Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acid - AR Practice Sheet - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)
Uploaded by
agrawaltwinkle2005Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acid - AR Practice Sheet - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)
Uploaded by
agrawaltwinkle2005Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Yakeen NEET 2.0 2024 (Legend)
AR Practice Sheet
Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
1. Assertion (A): Acetic acid does not give haloform 5. Assertion (A): Rate of decarboxylation of ethanoic
reaction. acid is greater than propanoic acid.
Reason (R): Acetic acid has no α-hydrogen. • •
(1) If both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the Reason (R): C H3 is less stable CH3 C H 2 .
correct explanation of (A). (1) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is a
(2) If both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
correct explanation of (A). (2) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is not
(3) If (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect. a correct explanation for Assertion.
(4) If (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct. (3) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
(4) Assertion is false, Reason is true.
2. Assertion (A): Compounds containing –CHO group
are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic
NaOH
acids. 6. Assertion (A): RCOOH ⎯⎯⎯→
heat
RH
Reason (R): Carboxylic acids can be reduced to
This reaction requires the presence of CaO.
alcohols by treatment with LiAlH4.
Reason (R): CaO absorbs the released CO2 in the
(1) Assertion and reason both are correct and
reaction and forms CaCO3.
reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(2) Assertion and reason both are wrong (1) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is a
statements. correct explanation for Assertion.
(3) Assertion is correct statement but reason is (2) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is not
wrong statement. a correct explanation for Assertion.
(4) Assertion and reason both are correct (3) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
statements but reason is not correct explanation (4) Assertion is false, Reason is true.
of assertion.
7. Assertion (A): 2-Methyl Propanal undergoes
3. Assertion (A): Trichloro ethanal cannot exhibit
Cannizzaro’s reaction.
Cannizzaro reaction.
Reason (R): It has an α-hydrogen atom.
Reason (R): It undergoes haloform test.
(1) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is a (1) If both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the
correct explanation for Assertion. correct explanation of (A).
(2) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is not (2) If both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the
a correct explanation for Assertion. correct explanation of (A).
(3) Assertion is true, Reason is false. (3) If (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
(4) Assertion is false, Reason is true. (4) If (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
4. Assertion (A): The addition of ammonia derivatives
8. Assertion (A): (CH3)3C-COOH does not give HVZ
on carbonyl compounds is carried in weakly acidic
reaction.
medium.
Reason (R): In weakly acidic medium, attacking Reason (R): It does not have any α-hydrogen.
nucleophile is also protonated. (1) If both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the
(1) If both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
correct explanation of (A). (2) If both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the
(2) If both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
correct explanation of (A). (3) If (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
(3) If (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect. (4) If (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
(4) If (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
2
9. Assertion (A): Primary alcohols can be easily oxidised 13. Assertion (A): Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
to aldehydes. Reason (R): It contains sp2 hybridised carbon atom.
Reason (R): Aldehydes are prone to further oxidation to (1) If both assertion and reason are correct and the
carboxylic acids. reason is the correct explanation of the
(1) If both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the assertion.
correct explanation of (A). (2) If both assertion and reason are correct but the
(2) If both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the reason is not the correct explanation of the
correct explanation of (A). assertion.
(3) If (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect. (3) If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
(4) If (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct. (4) If the assertion is false but the reason is true.
10. Assertion (A): Aldehydes and ketones, both react O
Assertion (A): Carboxylic acids
with Tollen’s reagent to form silver mirror. R − C− OH
14. ||
Reason (R): Both aldehydes and ketones contain a
carbonyl group. have a carbonyl group but it does not give the
(1) Assertion and reason both are correct and test of carbonyl group.
reason is correct explanation of assertion. Reason (R): Due to resonance, the double bond
(2) Assertion and reason both are wrong O
statements. ||
(3) Assertion is correct statement but reason is character of C group is greatly reduced.
wrong statement.
(4) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is
correct statement. (1) If both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the
correct explanation of (A).
(2) If both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the
11. Assertion (A): Fehling’s reagent is a test for all
correct explanation of (A).
aliphatic aldehydes.
(3) If (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
Reason (R): Aliphatic aldehydes can be easily
(4) If (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
oxidised even with mild oxidising agents.
