBSZoe FormosoNo ratings yet
- Neurologic AssessmentDocument105 pagesNeurologic AssessmentJeceli A. Nobleza100% (10)
- Neuro 1.27.22Document19 pagesNeuro 1.27.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in HADocument3 pagesReviewer in HAjulia.caballero0107No ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument0 pagesCranial Nervesjeenath justin dossNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument9 pagesAnaphy ReviewerPrince Chester CamaliganNo ratings yet
- Horner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationDocument3 pagesHorner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationVictorija Evania Lucille DeldioNo ratings yet
- Table 5.5 Glasgow Coma ScaleDocument6 pagesTable 5.5 Glasgow Coma ScaleYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- NCM 101A H.A Theory Module 7Document21 pagesNCM 101A H.A Theory Module 7Munira HatibbonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesChapter - 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemjarssooNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument1 pageCranial Nervesapi-26587879100% (1)
- Body Nervios CranealesDocument15 pagesBody Nervios CranealesEstrellaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic SystemDocument6 pagesNeurologic SystemNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Cns AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesCns AnesthesiaVIGNESH AJNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System - Lec 1Document6 pagesNeurologic System - Lec 1Farmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- NS Physiology For PC-IIDocument168 pagesNS Physiology For PC-IItemesgen belayNo ratings yet
- Nutshell NeuroDocument15 pagesNutshell NeuroAdeel abbas rajaNo ratings yet
- Macleod - S - Clinical - Examination - 15th NeuroDocument18 pagesMacleod - S - Clinical - Examination - 15th Neurowxyngtc4n9No ratings yet
- SISTEM SARAF MOTORIK - PD - SMT - 5 - ArdaniDocument24 pagesSISTEM SARAF MOTORIK - PD - SMT - 5 - ArdaniAlexander FernandoNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument102 pagesBiology Notesajabgul123493No ratings yet
- Olfactory Optic Oculomotor: Nerves in Order Modality FunctionDocument2 pagesOlfactory Optic Oculomotor: Nerves in Order Modality Functionjenish daveNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Trigeminal Nerve2Document41 pagesAnatomy of Trigeminal Nerve2Dr. Fatema HajiNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Mind MapDocument1 pageCranial Nerve Mind Map5f2grv57p9No ratings yet
- My Encephalo NDocument2 pagesMy Encephalo NC1 - RAZALAN NICKA JOYNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves SummaryDocument2 pagesCranial Nerves SummarylokohugpoNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesPeripheral Nervous SystemTanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: MR Christopher Simon BSC (Neuroscience / Cognitive Psychology) MSC (Human Anatomy)Document66 pagesCranial Nerves: MR Christopher Simon BSC (Neuroscience / Cognitive Psychology) MSC (Human Anatomy)checkmateNo ratings yet
- Lec 03 - Assessing of Neurological System and Special SensesDocument7 pagesLec 03 - Assessing of Neurological System and Special SensesIRISH MANIAGONo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve TableDocument1 pageCranial Nerve TableAnna DangNo ratings yet
- Stu - Spinal Cord - Cranial NervesDocument8 pagesStu - Spinal Cord - Cranial NervestansihuishNo ratings yet
- 5.4-Nervous System Cranial NervesDocument4 pages5.4-Nervous System Cranial NervesJoshua Dumanjug SyNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves For NUR 2249Document1 pageCranial Nerves For NUR 2249Janine Aytria SaleNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemEds SyNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - Part 1Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Part 1karageeNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesCranial NervesDenis QosjaNo ratings yet
- O Inferior Hypogastric Plexus/pelvis PlexusDocument11 pagesO Inferior Hypogastric Plexus/pelvis PlexusMaxinefgc BaculoNo ratings yet
- Brain Encephalon: - Brain: Embrionally Comes From Ectoderm PartDocument72 pagesBrain Encephalon: - Brain: Embrionally Comes From Ectoderm PartHana AdivaNo ratings yet
- 09 ColouredDocument30 pages09 ColouredSatyam ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Brain Areas - Location and FunctionDocument12 pagesBrain Areas - Location and FunctionMattGilmoreNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument40 pagesCranial NervesStephanie ArceoNo ratings yet
- k2 Neuroanatomy of The Musculo-Skeletal Disorders-2016Document85 pagesk2 Neuroanatomy of The Musculo-Skeletal Disorders-2016icha100% (1)
