Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psa - Cia Iii
Uploaded by
GLARIDAAMALA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThe document is an exam for a Power System Analysis course. It contains questions testing knowledge of symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults in power systems, sequence networks, stability concepts, and the swing equation. Specifically:
1) It asks students to name different types of unsymmetrical faults in power systems and define negative sequence components.
2) Questions also cover drawing sequence networks for different fault types and evaluating them.
3) Concepts of stability, critical clearing time, swing curves, and steady state stability limits are defined and formulas for these metrics are requested.
4) Problems involve explaining the symmetrical component model of a synchronous machine under faults, deriving the swing equation, and using the equal area criterion to find the
Original Description:
Original Title
PSA - CIA III
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is an exam for a Power System Analysis course. It contains questions testing knowledge of symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults in power systems, sequence networks, stability concepts, and the swing equation. Specifically:
1) It asks students to name different types of unsymmetrical faults in power systems and define negative sequence components.
2) Questions also cover drawing sequence networks for different fault types and evaluating them.
3) Concepts of stability, critical clearing time, swing curves, and steady state stability limits are defined and formulas for these metrics are requested.
4) Problems involve explaining the symmetrical component model of a synchronous machine under faults, deriving the swing equation, and using the equal area criterion to find the
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesPsa - Cia Iii
Uploaded by
GLARIDAAMALAThe document is an exam for a Power System Analysis course. It contains questions testing knowledge of symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults in power systems, sequence networks, stability concepts, and the swing equation. Specifically:
1) It asks students to name different types of unsymmetrical faults in power systems and define negative sequence components.
2) Questions also cover drawing sequence networks for different fault types and evaluating them.
3) Concepts of stability, critical clearing time, swing curves, and steady state stability limits are defined and formulas for these metrics are requested.
4) Problems involve explaining the symmetrical component model of a synchronous machine under faults, deriving the swing equation, and using the equal area criterion to find the
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
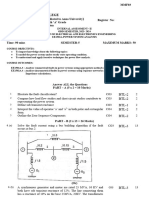
CIA– III
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
Year/sem:III/V Date :19.11.2021
Time : 1hr 30 Mins Marks: 50 Marks
EE8501-POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS
Part A (10 x 2= 20)
Name the various unsymmetrical fault in symmetrical fault
1. K1 CO4
Power system.
2. Define negative sequence. K1 CO4
Draw the connection of sequence network for double line
3. K2 CO4
to ground fault without fault impedance.
Evaluate the sequence network diagram for line to
4. K1 CO4
ground with fault impedance.
Name the faults which are having all three equal
5. sequence current and which do not have zero sequence K1 CO4
current.
Define Stability.
6. K1 CO5
7. Give the expression for critical clearing time. K1 CO5
8. Define swing curve. Give expression for swing equation. K1 CO5
9. What is steady state stability limit? K1 CO5
10. Point out equal area criterion. K2 CO5
Part B (2 x 15 = 30)
11a. Explain the short circuit model of a synchronous machine K2 CO4
under short circuit conditions. What symmetrical
components? Explain the symmetrical component
transformation
OR
11b. In the power system shown in figure three phase fault K2 CO4
occurs at point P and the faulty line was opened a little
late. Find the power output equations for the pre-fault
during fault and post fault calculation
12a. Derive the swing equation for a single machine connected K2 CO5
to infinite bus system. State the assumptions if any and
state the usefulness of this equation. Neglect the damping.
