Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.1 Adaptive Immunity
Uploaded by
tinininiw690 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pages3.1 Adaptive Immunity
Uploaded by
tinininiw69Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1
ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Bursa of Fabricius – counterpart of bone
marrow
Gamayot, MG | 3MT02
ACTIVE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Thymus
Natural exposure in response to an infection or For T cells
natural series of infections Small, flat, bilobed organ found in the thorax or
You are given an antigen chest cavity, right below the thyroid gland and
You are the one who produces the antibody overlying the heart
Long term immunity as long as the cell is alive As we age, the thymus decreases its size and
and can produce antibody activity
Slow response T cells further develop in the bone marrow
Virgin/Naive lymphocytes – lymphocytes that is
PASSIVE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY not yet exposed to an antigen
Infusion of serum of plasma containing high
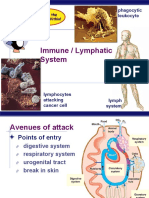
concentration of antibody or lymphocytes from SECONDARY LYMPHOID ORGAN
an actively immunized individual Spleen
You are given an antibody Lymph nodes
Short term immunity since antibody can get Tonsils
consumed Appendix
Immediate effect Peyer s patch
Adenoid
Rabies vaccine, snake anti-venom Mucosal-Associated lymphoid Tissue
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue
NATURALLY ACQUIRED Bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue
Active – includes the type of immunity that Skin-associated lymphoid tissue
develops during convalescence from an infection
o Chicken pox infection will give you Functions of secondary lymphoid organs
immunity from possible chicken pox Trapping site of pathogens
infection in the future Stand-by areas of T cells, B cells and phagocytes
Passive – develops after the placental passage Place of encounter for pathogens and the cells
of Ab from mother to fetus (colostrum from
Production of antibodies where it is produced by
breast milk, IgG)
plasma cells (B cells → Plasma cells) and
ARTIFICIALLY ACQUIRED cytokines (produced by T cells) and phagocytosis
(phagocytes)
Active – immunity obtained from vaccination w/
antigens Antigenic depended lymphopoiesis
Passive – immunity obtained after injection of
Spleen
gamma globulin for the induction of an immune
Largest secondary lymphoid organ
state (snake anti-venom)
o Snake antivenom Characterized as a large discriminating filter as
o Convalescent plasma (COVID-19) it removes old and damaged cells and foreign
antigen from the blood
LYMPHOID ORGANS Detect antigen found in the blood
PRIMARY LYMPHOID ORGANS Graveyard of blood cells
Bone marrow Red pulp – destroys RBC
Thymus White pulp – destroys WBC
Central lymphoid organ o Periarteriolar lymphoid sheath
Site of differentiation and maturation Main site of Ab production
Important in immunity
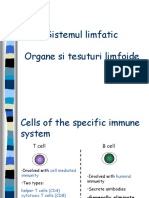
Bone marrow – site of maturation of B cells Lymph Nodes
Thymus – site of maturation of T cells Detects antigen in the tissue fluid
Central collecting points for lymph fluid from
Bone marrow adjacent tissues
Pluripotent stem hematopoietic stem cell Function: filtration of interstitial fluid from around
Largest tissue of the body cells in the tissues
All blood cells originated from the bone marrow
2
Provide an ideal environment for the generation It collects most of the body s lymph fluid and
of B-cell memory empties it into the left subclavian vein
B cell – mature in bone marrow; in charge w/
humoral immunity
T cells – mature in thymus; in charge w/ cell-
mediated immunity
Parts: Outer cortex, paracortex, medulla
Paracortex – contains T cells that are mainly
localized
Medulla – less densely populated than the
cortex but also contains some T cells
Cortex – contains macrophages, aggregates of B
cells in the primary follicles
Lymph fluid – flows slowly through spaces
(sinuses)
Sinuses – lined by macrophages, important in
phagocytosis
Afferent lymphatic vessels – where
lymphocytes and any foreign antigens present
enter nodes
Secondary follicles – contains of antigen and
consists of antigen-stimulated proliferating B cells
Germinal cells – interior of secondary follicles,
where transformation of the B cells takes place
Efferent lymph vessels – where fluid and
lymphocytes exit
T-cells are found on:
Perifollicular and paracortical regions of
lymph nodes
Medullary cords of the lymph nodes
Periarteriolar regions of spleen
Thoracic duct of the circulatory system
B cells are found on:
Follicular and medullary (germinal centers) of
lymph nodes
Primary follicles and red pulp of spleen
Follicular region of GALT
Follicular regions of lymph nodes
Summary
The thoracic duct is the largest lymphatic
vessel in the body
You might also like
- Transfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandTransfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- AllergenDocument2 pagesAllergenMyline TimcangNo ratings yet
