Professional Documents
Culture Documents
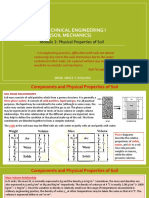
CH3 Weight Volume
Uploaded by
Gbenga AdewumiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH3 Weight Volume
Uploaded by
Gbenga AdewumiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3 Weight-Volume Relationships
In natural occurrence, soils are three-phase systems consisting of soil solids, water, and air.
3.1 Weight–Volume Relationships
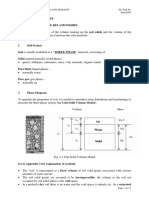
Figure 3.1a shows an element of soil of volume V and weight W as it would exist in a natural state. To develop
the weight–volume relationships, we must separate the three phases (that is, solid, water, and air) as shown in Figure
3.1b. Thus, the total volume of a given soil sample can be expressed as
Weight-Volume Relationship 3.1
can be %.
The relationship between void ratio and porosity can be also expressed below.
The common terms used for weight relationships are moisture content and unit weight. Moisture content (w) is also
referred to as water content and is defined as the ratio of the weight of water to the weight of solids in a given volume
of soil:
Soils engineers sometimes refer to the unit weight defined by Eq. (3.9) as the moist unit weight.
Often, to solve earthwork problems, one must know the weight per unit volume of soil, excluding water. This weight is
referred to as the dry unit weight, d. Thus,
Unit weight is expressed in English units (a gravitational system of measurement) as pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft3). In SI
(Système International), the unit used is kilo Newtons per cubic meter (kN/m3). Because the Newton is a derived unit,
working with mass densities () of soil may sometimes be convenient. The SI unit of mass density is kilograms per
cubic meter (kg/m3). We can write the density equations [similar to Eqs. (3.9) and (3.11)] as
Weight-Volume Relationship 3.2
3.2 Relationships among Unit Weight, Void Ratio, Moisture Content, and Specific Gravity
To obtain a relationship among unit weight (or density), void ratio, and moisture content, let us consider a
volume of soil in which the volume of the soil solids is one, as shown in Figure 3.2. If the volume of the soil solids is
one, then the volume of voids is numerically equal to the void ratio, e [from Eq. (3.3)]. The weights of soil solids and
water can be given as
Weight-Volume Relationship 3.3
Weight-Volume Relationship 3.4
3.4 Various Unit-Weight Relationships
3.5 Relative Density
The term relative density is commonly used to indicate the in situ denseness or looseness of granular soil. It is
defined as
Weight-Volume Relationship 3.5
Weight-Volume Relationship 3.6
You might also like
- Soil Weight-Volume RelationshipsDocument60 pagesSoil Weight-Volume RelationshipsJonniel De Guzman100% (1)
- W-V RelationshipDocument20 pagesW-V RelationshipThoa HồNo ratings yet
- التربةDocument118 pagesالتربةali hashemNo ratings yet
- Index Properties of SoilDocument17 pagesIndex Properties of SoilEstiven GierNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Chapter 3 Key RelationshipsDocument42 pagesSoil Mechanics Chapter 3 Key RelationshipsAbd El Rhman Mohamed50% (2)
- 02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume RelationshipsDocument42 pages02 Chapter 3 - Weight Volume RelationshipsLeandrow BacolodNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Weight-Volume Relationship of Soil 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Weight-Volume Relationship of Soil 1Elite OsiganNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Weight Volume Relationships 10 10 2019Document21 pagesCH 2 Weight Volume Relationships 10 10 2019Yousif MawloodNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document32 pagesLec 2ahmed alhajNo ratings yet
- Das 10e US CH 3Document26 pagesDas 10e US CH 3LE AHNo ratings yet
- GeotechDocument27 pagesGeotechGina ClamorNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Weight-Volume Relationship of Soil 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: Weight-Volume Relationship of Soil 1Li LiNo ratings yet