OR
12b. A generator is operating 50Hz,delivers 1.0 p.u power to K2 CO5
an infinite through a transmission circuit in which
resistance is ignored. A fault taken place reducing a
maximum power transferable to 0.5
p.u. Before the fault, this power was 2.0 p.u and after the
clearance of the fault it is 1.5p.u. By using equal area
criterion ,determine the critical clearing angle
Staffincharge HOD
You might also like
- Psa Cia - IiDocument2 pagesPsa Cia - IiGLARIDAAMALANo ratings yet
- 232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - End SemDocument3 pages232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - End Semrajasree Marine Engg-Asst ProfNo ratings yet
- Psa Ia2 QUESTION PAPER Set 1Document2 pagesPsa Ia2 QUESTION PAPER Set 1sankarsadaNo ratings yet
- 232EE2A14TA - Advanced Power System AnalysisDocument2 pages232EE2A14TA - Advanced Power System Analysisrajasree Marine Engg-Asst ProfNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit ISujeev GyawaliNo ratings yet
- Part-A Q. No Question(s) Skills CO: 34032 & Electrical Circuits and InstrumentationDocument2 pagesPart-A Q. No Question(s) Skills CO: 34032 & Electrical Circuits and InstrumentationDr.V.R.VelmuruganNo ratings yet
- CIA-III 2018-19 Even Kee 201Document2 pagesCIA-III 2018-19 Even Kee 201amit621988No ratings yet
- BEEE103 Set 1Document3 pagesBEEE103 Set 1pruthvichougule21No ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering, Chandrapur. (Department of Electrical Engineering AssignmentDocument5 pagesGovernment College of Engineering, Chandrapur. (Department of Electrical Engineering AssignmentShubham LodiNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering and TechnologyDocument2 pagesSchool of Engineering and TechnologyMegha SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Set A & BDocument6 pagesElectrical Set A & Bharshkumarsingh333231No ratings yet
- R-16m - Question Bank - Bee - Units III, IV, V, ViDocument4 pagesR-16m - Question Bank - Bee - Units III, IV, V, Viabhishektamte20No ratings yet
- Course Outcomes, Question Number, Marks: Cos Co1 Co2 Co3 Co4 Co5 Ques. No. Max. Marks Cos & K-LevelDocument14 pagesCourse Outcomes, Question Number, Marks: Cos Co1 Co2 Co3 Co4 Co5 Ques. No. Max. Marks Cos & K-LevelMATHAN RAJ MNo ratings yet
- 232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pages232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineeringrajasree Marine Engg-Asst ProfNo ratings yet
- USN 18EEEE62: High Voltage EngineeringDocument2 pagesUSN 18EEEE62: High Voltage Engineering1DA18EE013Gagana B.RNo ratings yet
- Knowledge K1 - Remembering K3 - Applying K5 - Evaluating Levels (KL) K2 - Understanding K4 - Analyzing K6 - CreatingDocument2 pagesKnowledge K1 - Remembering K3 - Applying K5 - Evaluating Levels (KL) K2 - Understanding K4 - Analyzing K6 - CreatingAnonymous R4WpNxNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Third Internal Assessment TestDocument1 pageDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Third Internal Assessment Testsyed1188No ratings yet
- Role of Marketing in Developing EconomyDocument1 pageRole of Marketing in Developing EconomyElujekwute BenjaminNo ratings yet
- 2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankJeril joseNo ratings yet
- Nirma University: Institute of TechnologyDocument2 pagesNirma University: Institute of TechnologyCiwahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledSoorya Priya Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BEE Assignment Even 2020Document5 pagesBEE Assignment Even 2020Aditya PatelNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Engineering Kamaraju and NaiduDocument2 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering Kamaraju and NaiduAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- 19eec44 - Analog Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsDocument2 pages19eec44 - Analog Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsKarunakaran M,47No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements EE42 EE402 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAM 4TH SEM AUG 2017Document2 pagesElectrical and Electronics Measurements EE42 EE402 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAM 4TH SEM AUG 2017RT PRAJWAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Kee 201Document2 pagesElectrical Engineering Kee 201Shuvam BhagatNo ratings yet
