Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch06 ApplicationsOfIntegration
Uploaded by
abhishek netiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch06 ApplicationsOfIntegration
Uploaded by
abhishek netiCopyright:
Available Formats
Applications of Integration
Chapter 6
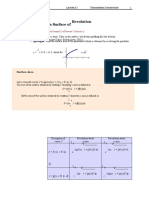
Area of a region between two curves: 6.1 p293 If f and g Definition of Arc Length: 6.4 p321 If f(x) represents a
are continuous on [a, b] and g ( x ) ≤ f ( x ) for all x in smooth curve on the interval [a, b], then the arc
[a, b], then the area of the region bounded by the length of f between a and b is given by:
S=∫
graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b b
is 1 + [ f ′( x )]2 dx
a
A = ∫ [ f ( x ) − g( x )]dx
b
a Definition of the Area of a Surface of Revolution: 6.4
p328 If f(x) has a continuous derivative on the interval
In other words, integrate the value obtained by [a, b], then the area S of the surface of revolution
subtracting the lower curve from the upper curve. For formed by revolving the graph of f about a horizontal
curves that intersect in more than two points, it is or vertical axis is:
necessary to treat each segment separately.
S = 2π ∫ r ( x ) 1 + [ f ′( x )]2 dx
b
(horizontal axis)
a
DISK METHOD: Finding the volume of a solid of or
revolution: 6.2 p303 Integrate the square of the radius
S = 2π ∫ r ( y ) 1 + [ f ′( y )]2 dy
d
and multiply by π . (vertical axis)
c
V = π ∫ [ f ( x )]2 dx
b
(revolving around the x-axis)
a where r ( x ) or r ( y ) is the distance between the graph of f
V = π ∫ [ f ( y )] dy
d
2
(revolving around the y-axis) and the axis of revolution.
c
Quadratic Equation
WASHER METHOD: Finding the volume of a solid of
− b ± b 2 − 4 ac
revolution: 6.2 p305 Subtract the square of the inner x =
radius from the square of the outer radius, integrate 2a
the result and multiply by π .
V = π ∫ ([ R( x )]2 − [r ( x )]2 )dx
b Tom Penick tomzap@eden.com www.teicontrols.com/notes
(horiz. axis of
a
revolution)
V = π ∫ ([ R( y )]2 − [r ( y )]2 )dy
d
(vert. axis of
c
revolution)
SHELL METHOD: Finding the volume of a solid of
revolution: 6.3 p313
V = 2π ∫ p( y )h( y ) dy
d
(horizontal axis of
c
revolution)
V = 2π ∫ p( x )h( x ) dx
b
(vertical axis of revolution)
a
where: p ( x ) and p ( y ) are radii in terms of x and y
respectively. (These will simply be x or y
where the axis of revolution is the y-axis or
x-axis.)
h (y ) is the horizontal distance across the area in
terms of y.
h ( x ) is the vertical distance across the area in
terms of x.
[a, b] is the interval on the x-axis.
[c, d] is the interval on the y-axis.
You might also like
- Area Bounded by CurvesDocument15 pagesArea Bounded by CurvesJulius JunioNo ratings yet
- Application of Integration-Lecture - VolumeDocument3 pagesApplication of Integration-Lecture - Volumesevenkenny0123No ratings yet
- 4.1 Area of A Surface of RevolutionDocument2 pages4.1 Area of A Surface of RevolutionisaackNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 (Vector Calculus)Document6 pagesAssignment 4 (Vector Calculus)Shail BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Functions of Three Variables and Their Level SurfacesDocument12 pagesFunctions of Three Variables and Their Level SurfacesMarioNo ratings yet
- DHS H2 2021 Prelim P1Document5 pagesDHS H2 2021 Prelim P1猪猪侠No ratings yet
- 02-Applications of The IntegralsDocument32 pages02-Applications of The IntegralsGeeta MNo ratings yet
- Project in Calculus IiDocument14 pagesProject in Calculus IiBunny DummyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - IntegrationDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - IntegrationSelvarani NadarajahNo ratings yet
- Area Under Curve Catjee QuesDocument10 pagesArea Under Curve Catjee QuesDETECTIVENo ratings yet
- Surfaceareaandvolume Ofatorus: by JakoblindbladblaavandDocument3 pagesSurfaceareaandvolume Ofatorus: by JakoblindbladblaavandabasakNo ratings yet
- Aamarasigan: Application of Definite IntegralsDocument20 pagesAamarasigan: Application of Definite IntegralsCyruz Lapinas100% (1)
- Ma 111 Tutorial 3Document2 pagesMa 111 Tutorial 3Pushkraj pathakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.2-Volumes by Slicing-SolutionsDocument7 pagesChapter 6.2-Volumes by Slicing-SolutionsMd Tanvir Chowdhury 2232122642No ratings yet