- Department of Geology University of Liberia Semester II-2019-2020Document37 pagesDepartment of Geology University of Liberia Semester II-2019-2020Edwin BallahNo ratings yet
- Soil volumetric and mass ratiosDocument55 pagesSoil volumetric and mass ratiosJOSE ESTEBAN SOTO TINCONo ratings yet
- Phase Relationships of SoilDocument5 pagesPhase Relationships of Soilmageshm1No ratings yet
- Module 2. Physical Properties of SoilDocument24 pagesModule 2. Physical Properties of SoilMark Andykenn Liaga MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document27 pagesLesson 2jrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-4Document43 pagesChapter 3-4yasirnoorischolarshipsNo ratings yet
- Weight Volume RelationshipsDocument32 pagesWeight Volume Relationshipssyedumairali100% (1)
- 5 - Weight Volume RelationshipsDocument32 pages5 - Weight Volume Relationshipsmaame25No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Phase RelationshipsDocument11 pagesChapter Three Phase Relationshipshussein darwishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Physical Properties of SoilDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Physical Properties of SoilChristian BonoanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Two 2. Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipsDocument12 pagesChapter - Two 2. Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipsbulchaNo ratings yet
- Phase Relations Key Terms and ConceptsDocument16 pagesPhase Relations Key Terms and ConceptsCasao JonroeNo ratings yet
- 02 Phase RelationshipDocument12 pages02 Phase RelationshipDE DECADENo ratings yet
- 1.introductions: Name of The TeacherDocument10 pages1.introductions: Name of The Teacherraj naikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SWP P PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 2 SWP P PDFShita AlemieNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsDocument32 pagesChapter Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsHiwot DemisseNo ratings yet
- Basic SoilDocument18 pagesBasic SoilThanes RawNo ratings yet
- Phase Relations and Soil PropertiesDocument12 pagesPhase Relations and Soil Propertiesjavier100% (1)
- Chapter 2-1Document36 pagesChapter 2-1Chalachew MesfinNo ratings yet
- Weight Volume Relationship: Fkaas, UthmDocument29 pagesWeight Volume Relationship: Fkaas, UthmShonTellaErrzoan'nieNo ratings yet
- 2 - Index PropertiesDocument78 pages2 - Index PropertiesKaranNo ratings yet
- Weight-Volume RelationshipsDocument33 pagesWeight-Volume RelationshipsAadolf ElÿasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Index PropertiesDocument26 pagesLecture 3 Index PropertiesMd. Ariful IslamNo ratings yet
- FE Lecture-1Document10 pagesFE Lecture-1Joey LarozaNo ratings yet
- Phase Relation of Soils: Index Properties of Soil: Mass-Volume RelationshipDocument4 pagesPhase Relation of Soils: Index Properties of Soil: Mass-Volume RelationshipMarben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2lNo ratings yet
- Nature of Soil and Functional RelationshipsDocument20 pagesNature of Soil and Functional RelationshipsSiddharth SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 Porosity - Density and Specific GravityDocument5 pages1 - 1 Porosity - Density and Specific GravitySalman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document7 pagesModule 1Shanu AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2chapter-2 PPT - (Final)Document61 pages2chapter-2 PPT - (Final)Muhe JsNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics of Soils ExplainedDocument34 pagesPhysical Characteristics of Soils ExplainedVijaykumar NagnaikNo ratings yet
- Soil Phase Relationships ChapterDocument8 pagesSoil Phase Relationships ChapterAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SWPRDocument16 pagesChapter 2 SWPRdereje werkuNo ratings yet
- 2 - Weight Volume RelationshipDocument29 pages2 - Weight Volume RelationshipMohd Asis LatipNo ratings yet
