Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ATI System Disorder Template Heart Failure
Uploaded by
max20020821Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ATI System Disorder Template Heart Failure
Uploaded by
max20020821Copyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|39373214
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System Disorder
Nicholas Au
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
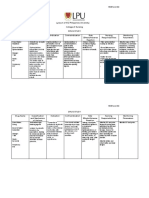
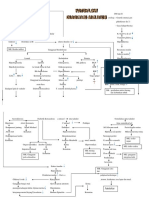
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS __________________________________________________________ 32
REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
Alterations in Pathophysiology Related Health Promotion and
Health (Diagnosis) to Client Problem Disease Prevention
Result of an acute of chronic n the heart muscle is unable to pump Maintain an exercise routine to remain physically active
effectively, resulting in inadequate cardiac and consult with provider before starting any exercise
cardiopulmonary problem. output, myocardial hypertrophy, and regimen
consume a diet low in sodium along with fluid
pulmonary/systemic congestion restrictions and consult with the profvider regarding diet
ASSESSMENT SAFETY
CONSIDERATIONS
Risk Factors Expected Findings Fall Risk,
Older adults have an increased risk for Dyspnea, orthopnea, nocturnal dyspnea, Risk of infection
heart failure and can have worse fatigue, displaced apical pulse, frothy
manifestations due to increased systolic sputum, pulmonary congestion, jugular
blood presure and some medications vein distention, ascending dependent
edema, weight gain, polyuria, nocturia
Laboratory Tests Diagnostic Procedures
Human B-type natriuretic peptides Hemodynamic monitoring - mixed venous oxygen
(hBNP) elevated hBNP confirms a saturation is directly related to cardiac output. a
drop in SvO2 indicates worsening cardiac function
diagnosis of heart failure in clients who Ultrasound - used to measure the systolic and
have dyspnea and rules out respiratory diastolic functioning of the heart
illnesses Transesophageal echocardiagraphy. Gives a
detailed view of cardiac structures
PATIENT-CENTERED CARE Complications
Nursing Care Medications Client Education Acute pulmonary
Use techniques to promote effective breathing
edema
Monitor daily weight and I/Os assess Diuretics - techniques understand prescribed medications and
Cardiogenic shock
forshortness of berath and dyspnea on how to administer them continue to take
exertion administer oxygen as furosemide medications even if feeling better follow instructions
Pericardial
for reasons to contact the provider remain on
prescribed monitor vital signs and Afterload low-sodium diet
tamponade
hemodynamic pressures position the
client to maximize ventiliation reducing Pulmonary edema
agents - ACE
inhibitors
Inotropic
Therapeutic Procedures Agents - digoxin Interprofessional Care
Ventricular assist device - a mechanical pump that Beta blockers - Cardiology and pulmonary services
assists a heart that is too weak to pump blood
Respiratory services for inhalers,
through the body used in clients who are awaiting carvedilol breathing treatments, and suctioning
heart transplants or who have severe end-stage
heart failure. Vasodilators - Cardiac rehab for prolonged weakness
Heart transplant- a possible option for end-stage
and assistance with increasing level of
heart failure nitroglycerin activity
Nutrition for diet modification
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Downloaded by max cheng (max20020821@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Lesson Plan Personality DisorderDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Personality DisorderRaj MeghwalNo ratings yet
- Planets in NakshatrasDocument6 pagesPlanets in Nakshatrasmurthyy55% (11)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPNurhaifa MocademaNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction, Management - ClinicalKeyDocument19 pagesAcute Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction, Management - ClinicalKeyJairo Vergara CorenaNo ratings yet
- MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION EditedDocument27 pagesMYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Editedczars cajayonNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Infographics Pulmonary EdemaDocument1 pageInfographics Pulmonary EdemaSwag MasterNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Ors 1Document3 pagesParacetamol Ors 1Mini BossNo ratings yet
