Professional Documents
Culture Documents
U2L6 DNA Structure and Function Notes
Uploaded by
Afaq Ahmad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views22 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views22 pagesU2L6 DNA Structure and Function Notes
Uploaded by
Afaq AhmadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
Cracking the Code
What is DNA?
• The genetic material in cells is contained in a
molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.
• Scientists describe DNA as containing a code. A
code is a set of rules and symbols used to carry
information.
• To understand how DNA functions, you first need
to learn about the structure of the DNA molecule.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
How was DNA discovered?
• Many scientists from all over the world contributed
to our understanding of DNA.
• Some scientists discovered the chemicals that
make up DNA, and others learned how these
chemicals fit together.
• Still others determined the three-dimensional
structure of the DNA molecule.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
Unraveling DNA
What does DNA look like?
• Experiments and imaging techniques have helped
scientists to infer the shape of DNA.
• The structure of DNA is a twisted ladder shape
called a double helix.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What does DNA look like?
• The two sides of the ladder are made of sugars
and phosphate groups.
• The rungs of the ladder are made of pairs of bases.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What does DNA look like?
• A base, a sugar, and a phosphate group make a
building block of DNA called a nucleotide.
• There are four different nucleotides in DNA.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What does DNA look like?
• The bases in nucleotides are paired, or
complementary.
• Adenine always pairs with thymine (A-T).
• Cytosine always pairs with guanine (C-G).
• The order of the nucleotides in DNA is a code that
carries information.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What does DNA look like?
• Genes are segments of DNA that relate to a certain
trait.
• The code in the nucleotide order has information
about which proteins the cells should build.
• The types of proteins that your body makes help
determine your traits.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
Replication and Mutation
How are copies of DNA made?
• The cell makes copies of DNA molecules through a
process known as replication.
• During replication, the two strands of DNA
separate.
• The bases on each side of the molecule are used
as a pattern for a new strand.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
How are copies of DNA made?
• As bases on the original molecule are exposed,
complementary nucleotides are added.
• When replication is complete, there are two
identical DNA molecules.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
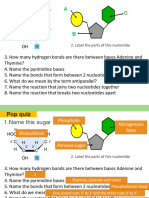
How are copies of DNA made?
• Describe what is happening in the diagram.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
When are copies of DNA made?
• Before a cell divides, it copies its DNA.
• Our cells can replicate DNA in just a few hours,
because replication begins in many places along a
DNA strand.
• Many groups of proteins are working to replicate
your DNA at the same time.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What are mutations?
• Mutations are changes in the number, type, or
order of bases on a piece of DNA.
• There are three main kinds of mutations:
deletions, insertions, and substitutions.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What are mutations?
• In a deletion mutation, a base is left out.
• In an insertion mutation, an extra base is added.
• The most common mutation, substitution, happens
when one base replaces another.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What are mutations?
• Which type of mutation is shown in each row? (The
first row is the original sequence.)
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What are mutations?
• Mutations can happen by random error, and also
by damage to the DNA molecule by physical or
chemical agents called mutagens.
• Cells make proteins that can fix errors in DNA, but
sometimes the mistake is not corrected.
• The mistake then becomes part of the genetic
code.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What are mutations?
• A genetic disorder results from mutations that
harm the normal function of the cell.
• Some genetic disorders are inherited, or passed on
from parent to offspring.
• Other disorders result from mutations during a
person’s lifetime. Most cancers fall in this category.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
Protein Factory
What is the role of DNA and RNA in
building proteins?
• Some of the information in the DNA is copied to a
separate molecule called RNA, or ribonucleic acid.
• RNA is used to build proteins.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What is the role of DNA and RNA in
building proteins?
• Like DNA, RNA has a sugar-phosphate backbone
and the bases adenine (A), guanine (G), and
cytosine (C).
• Instead of thymine (T), RNA contains uracil (U).
• Three types of RNA have special roles in making
proteins.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What is the role of DNA and RNA in
building proteins?
• When a cell needs to make a protein, it makes an
RNA copy of a section of the DNA. This is called
transcription.
