Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hibbeler D14 e CH 12 P 3
Uploaded by
razonablejhunrayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hibbeler D14 e CH 12 P 3
Uploaded by
razonablejhunrayCopyright:
Available Formats
Hibbeler Dynamics 14e: Problem 12-3 Page 1 of 1
Problem 12-3
A particle travels along a straight line with a velocity v = (12 − 3t2 ) m/s, where t is in seconds.
When t = 1 s, the particle is located 10 m to the left of the origin. Determine the acceleration
when t = 4 s, the displacement from t = 0 to t = 10 s, and the distance the particle travels during
this time period.
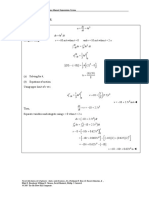
Solution
The acceleration is obtained by differentiating the given velocity function.
dv
a=
dt
d
= (12 − 3t2 )
dt
= −6t.
Therefore, at t = 4 s, the particle’s acceleration is
m
a(4) = −24 .
s2
On the other hand, the position and velocity are related by
ds
v= = 12 − 3t2 .
dt
Integrate both sides with respect to time from t = 0 to t = 10 to obtain the displacement during
this interval.
ˆ 10 ˆ 10
ds
dt = (12 − 3t2 ) dt
0 dt 0
10
3
s(10) − s(0) = (12t − t )
0
∆s = 12(10) − 103
= −880 m
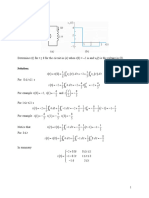
To obtain the total distance the particle travels from t = 0 to t = 10, integrate the speed over this
interval.
ˆ 10 ˆ 10
sT = |v(t)| dt = |12 − 3t2 | dt
0 0
ˆ 2 ˆ 10
= (12 − 3t2 ) dt + (3t2 − 12) dt
0 2
2 10
= (12t − t3 ) + (t3 − 12t)
0 2
= [12(2) − 23 ] + [103 − 12(10) − 23 + 12(2)]
= 912 m
www.stemjock.com
You might also like
- Ex 1Document1 pageEx 1samir_ssh7151No ratings yet
- Hibbeler D14 e CH 12 P 1Document2 pagesHibbeler D14 e CH 12 P 1Muhammad EhsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Homework SolutionDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Homework SolutionAndy SimbañaNo ratings yet
- P7.2-2, 4, 5, 7 P7.3-1, 2, 5 P7.4-1, 4 P7.5-2, 4, 13, 14, 20 P7.6-1, 3 P7.7-2, 6 P7.8-1, 3, 5, 6, 13Document20 pagesP7.2-2, 4, 5, 7 P7.3-1, 2, 5 P7.4-1, 4 P7.5-2, 4, 13, 14, 20 P7.6-1, 3 P7.7-2, 6 P7.8-1, 3, 5, 6, 13Vibhuti NarayanNo ratings yet
- Inbound 8103230202756823036Document54 pagesInbound 8103230202756823036zettoholenNo ratings yet
- Problems: Section 7-2: Capacitors P7.2-1Document6 pagesProblems: Section 7-2: Capacitors P7.2-1Heesoo YooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Energy Storage ElementsDocument45 pagesChapter 7 - Energy Storage ElementsGeoFurriel50% (2)
- Form 5: Chapter 20 (Motion Along A Straight Line) SPM Practice Fully-Worked SolutionsDocument4 pagesForm 5: Chapter 20 (Motion Along A Straight Line) SPM Practice Fully-Worked SolutionsTohsi AkiNo ratings yet
- Problem 12-26Document2 pagesProblem 12-26Amelia SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- SG BC FRQ 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesSG BC FRQ 2019 PDFQamariya AlbadiNo ratings yet
- Solution Worksheet Class 12 - Mathematics: DR DXDocument5 pagesSolution Worksheet Class 12 - Mathematics: DR DXAvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Relativity OxfordDocument10 pagesRelativity Oxfordgoyij85837No ratings yet
- Kinematics of Particles: Learning ContentDocument9 pagesKinematics of Particles: Learning ContentGIYANG BATANNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 PDFDocument13 pagesChapter2 PDFnur antashaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates (CHPT 10)Document6 pagesNOTES - Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates (CHPT 10)nyan kumamonNo ratings yet
- Resolucion Problema 3Document1 pageResolucion Problema 3Edilson VasquezNo ratings yet
- 12088-0130670227 Ismsec2 PDFDocument11 pages12088-0130670227 Ismsec2 PDFRigoberto ArosemenaNo ratings yet
- R (T) Sin T I+cost J+T K T 0: VectorsDocument3 pagesR (T) Sin T I+cost J+T K T 0: VectorsramsastryNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesEngineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions ManualAmyClarkcsgz100% (63)
- Remarks of T7 AppendixDocument9 pagesRemarks of T7 AppendixWong JiayangNo ratings yet
