Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ayush Brakes
Ayush Brakes
Uploaded by
coden8670 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesJwje
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentJwje
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesAyush Brakes
Ayush Brakes
Uploaded by
coden867Jwje
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
1.
Pedal ratio refers to the
relationship between the length
of the brake pedal and the
distance from the pivot point to
the point where the brake force is
applied. By adjusting the pedal
ratio, you can change the
mechanical advantage gained in
the brake system. This affects
how much force is required to
apply the brakes and how much
braking force is generated.
Optimizing the pedal ratio is
important for different vehicle
types and performance
requirements to ensure the
brakes are responsive and
provide the desired stopping
power.
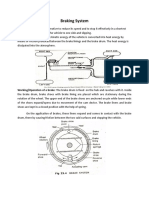
2.Brake calipers play a crucial
role in the braking system. They
house the brake pads and are
responsible for clamping them
onto the brake rotor. When
hydraulic pressure is applied, the
calipers use pistons to squeeze
the brake pads against the rotor,
creating friction. This friction
converts the hydraulic pressure
into mechanical force, which
slows down the vehicle by
causing the rotor to decelerate.
So, in simple terms, brake
calipers help convert hydraulic
pressure into the braking force
that helps your vehicle slow
down.
3.The primary function of a brake
master cylinder is to generate
hydraulic pressure in the braking
system. When you press the
brake pedal, the master cylinder
uses a piston and bore
mechanism to create this
pressure. The bore diameter of
the master cylinder affects the
fluid pressure and force exerted
on the brake system
components. A larger bore
diameter can generate higher
fluid pressure, resulting in more
force being exerted on the brake
components. On the other hand,
a smaller bore diameter can
generate lower fluid pressure,
which may require more pedal
effort to achieve the same
braking force. The bore diameter
is carefully chosen to ensure the
right balance between pedal feel
and braking performance.
5.The choice of brake fluid can
indeed impact the performance
and safety of a braking system.
Different brake fluids have
varying properties, such as
compatibility with different
materials and resistance to
moisture absorption.
There are several types of brake
fluid available, including DOT 3,
DOT 4, DOT 5, and DOT 5.1.
Among these, DOT 4 is
commonly preferred for most
vehicles. It has a higher boiling
point compared to DOT 3, which
can help prevent brake fade
under heavy braking conditions.
DOT 5, on the other hand, is
silicone-based and is not
compatible with most braking
systems, so it's not commonly
used.
It's important to consult your
vehicle's manual or a
professional mechanic to
determine the correct type of
brake fluid
for your specific vehicle, as using
the wrong type can lead to brake
system damage and
compromised safety.
You might also like
- 2017 Indian Full-Size Service ManualDocument649 pages2017 Indian Full-Size Service ManualBrianCook67% (3)
- Hyosung MS3-250 Serice ManualDocument257 pagesHyosung MS3-250 Serice ManualLaze LakiNo ratings yet
- Full Report PDFDocument30 pagesFull Report PDFDarshiKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Brochure Motul enDocument8 pagesBrochure Motul enNedelcu Aurelian0% (1)
- Peugeot HyrdrovacDocument45 pagesPeugeot HyrdrovacKarni100% (1)
- Carver Pellet Press ManualDocument20 pagesCarver Pellet Press ManualJoyleene YuNo ratings yet
- Akcela Aceites Fichas TecnicasDocument44 pagesAkcela Aceites Fichas TecnicasGUILLERMO SEGURANo ratings yet
- Braking SystemDocument22 pagesBraking SystemSIDNo ratings yet
- COMPLETE Report (Braking Department)Document30 pagesCOMPLETE Report (Braking Department)Dinie Abdullah ZamawiNo ratings yet
- Drum Brakes A Type of Mechanical BrakeDocument11 pagesDrum Brakes A Type of Mechanical Brakesubham dashNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Braking SystemDocument6 pagesHydraulic Braking SystemSanjay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Development of Combined Braking System For Two WheelerDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Combined Braking System For Two WheelerPromit ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Braking System InformationDocument30 pagesBraking System InformationLala GuanyesNo ratings yet
