Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Transport in Animals
Uploaded by
josephmukadi30Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Transport in Animals
Uploaded by
josephmukadi30Copyright:
Available Formats
## The need for a specialist transport system in a multicellular animal
- Small animals do not need a transport system< their cells are surrounded by or
are very close to the environment, and diffusion supplies sufficient oxygen and
nutrients
- Multicellular organisms however require a transport system. Three main factors
influence this size:
- Size
- Surface area: Volume ratio
- Metabolic Rate
# Factors
- [Size]
- Multicellular organisms are large and have a complex anatomy i.e. more than 2
layers of cells. The outer layers of cells use up the supplies, so that less
reaches the cells deep inside the organism.
- The cells inside a large organism are further from the surface hence the
diffusion pathway is increased. Diffusion rate is reduced and diffusion is too slow
to supply all the requirements.
- Molecules are produced in one part of the organism and need to be transported to
another part of the organism i.e. hormones
- Oxygen and nutrients need to be transported to cells and waste products need to
be transported away from cells.
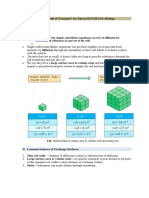
### SA:V Ratio
- Multicellular organisms always have a small surface area to volume ratio
- We have a smaller surface area compared to the volume inside of us
- Diffusion distances are therefore bigger and the amount of surface area over
which to absorb or remove substances becomes relatively smaller
- Single celled organisms have a higher surface area compared to the volume inside
of them
#### Metabolic Demands
- In large organisms metabolic demands are high, lots of oxygen and food is
required and lots of waste is produced and requires removal
- Diffusion over long distances would not be enough to supply the quantities
neeeded
- Some multicellular organisms may need to keep themselves warm (endotherms) E.G
mammals and will have higher metabolic demands
- Levels of activity may also be higher and will demand more energy to be released
from aerobic respiration
##### Common features of most transport systems
- [Liquid transport medium to circulate around the system]
- [Vessels to carry the transport medium (ours is blood)]
- [Pumping Mechanism to create a pressure gradient (your heart and muscular
movements)]
###### Mass Transport
- When substances are transported in a mass of fluid with a mechanism for moving
the fluid around the body it is known as [mass transport] or a mass flow system
- This is like a river carrying everything in it
- Mass flow always requires a source of energy to pump the fluid, but it has the
advantage of being much faster than diffusion, especially over large distances.
- Mass flow is completely independent of concentration differences
## Open and closed circulations
- Large multicellular animals usually have an open or a closed circulatory system
- Insects would usually have open circulation
- Fish, mammals would have closed circulation
## Open circulation
- Very few vessels to contain the transport medium
- Transport medium is pumped straight from the heart to the body cavity of the
animal
- The open body cavity is called a haemocoel
- In the haemocoel the transport medium is under low pressure, and it comes into
direct contact with the tissues and cells
- Exchange takes place in the haemocoel between the cells and the transport medium.
- The transport medium returns back to the heart through an open ended vessel
You might also like
- Chapter 1: Transport: - Problems Faced by Multicellular Organisms in Obtaining Their Cellular RequirementsDocument1 pageChapter 1: Transport: - Problems Faced by Multicellular Organisms in Obtaining Their Cellular RequirementsChan May KayNo ratings yet
- Transport System 1Document2 pagesTransport System 1Ashley ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Final Term - ZoologyDocument21 pagesFinal Term - ZoologyJustin LeeNo ratings yet
- The Principals of Circulation T1-4Document4 pagesThe Principals of Circulation T1-4SajaniNo ratings yet
- Transport System in HumanDocument3 pagesTransport System in HumanShaista AkbarNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument32 pagesTransport in AnimalsAshwika RajanNo ratings yet
- Ana&Physio 1 - The Human Body - An OrientationDocument59 pagesAna&Physio 1 - The Human Body - An OrientationShery Han Bint HindawiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDocument149 pagesIntroduction To Cell PhysiologyAlysaNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology NotesDocument11 pagesYear 11 Biology Notesayaan.huss207No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument5 pagesCell BiologyAaron LiuNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument5 pagesCell BiologyAaron LiuNo ratings yet