- Calculus Questions2019Document5 pagesCalculus Questions2019Martin NguyenNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT101P LO VL2022230106647 Reference Material I 01-11-2022 4. EXPERIMENT 2ADocument3 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT101P LO VL2022230106647 Reference Material I 01-11-2022 4. EXPERIMENT 2AVenkat BalajiNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Area Under The CurveDocument12 pagesBest Approach: Area Under The CurveAyush SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Updated - Tutorial On Unit IIDocument4 pagesUpdated - Tutorial On Unit IItejas chikhlikarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Applications of Definite IntegDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Applications of Definite IntegAbdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Study Guide # 1: MA 26100 - FALL 2019Document5 pagesStudy Guide # 1: MA 26100 - FALL 2019Chorale SopranoNo ratings yet
- Conic Section PDFDocument22 pagesConic Section PDFishad satyen100% (2)
- Bstat Bmath Uga 2017Document6 pagesBstat Bmath Uga 2017Surender SinghNo ratings yet
- Moi Lec 2 & 3Document14 pagesMoi Lec 2 & 3afzal taiNo ratings yet
- MAT300 2017 Sample Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesMAT300 2017 Sample Exam QuestionsjkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Volume of Solids of RevolutionDocument21 pagesLesson 13 Volume of Solids of RevolutionStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- MTH102 - Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageMTH102 - Cheat Sheet 1fsggafsdfNo ratings yet
- HCI 2023 H2 Maths PromoDocument7 pagesHCI 2023 H2 Maths PromoMarcus LinNo ratings yet
- SurfacesDocument13 pagesSurfacescuriosity100% (1)
- Math1 Tutorial5Document2 pagesMath1 Tutorial5KarthikRaoNo ratings yet
- Functions of Sev Var 21Document19 pagesFunctions of Sev Var 21Mohamed DORBANENo ratings yet
- Biology CellsDocument12 pagesBiology CellsGift ag bruhNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Area Under The CurveDocument4 pagesBest Approach: Area Under The CurveAyush SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Conic Section RevisionDocument111 pagesConic Section RevisionBsprogrammer100% (1)
- Schaumcalculus p2 PDFDocument131 pagesSchaumcalculus p2 PDFLouise RamosNo ratings yet
- 8221 - Tutorial 1 Line IntegralDocument6 pages8221 - Tutorial 1 Line IntegralVictor LoongNo ratings yet
- The EllipseDocument10 pagesThe Ellipseolowejohn.2006No ratings yet
- Week 019 - Application of Definite IntegralsDocument51 pagesWeek 019 - Application of Definite Integralsvit.chinnajiginisaNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics 1: It Doesn't Matter How Many Coordinates Are Given You Have To Just Add and Then Same ProcessDocument12 pagesPure Mathematics 1: It Doesn't Matter How Many Coordinates Are Given You Have To Just Add and Then Same ProcessAttique Rehman100% (1)
- Final14vector Analysis FBGRPDocument5 pagesFinal14vector Analysis FBGRPZaki NiaziNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Review Differential CalculusbDocument32 pagesIntroduction and Review Differential CalculusbRalph Piolo BuanNo ratings yet
- Area Between Curves PDFDocument9 pagesArea Between Curves PDFHussain HaiderNo ratings yet
- SMA 2116 - Tutotial 1 - 2018Document5 pagesSMA 2116 - Tutotial 1 - 2018PatrickNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 4 - 6Document2 pagesNotes Lesson 4 - 6khaizanjohnNo ratings yet
- Calculus (104) 08Document6 pagesCalculus (104) 08蕭卉妤No ratings yet
- Applications of IntegrationDocument42 pagesApplications of IntegrationLoraine Ruth LumenNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam QuestionDocument4 pagesSample Exam QuestionUmmi ThohirahNo ratings yet
- First Way: Af (BX+C) +DDocument18 pagesFirst Way: Af (BX+C) +DutpNo ratings yet
- Calculus Session 2 Volume of Solid RevolutionDocument4 pagesCalculus Session 2 Volume of Solid RevolutionJennie Gail RigorNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Area Under CurveDocument14 pagesSheet - 01 - Area Under Curvesarikapurwar0135No ratings yet
- Beams On Elastic Foundations TheoryDocument15 pagesBeams On Elastic Foundations TheoryCharl de Reuck100% (1)
- Beams On Elastic Foundation-1Document15 pagesBeams On Elastic Foundation-1Anonymous 0tT3SeNo ratings yet
- Circle: 2.1 General FormDocument102 pagesCircle: 2.1 General FormShaima Ahmed100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Jay KayyNo ratings yet
- Area Between CurvesExtraDocument6 pagesArea Between CurvesExtraTerry GaoNo ratings yet
- Anna's AssignmentDocument16 pagesAnna's Assignmenttumaini murrayNo ratings yet
- INTEGRATIONDocument6 pagesINTEGRATIONIeda WirnaNo ratings yet