- Math221: HW# 2 Solutions: Andy Royston October 12, 2005Document12 pagesMath221: HW# 2 Solutions: Andy Royston October 12, 2005Zahid KumailNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Problems Partial Solutions and AnswersDocument6 pagesFundamental Problems Partial Solutions and AnswersJamED ALRubio100% (1)
- Exercises-13 3Document2 pagesExercises-13 3David LiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics ch1Document104 pagesDynamics ch1Miguel A. ChávezNo ratings yet
- EJERCICIO 3 y 4 DINAMICADocument2 pagesEJERCICIO 3 y 4 DINAMICAGreysi Calderon RiosNo ratings yet
- Jfuture 202005025Document1 pageJfuture 202005025devi kumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General Relativity Solutions 31-35Document5 pagesIntroduction To General Relativity Solutions 31-35daveNo ratings yet
- Math 4013 Solutions To Homework Problems From Chapter 4 Section 4.2 4.2.1Document14 pagesMath 4013 Solutions To Homework Problems From Chapter 4 Section 4.2 4.2.1jair9torresNo ratings yet
- Nov7 PDFDocument6 pagesNov7 PDFMohamed SayedNo ratings yet
- LCHOsolnDocument4 pagesLCHOsolnDaniela F L BNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual PDFbaddishimmanetltp100% (10)
- Full Download Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions ManualDocument31 pagesFull Download Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manualthumbapofhyiu100% (36)
- Example 20Document1 pageExample 20revoltfxNo ratings yet
- HW& Midterm SolutionsDocument44 pagesHW& Midterm SolutionsSamuel HollisNo ratings yet
- The parabola is a curve in R parameterized as follows: C= ~ γ (x) := x x 0 x ∈ (−1, 2) Document4 pagesThe parabola is a curve in R parameterized as follows: C= ~ γ (x) := x x 0 x ∈ (−1, 2) Forsen ShungiteNo ratings yet
- Probset Answer SheetDocument4 pagesProbset Answer SheetPrincess Niña B. PedrosoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Differentiation PDFDocument26 pagesApplications of Differentiation PDFcheng linNo ratings yet
- Section - B: Multiple Choice Type Questions: 1. Answer (1, 3, 4) 2. Answer (2, 3, 4)Document22 pagesSection - B: Multiple Choice Type Questions: 1. Answer (1, 3, 4) 2. Answer (2, 3, 4)sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- MA1512 Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument7 pagesMA1512 Tutorial 1 SolutionsWeiyen NgNo ratings yet
- Soln 11013Document1 pageSoln 11013LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Step Strain Experiment Stress RelaxationDocument18 pagesStep Strain Experiment Stress RelaxationLakshmi SultaniaNo ratings yet
- Cet c599 Mec Apl Ft1 Movrect 1d Exe2Document1 pageCet c599 Mec Apl Ft1 Movrect 1d Exe2Francisco CostaNo ratings yet
- Math111 Application of DerivativesDocument26 pagesMath111 Application of DerivativesAbdul Halil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit-4, Vector Differential CalculusDocument31 pagesUnit-4, Vector Differential CalculusSujatha VivekNo ratings yet
- Potter SI ISM Chapter 03Document18 pagesPotter SI ISM Chapter 03Faris HishamNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Take Home Quiz 3Document5 pagesAnswer Key For Take Home Quiz 3Nexty GamingNo ratings yet
- Ap18 SG Calculus AbDocument7 pagesAp18 SG Calculus AbLiang LiuNo ratings yet
- D T T D T T D T D: D Represent The Distance Between A and B. LetDocument7 pagesD T T D T T D T D: D Represent The Distance Between A and B. LetDiego Escobar MoncadaNo ratings yet
- = Γ R I = Ρ G R I Vo= - R - IDocument8 pages= Γ R I = Ρ G R I Vo= - R - IWidya AprianiNo ratings yet
- Probset 2Document5 pagesProbset 2Princess Niña B. PedrosoNo ratings yet
- Exercicios Resolvidos 1Document2 pagesExercicios Resolvidos 1Andressa MaraNo ratings yet
- CH 12 A1 NoteDocument2 pagesCH 12 A1 NoteSam RajibNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 A AnsDocument5 pagesQuiz1 A Ansa0905585110No ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 2 Asal Physics CBDocument4 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 2 Asal Physics CBarnavpro23No ratings yet