- EET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDocument9 pagesEET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDeepa M SNo ratings yet
- Bee Mid-2 B19 Ee 1202Document1 pageBee Mid-2 B19 Ee 1202Karthik ReddyNo ratings yet
- Bee 20 KUKDocument3 pagesBee 20 KUKbabuNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityKAPADIA DEVNo ratings yet
- Eca Cia IDocument2 pagesEca Cia Ixavier jerfinNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem QPDocument16 pages3rd Sem QPRITHVIKHA VNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledJolly James KNo ratings yet
- EC8453 - LIC Question BankDocument8 pagesEC8453 - LIC Question BankdonavallishanmukasaiNo ratings yet
- Semester End Examinations - January 2019 Ee15Document2 pagesSemester End Examinations - January 2019 Ee15PuneethNo ratings yet
- Part A: (Government Aided Autonomous Institution)Document2 pagesPart A: (Government Aided Autonomous Institution)Dr.V.R.VelmuruganNo ratings yet
- GTD Model QP 2Document3 pagesGTD Model QP 2Jeevan N BNo ratings yet
- IAT-II Question Paper With Solution of 18ELE13 Basic Electrical Engineering March-2021-Lokasree B SDocument1 pageIAT-II Question Paper With Solution of 18ELE13 Basic Electrical Engineering March-2021-Lokasree B SJohanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Electical & Electronics Measurement Question BankDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering Electical & Electronics Measurement Question Bankvijay patilNo ratings yet
- PSP - PG - Cat 2 QPDocument2 pagesPSP - PG - Cat 2 QPSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- CT - IT - 2 - S1 - AnswerDocument6 pagesCT - IT - 2 - S1 - AnswerRaja pandiyanNo ratings yet
- Beee GGCT Mid Term 2 Paper 2023Document2 pagesBeee GGCT Mid Term 2 Paper 2023ShirishNo ratings yet
- C F1055 Pages: 3: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksDocument3 pagesC F1055 Pages: 3: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksPranav R KrishNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical 1st Year 2021 T101ADocument5 pagesBasic Electrical 1st Year 2021 T101ASukanta MallickNo ratings yet
- CT It 2 S1Document4 pagesCT It 2 S1Raja pandiyanNo ratings yet
- Ee306 ADocument3 pagesEe306 AAparna JoseNo ratings yet
- Semester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperDocument15 pagesSemester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperGopiNo ratings yet
- Beee Internal Test 1 QPDocument3 pagesBeee Internal Test 1 QPindraNo ratings yet
- SGP Assignment 1to 5Document17 pagesSGP Assignment 1to 5Fariha shaikhNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis - Set ADocument4 pagesCircuit Analysis - Set APandyselvi BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Be Winter 2020Document2 pagesBe Winter 2020DeepNo ratings yet
- C F192049 Pages:2: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksDocument2 pagesC F192049 Pages:2: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksPranav R KrishNo ratings yet
- Ee8002-Doea - Open Book TestDocument4 pagesEe8002-Doea - Open Book Testsaranraj rNo ratings yet
- FY Btech - EX - Electrical & Electronics Engineering - SEM - I - JAN 2023Document3 pagesFY Btech - EX - Electrical & Electronics Engineering - SEM - I - JAN 2023kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- KSR Institute For Engineering and Technology TIRUCHENGODE - 637 215Document5 pagesKSR Institute For Engineering and Technology TIRUCHENGODE - 637 215Karthikeyan SelvaNo ratings yet