- Brake GuideDocument63 pagesBrake GuideainginerNo ratings yet
- انظمه سياراتDocument18 pagesانظمه سياراتayman sweitiNo ratings yet
- Disc Brake ProjectDocument71 pagesDisc Brake ProjectgadhireddyNo ratings yet
- Brake Design ReportDocument29 pagesBrake Design ReportGökhan Yazar0% (4)
- TXN FluidDocument5 pagesTXN Fluidnikhil210492No ratings yet
- Braking SystemDocument11 pagesBraking Systemvenkat sai100% (1)
- Brake Systems in Automotive ApplicationsDocument2 pagesBrake Systems in Automotive ApplicationssoonapaanaNo ratings yet
- Hydrolic Breaking SystemDocument56 pagesHydrolic Breaking SystemAnkush JainNo ratings yet
- Brake SystemDocument14 pagesBrake SystemC/wali Axmed NuurNo ratings yet
- StopTech Racing CatalogDocument79 pagesStopTech Racing CatalogEduardo Medina CastellaroNo ratings yet
- What Is Brake Types of Braking System Notes PDFDocument15 pagesWhat Is Brake Types of Braking System Notes PDFPun hub update vlogsNo ratings yet
- Taller Formativo 2021Document5 pagesTaller Formativo 2021jaime riquelmeNo ratings yet
- Why Brake Fluid It Is ImportantDocument5 pagesWhy Brake Fluid It Is ImportantengrsurifNo ratings yet
- Disc BrakesDocument9 pagesDisc BrakesODANo ratings yet
- Saya Sedang Berbagi 'Hydraulic Brake System PPT Ilkhon-1' Dengan AndaDocument10 pagesSaya Sedang Berbagi 'Hydraulic Brake System PPT Ilkhon-1' Dengan AndaHandanu JNo ratings yet
- Automotive (2) Lab: Braking SystemDocument5 pagesAutomotive (2) Lab: Braking SystemMohammad YahyaNo ratings yet
- Brakes: Question: How Does A Brake System Inspection Work?Document3 pagesBrakes: Question: How Does A Brake System Inspection Work?Muhammad SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Hydraulic Braking SystemDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Hydraulic Braking Systemshjpotpif100% (1)
- Experiment No. 08: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 08: ObjectiveMoiz AamirNo ratings yet
- ATT Brakes - Example TextbookDocument15 pagesATT Brakes - Example TextbookSooraj KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Tyre Inflation SystemDocument53 pagesAutomatic Tyre Inflation SystemMayur Salunke100% (1)
- Report Suzika-Disk BrakeDocument7 pagesReport Suzika-Disk BrakeSuzika HussinNo ratings yet
- Brake System and Upgrade SelectionDocument5 pagesBrake System and Upgrade SelectionMichael SerraNo ratings yet
- MODULE V Lesson 1 3Document50 pagesMODULE V Lesson 1 3Sleepy SpettoNo ratings yet
- Master CylinderDocument8 pagesMaster Cylindershinoj psNo ratings yet
- Types of Automotive Braking Systems: Brake ComponentsDocument5 pagesTypes of Automotive Braking Systems: Brake ComponentsAsmaa Ahmad SharawyNo ratings yet
- Automatically Tyre PressureDocument18 pagesAutomatically Tyre PressureMujeeb RahmanNo ratings yet
- A Short Course On: BrakesDocument10 pagesA Short Course On: BrakesNdung'u Wa WaweruNo ratings yet
- Brakes: A Brake Is A Mechanical Device Which Inhibits MotionDocument22 pagesBrakes: A Brake Is A Mechanical Device Which Inhibits MotionSaurav DharawatNo ratings yet
- Brake System: 3rd Class Automobile Technology Chapter 8Document11 pagesBrake System: 3rd Class Automobile Technology Chapter 8abasNo ratings yet
- Clutch LiteratureDocument33 pagesClutch Literatureraj_kumartNo ratings yet
- Rajshahi University of Engineering & Technology (RUET) : How Braking System Works?Document17 pagesRajshahi University of Engineering & Technology (RUET) : How Braking System Works?Iftekhar AnamNo ratings yet
- Braking System-By GirlsDocument23 pagesBraking System-By Girlskrish0690No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Lesson 2 - MEEC 101ADocument35 pagesModule 4 - Lesson 2 - MEEC 101ADomingo NoverasNo ratings yet
- A Brake Is A Mechanical Device Which Inhibits MotionDocument8 pagesA Brake Is A Mechanical Device Which Inhibits MotionAnthropophobe NyctophileNo ratings yet
- Internal Expanding BrakeDocument11 pagesInternal Expanding BrakeGirish Sahare100% (1)
- Other Systems That Are Connected With The Brake SystemDocument13 pagesOther Systems That Are Connected With The Brake SystemEnoch MwesigwaNo ratings yet
- Mech Disc BrakesDocument17 pagesMech Disc BrakesShubham Kadam0% (2)
- Material Selection For Brake CaliperDocument10 pagesMaterial Selection For Brake CaliperNitin GaurNo ratings yet
