Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anaerobic Pathways Handout
Anaerobic Pathways Handout
Uploaded by
ashwinaaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anaerobic Pathways Handout
Anaerobic Pathways Handout
Uploaded by
ashwinaaCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Worksheet LSM 2.
3-3
Anaerobic Respiration
Fill in the blanks on the figures and in the summaries.
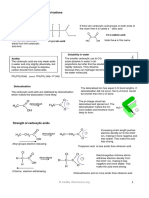
O− Lactic Acid Fermentation
After glycolysis occurs, the two
C O
molecules receive molecules
H C OH from , creating .
CH3 can be converted back into
in the . The
G
L can then enter the
Y
C and cellular respiration can
O
L proceed.
Y
S
I
S
O−
C O
C O
CH3
Lactic acid fermentation in muscle cells
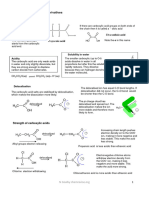
Ethanol Fermentation H
After glycolysis occurs, the two H C OH
molecules lose a molecule,
CH3
creating . The
combines with to create G
L
. receives a Y
C
atom from , O
L
resulting in the production of . Y
S
I H
S
C O
O− CO2
CH3
C O
C O
CH3
Alcohol fermentation in yeast
Copyright © 2003 Nelson Chapter 2 Cellular Respiration 61
Student Worksheet Solutions LSM 2.3-4
Anaerobic Respiration, Solution
Fill in the blanks on the figures and in the summaries.
O− Lactic Acid Fermentation
After glycolysis occurs, the two pyruvate
C O hydrogen
molecules receive molecules
H C OH from NADH , creating lactate .
glucose
CH3 Lactate can be converted back into
2 ADP 2 lactate pyruvate in the liver . The
G
pyruvate Krebs
2 ATP
L
Y 2 NAD+ can then enter the
C cycle and cellular respiration can
O 2 NADH
L proceed.
Y
S
I
S
O−
C O
2 pyruvate
C O
CH3
Lactic acid fermentation in muscle cells
Ethanol Fermentation H
After glycolysis occurs, the two pyruvate
H C OH
molecules lose a carbon molecule, glucose
CH3
creating acetaldehyde . The carbon
2 ADP 2 ethanol
combines with oxygen to create G
carbon dioxide . Acetaldehyde receives a 2 ATP
L
Y 2 NAD+
C
hydrogen atom from NADH , O
L
2 NADH
resulting in the production of ethanol . Y
S
I H
S
C O
O− CO2
CH3
C O
2 pyruvate 2 acetaldehyde
C O
CH3
Alcohol fermentation in yeast
62 Chapter 2 Cellular Respiration Copyright © 2003 Nelson
You might also like
- Coaching & Sport Science Review: AuthorDocument29 pagesCoaching & Sport Science Review: AuthorjovenlouNo ratings yet
- Lactated RingersDocument22 pagesLactated Ringerskiky_frakNo ratings yet
- Adequacy of Perfusion During Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument64 pagesAdequacy of Perfusion During Cardiopulmonary BypassBranka Kurtovic50% (2)
- Chem 44.1 Special SynthesisDocument86 pagesChem 44.1 Special SynthesisCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (2)
- Hydrocarbons - Halogen Derivatives For JEE Main - JEEced (Study Package For Chemistry) - Dr. O. P. Agarwal PDFDocument326 pagesHydrocarbons - Halogen Derivatives For JEE Main - JEEced (Study Package For Chemistry) - Dr. O. P. Agarwal PDFPaathshala Education IT100% (2)
- A Textbook of Dairy Chemistry PDFDocument208 pagesA Textbook of Dairy Chemistry PDFOner Altınsoy75% (4)
- Aldehyde, Ketones. Carboxylic Typed Notes STUDY RATEDocument52 pagesAldehyde, Ketones. Carboxylic Typed Notes STUDY RATEYASH SONARNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II: University of Lincoln PresentationDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry II: University of Lincoln PresentationkayannaNo ratings yet
- BO2 FermentationDocument11 pagesBO2 FermentationJazmin Adriana Proa SilvaNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry (2.1, 2.2)Document12 pagesStereochemistry (2.1, 2.2)VIGHNESH BALKRISHNA LOKARENo ratings yet
- Jurnal KimorDocument9 pagesJurnal Kimoraulia utamiNo ratings yet
- Quant Chem AnalDocument4 pagesQuant Chem AnalMisheelt TsolmonbaatarNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry & Reactions of MonosaccharidesDocument2 pagesStereochemistry & Reactions of MonosaccharidesSamiya ZamanNo ratings yet
- Saplaco, Nathan Angelo v. Bs Criminology 2a Experiment 1Document8 pagesSaplaco, Nathan Angelo v. Bs Criminology 2a Experiment 1cj santosNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Organic Chemistry BS Biology - 1 Semester, AY 2020 - 2021Document38 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes: Organic Chemistry BS Biology - 1 Semester, AY 2020 - 2021Rachel AgacoscosNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecules Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesOrganic Molecules Practice Problemsejs2004No ratings yet
- 1.6! Drawing Chemical StructuresDocument6 pages1.6! Drawing Chemical StructuresSadeeq ArtxzNo ratings yet
- Chem 115 Myers: Stereoselective, Directed Aldol ReactionDocument24 pagesChem 115 Myers: Stereoselective, Directed Aldol ReactionChemical MoleculeNo ratings yet
- TCI - Asymmetric OrganocatalystsDocument8 pagesTCI - Asymmetric OrganocatalystsDeath Dealer61No ratings yet