• In transcription, DNA is used as a template to
make a complementary strand of messenger RNA
(mRNA).
• The information in the mRNA is then used to build
proteins. This is called translation.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What is the role of DNA and RNA in
building proteins?
• In translation, the mRNA passes through a protein
assembly line within a ribosome.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 6 DNA Structure and Function
What is the role of DNA and RNA in
building proteins?
• A ribosome is a cell organelle made of ribosomal
RNA (rRNA) and protein.
• As mRNA passes through, transfer RNA (tRNA)
delivers amino acids to the ribosomes.
• The order of the bases codes for which amino acid
is attached.
• The amino acids are joined together to form a
protein.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
You might also like
- DNA StructureDocument6 pagesDNA StructureSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- IB Biology HL 2.6 WorksheetDocument10 pagesIB Biology HL 2.6 WorksheetKazeNo ratings yet
- Introductory Biochemistry Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesIntroductory Biochemistry Midterm ExamZachary McCoyNo ratings yet
- ZOO 114 DNA Function LectureDocument53 pagesZOO 114 DNA Function Lecturerakingbulugbe194No ratings yet
- ZOO 114 DNA Function LectureDocument53 pagesZOO 114 DNA Function LectureSamuel BanwoNo ratings yet
- III.C. DNA Its Role in Inheritance and Protein SynthesisDocument15 pagesIII.C. DNA Its Role in Inheritance and Protein SynthesisDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisDocument69 pagesDNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisRomelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Sandra Central DogmaDocument82 pagesSandra Central Dogmakaren milloNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - DNA and RNADocument53 pagesNucleic Acids - DNA and RNATom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument61 pagesDNA Structure and Replicationmanuela pardoNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument70 pagesDna & RnaEvette dela PenaNo ratings yet
- DNA Song: (Row, Row, Row Your Boat)Document43 pagesDNA Song: (Row, Row, Row Your Boat)fruity vegetableNo ratings yet
- 3 5 1 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA RNA)Document17 pages3 5 1 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA RNA)6ix9ine SoulNo ratings yet
- IB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherDocument77 pagesIB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherCoco LocoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication - PPT 1Document48 pagesDNA Replication - PPT 1Keira MendozaNo ratings yet
- DNA: The Molecule of HeredityDocument14 pagesDNA: The Molecule of HereditySUCKET BITCHNo ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument23 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationAleksandar KlingNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 - Lecture - REPLI Transcription and Translation For Class 2022Document138 pagesChapter10 - Lecture - REPLI Transcription and Translation For Class 2022butvNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument48 pagesDNA ReplicationAamir MumtazNo ratings yet
- Mira Molecular Biology Part1Document63 pagesMira Molecular Biology Part1Ranim MiraNo ratings yet
- 1.2 ReviewDocument3 pages1.2 ReviewAaryan ThavaranNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument45 pagesDNA ReplicationTchr Ezra ChangNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument23 pagesLearning Outcomes: Molecular Basis of InheritanceCrystal A-hahaNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- Disease and The Genome: Genetic, Developmental, and Neoplastic DiseaseDocument24 pagesDisease and The Genome: Genetic, Developmental, and Neoplastic DiseaseMegan CatilinaNo ratings yet
- BIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesDocument35 pagesBIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesSeo Eun KimNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic GenomesDocument50 pagesEukaryotic GenomesturkiNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesDNA ReplicationBilal SajidNo ratings yet
- 07 - What Are GenesDocument11 pages07 - What Are GenesMarcelline WijayaNo ratings yet
- DNADocument13 pagesDNAjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- DNA WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesDNA WPS OfficejakevcabauatanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthDocument7 pagesStructure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthRithish VikramNo ratings yet
- Heredity Test 1Document7 pagesHeredity Test 1Fried Chicken GamingNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication SlideshowDocument14 pagesDNA Replication SlideshowRennie SmolenskiNo ratings yet