- Kee101t Ee Aktu QP-2020-21Document14 pagesKee101t Ee Aktu QP-2020-21Sudhir ChandNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Q No. Marks CODocument27 pagesTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Q No. Marks COjatin kumarNo ratings yet
- Ee 501 SeriesDocument5 pagesEe 501 SeriesFLOWERNo ratings yet
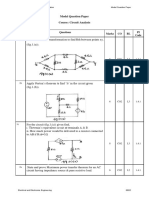
- Model Question Paper Course: Circuit Analysis: Q.No. Questions Marks CO BL PI CodeDocument5 pagesModel Question Paper Course: Circuit Analysis: Q.No. Questions Marks CO BL PI Codekrishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- TTL Serial CameraDocument25 pagesTTL Serial CameraJoseph Quezada Fellizar100% (1)
- Convert An ATX Power Supply Into A Regular DC PowerDocument11 pagesConvert An ATX Power Supply Into A Regular DC PowerhelderruiNo ratings yet
- Emona Fotex Sample Labmanual Ver1 1 PDFDocument76 pagesEmona Fotex Sample Labmanual Ver1 1 PDFANGEL MORENONo ratings yet
- HW 2Document1 pageHW 2Chani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- JCY-1850 SVDR MED Type ApprovalDocument4 pagesJCY-1850 SVDR MED Type ApprovalNishant PandyaNo ratings yet
- SM C37.94SDocument2 pagesSM C37.94SseanwrestlerNo ratings yet
- Arthrex Synergy Video CartDocument32 pagesArthrex Synergy Video CartdcgNo ratings yet
- KG-K125 Latching RelayDocument4 pagesKG-K125 Latching RelaySmain BendeddoucheNo ratings yet
- Dr. D. Sreenivasarao: Overview and Work Done at Nit WarangalDocument2 pagesDr. D. Sreenivasarao: Overview and Work Done at Nit WarangalSreenivasaraoDharmavarapuNo ratings yet
- 34401A Digital Multimeter: Product Discontinuance NoticeDocument9 pages34401A Digital Multimeter: Product Discontinuance NoticetomichelNo ratings yet
- Harmony XB4 XB5 XB6 Brochure 2013Document8 pagesHarmony XB4 XB5 XB6 Brochure 2013nooruddinkhan1No ratings yet
- Oscillator CircuitDocument16 pagesOscillator CircuitSiddhartha PalNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge IEC 60270Document9 pagesPartial Discharge IEC 60270Kamal Tomar0% (9)
- Muhammad Khalid: Cell: 03228620826, 03349087573 Tel: 0923631318Document1 pageMuhammad Khalid: Cell: 03228620826, 03349087573 Tel: 0923631318Abdourahmane BaNo ratings yet
- 2N3553 Silicon NPN Transistor RF Power Driver: Absolute Maximum RatingsDocument2 pages2N3553 Silicon NPN Transistor RF Power Driver: Absolute Maximum RatingsAhmad AftalNo ratings yet
- Pricelist - Rafa SelularDocument23 pagesPricelist - Rafa SelularNaim MalzzNo ratings yet
- RAM/Peripheral Interfacing Device For 8085 and 8088: Hitesh PatelDocument28 pagesRAM/Peripheral Interfacing Device For 8085 and 8088: Hitesh Patelhitesh_maxi100% (1)
- Industry's Highest Performance Simulation Solution: Key BenefitsDocument7 pagesIndustry's Highest Performance Simulation Solution: Key BenefitsektaNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Byte Keyboard - Google SearchDocument3 pagesCosmic Byte Keyboard - Google SearchAveNo ratings yet
- Dual-Band A-Panel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Integrated CombinerDocument1 pageDual-Band A-Panel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Integrated CombinerAromaro AmarNo ratings yet
- Pip-Hse Mse Msxe DatasheetDocument2 pagesPip-Hse Mse Msxe DatasheetFrancisco YunesNo ratings yet
- Panthera Camera TrapDocument10 pagesPanthera Camera TrapCitra Novalina Panjaitan100% (1)
- BT578 enDocument2 pagesBT578 enAnonymous wf984aw4dNo ratings yet
- Naila Shahzadi 1081 Sec BDocument9 pagesNaila Shahzadi 1081 Sec BZeeshan ch 'Hadi'No ratings yet
- Aelzp0be (SMART-DISPLAY-ing) PDFDocument46 pagesAelzp0be (SMART-DISPLAY-ing) PDFalberto100% (4)
- GPH6DU TH 42PX20U P - Schematics PDFDocument176 pagesGPH6DU TH 42PX20U P - Schematics PDFdrone001No ratings yet
- CV Richa HanikDocument5 pagesCV Richa HanikAriefSuryoWidodoNo ratings yet
- Quadrature Amplitude ModulationDocument8 pagesQuadrature Amplitude Modulationj_mmouraNo ratings yet
- LTE Protocol Stack TestingDocument2 pagesLTE Protocol Stack Testingmohdwajid200950% (4)