Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Reviewer Part 1
Uploaded by
kurtbusbus10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Chemistry-Reviewer-Part-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesChemistry Reviewer Part 1
Uploaded by
kurtbusbus1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
KIMISTRI RIBYUWER
Ex. Oxygen – has 8 electrons
Contents: Electron Configuration of Oxygen:
- Electron Configuration 1s2 2s2 2p2
- Orbital Diagram Note: Always count the electrons in each shell
- LEDS for you not to go over the needed electron
- Aliphatic Hydrocarbons count
ELECTRON CONFIGURATION Other Examples:
Electron configurations describe where
electrons are located around the nucleus of an Chlorine – 17 electons - 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p5
atom. Magnesium – 12 electrons – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
Gold – 79 – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6
How do you write the electron 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d2
configuration of an Element? Fluorine – 9 – 1s2 2s2 3p4
Manganese – 25 – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6
Lets check your understanding:
Aluminum
Iron
Scandium
Lithium
Neon
Did you notice any mistake from the “other
Step 1. Identify the Atomic Number of the examples”?
Element. Do note that the Atomic number = no. of
Electrons. Orbital Diagram
Ex. Oxygen – O – 6 electrons Electron orbital diagrams are diagrams
used to show the energy of electrons within the
Step 2. Carefully distribute the electrons to sublevels of an atom or atoms when used in
the Configuration. It must follow the sequence 1s2 bonding.
2s2 2p6 3s2 and so forth. (Found in your Periodic
Table) Remember that
> s-shell contains 1 box
Remember that: > p-shell contains 3 boxes
> s-shell holds 2 electrons, > d-shell contains 5 boxes
> p-shell holds 6 electrons, > f-shell contains 7 boxes
> d-shell holds 10 electrons,
> and f-shell holds 14 electrons. Two Known Types in Orbital Diagram
- Aufbau Principle
Parts of the Electron Configuration Sequence. - Hunds Rule
Note: The arrows represent the
1s2 electrons, it is the same with the electron
“1” at the front states what orbit the electrons are configuration where you have to look for the no.
“S” states what shell is being used of electrons of the element.
“2” states how many electrons are in the shell
What is the difference of these two? Nitrogen
Aufbau Principle
- each boxes per shell must contain an up arrow
before adding the down arrow
Helium
Hunds Rule
- a box in the shell must be filled with up and down
arrow before moving to another box
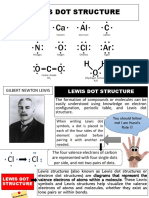
LEDS – Lewis Electron Dot System
(ang simula ng impyerno)
A Lewis Structure is a very simplified
representation of the valence shell electrons in a
Question: What element is being used as an molecule. So how does this monstrosity work?
example?
But First, how to we identify the number
Lets Check Your Understanding: of valence electrons of an element?
Make the electron configuration of the
following using both Aufbau Principle and Hunds Valence electrons are the electrons that is
Rule. found in the outermost layer of an atom. To
identify the number of Valence Electrons, look at
Phosphorous your Periodic table and look at the group
numbers of elements written in Roman
Numerals. The group number determines the
number of valence electron of an element.
I II III IV V VI VII VII
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Step 1. Identify the number of Valence
Electron of an Element. Using Fluorine as an
example.
Fluorine is found at Group VII, therefore
having 7 valence electrons Easy right? Time to go to the fun part.
To Be Continued...
Fluorine = 7 Valence Electrons
Step 2. Using the Element Symbol, draw
dots around the symbol, typically in a
counterclockwise rotation.