- Drug study-SECOND TWO MEDICAL WARDSDocument2 pagesDrug study-SECOND TWO MEDICAL WARDSErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPMae Denn LabordoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument10 pagesCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFdubsNo ratings yet
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- NCP Partial, Micu Medcor DutyDocument7 pagesNCP Partial, Micu Medcor DutyYana PotNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic COPDDocument15 pagesAcute and Chronic COPDZyrene JaroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanSiena KaleiNo ratings yet
- Vision KINGGILTHEGREATDocument2 pagesVision KINGGILTHEGREATGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Document2 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- Activity#2: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesActivity#2: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentCLOYD JHON OBISPONo ratings yet
- Management of ARDS in Adults: JAMA Clinical Guidelines SynopsisDocument2 pagesManagement of ARDS in Adults: JAMA Clinical Guidelines SynopsisEmman AbelardoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP (Craniotomy)Document2 pagesDrug Study and NCP (Craniotomy)Deinielle Magdangal Romero100% (1)
- NCP BeeaDocument3 pagesNCP BeeaKiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideCrissah LacernaNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus - Nov 20 FDocument11 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus - Nov 20 FZwinglie SandagNo ratings yet
- Drug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Activity 11 Cardiac Tamponade NCPDocument3 pagesActivity 11 Cardiac Tamponade NCPCloe CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Sir MarkDocument5 pagesDrug Study Sir MarkKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Document5 pagesAngiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Isabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument2 pagesDrug Study TemplateMary hope DomalaonNo ratings yet
- Management of ARDS in AdultsDocument2 pagesManagement of ARDS in AdultsCarlos PalominoNo ratings yet
- Kish Drug Study and NCPDocument5 pagesKish Drug Study and NCPKish Gabriel GanadoNo ratings yet
- JemarcoSpear Assign3Document14 pagesJemarcoSpear Assign3Martin OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- (JURNAL, Eng) A Retrospective Cohort Review of Prescribing in Hospitalised Patients With Heart Failure Using Beers Criteria and STOPP RecommendationsDocument7 pages(JURNAL, Eng) A Retrospective Cohort Review of Prescribing in Hospitalised Patients With Heart Failure Using Beers Criteria and STOPP RecommendationsAurellia Annisa WulandariNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisRiska RamadaniNo ratings yet
- 10 5694mja18 00647 PDFDocument7 pages10 5694mja18 00647 PDFandiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure BrochureDocument2 pagesCongestive Heart Failure BrochureTran Nguyen Cat TuongNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - NursingDocument14 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - NursingyellowbyunsNo ratings yet
- Sheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvDocument2 pagesSheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Adeera Levin Ckd-Cv-Lipid-Sharp Web HandoutsDocument12 pagesAdeera Levin Ckd-Cv-Lipid-Sharp Web Handoutsmariatul fithriasariNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Topic OutlineDocument2 pagesPulmonary Edema: Topic OutlineKdamnz100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Congestive Heart FailureMyrshaida IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Di Abetes Insipidus: Collaboration & Referral - PhysicianDocument1 pageDi Abetes Insipidus: Collaboration & Referral - PhysicianDaisy Jane KoNo ratings yet
- NCP Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decrease Cardiac OutputAnonymous 2hJKVrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- BupivacainDocument1 pageBupivacainKerra AnasatasiaNo ratings yet
- EBCR FurosemideDocument10 pagesEBCR FurosemideFian AldyNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug Reaction JalpaDocument7 pagesAdverse Drug Reaction Jalpaparmar jalpabenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument1 pageDrug Study FormatArianne Nicole PinuelaNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument41 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsD'Angela SweetingNo ratings yet
