Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetism Divided Into
Electromagnetism Divided Into
Uploaded by
Prishita KapoorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromagnetism Divided Into
Electromagnetism Divided Into
Uploaded by
Prishita KapoorCopyright:
Available Formats
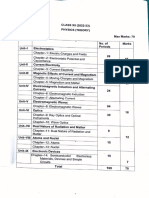
Electromagnetism divided into
1. Electrostatics
2. Electrodynmaics
Electric Charge
Definition and formula
Types of charge - positive and negative
Units of charge
Properties of charge
Any objects /bodies can be classified in either -
1. conductor
2. insulator
Charging of objects / bodies -
1. Charging of conductor
2. Charging of Insulator
Methods of charging-
1. Friction
2. Induction
3. Conduction
Coulomb's Law
Definition and formula (in basic form , in vector form , in terms of positon
vector)
Coulomb’s law in a medium -
1. Relative Permittivity---------------what is Permittivity
2. Force dependency on medium
Electric field
ELECTRIC FIELD INTENSITY
Electric Field due to Point Charge
Electric field due to a Charged ring at a point on its axis
Electric Field due to Charge Disc
Electric Field due to Uniformly Charged Wire
1. Line charge of finite length
2. We can derive a result for infinitely long line charge
3. For Semi- infinite wire
ELECTRIC LINES OF FORCE
Conservative force .
Electrostatic Potential Energy
Electric Potential
Relation Between E and V
Electric lines of force
Equipotential Surface
Electric dipole
You might also like
- Lesson Plan 10 ElectricityDocument12 pagesLesson Plan 10 Electricityjatinder kaur100% (7)
- Unit 1 & 2Document1 pageUnit 1 & 2Mayank Chaudhary 12ANo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric & Electronics: BEKG 1123Document64 pagesPrinciples of Electric & Electronics: BEKG 1123Kugan Tamil KumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric & Electronics: BEKG 1123Document64 pagesPrinciples of Electric & Electronics: BEKG 1123Kugan Tamil Kumar100% (1)
- Fundamental of Electric & Electronics: BENR 1113Document51 pagesFundamental of Electric & Electronics: BENR 1113faizu77No ratings yet
- Chap1 BEKG1123 2019-2020Document56 pagesChap1 BEKG1123 2019-2020Fikri ZdinNo ratings yet
- Exam Topics of XII - ScienceDocument17 pagesExam Topics of XII - ScienceAnish BelelNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS (Week 1)Document4 pagesELECTROSTATICS (Week 1)Philip MooreNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsAlyssa BihagNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticsJannice Anne SantosNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM LessonDocument8 pagesELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM LessonBernard PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electromagnetism 1Document89 pagesBasic Electromagnetism 1Waruni NisansalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesChapter-1: Basics of Electrical EngineeringAONLANo ratings yet
- Physics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismDocument10 pagesPhysics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument14 pagesELECTRICITYTia-marie Mc AlisterNo ratings yet
- Contentpage 33 119 128Document6 pagesContentpage 33 119 128DhruvNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics Complete SyllabusDocument12 pagesClass Xii Physics Complete SyllabusNishanthNo ratings yet
- E AllDocument104 pagesE AllCHRISTIANNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: How To Charge A BodyDocument10 pagesElectrostatics: How To Charge A BodyMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Lecture No1Document27 pagesLecture No1Hassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wldbe301 Basic of ElectricityDocument116 pagesWldbe301 Basic of ElectricityNshimiyimana pacifiqueNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Static Electricity and Conduction (24 Slides)Document24 pagesTopic 2 Static Electricity and Conduction (24 Slides)crye shotNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Coulomb's LawDocument16 pagesElectrostatics: Coulomb's LawTafazzul HazqueelNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Energy and Electricity ConservationDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Energy and Electricity ConservationParth KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Physics 22 23Document9 pagesSyllabus Physics 22 23the SkulptorNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFAryanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDipayan DasNo ratings yet
- Summary-Smme422 Marine Electrotechnology: Ohm Ve Krichhof Yasalarinin UygulamalariDocument63 pagesSummary-Smme422 Marine Electrotechnology: Ohm Ve Krichhof Yasalarinin UygulamalariCemre berk TUNANo ratings yet