(1) If both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is
15. Assertion (A): Acetophenone and benzophenone can
correct explanation of (A).
be distinguished by the iodoform test.
(2) If both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not
Reason (R): Acetophenone and benzophenone both
correct explanation of (A).
are carbonyl compounds.
(3) If (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
(1) If both assertion and reason are true and the
(4) If (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
reason is the correct explanation of the
assertion.
12. Assertion (A): Lower aldehydes and ketones are
(2) If both assertion and reason are true but the
soluble in water but the solubility decreases as
reason is not the correct explanation of the
molecular mass increases.
assertion.
Reason (R): Aldehydes and ketones can be
(3) If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
distinguished by Tollen’s reagent.
(4) If the assertion is false but the reason is true.
(1) If both assertion and reason are correct and the
reason is the correct explanation of the
assertion.
(2) If both assertion and reason are correct but the
reason is not the correct explanation of the
assertion.
(3) If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
(4) If the assertion is false but the reason is true.
3
Answer Key
1. (3) 9. (4)
2. (4) 10. (4)
3. (1) 11. (1)
4. (3) 12. (2)
5. (2) 13. (1)
6. (1) 14. (1)
7. (4) 15. (2)
8. (1)
PW Web/App - https://smart.link/7wwosivoicgd4
Library- https://smart.link/sdfez8ejd80if
You might also like
- Question-682442 230104 211025Document3 pagesQuestion-682442 230104 211025Aryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assertion and Reason ChemistryDocument2 pagesAssertion and Reason ChemistryarprmrjNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Question-988026-A - R, C.S - FILLUPDocument13 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Question-988026-A - R, C.S - FILLUPabiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Assertion Reason Aldehydes KetonesDocument3 pagesAssertion Reason Aldehydes KetonessuryaisonemailNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988026Document5 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988026abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Question-682447 230104 211828Document4 pagesQuestion-682447 230104 211828Avesh SinghNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY question-989411-ACID-A - R - CSDocument13 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY question-989411-ACID-A - R - CSabiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Question Chap 8 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesQuestion Chap 8 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsakshayorbgkapapaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Naming - AR Practice Sheet - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document3 pagesIUPAC Naming - AR Practice Sheet - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)agrawaltwinkle2005No ratings yet
- ALKENES PropertiesDocument8 pagesALKENES PropertiesSai SreyanNo ratings yet
- 5 6273633161326889635Document2 pages5 6273633161326889635anikarbsrsecNo ratings yet
- Oh, C6h5ohDocument3 pagesOh, C6h5ohSjhsjsjNo ratings yet
- 12 AldehydesDocument2 pages12 Aldehydesmystical moonbeamNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989411Document5 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989411abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- ChrmistryDocument6 pagesChrmistryGagandeep vaidNo ratings yet
- NEET Chemistry Solved Paper 2022Document7 pagesNEET Chemistry Solved Paper 2022Lol BoiNo ratings yet
- Final Jee Main Examination July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With AnswerDocument2 pagesFinal Jee Main Examination July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With AnswernidhirajeshrajuNo ratings yet
- Assertion and Reason PhysicsDocument3 pagesAssertion and Reason PhysicsarprmrjNo ratings yet
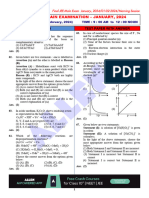
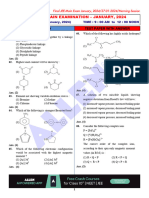
- Final Jee-Main Examination - January, 2024: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionDocument8 pagesFinal Jee-Main Examination - January, 2024: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionPriyanshu GehlotNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules - Grade 9th - QuestionsDocument4 pagesAtoms and Molecules - Grade 9th - QuestionsAnonymous BPFIMnCdNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept - Toppers Assignment 03 - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document5 pagesMole Concept - Toppers Assignment 03 - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Ashwani khatterNo ratings yet