- Science 7th Grade Quarter 1 NotesDocument8 pagesScience 7th Grade Quarter 1 NotesBLESS MARGARETH B. PALMAIRANo ratings yet
- Science Q1Document9 pagesScience Q1TRISTAN ZALDY GERIANE ARROZNo ratings yet
- Concepts of The Cell Theory: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument31 pagesConcepts of The Cell Theory: Cell Structure and FunctionGracious Angel Bautista IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Organismal BiologyDocument49 pagesOrganismal BiologycelinaNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument1 pageGenbioNicaNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument7 pagesScience NotestehkhyrinnNo ratings yet
- Comparing Transport in Plants & AnimalsDocument2 pagesComparing Transport in Plants & AnimalsBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Theory of Special CreationDocument9 pagesTheory of Special Creationnico peregrinoNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewDocument62 pagesBiology ReviewGreg Smith80% (5)
- Life Process Text SolutionDocument11 pagesLife Process Text Solutionkamruleslaam_5123739No ratings yet
- AnapehDocument25 pagesAnapehKayNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyDocument16 pagesFUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyAuliya AlfaNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport System 1Document41 pagesAnimal Transport System 1Ashley JibrielleNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Review Sec 3 MaterialDocument176 pagesIGCSE Review Sec 3 MaterialStevenNo ratings yet
- Biology Honors Midterm ReviewDocument36 pagesBiology Honors Midterm ReviewGreg SmithNo ratings yet
- CH 2 ScineceDocument4 pagesCH 2 Scinece07carbonmanNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Lipid Bilayer - 2 Layers of PhospholipidsDocument18 pagesHomeostasis: Lipid Bilayer - 2 Layers of PhospholipidsLoraine Anne Marie BaguioNo ratings yet
- 2020 P BIO - Year 11 Biology Study NotesDocument16 pages2020 P BIO - Year 11 Biology Study NotesAdam QuinnNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need A Transport SystemDocument2 pagesWhy Do We Need A Transport Systemkirstinrose100% (3)
- Class Notes Bio ClassificationDocument9 pagesClass Notes Bio ClassificationRahil ShahNo ratings yet
- Transport System in Living ThingsDocument1 pageTransport System in Living ThingsWEI SHANGLI STANLEY NGAINo ratings yet
- Cells The Basic Unit of LifeDocument20 pagesCells The Basic Unit of LifeJyra Bianca CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- 007 - Comparing Transport in Mammals and PlantsDocument2 pages007 - Comparing Transport in Mammals and PlantsCoran St Nicholi Beckford INo ratings yet
- Basics of Embryonic Development 2Document39 pagesBasics of Embryonic Development 2Ma Cristina VelascoNo ratings yet
- 1B-1 The Principles of CirculationDocument18 pages1B-1 The Principles of CirculationChristina HerculesNo ratings yet
- A - Level Transport in Organisms.2021.Mbogo MixedDocument51 pagesA - Level Transport in Organisms.2021.Mbogo Mixedasadukimbugwe20No ratings yet
- Cells The Basic Unit of LifeDocument17 pagesCells The Basic Unit of LifeJoy AlojadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Three Structure of The CellDocument4 pagesCell Three Structure of The CellGrace Rabino IINo ratings yet
- Notes 1 and 4Document9 pagesNotes 1 and 4lovj melNo ratings yet
- Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesKey ConceptsJhoize Cassey Belle OrenNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells PDFDocument51 pagesBiology Cells PDFTanaka ChirawuNo ratings yet
- Plants Transport Edexcel IGCSEDocument9 pagesPlants Transport Edexcel IGCSETZ AZNo ratings yet
- 3.cell - TissuesDocument79 pages3.cell - TissuesRawal Rafiq LeghariNo ratings yet
- Life Science. Added InfoDocument30 pagesLife Science. Added InfoJulie VallesNo ratings yet
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Document4 pagesGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedDocument12 pagesQ4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedXyreen GalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Transport in PlantsDocument17 pagesCh-11 Transport in PlantsSam RNo ratings yet
- Cells The Basic Unit of LifeDocument17 pagesCells The Basic Unit of LifeSwastiNo ratings yet
- Cells The Basic Unit of LifeDocument17 pagesCells The Basic Unit of LifePrecious FacinalNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint 1.1.why Heart and CirculationDocument9 pagesCheckpoint 1.1.why Heart and CirculationYamaany HabeebNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Importance of Having A Transport System in Some Multicellular OrganismsDocument27 pages1.1 The Importance of Having A Transport System in Some Multicellular Organismsdania0% (1)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument51 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyMa Ruth Parel86% (7)
