Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cc2 l4 Trace Elements
Uploaded by
Rose Denisse EstrellaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cc2 l4 Trace Elements
Uploaded by
Rose Denisse EstrellaCopyright:
Available Formats
CLINICAL CHEM 2 MLS 115
LESSON 4: TRACE ELEMENTS 01-03-22
WILLIAM CHRISTOPHER C. SALAZAR, RMT
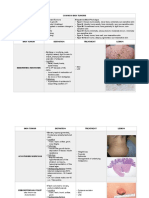
TRACE ELEMENTS
• Consists of metals, halogens, fluoride, and iodine.
• Essential trace elements are important for the maintenance of normal health, and tissue and organ functions.
• Trace elements have specific in vivo metabolic functions that cannot be effectively performed by other similar elements.
• Concentration in tissue: <1 μg/g of wet tissue and <0.01% of dry body weight.
TRACE
FUNCTION DEFICIENCY TOXICITY
ELEMENTS
• Insulin resistance
Enhances insulin action: for glucose and • Impaired glucose tolerance (type 2 • Skin ulcers.
Chromium
lipid metabolism. DM) • Renal and Hepatic necrosis.
• Hyperlipidemia
• Hgb synthesis. • Anemia. • Heart failure.
Cobalt
• Component of vit. B12. • Growth depression. • Hypothyroidism.
• Cellular respiration. • Menkes’ kinky hair syndrome. Interferes with absorption of iron and
Copper
• Collagen synthesis. • Muscle weakness. zinc.
Fluoride Prevents dental caries Dental caries
• Goiter.
Iodine Thyroid hormone synthesis. • Cretinism. Thyrotoxicosis.
• Myxedema.
• Oxy transport.
Iron Anemia Hemachromatosis.
• Component of hgb.
• Psychiatric disorders.
Manganese Bone and connective tissue functions. Skeletal defects.
• Parkinson’s disease.
• Growth depression.
• Anemia.
Molybdenum DNA metabolism. • Cretinism.
• Thyrotoxicosis.
• Goiter.
• Hair and nail loss.
Selenium Prevents oxidative damage of lipids. Keshan disease.
• Liver failure.
• Acrodermatitis.
• Enteropathica • Infants:
- Seizures
• Growth retardation.
• Protein synthesis. - Irritability
Zinc • Immune deficiency.
• Enzyme cofactor. - Anemia
• Infertility.
• Adults:
• Delayed wound healing. - Facial seborrhea.
• Osteoporosis.
KUNG NA KAYA NILA, KAYA RIN NATEN!!!
#RMTCutie L4 | GALLENO 1
You might also like
- Genetic and Metabolic DisordersDocument16 pagesGenetic and Metabolic DisordersErin HillNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminDocument2 pagesWater Soluble VitaminJane DemenciaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & Minerals: Slam Shraf AhmyDocument5 pagesVitamins & Minerals: Slam Shraf AhmyAfsal Ur FriendNo ratings yet
- NUTRIDocument16 pagesNUTRIthisswannNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument7 pagesAnemiaMaria Jose BravoNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics Hound OutDocument3 pagesGeriatrics Hound Outpasabay270No ratings yet
- Nutrient Chart: Nutrient Function Deficiency Other DataDocument4 pagesNutrient Chart: Nutrient Function Deficiency Other DataDashie XPNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metal Intoxication 2012Document3 pagesHeavy Metal Intoxication 2012Rem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document18 pagesLecture 4WoW brendon WoWNo ratings yet
- Clinical Assessments of NutrientsDocument6 pagesClinical Assessments of NutrientsDarlene Shaira JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Anemia Pathophysiology by Francis Oliveros, BSN 4Document2 pagesAnemia Pathophysiology by Francis Oliveros, BSN 4francis00090100% (1)
- Oral Aspects of Metabolic DiseasesDocument39 pagesOral Aspects of Metabolic DiseasesriyaNo ratings yet
- Metals in Biological SysytemDocument24 pagesMetals in Biological SysytemAnjanaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (20 Points)Document8 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (20 Points)ODESSEY SERQUI�ANo ratings yet
- Trace ElementsDocument2 pagesTrace ElementsAbc DefNo ratings yet
- 19 Salivary GlandsDocument14 pages19 Salivary GlandsIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing (Word) Bulleted For NSG RevieweesDocument8 pagesOncology Nursing (Word) Bulleted For NSG Revieweesswitlipz100% (1)
- FBCA Biomarkers and ConditionsDocument8 pagesFBCA Biomarkers and Conditionsmet50% (2)
- Assoc of Erythrocytes With Clinical ConditionsDocument3 pagesAssoc of Erythrocytes With Clinical ConditionsHaniGirlAlay-ayCachoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins MineralsDocument42 pagesVitamins MineralsDivyanga SivapragasamNo ratings yet