- Dna & Dna ReplicationDocument60 pagesDna & Dna ReplicationJoeric CarinanNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Heredity: Inheritance and VariationDocument4 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Heredity: Inheritance and VariationMaam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- Me Sci 10 q3 1301 PsDocument27 pagesMe Sci 10 q3 1301 PsCassy Leighz BagonocNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument10 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Composition, Structure and Functions of The Major Types of Nucleic AcidDocument36 pagesModule 6-Composition, Structure and Functions of The Major Types of Nucleic AcidSusana N peNo ratings yet
- Stage IIDocument4 pagesStage IIapi-374854816No ratings yet
- DNA and Its ComponentsDocument109 pagesDNA and Its ComponentsAisha A RehmanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesNucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Structure and Functions of Nucleic AcidsDocument15 pagesModule 6: Structure and Functions of Nucleic AcidsMadhuri Gupta100% (1)
- Molecular GeneticsDocument62 pagesMolecular GeneticsOpheliaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Nucleic AcidDocument7 pagesWeek 8 - Nucleic Acidjvlegaspi7463valNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesDNA RNA Protein Synthesisjohairah merphaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of ReplicationDocument23 pagesMolecular Mechanism of ReplicationIarrNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesDNA Structure and FunctionJomar Ison100% (2)
- DNA JA NewDocument41 pagesDNA JA NewHamza TahaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis 2023Document24 pagesProtein Synthesis 2023Arlene SantosNo ratings yet
- 3.9 DNA Replicaton and The Genetic CodeDocument27 pages3.9 DNA Replicaton and The Genetic CodePratika MNo ratings yet
- Biology 30 Unit C - Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular Genetics - Chapter 18Document165 pagesBiology 30 Unit C - Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular Genetics - Chapter 18kimmoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Investigating The Structure & Function of DNADocument23 pages2022 Investigating The Structure & Function of DNAayaanaghariaNo ratings yet
- 5 Nucleic AcidsDocument73 pages5 Nucleic AcidsmjmonforteNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure & ReplicationDocument25 pagesDNA Structure & Replicationivanam0202No ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument4 pagesChromosomesyunisnaquilaNo ratings yet
- Inhibition of DNA Replication and TranscriptionDocument111 pagesInhibition of DNA Replication and TranscriptionPranav Kumar PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BiologyDocument40 pagesChapter 3 BiologyAnam FNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 7 Genes & Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesAssignment # 7 Genes & Nucleic AcidsCharlou SindacNo ratings yet
- What Is DNADocument22 pagesWhat Is DNASehar AslamNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocument15 pagesCentral Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationCristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 DNA Structure, DNA Library, DNA IsolationDocument45 pagesLecture 5 DNA Structure, DNA Library, DNA IsolationDr.Fahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Popgen2016 Isabel Novella 2016 02 03Document8 pagesPopgen2016 Isabel Novella 2016 02 03Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Inbreeding FST F2017Document12 pagesLecture 8 Inbreeding FST F2017Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Origin and Evolution of Viruses-2-1Document26 pagesThe Origin and Evolution of Viruses-2-1Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Golden +Document50 pagesGolden +Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Classification andDocument15 pagesProkaryote Classification andAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Virid and Virion (New)Document20 pagesVirid and Virion (New)Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Detection and Identification of Microorganisms by Gene Amplification and SequencingDocument14 pagesDetection and Identification of Microorganisms by Gene Amplification and SequencingAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- 7.21.09 Kruska Multiple MyelomaDocument15 pages7.21.09 Kruska Multiple MyelomaAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- CB 6 2 Full Length 8Document10 pagesCB 6 2 Full Length 8Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma and Understanding Your LabsDocument44 pagesMultiple Myeloma and Understanding Your LabsAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document19 pagesPresentation 1Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of MicroorganismsDocument34 pagesCultivation of MicroorganismsAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ihr L8baculture enDocument29 pagesIhr L8baculture enAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- MacConkey AgarDocument4 pagesMacConkey AgarAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Immune System Part 2 OutlineDocument1 pageAP