- Biology Mod 1 BioDocument5 pagesBiology Mod 1 BiograceNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Animal Comparison For EvolutionDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Animal Comparison For Evolutionapi-252172239No ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsLhey JesNo ratings yet
- Fibrous Connective Tissue Cells Called Osteoblasts Form BoneDocument135 pagesFibrous Connective Tissue Cells Called Osteoblasts Form Boneapi-12366768100% (2)
- The Animal Organ System - Lesson OutlineDocument5 pagesThe Animal Organ System - Lesson OutlineMa. Cristina UyNo ratings yet
- Biology Practical NotesDocument43 pagesBiology Practical NotesAnonymous qJ5US9NNo ratings yet
- Parts: ManualDocument78 pagesParts: ManualSergey TrakselNo ratings yet
- Crane Inspection ChecklistDocument1 pageCrane Inspection ChecklistdnmuleNo ratings yet
- Regcheck Api Reference: Infinite Loop Development LTDDocument122 pagesRegcheck Api Reference: Infinite Loop Development LTDWilson CunalataNo ratings yet
- SFTY 409 HFACS Phillip ReedDocument4 pagesSFTY 409 HFACS Phillip ReedPhillip ReedNo ratings yet
- Ajuste Valvulas Motor 336DDocument5 pagesAjuste Valvulas Motor 336Djuan sebastianNo ratings yet
- Volvo XC90 AccessoryDocument4 pagesVolvo XC90 AccessoryTeravut SuwansawaipholNo ratings yet
- Delhi Mandi (Himachal Pradesh) : Bus BookingDocument6 pagesDelhi Mandi (Himachal Pradesh) : Bus BookingsanatanNo ratings yet
- OCC WokingDocument20 pagesOCC WokingTPC 78No ratings yet
- New York Daily News - Vol. 105 No. 025 (20 Jul 2023)Document58 pagesNew York Daily News - Vol. 105 No. 025 (20 Jul 2023)mariuscsmNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Make A Check Sheet and Then A Pareto Diagram For The Following Car Repair Shop Data: Ticket No. Work Ticket No. Work Ticket No. WorkDocument5 pagesProblem 1: Make A Check Sheet and Then A Pareto Diagram For The Following Car Repair Shop Data: Ticket No. Work Ticket No. Work Ticket No. WorkThùy DungNo ratings yet
- Case Digest - Transportation LawDocument14 pagesCase Digest - Transportation LawAiko DalaganNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris MaritimDocument288 pagesBahasa Inggris MaritimdudiNo ratings yet
- Fix Ballas Simulation To Achieve The Stability of The Shipyard Graving Dock DoorDocument6 pagesFix Ballas Simulation To Achieve The Stability of The Shipyard Graving Dock DoorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- DFG TFG 425s 435sDocument227 pagesDFG TFG 425s 435sАнатолій КорнейчукNo ratings yet
- Minimums On Jeppesen Charts-1Document9 pagesMinimums On Jeppesen Charts-1Gopikrishnan MenonNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Gyro Bike Report Without HeaderDocument40 pagesFinal Year Project Gyro Bike Report Without HeaderMustafa Fazal AbbasNo ratings yet
- Highway Geometric Design (CE 532) Handout Part 1Document18 pagesHighway Geometric Design (CE 532) Handout Part 1Jeewana MeegahageNo ratings yet
- Mazda SkyActiv OBD-II Calc (FORScan) v6.25Document222 pagesMazda SkyActiv OBD-II Calc (FORScan) v6.25manolitasanchezcarmonaNo ratings yet
- Harsh Project 2Document44 pagesHarsh Project 2Monty MishraNo ratings yet
- PoulanPro PP24VA54 OwnersManualDocument60 pagesPoulanPro PP24VA54 OwnersManualDarren MayNo ratings yet
- Final - Draft Specification - BWSC Pipe Revise1Document21 pagesFinal - Draft Specification - BWSC Pipe Revise1Chief Engineer Hydro Project & Quality ControlNo ratings yet
- M11.5A 2 Gyroscopic Instrument OkDocument73 pagesM11.5A 2 Gyroscopic Instrument OkellysazainudinNo ratings yet
- DIN Low Pressure Fittings and AccessoriesDocument184 pagesDIN Low Pressure Fittings and AccessoriesImtiaz NusratNo ratings yet
- List Size Uniform Karyawan Pt. MMJDocument5 pagesList Size Uniform Karyawan Pt. MMJHiez DoankNo ratings yet
- Pa-31 - Pa-31-300-325 - pcv1994 (Navajo) Ou EMB-820Document1,036 pagesPa-31 - Pa-31-300-325 - pcv1994 (Navajo) Ou EMB-820aero estoqueNo ratings yet
- Foundry Industry 2025 - Tomorrow S Challenges Due To Changing Market ConditionsDocument40 pagesFoundry Industry 2025 - Tomorrow S Challenges Due To Changing Market ConditionsVALANSNo ratings yet
- KA01MF6346Document29 pagesKA01MF6346kamran.shahNo ratings yet
- Cilindros Hidraulicos OEM ServicesDocument52 pagesCilindros Hidraulicos OEM ServicesGiancarloNo ratings yet
- Ubicacion Fusibles Hilux 2016 SM - 2Document36 pagesUbicacion Fusibles Hilux 2016 SM - 2amdresamadorNo ratings yet
- Bid DirectionDocument5 pagesBid DirectionChristian ApfelmannNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessFrom EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsFrom EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (116)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Civilized To Death: The Price of ProgressFrom EverandCivilized To Death: The Price of ProgressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (215)