- MergeResult 2022 09 12 01 31 19Document3 pagesMergeResult 2022 09 12 01 31 19Reca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System (Week 13)Document41 pagesLymphatic System (Week 13)Krisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- ImmunoSero Side NotesDocument2 pagesImmunoSero Side NotesReca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- Immuno Notes LectureDocument30 pagesImmuno Notes LectureSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Immunity2009Document42 pages2016 Immunity2009api-277471896No ratings yet
- Immuno Uphsi ProtectedDocument18 pagesImmuno Uphsi ProtectedAngge Aquino OfficialNo ratings yet
- Immunology Seminar by Hari HaranDocument26 pagesImmunology Seminar by Hari HaranToons rookieNo ratings yet
- Organsof ImmunityDocument38 pagesOrgansof ImmunitysaimNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System (Week 13)Document6 pagesLymphatic System (Week 13)Krisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System ReviewerDocument5 pagesLymphatic System ReviewerCHRISTIAN JUSTINE NARVAZANo ratings yet
- Immunity: Natural Defence BarriersDocument6 pagesImmunity: Natural Defence Barriersskarun1No ratings yet
- Hematology Review Notes Dela Cruz TopicDocument22 pagesHematology Review Notes Dela Cruz TopicShienna Rose Ann ManaloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10. Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesLecture 10. Lymphatic Systemyancereno19No ratings yet
- 4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFDocument63 pages4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFGigiEnergieNo ratings yet
- Aspectos Gerais Do Sistema Imunoló Gico 2022Document34 pagesAspectos Gerais Do Sistema Imunoló Gico 2022Laura FernandesNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument28 pagesIntroductionRamona Alexandra GaleruNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument28 pagesIMMUNITYanmolz.ghNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic - StudentDocument9 pagesLymphatic - StudentLeslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseDocument8 pagesIsabela State University: Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseAbigail Basco100% (1)
- Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument62 pagesChapter 22: The Lymphatic System and ImmunityEunice PalloganNo ratings yet
- 3 Organs of The Immune SystemDocument30 pages3 Organs of The Immune SystemRayNo ratings yet
- Immunity: by Ashok K TiwariDocument42 pagesImmunity: by Ashok K TiwariXEDGER09No ratings yet
- Lecture 20 - Lymphatics & Immune SystemDocument48 pagesLecture 20 - Lymphatics & Immune SystemberhanuNo ratings yet
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment # 1 Immune SystemDocument7 pagesSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment # 1 Immune SystemOmar FarooqNo ratings yet
- 1 Overview of Immunity Workshop SSCDocument28 pages1 Overview of Immunity Workshop SSCPraveen DeepakNo ratings yet
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument47 pagesImmune Systemapi-502940689No ratings yet
- 14b Lymphatic System 2021Document48 pages14b Lymphatic System 2021Jasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemDocument5 pagesDefinitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemanonymousNo ratings yet
- ImmunoDocument2 pagesImmunoStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Immuno-Sero Handout For Seminar1Document31 pagesImmuno-Sero Handout For Seminar1Jeanel Anne JovellanoNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immune SystemDocument28 pagesAdaptive Immune SystemRiana AgathaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOLOGY - 2 - Lymphoid SystemDocument2 pagesIMMUNOLOGY - 2 - Lymphoid SystemFelix NepumocenoNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction To ImmunologyDocument39 pages2.introduction To ImmunologyZakaria MakereNo ratings yet
- 11 Compressed Notes ImmunityDocument9 pages11 Compressed Notes ImmunityLIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues of The Immune SystemDocument32 pagesCells and Tissues of The Immune SystemSathiyaraj100% (13)
- Week 1 Study GuideDocument16 pagesWeek 1 Study GuideKateNo ratings yet
- Elearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newDocument28 pagesElearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newpiano357sidNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Review OF Introductory ProcessesDocument4 pagesImmune System: Review OF Introductory ProcessesaudreyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Semis QuizDocument2 pagesAnaphy Semis QuizElijah Mae MandalunesNo ratings yet
- 1 - Hema Lec FinalsDocument8 pages1 - Hema Lec FinalsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Immunology & Serology Review NotesDocument4 pagesImmunology & Serology Review Notesmaria email86% (7)
- Immunity: Fungi, Protozoans, Bacteria and VirusesDocument6 pagesImmunity: Fungi, Protozoans, Bacteria and VirusesShainee Delle PalmeraNo ratings yet
- The Immune System and Immunity: By: Princess Nhoor A. AgcongDocument24 pagesThe Immune System and Immunity: By: Princess Nhoor A. AgcongCess Abad AgcongNo ratings yet
- Functions:: Four Functions of SpleenDocument5 pagesFunctions:: Four Functions of SpleenRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: Morphofunctional Peculiarities, Methods of Examination, Semiology of DiseasesDocument45 pagesThe Immune System: Morphofunctional Peculiarities, Methods of Examination, Semiology of DiseasesHIDE & ATTACKNo ratings yet