- Lecture 12: MD Thermostats: 12.1 Recommended TextbooksDocument10 pagesLecture 12: MD Thermostats: 12.1 Recommended TextbooksJay SteeleNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Ion Beams for Materials AnalysisFrom EverandIon Beams for Materials AnalysisR. Curtis BirdNo ratings yet
- 2016 Updated Objectives With Answer Key & Topic Wise Numericals With Formulae Physics XI PDFDocument95 pages2016 Updated Objectives With Answer Key & Topic Wise Numericals With Formulae Physics XI PDFSameer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Transpiration - Bot Lab ReportDocument2 pagesTranspiration - Bot Lab ReportPatricia De AsisNo ratings yet
- Hiwin BallscrewsDocument193 pagesHiwin BallscrewsJeka MazurovskyNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of Piston Using Pressure Load and Thermal LoadDocument8 pagesStress Analysis of Piston Using Pressure Load and Thermal LoadInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- MIGUA MIGUMAX EN CatalogueDocument32 pagesMIGUA MIGUMAX EN CataloguejajayttNo ratings yet
- (Ebook) - 3ds Max Glass MaterialDocument4 pages(Ebook) - 3ds Max Glass MaterialUchith IdunilNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ExperimentsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Experimentsdolores salomonNo ratings yet
- Jrs Tutorials: Chemical BondingDocument28 pagesJrs Tutorials: Chemical BondingPriyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Work, Power & Energy (Practice Questions)Document20 pagesWork, Power & Energy (Practice Questions)SakshamNo ratings yet
- Hammer Peening s00170-021-07993-5Document19 pagesHammer Peening s00170-021-07993-5Md MehtabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hull GaugingDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Hull GaugingMengotah NkanghaNo ratings yet
- (Duerr, D.,2006) - Pinned Connection Strength and BehaviorDocument14 pages(Duerr, D.,2006) - Pinned Connection Strength and Behaviorchristos032No ratings yet
- Electo Stream DrillingDocument3 pagesElecto Stream DrillingShubhamNo ratings yet
- Standard Test Method For Compressive Properties of Rigid Cellular Plastics (D1621)Document5 pagesStandard Test Method For Compressive Properties of Rigid Cellular Plastics (D1621)Gholamhossein Tavakoli MehrjardiNo ratings yet
- SurbyDocument7 pagesSurbykostas formulagrNo ratings yet
- Saracrease HG 10Document2 pagesSaracrease HG 10NAGARAJNo ratings yet
- AnwanaDocument16 pagesAnwanaHiongyiiNo ratings yet
- Tuition Notes For 3.3U CourseDocument417 pagesTuition Notes For 3.3U Coursepoetazzo80No ratings yet
- Concrete Fireproofing Analysis Evaluation and Repair StrategiesDocument30 pagesConcrete Fireproofing Analysis Evaluation and Repair StrategiessvprskNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Radiation Fundamentals 2Document20 pagesChapter 11 - Radiation Fundamentals 2Rithish MouryaNo ratings yet
- Daniel Baumann - Cosmology (2021)Document468 pagesDaniel Baumann - Cosmology (2021)Gustavo VillarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Statics and Dynamics 2nd Edition Plesha Solutions Manual DownloadDocument144 pagesEngineering Mechanics Statics and Dynamics 2nd Edition Plesha Solutions Manual DownloadJohn Durant100% (22)
- Extrusion Review: MechanicalDocument29 pagesExtrusion Review: MechanicalAdnan JavedNo ratings yet
- CLEANING, OPERATION & CALIBRATION OF PH METERDocument3 pagesCLEANING, OPERATION & CALIBRATION OF PH METERraveen tanwar100% (1)
- MF898 (Technical Data)Document3 pagesMF898 (Technical Data)Loui BarciaNo ratings yet
- T Cosmetic CreamsDocument4 pagesT Cosmetic CreamsRaul DiazNo ratings yet
- Minichiller CatalogDocument18 pagesMinichiller CataloghungNo ratings yet
- 599 PR 04 Lagrangian Density For Schrodinger Equation FieldsDocument1 page599 PR 04 Lagrangian Density For Schrodinger Equation Fields呂英樟No ratings yet
- Fin TutorialDocument7 pagesFin TutorialmanasgartiaNo ratings yet
- 2 Aakash Test NeetDocument15 pages2 Aakash Test Neethardik cheema100% (1)