- Conic Section NcertDocument22 pagesConic Section NcertRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Section11 6notes PDFDocument18 pagesSection11 6notes PDFHesham ArifNo ratings yet
- First Order Diff EqDocument1 pageFirst Order Diff Eqabhishek netiNo ratings yet
- Variation of ParametersDocument1 pageVariation of Parametersabhishek netiNo ratings yet
- Types of FunctionsDocument7 pagesTypes of Functionsabhishek netiNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals (DP-900) Master Cheat SheetDocument32 pagesMicrosoft Azure Data Fundamentals (DP-900) Master Cheat SheetChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Java Script&DHTMLDocument87 pagesJava Script&DHTMLabhishek netiNo ratings yet
- Atc19 PangDocument15 pagesAtc19 PangMalik TwainNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 Ed - Section 9, Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesNomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 Ed - Section 9, Heat ExchangerstizeskiNo ratings yet
- Mat495 Chapter 8Document18 pagesMat495 Chapter 8MuhamadSadiqNo ratings yet
- SmalloscillationsDocument12 pagesSmalloscillationsrajbaxeNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument18 pagesProblemsBrahmanand SinghNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Single-Phase SPWM Inverter: A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree ofDocument46 pagesAnalysis of Single-Phase SPWM Inverter: A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree ofCho Thandar LwinNo ratings yet
- Dray Etal 2014 EcologyDocument8 pagesDray Etal 2014 EcologySofia Julieta AcBäNo ratings yet
- GplayDocument9 pagesGplayΣατανάς ΣατανάςNo ratings yet
- Multiaxial FatigueDocument32 pagesMultiaxial FatigueKittikun JitpairodNo ratings yet
- Cell Name Original Value Final Value IntegerDocument5 pagesCell Name Original Value Final Value IntegerBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Ieep 109Document3 pagesIeep 109ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Cam Profile AnalysisDocument4 pagesCam Profile AnalysisPremjeetSingh100% (1)
- CGCR502 - P1Document35 pagesCGCR502 - P1Academic HubNo ratings yet
- LAb Manual For Deflection of Beam Experiment Three Handout PDFDocument6 pagesLAb Manual For Deflection of Beam Experiment Three Handout PDFmehwish arshadNo ratings yet
- MUNAR - Linear Regression - Ipynb - ColaboratoryDocument30 pagesMUNAR - Linear Regression - Ipynb - ColaboratoryTRISTAN JAYSON MUNARNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document4 pagesQuiz 2Clash ClanNo ratings yet
- M&SCE NotesPart IDocument65 pagesM&SCE NotesPart IHassane AmadouNo ratings yet
- A Shortcoming in The Geometrically Non-Linear Shakedown TheoremDocument2 pagesA Shortcoming in The Geometrically Non-Linear Shakedown TheoremRui CbNo ratings yet
- K2 MathsDocument49 pagesK2 MathsNaina Mohamed HNo ratings yet
- Practicals OS GTU For PracticeDocument34 pagesPracticals OS GTU For PracticeAashish JanardhananNo ratings yet
- Method of Differentiation DPP - 7Document3 pagesMethod of Differentiation DPP - 7tanayNo ratings yet
- Gaussian & Gaussview: Shubin Liu, Ph.D. Research Computing Center, Its University of North Carolina at Chapel HillDocument86 pagesGaussian & Gaussview: Shubin Liu, Ph.D. Research Computing Center, Its University of North Carolina at Chapel HillRAMKUMARNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis in Industrial Engineering PDFDocument7 pagesPHD Thesis in Industrial Engineering PDFcyndiruppelspringfield100% (2)
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledapi-233604231No ratings yet
- A Neural Network Approach For Early Cost Estimation of Structural Systems of BuildingsDocument8 pagesA Neural Network Approach For Early Cost Estimation of Structural Systems of BuildingsHai Dai GiaNo ratings yet
- Fibre Reinforced CompositesDocument2 pagesFibre Reinforced CompositesDikshant HasbeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Class IX: Compiled By: Mahad Salman Jawed Teacher of Department of Mathematics Regular Boys BranchDocument12 pagesMathematics For Class IX: Compiled By: Mahad Salman Jawed Teacher of Department of Mathematics Regular Boys BranchMahad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Various A-Level Economics NotesDocument7 pagesVarious A-Level Economics NotesYasheelNo ratings yet
- Consumer's EquilibriumDocument4 pagesConsumer's EquilibriumMahendra ChhetriNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument7 pagesOutputUna Balloons0% (1)
- Rocket Equation Derivation NotesDocument7 pagesRocket Equation Derivation NotesSrikar GhooliNo ratings yet