- Local Conditions Associated With Delayed Eruption Systemic Conditions Associated With Delayed EruptionDocument2 pagesLocal Conditions Associated With Delayed Eruption Systemic Conditions Associated With Delayed EruptionMartha Cruz HernandezNo ratings yet
- Pages From Rajesh Bardale Prinrensic Medicine and Toxicology 1Document1 pagePages From Rajesh Bardale Prinrensic Medicine and Toxicology 1mueen hashmiNo ratings yet
- Anemia Dalam Kehamilan-OliviaDocument20 pagesAnemia Dalam Kehamilan-OliviaSwitha Martha Sinaga100% (1)
- Revision 21.7.23-Y3Document7 pagesRevision 21.7.23-Y3leexinyiNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument42 pagesEndocrineNisini ImanyaNo ratings yet
- English Task in Nursing 2 SondaDocument4 pagesEnglish Task in Nursing 2 SondayulisulistiyoNo ratings yet
- 02 Muskuloskeletal 2Document78 pages02 Muskuloskeletal 2Gerald BatugalNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiencies & ExcessDocument2 pagesVitamin Deficiencies & Excessapi-26123997No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Previous Year QuestionsDocument21 pagesBiochemistry Previous Year QuestionsHaroon RashithNo ratings yet
- Nursing Clients With Hematologic DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Clients With Hematologic DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metal Detection Using Aas (Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer) in Leafy VegetablesDocument30 pagesHeavy Metal Detection Using Aas (Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer) in Leafy VegetablesKatlene Joy BaytingNo ratings yet
- Blood: Nikita Sebastian 1 Year Post Graduate Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics JSSDCHDocument94 pagesBlood: Nikita Sebastian 1 Year Post Graduate Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics JSSDCHNikita SebastianNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument44 pagesPathologyBENEDICT ATUJENGANo ratings yet
- Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - Quick Reference GuideDocument29 pagesBlood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - Quick Reference Guidejamesilluminare73% (15)
- Nervo US Syste M: Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesNervo US Syste M: Endocrine SystemEric A Colinares Jr.No ratings yet
- (PPT) IM (Onco and Hema)Document78 pages(PPT) IM (Onco and Hema)ricaannpanugalinogNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument2 pagesImmunologyAinaa MalikNo ratings yet
- How To Choose The Right Statistical Test?: Indian Journal of Ophthalmology March 2011Document11 pagesHow To Choose The Right Statistical Test?: Indian Journal of Ophthalmology March 2011L.RNo ratings yet
- Anemia 1Document30 pagesAnemia 1Aishwarya JeeNo ratings yet
- NutrientsDocument6 pagesNutrientsMarcelo Sakiting100% (2)
- NCM 107 Rle Nicu ResearchDocument3 pagesNCM 107 Rle Nicu ResearchIsha Catimbang GenerilloNo ratings yet
- Anemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionDocument5 pagesAnemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionJette Charmae OlboNo ratings yet
- HEMA-Iron Deficiency Anemia & MegaloBalstic Anemia DRA CRUZDocument5 pagesHEMA-Iron Deficiency Anemia & MegaloBalstic Anemia DRA CRUZShams JailaniNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument23 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro Module1 Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBarecuatro Module1 Drug StudyANGELICA CLAIRE BARECUATRONo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae 2Document11 pagesEnterobacteriaceae 2odhiambo samwelNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology SampleDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology Samplerowelyn_ann18No ratings yet
- June Schedule Part - 1Document4 pagesJune Schedule Part - 1Andi MontesNo ratings yet
- Taking The Long View of Canine Hypoadrenocorticism OutlineDocument4 pagesTaking The Long View of Canine Hypoadrenocorticism OutlineJuniClaudia13No ratings yet
- Histology Finals ReviewerDocument14 pagesHistology Finals ReviewerRYABELLE JESUSA SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Common Skin TumorsDocument6 pagesCommon Skin TumorskateverdadNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument4 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsSummiyah ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Outline: Anaemias I Microcytic, Iron Deficiency Microcytic, Iron Deficiency & Iron OverloadDocument11 pagesOutline: Anaemias I Microcytic, Iron Deficiency Microcytic, Iron Deficiency & Iron Overloaddorsa koraeiNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Disorders General LectureDocument34 pagesEndocrinology Disorders General LecturejawadNo ratings yet