- Seeking Closure For Pda - Neonatal Care UpdateDocument46 pagesSeeking Closure For Pda - Neonatal Care Updateapi-602288180No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Effective Hemodynamic Monitoring 2Document10 pagesEffective Hemodynamic Monitoring 2Shirley castañedaNo ratings yet
- I. Pharmacist's Workup of Drug Therapy For Bronchial AsthmaDocument7 pagesI. Pharmacist's Workup of Drug Therapy For Bronchial AsthmaDave Cabuyadao0% (1)
- Drug Study (Print3copiesDocument8 pagesDrug Study (Print3copiesPhylum ChordataNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mcp1Document2 pagesDrugs Mcp1Ahrjey DUey PanganNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument6 pagesPharmacology Drug StudyShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Determinants of Dyspnea Improvement in Acute Decompensated Heart FailureDocument8 pagesHemodynamic Determinants of Dyspnea Improvement in Acute Decompensated Heart FailureDannyNo ratings yet
- NCP For Hodgkins DiseaseDocument6 pagesNCP For Hodgkins DiseaseROMER LOZADANo ratings yet
- Excellent Achievers Learning, Center, IncDocument5 pagesExcellent Achievers Learning, Center, IncJoyR.Alota100% (1)
- Service ProgramDocument47 pagesService ProgramHuseyn aliyevNo ratings yet
- Aaron Magana's Resume, Business AnalystDocument3 pagesAaron Magana's Resume, Business AnalystEmiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial SessionDocument5 pagesTutorial SessionKhánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Account Transfer Form: Fax Cover SheetDocument6 pagesAccount Transfer Form: Fax Cover SheetJitendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Fitness Training PrinciplesDocument80 pagesChapter 10 Fitness Training Principlesapi-115744109No ratings yet
- One Village One Product Movement in Laos: AbstractDocument5 pagesOne Village One Product Movement in Laos: Abstractoeleong19699685No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument41 pagesUntitledDion AdalaNo ratings yet
- Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Plan: Poblacion Sur, Carmen, BoholDocument6 pagesCommunity-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Plan: Poblacion Sur, Carmen, BoholMarah RabinaNo ratings yet
- 1.ar-315 BC&BL Lighting & IlluminationDocument28 pages1.ar-315 BC&BL Lighting & IlluminationUsha Sri GNo ratings yet
- Name of Learner: Section: Subject Teacher: Date:: Practical Research 2Document4 pagesName of Learner: Section: Subject Teacher: Date:: Practical Research 2J-heart Basabas Malpal100% (6)
- Nasoalveolar Moulding Seminar at MalakkaraDocument54 pagesNasoalveolar Moulding Seminar at MalakkaraAshwin100% (1)
- Request For New Tax DeclarationDocument2 pagesRequest For New Tax DeclarationAsterio MagootNo ratings yet
- Sample Cylinders - PGI-CYLDocument8 pagesSample Cylinders - PGI-CYLcalpeeNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Argex 0032/32.50.15.08 4/10 MM EN 13055: EN 15732 NL BSB K73820/01 (1/01/2004)Document1 pageQuality Control Argex 0032/32.50.15.08 4/10 MM EN 13055: EN 15732 NL BSB K73820/01 (1/01/2004)joe briffaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitDocument3 pagesLab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitManoj PardhanNo ratings yet
- FilterFlow Cartridge Installation GuideDocument8 pagesFilterFlow Cartridge Installation GuideSilver FoxNo ratings yet
- JSLHR Author InstructionsDocument14 pagesJSLHR Author InstructionsChanyanit CharoenpholNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract PDFDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal Tract PDFAlexandra Suan CatambingNo ratings yet
- Birthday QuotesDocument24 pagesBirthday QuotesArniel CatubigNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage 1: IELTS Recent Actual Test With Answers Volume 1Document17 pagesReading Passage 1: IELTS Recent Actual Test With Answers Volume 1Amogha GadkarNo ratings yet
- QTR-2 2023 Meeting Format Nov.23Document45 pagesQTR-2 2023 Meeting Format Nov.23skumar31397No ratings yet
- Patoflow DMDocument2 pagesPatoflow DMAngel da CostaNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning in Clinical MedicalDocument7 pagesDistance Learning in Clinical MedicalGeraldine Junchaya CastillaNo ratings yet
- CORONADocument25 pagesCORONAMohammedNo ratings yet
- IWGIA Book The Indigenous World 2021 ENGDocument824 pagesIWGIA Book The Indigenous World 2021 ENGREy FOxNo ratings yet
- SEI BasicDocument146 pagesSEI BasicYuthia Aulia Riani100% (1)
- Key MechanicalDocument72 pagesKey MechanicalDasuki FahmiNo ratings yet