- 09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Document12 pages09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Sheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Immune / Lymphatic System: Phagocytic LeukocyteDocument34 pagesImmune / Lymphatic System: Phagocytic LeukocyteMiranda Sekar ArumNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument63 pagesImmune SystemRichard ZatanNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Lymphatic SystemDocument35 pagesGroup 3 - Lymphatic SystemGLTSyed MiqueNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument8 pagesDiseases of The Immune SystemRuel MateoNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument7 pagesThe Lymphatic System and ImmunityAbi ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System PPT Notes SBDocument13 pagesLymphatic System PPT Notes SBnoshNo ratings yet
- Finals (Lesson 1)Document4 pagesFinals (Lesson 1)Kevin Vincent AquinoNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument21 pagesImmune SystemAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Phagocytic LeukocyteDocument23 pagesImmune System: Phagocytic LeukocyteikaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument12 pagesCardiac Cycleanupam manu100% (1)
- Vascular MalformationDocument37 pagesVascular MalformationDudu LeeNo ratings yet
- Sunandan Sikdar - Handbook of Cardiac Critical Care and Anaesthesia-CRC Press (2023)Document332 pagesSunandan Sikdar - Handbook of Cardiac Critical Care and Anaesthesia-CRC Press (2023)orlovacz.katusNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic CrisisDocument60 pagesAcute Biologic Crisisraidis100% (4)
- Cardio Quiz For NSG 128 HDocument22 pagesCardio Quiz For NSG 128 HMac MacapilNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Signs: Compartment SyndromeDocument4 pagesSymptoms and Signs: Compartment SyndromeajeikoNo ratings yet
- Skills - Masuring Apical - Radial PulseDocument1 pageSkills - Masuring Apical - Radial PulseJoanna Mae Movido CarolinoNo ratings yet
- 789778Document14 pages789778Yuna YulianaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot and PVDDocument17 pagesDiabetic Foot and PVDKriel BajarNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument7 pagesAngina PectorisMovie Clips InternationalNo ratings yet
- HA Procedures Respi Heart and PeripheralDocument10 pagesHA Procedures Respi Heart and Peripheralako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- 5 CathDocument14 pages5 CathHashem AlsmadiNo ratings yet
- Angina Set #8Document26 pagesAngina Set #8Zaid Al-KadhimiNo ratings yet
- Echo Curriculum Delivery Tool Nov2016Document11 pagesEcho Curriculum Delivery Tool Nov2016Joseph BarkerNo ratings yet
- 3.8.06 Aortoiliac DiseaseDocument21 pages3.8.06 Aortoiliac DiseaseAndri Feisal NasutionNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Daun Seledri HipertensiDocument8 pagesJurnal Daun Seledri HipertensiNurelza SafiraNo ratings yet
- Aging Changes in The Heart and Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesAging Changes in The Heart and Blood VesselsTotalenesya Reforrent SutiknoNo ratings yet
- Brief Analysis and Review of Coronary Artery Disease.Document6 pagesBrief Analysis and Review of Coronary Artery Disease.Johnson muhaviNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiovascular System History & ExaminationDocument74 pagesPediatric Cardiovascular System History & Examinationعبدالله Abdullah INo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi LimfomaDocument5 pagesKlasifikasi LimfomaBadlina Fitrianisa YulianingrumNo ratings yet
- Medical Supplies Philippine Heart Center 2015Document146 pagesMedical Supplies Philippine Heart Center 2015Emmeline Roy DoblaNo ratings yet
- IB Biology HL: 6.2 The Blood System - Human PhysiologyDocument12 pagesIB Biology HL: 6.2 The Blood System - Human PhysiologypetraNo ratings yet
- Stroke Dan Sepsis: Pembimbing: Dr. Bambang Supriadi, SP.SDocument24 pagesStroke Dan Sepsis: Pembimbing: Dr. Bambang Supriadi, SP.SIcha NathaliaNo ratings yet
- 3a. Parts of The Body 1Document14 pages3a. Parts of The Body 1Semuel LukuNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi AritmiaDocument27 pagesPatofisiologi AritmiaVedora Angelia GultomNo ratings yet
- GPAT Online Class For B Pharm Students Human Anatomy and Physiology Part - 1Document62 pagesGPAT Online Class For B Pharm Students Human Anatomy and Physiology Part - 1Kuch BhiNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular PDFDocument148 pagesCardio Vascular PDFStefana RoxanaNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL SUBSTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY & INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGYnewDocument79 pagesDIGITAL SUBSTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY & INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGYnewDaniel MontesNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Venous Leg Ulcer Healing and Recurrence Rate After Endovenous Radiofrequency Ablation of Incompetent Saphenous VeinDocument6 pagesFactors That Influence Venous Leg Ulcer Healing and Recurrence Rate After Endovenous Radiofrequency Ablation of Incompetent Saphenous VeinHan's OfficialNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument31 pagesPharmacology Summarydesshe09No ratings yet