- Assignment Weight Volumn RelationshipDocument8 pagesAssignment Weight Volumn RelationshipAbdulrauf Ismail BusayoNo ratings yet
- Week 3. CE322 Volume-Weight RelationshipDocument39 pagesWeek 3. CE322 Volume-Weight RelationshipreanNo ratings yet
- Soil Properties & PhasesDocument8 pagesSoil Properties & Phasesmidju dugassaNo ratings yet
- Geotecheng Module 01 Chapter 02Document32 pagesGeotecheng Module 01 Chapter 02Ace De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Soil Properties) PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 1 (Soil Properties) PDFSufian PianNo ratings yet
- CEGB233 Soil Mechanics Chapter 1Document4 pagesCEGB233 Soil Mechanics Chapter 1Sufian PianNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering I: Phase RelationshipsDocument12 pagesGeotechnical Engineering I: Phase RelationshipsKavish DayaNo ratings yet
- Soil Engineering Chapter -2-2Document15 pagesSoil Engineering Chapter -2-2Bhavya zaveriNo ratings yet
- CON4341 - E - Note - 02 Phase RelationshipDocument12 pagesCON4341 - E - Note - 02 Phase Relationship123No ratings yet
- Weight and Volume RelationshipsDocument23 pagesWeight and Volume RelationshipsGuino Veramendi ReyesNo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationGuilhem BourrieNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldFrom EverandDynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldNo ratings yet
- Stoke LawDocument2 pagesStoke LawGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Open Pit Planning and Design 20Document167 pagesAdvanced Open Pit Planning and Design 20Gbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Water Quality Control Technology-NoteDocument43 pages7.1 Water Quality Control Technology-NoteGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Unit8. Wastewater EngineeringDocument87 pagesUnit8. Wastewater EngineeringGbenga Adewumi100% (1)
- 7.1 Water Quality Control Technology-NoteDocument43 pages7.1 Water Quality Control Technology-NoteGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- 12 Rock Mass PropertiesDocument47 pages12 Rock Mass PropertiesMilton TeranNo ratings yet
- Determination of Optimum Production Capacity and Mine Life Considering Net Present Value in Open Pit Mining at Different Overall Slope AnglesDocument9 pagesDetermination of Optimum Production Capacity and Mine Life Considering Net Present Value in Open Pit Mining at Different Overall Slope AnglesCarlos A. Espinoza MNo ratings yet
- Open Pit Optimization Strategies For ImpDocument6 pagesOpen Pit Optimization Strategies For ImpGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- EE20 3 - 4 SonibareDocument15 pagesEE20 3 - 4 SonibareGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- 10 Mining and Petroleum EngineeringDocument12 pages10 Mining and Petroleum EngineeringGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- TE4 Example Calculations PDFDocument11 pagesTE4 Example Calculations PDFestebandidochasconNo ratings yet
- Paper4gmjvol15no.1 11111Document10 pagesPaper4gmjvol15no.1 11111RODRIGUEZ GONZALEZ EDUARDO JAVIERNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Coal Resources and ReservesDocument17 pages2.5 Coal Resources and ReservesGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Application of Coal Price Prediction Method BasedDocument22 pagesApplication of Coal Price Prediction Method BasedGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- A Novel Economic Benefit Calculation Modeling ApplDocument26 pagesA Novel Economic Benefit Calculation Modeling ApplGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Open Pit Optimisation of Tabakoto Pit Using Surpac and WhittleDocument12 pagesOpen Pit Optimisation of Tabakoto Pit Using Surpac and WhittleBoukaré OUEDRAOGONo ratings yet
- CPM - Pert-Project - MGMT - 28.4.23 - Compatibility ModeDocument75 pagesCPM - Pert-Project - MGMT - 28.4.23 - Compatibility ModeGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- The First Step: Permission Granted To Distribute For Non-Commercial Educational PurposesDocument56 pagesThe First Step: Permission Granted To Distribute For Non-Commercial Educational Purposesapi-3745851No ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument23 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsRezaNo ratings yet
- Minerals 12 00250Document31 pagesMinerals 12 00250Gbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Wet Magnetic.217479.1608050700.7645.th - enDocument11 pagesWet Magnetic.217479.1608050700.7645.th - enGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Registered Architects 2019 Grade 1Document3 pagesRegistered Architects 2019 Grade 1santosh bharathy100% (1)
- Negotiation Self-Assessment and Vision Report - by Umang DharDocument1 pageNegotiation Self-Assessment and Vision Report - by Umang Dharumangdhar8No ratings yet
- Recorder SongsDocument15 pagesRecorder SongsBich LeNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Assignment On MelitaDocument17 pagesMarketing Management Assignment On MelitaarjunNo ratings yet
- DLP Pe - 1 & 2Document1 pageDLP Pe - 1 & 2Dn AngelNo ratings yet
- Sex Work in Cyberspace Who Pays The PriceDocument14 pagesSex Work in Cyberspace Who Pays The PriceйцукеячсмNo ratings yet
- Liturgical Music For LentDocument11 pagesLiturgical Music For LentShirly Benedictos100% (1)
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumeAbhinav kaliaNo ratings yet
- Shades of White: Rendering in WatercolorDocument4 pagesShades of White: Rendering in WatercolorMichael Reardon100% (4)
- Xerosis CutisDocument6 pagesXerosis CutisHadi FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Four Modes of DeliveryDocument21 pagesFour Modes of DeliveryRyan AbellaNo ratings yet
- Nick & Sammy - Baby You Love Me (Bass Tab)Document6 pagesNick & Sammy - Baby You Love Me (Bass Tab)Martin MalenfantNo ratings yet
- DLP Reading Comprehension 15th SeptemberDocument3 pagesDLP Reading Comprehension 15th SeptemberHanaa ElmostaeenNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Misconceptions About The Catholic Church - Listverse PDFDocument15 pagesTop 10 Misconceptions About The Catholic Church - Listverse PDFMaryvincoNo ratings yet
- GaDocument101 pagesGaSugan GeeNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris ASPD Dikpora Feb 2022Document15 pagesBahasa Inggris ASPD Dikpora Feb 2022WIBI CAM100% (1)
- Revised Revenue Code of Puerto Galera 2010Document157 pagesRevised Revenue Code of Puerto Galera 2010Jesselle MamintaNo ratings yet
- NITI AayogDocument6 pagesNITI Aayogs100% (1)
- PresentationDocument5 pagesPresentationAnsh RebelloNo ratings yet
- Wax Rolls For Your Success: Yarn Yearns For The One and OnlyDocument9 pagesWax Rolls For Your Success: Yarn Yearns For The One and Onlyangga widayantoNo ratings yet
- International SellingDocument28 pagesInternational SellingShoaib ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Sharp Troubleshooting Guide for AR CopiersDocument7 pagesSharp Troubleshooting Guide for AR CopiersBushara MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Best Sellers - Books & AudiobooksDocument7 pagesBest Sellers - Books & AudiobooksRykan KolbyNo ratings yet
- E. Philip Davis, Dr. Benn Steil - Institutional Investors-The MIT Press (2001)Document370 pagesE. Philip Davis, Dr. Benn Steil - Institutional Investors-The MIT Press (2001)German StefanoffNo ratings yet
- I) Complete With The Correct Form of The Given Verb: - /5Document3 pagesI) Complete With The Correct Form of The Given Verb: - /5Jasmina PedišićNo ratings yet
- Community Psychology Rudkin PDFDocument2 pagesCommunity Psychology Rudkin PDFLance0% (2)
- Energy Conservation Techniques For Manufacturing IndustriesDocument11 pagesEnergy Conservation Techniques For Manufacturing IndustriesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- PE Week QuizDocument2 pagesPE Week QuizMarvin RetutalNo ratings yet
- Ethics Short Essay 3Document4 pagesEthics Short Essay 3api-284664489No ratings yet
- Mind Map of Emphasis MarkersDocument1 pageMind Map of Emphasis MarkersJHONA THE IGUANANo ratings yet