- Presentation 1eddDocument44 pagesPresentation 1eddMamo ZelalemNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Strengthin An Uniform Electric FieldDocument12 pagesElectric Field Strengthin An Uniform Electric Fieldadhitya2535No ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument28 pagesElectric FieldABOOTHAHIR AFZALNo ratings yet
- Electricity I 1Document9 pagesElectricity I 1Charles Daniel Torre MalolesNo ratings yet
- ABC of Battery TestingDocument18 pagesABC of Battery TestingAbid HussainNo ratings yet
- RT4 - Reviewer For Comprehensive Exam 1Document11 pagesRT4 - Reviewer For Comprehensive Exam 1Aj PlacidoNo ratings yet
- Archt33 - Electrical SystemDocument35 pagesArcht33 - Electrical SystemRoxette Jane SedonioNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Class 12 and Iitjee Summary (PDF Download) : Skip To ContentDocument15 pagesElectrostatics Class 12 and Iitjee Summary (PDF Download) : Skip To ContentPemmasaniSrinivasNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Class 12 and Iitjee Summary (PDF Download) : Skip To ContentDocument15 pagesElectrostatics Class 12 and Iitjee Summary (PDF Download) : Skip To ContentPemmasaniSrinivasNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument2 pagesHandoutsShiella BaculpoNo ratings yet
- CoulombsDocument47 pagesCoulombsTrishia LimpinNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document2 pagesGeneral Physics 2Ryan GañaNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument47 pagesBasic ElectronicsPolyn LopezNo ratings yet
- APC EFieldDocument5 pagesAPC EFieldRana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Unit - 1 Syllabus: Electrostatics: Chapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Unit - 1 Syllabus: Electrostatics: Chapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsRitesh SoniNo ratings yet
- Electrical PropertiesDocument50 pagesElectrical PropertiesLouise UmaliNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument11 pagesBasic ElectricityFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ElectricityDocument229 pagesBasic Concepts of ElectricityDaniel QuarteyNo ratings yet
- HS Physics EM II Year Learning MaterialDocument43 pagesHS Physics EM II Year Learning MaterialNidhi100% (3)
- 1st Sem Basic ElectricalDocument98 pages1st Sem Basic ElectricalkmanikecNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit TheoryDocument266 pagesElectrical Circuit TheoryTOBIN C THOMASNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering NotesDocument45 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering NotesmnmnNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document75 pagesGeneral Physics 2tinay ciprixxNo ratings yet
- E2 Electric Potential !: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesE2 Electric Potential !: ObjectivesMurtaza LokhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2, 3Document69 pagesUnit 2, 3Mehul VermaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document88 pagesLecture 1rafiqshariatpur1200No ratings yet
- M3 Training NotesDocument64 pagesM3 Training NotessushilNo ratings yet
- ELL 103 fUNDAMENTALS OF eLECTRICITYDocument4 pagesELL 103 fUNDAMENTALS OF eLECTRICITYHannah Cesaree Mae TadeoNo ratings yet
- B.SC - Physics Complete Notes of Electricity and MagnetismDocument134 pagesB.SC - Physics Complete Notes of Electricity and Magnetismizza ghafoorNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - 1: Charges and ChargingDocument90 pagesElectrostatics - 1: Charges and ChargingCat123No ratings yet
- Main Topic Ce0053Document49 pagesMain Topic Ce0053JOSHUA MEYER ANGELESNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2Prishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1Prishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4Prishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- 3Document3 pages3Prishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- SDE1 Resume Vishal LiDocument1 pageSDE1 Resume Vishal LiPrishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- Soumyajit Behera-BIT MESRA.a1cb5c1907e31e31991aDocument1 pageSoumyajit Behera-BIT MESRA.a1cb5c1907e31e31991aPrishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- Day0 - Disk StorageDocument50 pagesDay0 - Disk StoragePrishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- Shireen Nagdive: EducationDocument1 pageShireen Nagdive: EducationPrishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- Without Using SpaceDocument3 pagesWithout Using SpacePrishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- What Is Data StructureDocument6 pagesWhat Is Data StructurePrishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - CompressedDocument30 pagesChapter 2 - CompressedPrishita KapoorNo ratings yet