- What Is Chemical Reaction: C H E M I S T R YDocument1 pageWhat Is Chemical Reaction: C H E M I S T R Yhacker johnNo ratings yet
- Ch3e4 Stereoselective Synthesis MW Handout Reorganised 021111Document51 pagesCh3e4 Stereoselective Synthesis MW Handout Reorganised 021111Kethavath VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Alchohol ResearchASDocument18 pagesAlchohol ResearchASAhmed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Proceso Oxo (Hidroformilación) : Andrea Dávila AlvarezDocument22 pagesProceso Oxo (Hidroformilación) : Andrea Dávila AlvarezkrmeliNo ratings yet
- Test 4 (GC F 03) W AnsDocument3 pagesTest 4 (GC F 03) W AnsLuis glezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios ElectroquimicaDocument6 pagesEjercicios ElectroquimicaEthel Elsa D ́ Arendelle Lan WanJi IPNNo ratings yet
- CY2102Document2 pagesCY2102Prarabdha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding FULL NOTES PDFDocument77 pagesChemical Bonding FULL NOTES PDFArsh KumarNo ratings yet
- JB CI 13.1 HalogenoalkanesDocument6 pagesJB CI 13.1 HalogenoalkanesOCRChemistrySaltersNo ratings yet
- Topic 16 Aldehydes, Ketones and Optical Isomerism Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Optical IsomerismDocument15 pagesTopic 16 Aldehydes, Ketones and Optical Isomerism Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Optical Isomerismclip215No ratings yet
- Organo AntimonyDocument7 pagesOrgano AntimonyDharmendra Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Substitution ReactionDocument1 pageSubstitution ReactionAbhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- Benzene (B)Document17 pagesBenzene (B)Variganji Sumanth BabuNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Hangovers PDFDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Hangovers PDFSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Phenol - 18290367 - 2023 - 06 - 20 - 12 - 13Document6 pagesAlcohol and Phenol - 18290367 - 2023 - 06 - 20 - 12 - 13telate6613No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons & Halogen Derivatives PDFDocument326 pagesHydrocarbons & Halogen Derivatives PDFSuraj panditNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives AqaDocument8 pages3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives AqaDocument8 pages3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Aqakhadijah aliNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Polymers: Polythene (Or Polyethylene)Document12 pagesSynthetic Polymers: Polythene (Or Polyethylene)Adrian LeivaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2021Document112 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2021Omer Muhammad janNo ratings yet
- E12 AtqDocument5 pagesE12 AtqCharlene InaoNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Print PDFDocument5 pagesBiomolecules Print PDFsinghatmesh685No ratings yet
- Isomers of Coordination ComplexesDocument12 pagesIsomers of Coordination ComplexesNov IndaNo ratings yet
- OAREDocument2 pagesOARELurthu PushparajNo ratings yet
- Mike Virnig - Crud PresentationDocument34 pagesMike Virnig - Crud Presentationworquera2507No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Amino Acids Polymers IIT TheoryDocument53 pagesCarbohydrates Amino Acids Polymers IIT TheoryAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4Document2 pagesTutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4fatinNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Salicylic Acid: Practical Lab. 3Document12 pagesSynthesis of Salicylic Acid: Practical Lab. 3Saba GheniNo ratings yet
- CakeSenese Label 4.5x6.5cm-PrintA4Document1 pageCakeSenese Label 4.5x6.5cm-PrintA4phamngocdinh.1124No ratings yet
- Alchohols, Ethers, PhenolsDocument45 pagesAlchohols, Ethers, PhenolsMohammed JunaidNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument22 pagesAlcoholsSai Sasivardhan GampaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #8 2018-2019 AnswersDocument6 pagesCarbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #8 2018-2019 AnswersZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Lec18InsertionandEliminationReactions 001Document27 pagesLec18InsertionandEliminationReactions 001Hildayanti MustikasariNo ratings yet
- Reviw RemiDocument4 pagesReviw RemiBuena QuintinNo ratings yet
- Theo Chem: A Theoretical Study of Co2 Adsorption On Tiot1Document17 pagesTheo Chem: A Theoretical Study of Co2 Adsorption On Tiot1SafatNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin and Wintegreen Spring 2006Document6 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin and Wintegreen Spring 2006apzzzzNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 18Document1 pageSAQ Ans 18Zareen KidwaiNo ratings yet