- Why, . Sign and Symptom!!!: Anwar Wardy, MD - Neu Department of Neurology FKK UmjDocument29 pagesWhy, . Sign and Symptom!!!: Anwar Wardy, MD - Neu Department of Neurology FKK UmjNurul Wandasari SNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionDocument11 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionMarian AlecsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Neuro: DR.M.Shahid Shabbir DPT, MSNMPTDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Neuro: DR.M.Shahid Shabbir DPT, MSNMPTrabia khalidNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Hijacking the mind: The tricks and strategies used to control your mind and how to break freeFrom EverandHijacking the mind: The tricks and strategies used to control your mind and how to break freeNo ratings yet
- Class II Bimaxillary ProtrusionDocument13 pagesClass II Bimaxillary ProtrusionPrasne SriNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review of Animals in NeuroradiologyDocument8 pagesA Comprehensive Review of Animals in NeuroradiologySupercilious SagittariusNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousaDocument42 pagesOrthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousahashimalarwliaNo ratings yet
- Harga Cream Atlana House of Beauty: N0 Jenis Cream Nama CreamDocument22 pagesHarga Cream Atlana House of Beauty: N0 Jenis Cream Nama Creamcynthia perdana putriNo ratings yet
- Ben's Loose Tooth: NameDocument3 pagesBen's Loose Tooth: NameVinu PatilNo ratings yet
- Golden Proportion Himachal IndiaDocument7 pagesGolden Proportion Himachal IndiaJan AlmashharaNo ratings yet
- Viva Ear For MBBSDocument7 pagesViva Ear For MBBSDr.Riashat azimNo ratings yet
- What Is An Ear InfectionDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Ear InfectionGladie Ann Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Skin CareDocument6 pagesSkin Carejunghyun parkNo ratings yet
- Time Table PanitiaDocument4 pagesTime Table PanitiacelinNo ratings yet
- Frankel 4Document10 pagesFrankel 4Lisdany BecerraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12&13 Myofunctional ApplianceDocument11 pagesLecture 12&13 Myofunctional ApplianceIbrahim HysamNo ratings yet
- The Aetiology, Diagnosis and Management of Mandibular AsymmetryDocument9 pagesThe Aetiology, Diagnosis and Management of Mandibular AsymmetryKaram EidNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology SlidesDocument60 pagesOral Histology SlidesRan And SanNo ratings yet
- Makeup Lesson 20-ItemssDocument4 pagesMakeup Lesson 20-ItemssLendin RealNo ratings yet
- #0、aneurysmDocument39 pages#0、aneurysmMargaret ThatcherNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors and Surgical Outcomes of Intraocular Lens Dislocation After PhacoemulsificationDocument7 pagesPredisposing Factors and Surgical Outcomes of Intraocular Lens Dislocation After PhacoemulsificationUmmul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Congenital Defect On Maxillofacial Region: Developmental Defects of The Oral and Maxillofacial RegionDocument134 pagesCongenital Defect On Maxillofacial Region: Developmental Defects of The Oral and Maxillofacial RegionRedy Pristanto PutraNo ratings yet
- Development of Face & Oral CavityDocument56 pagesDevelopment of Face & Oral CavityGanesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Describing 2Document2 pagesDescribing 2Ana RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Anatomicohistologic Study of The Retaining Ligaments of The Face and Use in Face LiftDocument14 pagesAnatomicohistologic Study of The Retaining Ligaments of The Face and Use in Face LiftTavo PachecoNo ratings yet
- NQVH The Hall Technique ManualDocument19 pagesNQVH The Hall Technique Manualpriti adsulNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Eyes and EarsDocument31 pagesAssessment of Eyes and EarsShahmeerNo ratings yet
- Wound Healing After Multisegmental Lefort I Osteotomy and Transection of The Descending Palatine VesselsDocument9 pagesWound Healing After Multisegmental Lefort I Osteotomy and Transection of The Descending Palatine VesselshiramNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply Lymphatic System and Nerve Supply ofDocument16 pagesBlood Supply Lymphatic System and Nerve Supply ofHina MahmoodNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument68 pagesUntitledRere AaserNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive When? How? Why?: Access Cavity Preparation in EndodonticsDocument4 pagesMinimally Invasive When? How? Why?: Access Cavity Preparation in EndodonticsdoctorlupuNo ratings yet
- Hair and Its SettingDocument4 pagesHair and Its SettingAufin SmartNo ratings yet
- Chronic Dacryocystitis Case PresentationDocument19 pagesChronic Dacryocystitis Case Presentationr7ptzc5kcmNo ratings yet
- ICSE Skin WorksheetDocument1 pageICSE Skin WorksheetpreetaNo ratings yet