- The Brake Bible by BillavistaDocument60 pagesThe Brake Bible by BillavistaAmeya Gidh100% (1)
- Lubrication GuideDocument22 pagesLubrication GuideRizalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document34 pagesUnit 5A ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- To Whom It May ConcernDocument96 pagesTo Whom It May ConcernKamal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drum Brake System Backing Plate: Braking PrincipleDocument3 pagesDrum Brake System Backing Plate: Braking PrincipleSamiullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- Direct vs. Belt Drive Pumps Which Is Best For Your BusinessDocument3 pagesDirect vs. Belt Drive Pumps Which Is Best For Your BusinessKennedi PangaribuanNo ratings yet
- Brake SystemDocument14 pagesBrake SystemJason James GagnanNo ratings yet
- In-House Practical Training: Fabrication of Disc BrakesDocument22 pagesIn-House Practical Training: Fabrication of Disc BrakesBharat100% (1)
- Seminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted byDocument34 pagesSeminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted bySouraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Mech Disc BrakesDocument19 pagesMech Disc BrakesAKHIL KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Types & Working of Drum BrakeDocument9 pagesTypes & Working of Drum BrakeranerxNo ratings yet
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- 10 Tips on How To Take Care of Your Car: Automotive Maintenance Anyone Can Do, #1From Everand10 Tips on How To Take Care of Your Car: Automotive Maintenance Anyone Can Do, #1No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of A Hydraulic Brake Caliper: ArticleDocument10 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Hydraulic Brake Caliper: ArticleRohit KoushikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureJovilyn SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Piaggio Carnaby 250ie (EN)Document300 pagesPiaggio Carnaby 250ie (EN)ManuallesNo ratings yet
- Piaggio Fly150 Service Manual 150ccmDocument239 pagesPiaggio Fly150 Service Manual 150ccmgtperformasNo ratings yet
- MSS-Senda-DRD-X-Treme-en PDFDocument126 pagesMSS-Senda-DRD-X-Treme-en PDFZoranNo ratings yet
- Caliper Disassembly and AssemblyDocument2 pagesCaliper Disassembly and AssemblyMichael HernandezNo ratings yet
- Skoda Octavia Mk1 - 06 - Power Transmission Gearbox 02KDocument167 pagesSkoda Octavia Mk1 - 06 - Power Transmission Gearbox 02KTamás AlföldiNo ratings yet
- Assessment B103Document56 pagesAssessment B103Ahmad Tarar100% (1)
- Electro Hydraulic Thruster Drum BrakesDocument18 pagesElectro Hydraulic Thruster Drum BrakesMani Maran100% (1)
- Mannol WS Pricelist (T1) - Pen. 2023 - R1aDocument4 pagesMannol WS Pricelist (T1) - Pen. 2023 - R1aNur Azlina NazriNo ratings yet
- Irjet V7i3447 PDFDocument9 pagesIrjet V7i3447 PDFURVASHI PATILNo ratings yet
- 06.clutch SystemDocument24 pages06.clutch SystemTony D'AngeloNo ratings yet
- HD Maintenance and LubricationDocument42 pagesHD Maintenance and LubricationCarloVanZylNo ratings yet
- Automotive Vehicle MaintenanceDocument61 pagesAutomotive Vehicle MaintenanceMohd FairusNo ratings yet
- Electronic Brake Control Module 2005 Chevrolet ColoradoDocument16 pagesElectronic Brake Control Module 2005 Chevrolet Coloradozdwkxgnjd7No ratings yet
- Product Catalogue 2006: Clutch Servo Master Cylinder Servomaster Hydraulic Gearshift ComponentsDocument64 pagesProduct Catalogue 2006: Clutch Servo Master Cylinder Servomaster Hydraulic Gearshift ComponentsВЛАДИМИРNo ratings yet
- Valvoline Service PlusDocument2 pagesValvoline Service PlusVictor ZhicayNo ratings yet
- hyosung-RT125Document162 pageshyosung-RT125panpols1No ratings yet
- Ideal Vacuum Catalog 2017 - Oils, Greases, Sealants, HosesDocument18 pagesIdeal Vacuum Catalog 2017 - Oils, Greases, Sealants, HosesFilipe LaínsNo ratings yet
- SWAG Fluessigkeiten 2012 2013Document33 pagesSWAG Fluessigkeiten 2012 2013Hatem NasrNo ratings yet
- Exhibitor Directory PDF 201 223Document27 pagesExhibitor Directory PDF 201 223infoNo ratings yet
- Owner Manual Cforce 820 Euro 4Document160 pagesOwner Manual Cforce 820 Euro 4Sebastian JofreNo ratings yet
- Castrol DOT 3 IndonesiaDocument2 pagesCastrol DOT 3 IndonesiaindeskeyNo ratings yet
- Abs Wabco HabsDocument20 pagesAbs Wabco HabsBom_Jovi_681No ratings yet