- 0102 Chemistry Paper With Answer MorningDocument5 pages0102 Chemistry Paper With Answer MorningVidushi KochharNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PQDocument15 pagesChemistry PQKrishna Mani100% (1)
- Chem, Ln-1Document6 pagesChem, Ln-1sharonscoachingcentreNo ratings yet
- 2 12th Chemistry CBSE SET 2Document10 pages2 12th Chemistry CBSE SET 2dsrvdsrv8No ratings yet
- Board Pattern - 01 - Physics Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Document5 pagesBoard Pattern - 01 - Physics Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Janhavi kulkarniNo ratings yet
- A K Ar ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesA K Ar ElectrochemistrysuryaisonemailNo ratings yet
- Class 12th NEET Chemistry Sample Paper 4 Alka Meena Mem Vijay Kr. Kashyap Questions Final 1Document5 pagesClass 12th NEET Chemistry Sample Paper 4 Alka Meena Mem Vijay Kr. Kashyap Questions Final 1revathiprasady1987No ratings yet
- 100 Question For BoardsDocument352 pages100 Question For BoardsADITYA TIWARINo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 10 Science Assertion - Reason Questions For Term 1 ExamDocument19 pagesCbse Class 10 Science Assertion - Reason Questions For Term 1 ExamArushi100% (1)
- 3001 Chemistry Paper With Answer MorningDocument6 pages3001 Chemistry Paper With Answer Morningthakartanishq07No ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument3 pagesSolid StateEswara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Final Jee-Main Examination - January, 2024: Chemistry Test Paper With AnswerDocument5 pagesFinal Jee-Main Examination - January, 2024: Chemistry Test Paper With AnswerPriyanshu GehlotNo ratings yet
- Chem Class 11Document7 pagesChem Class 11eagleankush5No ratings yet
- CLASS 12 Chemistry-PQDocument24 pagesCLASS 12 Chemistry-PQJeremiah ShibuNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - HHDocument74 pagesClass 12 - HHgujjarvikram123456No ratings yet
- 2024 Set 2Document23 pages2024 Set 2Manab GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PQDocument13 pagesChemistry PQAman SilayachNo ratings yet
- Science Sample QP - 1Document16 pagesScience Sample QP - 1Aswathi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Full Portion TestDocument4 pagesChemistry Full Portion TestsharonscoachingcentreNo ratings yet
- Science Sample Paper 2Document8 pagesScience Sample Paper 2LVAM GAMINGNo ratings yet
- XLLB, Practice Paper - 2Document7 pagesXLLB, Practice Paper - 2rajatNo ratings yet
- ST Columba's School Class 12 - Chemistry: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesST Columba's School Class 12 - Chemistry: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesKushar Dev Chhibber100% (1)
- MCQ Based Paper (Isc Pattern) : Mark: 70 Time 90 MinDocument4 pagesMCQ Based Paper (Isc Pattern) : Mark: 70 Time 90 MinDisha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Assertion Reason - Coordination CompoundsDocument4 pagesAssertion Reason - Coordination Compoundssteevejan541No ratings yet
- Holiday Home Work Mid Term 12Document5 pagesHoliday Home Work Mid Term 12Gopala krishnanNo ratings yet
- Test Paper Class 9Document6 pagesTest Paper Class 9anitNo ratings yet
- ARQ AminesDocument4 pagesARQ AminesPavankumar SNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry QPDocument6 pagesXII Chemistry QPSaraswati maharanaNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 III-IDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 III-IAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- X Add Practice Ques SCDocument26 pagesX Add Practice Ques SCssachdev123No ratings yet
- Science PQDocument14 pagesScience PQFELLING HAPPYNo ratings yet
- 2401 Chemistry Paper+With+Solution MorningDocument7 pages2401 Chemistry Paper+With+Solution MorningSmita BachhavNo ratings yet
- Aakash QuestionsDocument2 pagesAakash QuestionsPinakpani DasNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS - Practice Sheet & Solution - Warrior 2023Document2 pagesCHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS - Practice Sheet & Solution - Warrior 2023Manoj KunarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 01, 2023Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 01, 2023dashabhijit761No ratings yet