- Childhood Anaemia: Paediatric Haematologist and Oncologist Deparment of Paediatrics & Child Health MustDocument34 pagesChildhood Anaemia: Paediatric Haematologist and Oncologist Deparment of Paediatrics & Child Health MustSsenyonga DominicNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument4 pagesVitaminsJosef ValloNo ratings yet
- Pir Refeeding PPT FinalDocument13 pagesPir Refeeding PPT FinalbentoeNo ratings yet
- DyslipidemiaDocument16 pagesDyslipidemiaWateen KhasawnehNo ratings yet
- Tangerine - Breakfast Set Menu Wef 16 Dec UpdatedDocument3 pagesTangerine - Breakfast Set Menu Wef 16 Dec Updateddeveloper louNo ratings yet
- Module 5 What Is Matter PDFDocument28 pagesModule 5 What Is Matter PDFFLORA MAY VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Tese Beatbox - Florida PDFDocument110 pagesTese Beatbox - Florida PDFSaraSilvaNo ratings yet
- Very Narrow Aisle MTC Turret TruckDocument6 pagesVery Narrow Aisle MTC Turret Truckfirdaushalam96No ratings yet
- Sap Consultant Cover LetterDocument3 pagesSap Consultant Cover LetterrasgeetsinghNo ratings yet
- PD3 - Strategic Supply Chain Management: Exam Exemplar QuestionsDocument20 pagesPD3 - Strategic Supply Chain Management: Exam Exemplar QuestionsHazel Jael HernandezNo ratings yet
- Borges, The SouthDocument4 pagesBorges, The Southdanielg233100% (1)
- NHD Process PaperDocument2 pagesNHD Process Paperapi-203024952100% (1)
- Session 1Document18 pagesSession 1Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHARACTER FORMATION 1 PrelimDocument15 pagesCHARACTER FORMATION 1 PrelimAiza Minalabag100% (1)
- The Mooring Pattern Study For Q-Flex Type LNG Carriers Scheduled For Berthing at Ege Gaz Aliaga LNG TerminalDocument6 pagesThe Mooring Pattern Study For Q-Flex Type LNG Carriers Scheduled For Berthing at Ege Gaz Aliaga LNG TerminalMahad Abdi100% (1)
- Sla At&tDocument2 pagesSla At&tCésar Lainez Lozada TorattoNo ratings yet
- G10 Lesson2 DLPDocument13 pagesG10 Lesson2 DLPAngeles, Mark Allen CNo ratings yet
- Trina 440W Vertex-S+ DatasheetDocument2 pagesTrina 440W Vertex-S+ DatasheetBrad MannNo ratings yet
- GGG Sri MDocument2 pagesGGG Sri MGiovanni LuigiNo ratings yet
- 220245-MSBTE-22412-Java (Unit 1)Document40 pages220245-MSBTE-22412-Java (Unit 1)Nomaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Diogenes Laertius-Book 10 - Epicurus - Tomado de Lives of The Eminent Philosophers (Oxford, 2018) PDFDocument54 pagesDiogenes Laertius-Book 10 - Epicurus - Tomado de Lives of The Eminent Philosophers (Oxford, 2018) PDFAndres Felipe Pineda JaimesNo ratings yet
- Computer System Validation - Definition and Requirements - MustRead PDFDocument3 pagesComputer System Validation - Definition and Requirements - MustRead PDFtraining validNo ratings yet
- Institutional Group Agencies For EducationDocument22 pagesInstitutional Group Agencies For EducationGlory Aroma100% (1)
- Sundar Pichai PDFDocument6 pagesSundar Pichai PDFHimanshi Patle100% (1)
- Catheter Related InfectionsDocument581 pagesCatheter Related InfectionshardboneNo ratings yet
- Toolbox TalkDocument14 pagesToolbox Talkcall_mustafas2361No ratings yet
- Sale Counter List JuneDocument9 pagesSale Counter List Junep6a4nduNo ratings yet
- VimDocument258 pagesVimMichael BarsonNo ratings yet
- Worst of Autocall Certificate With Memory EffectDocument1 pageWorst of Autocall Certificate With Memory Effectapi-25889552No ratings yet
- PlateNo 1Document7 pagesPlateNo 1Franz Anfernee Felipe GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Jul - Dec 09Document8 pagesJul - Dec 09dmaizulNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Cat C7 Marine Engine Parts Catalogue ManualDocument21 pagesCaterpillar Cat C7 Marine Engine Parts Catalogue ManualkfsmmeNo ratings yet
- Victor 2Document30 pagesVictor 2EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Precursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationDocument7 pagesPrecursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationAlv R GraciaNo ratings yet