Check Your Understanding:
Draw the LEDS of the following Element:
Beryllium
Neon
Boron
Hydrogen
Silicon
You might also like
- Electronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestFrom EverandElectronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestNo ratings yet
- Konfigurasi e Dan Periodik 2020Document69 pagesKonfigurasi e Dan Periodik 2020Reza FebryanNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument10 pagesScienceAmber RoselNo ratings yet
- Ionization Energy and Configuration 3Document48 pagesIonization Energy and Configuration 3Mr. CrustNo ratings yet
- ENGG 103 Atomic Structure I Dippenaar 2016 - MoodleDocument28 pagesENGG 103 Atomic Structure I Dippenaar 2016 - MoodleJB HIFINo ratings yet
- Introduction: What Are Electron Configurations?Document9 pagesIntroduction: What Are Electron Configurations?Julius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document29 pagesChapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..MPRajNo ratings yet
- Electrons Activity SheetDocument8 pagesElectrons Activity SheetTonette ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Konfigurasi ElektronDocument70 pagesKonfigurasi ElektronAnisa NurulNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms: Electron Configuration Valence Electrons Orbital Notation Lewis-Electron Dot Diagram Octet RuleDocument26 pagesElectrons in Atoms: Electron Configuration Valence Electrons Orbital Notation Lewis-Electron Dot Diagram Octet RuleMa. Charlene Stephanie HilvanoNo ratings yet
- Konfigurasi Elektron: by Maidawati, M.SiDocument24 pagesKonfigurasi Elektron: by Maidawati, M.Simuhammad ariefNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Notes Submision - Science Journal - Chesney GaskinDocument17 pagesModule 2 Notes Submision - Science Journal - Chesney GaskinChesney Anne GaskinNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations Orbital Notation and Quantum NumbDocument11 pagesElectron Configurations Orbital Notation and Quantum NumbKenneth FriasNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Module 6 Answer PDFDocument5 pagesGen Chem Module 6 Answer PDFjhon paul espinarNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 51Document1 pageDokumen PDF 51Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration (Kimia) PDFDocument20 pagesElectron Configuration (Kimia) PDFalbertNo ratings yet
- G9 Lesson 1 ChemDocument12 pagesG9 Lesson 1 ChemEleazar Valencia IIINo ratings yet
- LEWIS DOT STRUCTURE, QUANTUM NUMBERS and ELECTRON CONFIGUARATION (Autosaved)Document32 pagesLEWIS DOT STRUCTURE, QUANTUM NUMBERS and ELECTRON CONFIGUARATION (Autosaved)nova novaNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration NotesDocument4 pagesElectron Configuration NotesapriantokaNo ratings yet
- "Electrons in Atoms": Chemistry Atlantic Bilingual School Christian Campbell MDDocument75 pages"Electrons in Atoms": Chemistry Atlantic Bilingual School Christian Campbell MDusmcdoc113597No ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument35 pagesGeneral ChemistryArlynn Lontoc De RamosNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry New Orientation Class Notes 09-03-22Document42 pagesClass 12 Chemistry New Orientation Class Notes 09-03-22Joel GladsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Elements in The PeriodicDocument61 pagesLesson 2: Elements in The PeriodicAngel FaythNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document45 pagesCH 02Defne SunerNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Atoms RevDocument10 pagesElectronic Structure of Atoms RevGethan AbsalomNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Review of General Chemistry ConceptsDocument32 pagesLesson 1 Review of General Chemistry Conceptsnorlene narita macedaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Atoms and Nucleus - Reg - 2019 - REVDocument66 pagesUnit 2 Atoms and Nucleus - Reg - 2019 - REVRecilia MarthaNo ratings yet
- Pointers 1Document4 pagesPointers 1Siako IkawNo ratings yet
- 13: Electron Configuration: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetDocument1 page13: Electron Configuration: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Periodic Table)Document46 pagesChapter 4 (Periodic Table)Tunku Hilman Al-nordinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Lewis Electron Dot StructureDocument22 pagesLesson 2 Lewis Electron Dot StructureAngel CapinpinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document22 pagesChapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..poqer_88No ratings yet
- Tomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document22 pagesTomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..mohamd jehadNo ratings yet
- Tomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document22 pagesTomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Yahya AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Bonding - Live LectureDocument35 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding - Live LecturebasitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Electrons in AtomDocument69 pagesChapter 2 Electrons in AtomZuhailimuna MudaNo ratings yet
- Lewis TructuresDocument12 pagesLewis TructuresNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument19 pagesReviewerJulia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document9 pagesWeek 2Christine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - 1 - Atomic Structure & Interatomic BondingDocument45 pagesChap 1 - 1 - Atomic Structure & Interatomic BondingYap Feng100% (2)
- General Chemistry q2 Week 7Document64 pagesGeneral Chemistry q2 Week 7Keisha Mae Custodio100% (1)
- GenChemistry1 Q2ReviewerDocument16 pagesGenChemistry1 Q2ReviewerSam JangNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q3 - Week 5-6 - Elements and AtomsDocument30 pagesG8 Science Q3 - Week 5-6 - Elements and AtomsIemmee Jane DinglasanNo ratings yet
- CHEM Part2Document90 pagesCHEM Part2Reiniel Cirujano AntonioNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of AtomDocument67 pagesElectronic Structure of AtomdwyquishNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Quantum Mechanical ModelDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Quantum Mechanical ModelAcel PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Quarter 2 Week 1Document5 pagesScience 9 Quarter 2 Week 1Leslie Darwin DumasNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Lewis StructureDocument49 pagesWeek 3: Lewis StructureYay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument13 pagesAtomic Structurerenan.masangya-18No ratings yet
- Q2 W2 Electron ConfigurationDocument40 pagesQ2 W2 Electron ConfigurationsauvarizziNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q2 Week 1Document11 pagesScience 9 Q2 Week 1Sofia ErruaNo ratings yet
- AIM: How To Write Lewis Dot Structures (Electron Dot Structures)Document13 pagesAIM: How To Write Lewis Dot Structures (Electron Dot Structures)mayonaissedelight smoothieNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: Faculty OF EngineeringDocument45 pagesMetallurgy: Faculty OF EngineeringAhmad SafaanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Module 2 - Electrons Bonding StructureDocument12 pagesUNIT 1 Module 2 - Electrons Bonding StructureMuhammadNo ratings yet
- q2 General Chemistry 1Document27 pagesq2 General Chemistry 1Severus S Potter100% (2)
- Atomic Structure and Bonding in Solids: Issues To Address..Document22 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding in Solids: Issues To Address..springmay100% (1)
- ME150 - Week 2Document44 pagesME150 - Week 2Gülden ÇimenNo ratings yet
- CH 2 BondingDocument48 pagesCH 2 BondingMusab Abdrabbuh100% (1)
- Approximation Solutions: Multi-E Atoms: RecapDocument10 pagesApproximation Solutions: Multi-E Atoms: RecapDmidNo ratings yet
- Aakash NeetDocument32 pagesAakash NeetHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Beckmann Nickel AcetateDocument5 pagesBeckmann Nickel AcetateDavideGiacomelliNo ratings yet
- 9701 s09 QP 1 PDFDocument16 pages9701 s09 QP 1 PDFAinthu IbrahymNo ratings yet
- The Reduction of Nickel From Low-Grade Nickel Laterite Ore Using A Solid-State Deoxidisation MethodDocument7 pagesThe Reduction of Nickel From Low-Grade Nickel Laterite Ore Using A Solid-State Deoxidisation Methodjeha kunramadiNo ratings yet
- 1411 - Chapter 6 Exercises With AnswersDocument12 pages1411 - Chapter 6 Exercises With AnswersNor Afidah100% (1)
- Analysis of 15 Simple Salts Xi STD-1 PDFDocument38 pagesAnalysis of 15 Simple Salts Xi STD-1 PDFAnisha Fathima Begum100% (1)
- Coordination Compound: Inorganic ChemistryDocument55 pagesCoordination Compound: Inorganic ChemistrySaanvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Norma Astm e 478Document22 pagesNorma Astm e 478luisa100% (1)
- Osha PelsDocument30 pagesOsha PelshydroNo ratings yet
- AGA Aluminum Welding BrochureDocument16 pagesAGA Aluminum Welding Brochureaghosh704No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Coal QualityDocument20 pagesAn Introduction To Coal QualitySyahreza AngkasaNo ratings yet
- Metal Reactivity With 02 H20 & AcidDocument1 pageMetal Reactivity With 02 H20 & AcidAnthea Guo100% (1)
- Battery Waste Management Rules 2020 (Draft) PDFDocument14 pagesBattery Waste Management Rules 2020 (Draft) PDFantony k l100% (1)
- 0620 w14 QP 33Document12 pages0620 w14 QP 33Haider AliNo ratings yet
- 2013-UKChO-Round 1 - tcm1Document12 pages2013-UKChO-Round 1 - tcm1vermouth020No ratings yet
- An Overview On Types of White Cast Irons and HighDocument13 pagesAn Overview On Types of White Cast Irons and HighThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry 0620 - 2010 - Ques Paper - 61Document16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry 0620 - 2010 - Ques Paper - 61MinakshiNo ratings yet
- 63bf9a174bd97900186e0589 - ## - Periodic Classification of Elements - One Shot - Class Notes II (Udaan 2023)Document54 pages63bf9a174bd97900186e0589 - ## - Periodic Classification of Elements - One Shot - Class Notes II (Udaan 2023)anita933688No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationWENDY MENDIOLANo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure (Past Papers Questions)Document1 pageAtomic Structure (Past Papers Questions)zafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- MW CP CV CP CV R R GAS Lb/pmole Btu/lbDocument10 pagesMW CP CV CP CV R R GAS Lb/pmole Btu/lbme coowNo ratings yet
- Metal Joining Processes: Prof. Mayur S Modi Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department Ssasit, SuratDocument79 pagesMetal Joining Processes: Prof. Mayur S Modi Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department Ssasit, SuratPrateekNo ratings yet
- Fullerene Informtaion 02Document3 pagesFullerene Informtaion 02api-270516716No ratings yet
- NSRP LLM WPQTDocument3 pagesNSRP LLM WPQTtranvando1986No ratings yet
- CMY 285 Experiment 1 - U20518073Document10 pagesCMY 285 Experiment 1 - U20518073Suné MartinsNo ratings yet
- DubniumDocument8 pagesDubniumKevinNo ratings yet
- Effects of MN Content and Heat TreatmentDocument5 pagesEffects of MN Content and Heat TreatmentTrần Xuân VịnhNo ratings yet
- AAS CookbookDocument166 pagesAAS CookbookdewiNo ratings yet
- 6.02 - Aircraft Materials - Non FerrousDocument16 pages6.02 - Aircraft Materials - Non FerroushmaterialscienceNo ratings yet
- Ellingham Diagram UsesDocument4 pagesEllingham Diagram Usesnanda rizkyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Test From Online Source AnswersDocument32 pagesElectrochemistry Test From Online Source AnswersglaubersgNo ratings yet