Biology Immune System Part 2 OutlineAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis and ApplicationDocument20 pagesPedigree Analysis and ApplicationAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- ToleranceDocument5 pagesToleranceAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document37 pagesMeiosis 1Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument21 pagesNitrogen CycleAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Classical GeneticsDocument14 pagesClassical GeneticsAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Global Warming-Climate ChangeDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming-Climate ChangeAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Priciples of HeredityDocument45 pagesBasic Priciples of HeredityAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Email DocumentsDocument4 pagesEmail DocumentsAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio 18 NotesDocument6 pagesAp Bio 18 NotesAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow in EcossytemDocument12 pagesEnergy Flow in EcossytemAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Document Security in Word 2010Document8 pagesDocument Security in Word 2010Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Methods of ReproductionDocument22 pagesMethods of ReproductionAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Food PreservationDocument19 pagesFood PreservationAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Borders and Shades in Word 2010Document6 pagesBorders and Shades in Word 2010Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Set Watermark in Word 2010Document6 pagesSet Watermark in Word 2010Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet16 Transcription To TranslationDocument3 pagesWorksheet16 Transcription To Translationliterally deadNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: WWW - Ncert.onlineDocument31 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance: WWW - Ncert.onlineMamataMaharanaNo ratings yet
- Lipids NotesDocument4 pagesLipids NoteskatNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Research: François Ferron, Etienne Decroly, Barbara Selisko, Bruno CanardDocument11 pagesAntiviral Research: François Ferron, Etienne Decroly, Barbara Selisko, Bruno CanardJose QuinteroNo ratings yet
- BCH 201Document77 pagesBCH 201Obinna OjeNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Other Amino Acids: GlycineDocument9 pagesMetabolism of Other Amino Acids: GlycineAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Digital Proofer SBA MRCOG Part1Document118 pagesDigital Proofer SBA MRCOG Part1aaaNo ratings yet
- BT301 Tutorial-2 SolutionsDocument17 pagesBT301 Tutorial-2 SolutionsShivaani EswaranNo ratings yet
- Balanced Nutrition For Different Phases of Chicken: Nutrition and Nutrient ManagementDocument12 pagesBalanced Nutrition For Different Phases of Chicken: Nutrition and Nutrient Managementamamùra maamarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry, KyDocument9 pagesBiochemistry, KyHay DayNo ratings yet
- MWC ModelDocument2 pagesMWC Modelrajwill1No ratings yet
- Lasa High Alert PelayananDocument6 pagesLasa High Alert PelayananUlfa ErviliaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Lipid Metabolism Tutorial CaseDocument8 pagesTutorial 5 - Lipid Metabolism Tutorial CaseSofíaGriggsNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism PDFDocument29 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism PDFtrinitysugumar100% (1)
- Chemistry Project Class Xii MPCDocument28 pagesChemistry Project Class Xii MPCSowjanya Vemulapalli100% (2)
- Urea CycleDocument10 pagesUrea CycleSragwin ThridhamnaNo ratings yet
- Naglaa Ibrahim Mohamed Azab - Protein MetabolismDocument80 pagesNaglaa Ibrahim Mohamed Azab - Protein MetabolismIbi Yulia SetyaniNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Biochemistry QuizDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Biochemistry QuizJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Functional Nucleic Acids For Analytical ApplicationsDocument393 pagesFunctional Nucleic Acids For Analytical ApplicationsDaniel Papadopol100% (1)
- P.Babu M.Pharm.,Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument72 pagesP.Babu M.Pharm.,Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutical ChemistryBabu Palani100% (1)
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MacromoleculesglennNo ratings yet
- Power Point BiomolecoleDocument14 pagesPower Point BiomolecoleEnrico SbaragliaNo ratings yet
- EMGBS-Bio 11. U.3 NoteDocument37 pagesEMGBS-Bio 11. U.3 NoteDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Used in Animal NutritionDocument32 pagesAmino Acids Used in Animal NutritionNhi LeNo ratings yet
- Principles of PCR SmallDocument26 pagesPrinciples of PCR SmallMuhammad Haris LuckyNo ratings yet
- Antioxidants PresentationDocument12 pagesAntioxidants Presentationncjc8591No ratings yet
- Bungkil WijenDocument5 pagesBungkil Wijenbrandy farmNo ratings yet