Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Primo
Uploaded by
jhosonprimo40 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesPrimo
Uploaded by
jhosonprimo4Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Primo, Jhoson G.
BSED 3 – 3
11 system of the human body
1. Integumentary system – the largest organ of the body that forms a
physical barrier between the external environment and the internal
environment that it serves to protect and maintain.
Function: physical protection, immunity, wound healing, Vitamin D
synthesis, regulation of body temperature, and sensation.
2. Skeletal system - body’s central framework. It consists of bones and
connective tissue, including cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. It’s
also called the musculoskeletal system.
Function: allows movement, produces blood cells, protects and support
organs, and stores minerals
3. Muscular system - composed of specialized cells called muscle
fibers. Their predominant function is contractibility. Muscles, attached
to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for
movement.
Function: mobility, stability, posture, circulation, respiration, digestion,
and urination.
4. Lymphatic system - part of the immune system. It also maintains fluid
balance and plays a role in absorbing fats and fat-soluble nutrients.
Function: balances fluid homeostasis, forms body of immune system
that defend against bacteria, and facilitates absorption of fats and fat –
soluble nutrients in the digestive system
5. Respiratory system - The respiratory system is the network of organs
and tissues that help you breathe. It includes your airways, lungs and
blood vessels.
Function: allows to talk and smell, delivers oxygen to the cells in your
body, removes waste gases including carbon dioxide, from the body
when you exhale and protects your airways from harmful substance and
irritants.
6. Digestive system - is made up of the gastrointestinal tract—also
called the GI tract or digestive tract—and the liver, pancreas, and
gallbladder. The GI tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long,
twisting tube from the mouth to the anus. The hollow organs that
make up the GI tract are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small
intestine, large intestine, and anus. The liver, pancreas, and
gallbladder are the solid organs of the digestive system.
Function: motility, digestion, absorption, and secretion.
7. Nervous system - is the major controlling, regulatory, and
communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
activity including thought, learning, and memory.
Function: control of body’s internal environment to maintain
homeostasis, programming of spinal cord reflexes, memory and
learning, and voluntary control of movement
8. Endocrine system - is made up of several organs called glands.
These glands, located all over your body, create and secrete
(release) hormones.
Function: metabolism, growth and development, emotions and mood,
fertility and sexual function, sleep, and blood pressure
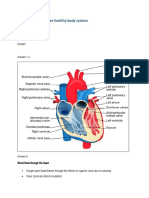
9. Circulatory system - Your circulatory system, also known as your
cardiovascular system, is made up of your heart and blood vessels. It
works to transport oxygen and other nutrients to all the organs and
tissues in your body. It also works to remove carbon dioxide and
other waste products.
Function: transports oxygen, other nutrients to all the organs and tissues
in your body.
10. Urinary system - body takes nutrients from food and changes
them to energy. After the body has taken the food components that it
needs, waste products are left behind in the bowel and in the blood.
Function: filters blood and create urine as a waste by – product
You might also like
- Reviewer in Science 6Document5 pagesReviewer in Science 6Kristel Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Systems of AnimalDocument2 pagesSystems of AnimalMuhammad AdibNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems VocabularyDocument3 pagesHuman Body Systems Vocabularyapi-325864985100% (1)
- Name: Udoy Saha Class: 8 ID: 59 Subject: Science (Human Biology) Submitted To: Mr. Bishawjit Roy Topic: SystemDocument2 pagesName: Udoy Saha Class: 8 ID: 59 Subject: Science (Human Biology) Submitted To: Mr. Bishawjit Roy Topic: SystemUdoy SahaNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH. Memahami Dasar Anatomi Tubuh ManusiaDocument19 pagesMAKALAH. Memahami Dasar Anatomi Tubuh ManusiadediNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument1 pageBody SystemsJnz OlanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Body Nursing EnglishDocument5 pagesParts of Body Nursing EnglishZulyana PutriNo ratings yet
- Hbs Unite 1 Summary FinalDocument45 pagesHbs Unite 1 Summary Finalapi-277775953No ratings yet
- Overview of the Major Human Body SystemsDocument4 pagesOverview of the Major Human Body SystemsleonielainecolbornNo ratings yet
- Organ System 7Document2 pagesOrgan System 7verenicaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- Systems of Human BodyDocument13 pagesSystems of Human BodyMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- II. (5) Organ System in Our BodyDocument3 pagesII. (5) Organ System in Our BodyVirgie Pangilinan ErandioNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyArif HidyawanNo ratings yet
- System of The Human BodyDocument31 pagesSystem of The Human BodyMari Thomas100% (1)
- MAPE 3 Anatomical, Mechanical and Physiological Bases of MovementDocument19 pagesMAPE 3 Anatomical, Mechanical and Physiological Bases of MovementPatricia Jean San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Hbs Unit 1 Summary OutlineDocument39 pagesHbs Unit 1 Summary Outlineapi-277771710No ratings yet
- 11 Organ SystemsDocument2 pages11 Organ Systemsjonar parinasNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument116 pagesBody SystemskarunaNo ratings yet
- HLTAAP001 Recognize Healthy Body System 9Document17 pagesHLTAAP001 Recognize Healthy Body System 9yESHEy T100% (2)
- Veterinary Clinical AnatomyDocument2 pagesVeterinary Clinical AnatomyBrenda VictoriaNo ratings yet
- The 11 Human Body Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument79 pagesThe 11 Human Body Organ System and Their FunctionsXin Ssai XaveraNo ratings yet
- Physiology-1 Department of Physiotherapy: BY DR - Laraib Jameel RPHDocument113 pagesPhysiology-1 Department of Physiotherapy: BY DR - Laraib Jameel RPHHashir SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Science Human Body SystemDocument9 pagesScience Human Body SystemJOSE RENE CASILINo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Human BodyDocument2 pagesBIOLOGY Human BodyDonnia MayeNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument13 pagesScienceCheryl ArquiolaNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Zajuli E2214401059 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEM-1Document2 pagesAhmad Zajuli E2214401059 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEM-1AhmadNo ratings yet
- Visit The Human BodyDocument7 pagesVisit The Human BodyAnonymous lSTzdU8PgNo ratings yet
- Science 5: Types of CellsDocument2 pagesScience 5: Types of CellsJonathan StoneNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ii Task 1Document12 pagesTugas Ii Task 1Husnul KhotimahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- Refresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Document21 pagesRefresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Kirby AnaretaNo ratings yet
- How Does Ruminant Digestion Work?Document2 pagesHow Does Ruminant Digestion Work?Vincent SantosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PretestDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PretestMary Regine BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Central Luzon Doctors' Hospital Educational Institution Anatomy SystemsDocument5 pagesCentral Luzon Doctors' Hospital Educational Institution Anatomy SystemsJenny Sumangil EspejoNo ratings yet
- The Ten Systems of The Human BodyDocument3 pagesThe Ten Systems of The Human BodyMoses AbiodunNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Animal SciDocument5 pagesActivity 1 Animal SciKylle BedisNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesOrgan SystemsArnel LaspinasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Human Organization: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth EditionDocument3 pagesChapter 11: Human Organization: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth Editionjadusingh000No ratings yet
- P.E Anatomical TermsDocument26 pagesP.E Anatomical TermsGerald Mapalo FactorNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Pre LimDocument13 pagesAnaphy Pre LimKyle M. BayangosNo ratings yet
- Human Body Terms ExplainedDocument5 pagesHuman Body Terms ExplainedRed DemonNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument27 pagesBiology Projectswatipatel200816No ratings yet
- Movement Enhancement 1 LESSON 1Document53 pagesMovement Enhancement 1 LESSON 1Marckim DangoNo ratings yet
- Different Systems of BodyDocument16 pagesDifferent Systems of BodygracetingNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScience0221278No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human Movement and Performance Lesson 1Document22 pagesAnatomy of Human Movement and Performance Lesson 1Alfredo Arvin Nieva100% (1)
- Circulatory+Digestive System 2Document20 pagesCirculatory+Digestive System 2madeleine.gaudissartNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Human Body: Structural Organization, Body Systems, and Basic Anatomical TerminologyDocument43 pagesAn Introduction to the Human Body: Structural Organization, Body Systems, and Basic Anatomical TerminologySherleen Jane D. Fernandez50% (2)
- Chapter 1 - AnaphyDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - AnaphyCinderilla De AngelNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy and FunctionDocument24 pagesBrain Anatomy and FunctionAdamu GudinaNo ratings yet
- Animal Organ SystemsDocument3 pagesAnimal Organ SystemsmaygracedigolNo ratings yet
- 10-Organs and Body PartsDocument7 pages10-Organs and Body PartsSfiat MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemsDocument3 pagesOrgan Systemsapi-335940126No ratings yet
- Introduction to Human Body Systems & StructuresDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Human Body Systems & StructuresChristina Markwart100% (1)
- Our BodyDocument16 pagesOur Bodynarensathya967No ratings yet
- Module 1 RAWDocument25 pagesModule 1 RAWCordelia TobinNo ratings yet
- AUTOBIOGRAPHYDocument2 pagesAUTOBIOGRAPHYjohncarlo ramosNo ratings yet
- The Human Body A Complex and Remarkable SystemDocument1 pageThe Human Body A Complex and Remarkable Systemurushadzelazare1No ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Nutrition Health and Safety For Young Children Promoting Wellness 3rd Edition PDFDocument51 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Nutrition Health and Safety For Young Children Promoting Wellness 3rd Edition PDFbessie.skubis114100% (40)
- To Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary AmylaseDocument17 pagesTo Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylasesudhanshusingh.clgNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps To The Gluten-Free Diet: BreakfastsDocument4 pages10 Steps To The Gluten-Free Diet: BreakfastskatNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A FinalDocument64 pagesVitamin A FinalLiaqat HussainNo ratings yet
- Microalgal cell structure and applicationsDocument2 pagesMicroalgal cell structure and applicationsGede AdityaNo ratings yet
- MTS cooking data charactersDocument4 pagesMTS cooking data charactersvgtallNo ratings yet
- Ms. Afsana Akhtar: Letter of TransmittalDocument20 pagesMs. Afsana Akhtar: Letter of Transmittalndc6105058100% (3)
- CFN-1 20-21 emDocument23 pagesCFN-1 20-21 emSaisree TatikondaNo ratings yet
- ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY of NIPA SAP DRAFT 1 PDFDocument13 pagesANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY of NIPA SAP DRAFT 1 PDFnabilaNo ratings yet
- Gluten-Free Flour Power Bringing Your Favorite FoodsDocument490 pagesGluten-Free Flour Power Bringing Your Favorite FoodsdonNo ratings yet
- Insulin Pump Therapy BasicsDocument57 pagesInsulin Pump Therapy BasicsSperaPerpetuumNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten School Action Plan for Nutrition MonthDocument12 pagesKindergarten School Action Plan for Nutrition MonthSheryl Cruz Espiritu100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectIshita Singh100% (1)
- Tunnel Farming HPFMDocument83 pagesTunnel Farming HPFMUsman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Health Respiratory and Circulatory Systems - One's Lifestyle PDFDocument20 pagesHealth Respiratory and Circulatory Systems - One's Lifestyle PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Letter of Intent.2Document1 pageLetter of Intent.2Aileen Castro Rigor100% (10)
- Basbousa Recipe (Semolina Cake) - The Mediterranean DishDocument30 pagesBasbousa Recipe (Semolina Cake) - The Mediterranean DishRoxana ComanNo ratings yet
- 5-Day Workout Routine For BeginnersDocument5 pages5-Day Workout Routine For BeginnersChinda JCV100% (1)
- Guidelines For Case Report IPDDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Case Report IPDMohd TempahanNo ratings yet
- Paddy Straw MushroomDocument38 pagesPaddy Straw MushroomShivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- PNAAT662Document309 pagesPNAAT662Ganesh KashinathNo ratings yet
- Vegan Keto Recipe BookDocument41 pagesVegan Keto Recipe BookWeronika Zając100% (3)
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh 7 I Learn Smart World Unit 2Document3 pagesBai Tap Tieng Anh 7 I Learn Smart World Unit 2ReDragNo ratings yet
- Biosignature Modulation for Spot Fat ReductionDocument3 pagesBiosignature Modulation for Spot Fat ReductionMiguel Kennedy67% (3)
- Nutrition Facts Beverages by Cup SizeDocument1 pageNutrition Facts Beverages by Cup SizeSkater KoiNo ratings yet
- STAMP (Kids)Document8 pagesSTAMP (Kids)Rika LedyNo ratings yet
- Ip PT Ip Science Y5 DDDocument6 pagesIp PT Ip Science Y5 DDane lwanNo ratings yet
- Goitrogenic List (Encompass)Document2 pagesGoitrogenic List (Encompass)Filipe RicardoNo ratings yet
- Integration of MetabolismDocument10 pagesIntegration of MetabolismAditya NayakNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH - 3 WordsDocument13 pagesENGLISH - 3 WordsJester GamingNo ratings yet