- Class 11 Annual ExamDocument9 pagesClass 11 Annual ExamAshraf KhanNo ratings yet
- 15500-24-01-2023 Chemistry Paper+With+Answer MorningDocument7 pages15500-24-01-2023 Chemistry Paper+With+Answer MorningLanaNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Activity 5Document4 pagesPost Lab Activity 5Shaira Soriano CincoNo ratings yet
- Coursesaver (Chad) College Physics OutlinesDocument40 pagesCoursesaver (Chad) College Physics Outlinescalong558No ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 2 - Sodium Borohydride Reduction of CyclohexanoneDocument11 pagesLab Report Experiment 2 - Sodium Borohydride Reduction of CyclohexanoneSITI NUR AFIQAH MAHAZANNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Aldehydes and Ketones: EngageDocument10 pagesUnit 3: Aldehydes and Ketones: Engagejerome timmangoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 CHM 557 PDFDocument19 pagesExperiment 4 CHM 557 PDFinsyirah shazrinNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Seyden-Penne - Reductions by The Alumino - and Borohydrides in Organic Synthesis-Wiley-VCH (1997) PDFDocument236 pagesJacqueline Seyden-Penne - Reductions by The Alumino - and Borohydrides in Organic Synthesis-Wiley-VCH (1997) PDFHamilton MorrisNo ratings yet
- Reactions of - Hydrogens: Aldol and Claisen Condensation ReactionsDocument26 pagesReactions of - Hydrogens: Aldol and Claisen Condensation ReactionsSagung DyahNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation For Organic Synthesis 2001 2 PDFDocument747 pagesHandbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation For Organic Synthesis 2001 2 PDFlidiane_nobre5659No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Paper 9701/12 Multiple ChoiceDocument14 pagesChemistry: Paper 9701/12 Multiple ChoiceAbubakar shaban omarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument35 pagesChapter 19 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDF91100% (10)
- Determination of Molecular Structures: CHM 3402 Dr. Mohd Rashidi Abdull ManapDocument40 pagesDetermination of Molecular Structures: CHM 3402 Dr. Mohd Rashidi Abdull ManapMUHAMAD NURUL AIMAN BIN YUNUS / UPMNo ratings yet
- 19.8 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones To Alcohols: Cyclobutanone Lithium Aluminum Hydride CyclobutanolDocument5 pages19.8 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones To Alcohols: Cyclobutanone Lithium Aluminum Hydride CyclobutanolHimanshu Panchal100% (1)
- Estimation of Amino Acids by Ninhydrin MethodDocument3 pagesEstimation of Amino Acids by Ninhydrin MethodSukaina AbbasNo ratings yet
- Isomerism and Carbonyls Compounds FlashcardsDocument6 pagesIsomerism and Carbonyls Compounds FlashcardsHarleen BalNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (2) 1 26Document26 pagesOrganic Chemistry (2) 1 26Mr valorant ipadNo ratings yet
- 15 Naming and Drawing Functional Groups Practice WorksheetDocument4 pages15 Naming and Drawing Functional Groups Practice WorksheetCorey Becker33% (6)
- Aldol CondensationDocument4 pagesAldol Condensationrjbagh08No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Methods of Lead OptimizationDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Methods of Lead Optimizationمها عقديNo ratings yet
- The Haloform Reaction PDFDocument36 pagesThe Haloform Reaction PDFSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde KetonesDocument64 pagesAldehyde KetonesDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For The Theoretical Part of The Icho CompetitionDocument10 pagesSyllabus For The Theoretical Part of The Icho CompetitionvikramNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecules React in Predictable Ways: Functional GroupsDocument21 pagesOrganic Molecules React in Predictable Ways: Functional GroupsNia Rakhmayanti NurdinNo ratings yet
- Wood Fiser RulesDocument78 pagesWood Fiser RulesHardik Prajapati100% (1)
- Experiment No 9cDocument18 pagesExperiment No 9cSharmaine DoronNo ratings yet
- 13 Goc Revision Notes QuizrrDocument145 pages13 Goc Revision Notes QuizrrRohit sharma100% (1)
- OXIDATIONS FinalDocument9 pagesOXIDATIONS Finalgamer boomerNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsDocument1 pageAldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- 238 Finial ExamDocument10 pages238 Finial Exammominamin100% (2)
- Carbonyl Group: Shahzad KhanDocument45 pagesCarbonyl Group: Shahzad KhanShahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportAllan PinkertonNo ratings yet