- مقدمة في البحث (رنا الجهني)Document4 pagesمقدمة في البحث (رنا الجهني)Abdalmalek shamsanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules SHORT NotesDocument2 pagesBiomolecules SHORT NotesAstha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Nuevas Sustancias Ingles WebDocument126 pagesNuevas Sustancias Ingles WebMargari MargasNo ratings yet
- 1 Insertion / DeinsertionDocument7 pages1 Insertion / DeinsertionJ S.TNo ratings yet
- Roadmap Problem - 5Document1 pageRoadmap Problem - 5abhyudaipathwayNo ratings yet
- 01 Aldket ReducDocument1 page01 Aldket ReducSarvik The Pokémon Master RaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Session - 1 AIMDocument100 pagesChemical Bonding: Session - 1 AIMMOHAMMED RASHIDNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryF. G. A. StoneNo ratings yet
- Alex Barrows Training Doc V2 For Training Beta PDFDocument12 pagesAlex Barrows Training Doc V2 For Training Beta PDFPaulo G B CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- 2017 OrganicAcids CharacteristicsPropertiesandSynthesis 978-1-63485-952-3 EBookAUTHORSCOMPLEMENTARYDocument157 pages2017 OrganicAcids CharacteristicsPropertiesandSynthesis 978-1-63485-952-3 EBookAUTHORSCOMPLEMENTARYAfrad HossainNo ratings yet
- Coconut FermentationDocument9 pagesCoconut FermentationPedro Peláez Sánchez100% (1)
- Microbial Ecology and Starter Culture Technology in Coffee ProcessingDocument15 pagesMicrobial Ecology and Starter Culture Technology in Coffee ProcessingLael IsazaNo ratings yet
- Shredded in Six Fat Loss AcceleratorDocument35 pagesShredded in Six Fat Loss AcceleratorntnzzmxzkgznblhodtNo ratings yet
- Food TechnologyDocument27 pagesFood Technologysneh lataNo ratings yet
- Technological Aspects of Kombucha, Its Applications and The Symbiotic Culture (SCOBY), and Extraction of Compounds of Interest - A Literature ReviewDocument12 pagesTechnological Aspects of Kombucha, Its Applications and The Symbiotic Culture (SCOBY), and Extraction of Compounds of Interest - A Literature ReviewNayeli MartinezNo ratings yet
- System For Heavy Lifting and Strenuous ActivitiesDocument7 pagesSystem For Heavy Lifting and Strenuous ActivitiesMaryAnnAnabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FermentationDocument6 pagesChapter 7 FermentationBRENDAN CHIEW CHANG RONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Xanthan Biopolymer A Review of Methods For The Determination of Concentration and For The Measurement of Acetate and Pyruvate ContentDocument7 pagesXanthan Biopolymer A Review of Methods For The Determination of Concentration and For The Measurement of Acetate and Pyruvate ContentSorin LazarNo ratings yet
- Kung Et Al. (2018)Document14 pagesKung Et Al. (2018)Henry Daniel Ruiz AlbaNo ratings yet
- 3 GlycolysisDocument27 pages3 GlycolysisHammad KambohNo ratings yet
- Effective Use of A Tropical Hop Named Bitter Leaf (Vernonia Amygdalina) Extract As A Means of Extending The Shelf - Life ofDocument91 pagesEffective Use of A Tropical Hop Named Bitter Leaf (Vernonia Amygdalina) Extract As A Means of Extending The Shelf - Life ofSamuel UdoemaNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and Technology University: Department of Food EngineeringDocument15 pagesAddis Ababa Science and Technology University: Department of Food EngineeringmikialeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0141022999001556 MainDocument21 pages1 s2.0 S0141022999001556 MainRenata ScoralickNo ratings yet
- IsotachophoresisDocument7 pagesIsotachophoresisEka HerlinaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Spoilage of Milk and Milk ProductsDocument5 pagesMicrobial Spoilage of Milk and Milk ProductsAqiba Tus SaharNo ratings yet
- FermentationDocument10 pagesFermentationBenedict Marzan100% (1)
- Food Control: C. Chatelard-Chauvin, F. Pelissier, S. Hulin, M.C. MontelDocument13 pagesFood Control: C. Chatelard-Chauvin, F. Pelissier, S. Hulin, M.C. Montellordmoises MilanèsNo ratings yet
- 3 StaminaDocument11 pages3 StaminaYago Piccin PoloNo ratings yet
- Food Additives PDFDocument12 pagesFood Additives PDFHerianka DefriNo ratings yet
- ShakiDocument13 pagesShakiAnoshKhanNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Cytotoxic Potential of Bacterial Pigments Chapter-2 Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesEvaluation of Cytotoxic Potential of Bacterial Pigments Chapter-2 Literature ReviewChanakya ResearchNo ratings yet
- Rhizopus Oryzae: Production of L-Lactic Acid From Starch and Food Waste by Amylolytic MTCC 8784Document11 pagesRhizopus Oryzae: Production of L-Lactic Acid From Starch and Food Waste by Amylolytic MTCC 8784Christin SimamoraNo ratings yet
- III UG Physiology Respiration AVJDocument27 pagesIII UG Physiology Respiration AVJHead 4KNo ratings yet
- Alternating Hot and Cold Water ImmersionDocument7 pagesAlternating Hot and Cold Water ImmersionAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet