Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antimicrobial Regimens For The Treatment of Streptococcus Anginosus G
Uploaded by
Khor Chin PooOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antimicrobial Regimens For The Treatment of Streptococcus Anginosus G
Uploaded by
Khor Chin PooCopyright:
Available Formats
Antimicrobial regimens for the treatment of <em>Streptococcus anginosus</em> group infections
Official reprint from UpToDate® www.uptodate.com
©2024 UpToDate®
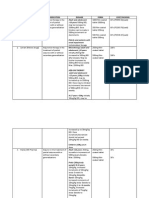
Antimicrobial regimens for the treatment of Streptococcus anginosus group infections
Adult dosing Pediatric dosing
Initial antimicrobial regimen*
Preferred regimens Ceftriaxone 2 g IV every 24 hours, or Ceftriaxone 50 to 100 mg/kg/dose IV every 24
Penicillin G 2 to 4 million units IV every 4 to 6 hours (maximum: 1000 mg/dose), or
hours Penicillin G 100,000 to 300,000 units/kg/day IV
divided every 4 to 6 hours (maximum dose: 24
PLUS
million units/day)
Metronidazole 500 mg orally or IV every 8
PLUS
hours
Metronidazole 30 to 40 mg/kg/day orally or IV
in 3 divided doses (maximum: 500 mg/dose)
Ampicillin-sulbactam ¶ 3 g IV every 6 hours Ampicillin-sulbactam ¶ 100 to 200 mg
ampicillin/kg/day IV divided every 6 hours
(maximum: 2000 mg ampicillin/dose)
Alternative regimens For patients who require anti-anaerobic For patients who require anti-anaerobic
(for patients who therapy: therapy:
cannot tolerate or Ertapenem 1 g IV every 24 hours Ertapenem
have
Children ≥3 months to <13 years: 15
contraindications to
mg/kg/dose IV every 12 hours
preferred regimens)
(maximum: 500 mg/dose)
Children ≥13 years: 1 g IV every 24
hours
For patients with endovascular infections For patients with endovascular infections
without associated abscess: without associated abscess:
Δ
Vancomycin IV or Vancomycin IV ◊ or
Linezolid 600 mg orally or IV every 12 hours Linezolid
Children <12 years: 10 mg/kg/dose
orally or IV every 8 hours (maximum:
600 mg/dose)
Children ≥12 years: 600 mg orally or IV
every 12 hours
Oral step-down regimens for select cases §
Preferred regimens Amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally 2 Amoxicillin-clavulanate ¥ 45 mg
to 3 times daily amoxicillin/kg/day orally in 2 divided doses
(maximum: 1750 mg/day)
Cefuroxime 500 mg orally twice daily Cefuroxime 20 to 30 mg/kg/day orally in 2
divided doses (mild to moderate infection,
PLUS
maximum: 500 mg/dose)
Metronidazole 500 mg orally 3 times daily, or
PLUS
Clindamycin 300 mg orally 4 times daily or 300
to 450 mg orally 3 times daily Metronidazole 30 to 40 mg/kg/day orally in 3
divided doses (maximum: 500 mg/dose), or
Clindamycin 10 to 25 mg/kg/day orally in 3
divided doses (maximum: 1800 mg/day)
- Page 1 of 2 -
Antimicrobial regimens for the treatment of <em>Streptococcus anginosus</em> group infections
Alternative regimens Linezolid 600 mg orally twice daily Linezolid
(for patients who Children <12 years: 10 mg/kg/dose orally
PLUS
cannot tolerate or every 8 hours (maximum: 600 mg/dose)
have Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally twice daily
Children ≥12 years: 600 mg orally twice
contraindications to PLUS daily
preferred regimens)
Metronidazole 500 mg orally every 8 hours, or PLUS
Clindamycin 300 mg orally 4 times daily or 300
Ciprofloxacin 10 to 15 mg/kg/dose orally twice
to 450 mg orally 3 times daily
daily (maximum: 500 mg/dose) ‡
PLUS
Metronidazole 30 to 40 mg/kg/day orally in 3
divided doses (maximum: 500 mg/dose), or
Clindamycin 10 to 25 mg/kg/day orally in 3
divided doses (maximum: 1800 mg/day)
Selected antimicrobial regimens are listed here. Other regimens with the same spectrum of activity are also appropriate. The
doses recommended in this table are intended for patients with normal kidney and liver function. Pediatric dosing is intended
for patients >28 days of age, unless otherwise noted. Refer to Lexicomp drug monographs and the UpToDate clinical topic
review of S. anginosus group infections for additional information.
IV: intravenously.
* Dosing of certain antimicrobials (eg, ceftriaxone, penicillin G, ampicillin, clindamycin) for treatment of severe infections (eg,
central nervous system infections, endocarditis) differs from the doses listed in this table. Refer to Lexicomp drug monographs.
¶ Ampicillin-sulbactam is a combination product formulated in a 2:1 ratio (eg, each vial contains 2 g of ampicillin and 1 g of
sulbactam). Adult dosing is provided as total grams of ampicillin and sulbactam. Pediatric dosing is expressed as mg of
ampicillin component.
Δ For severely ill patients, a vancomycin loading dose (20 to 35 mg/kg) is appropriate; within this range, we use a higher dose
for critically ill patients. The loading dose is based on actual body weight, rounded to the nearest 250 mg increment and not
exceeding 3000 mg. The initial maintenance dose and interval are determined by nomogram (typically 15 to 20 mg/kg every 8 to
12 hours for most patients with normal kidney function). Subsequent dose and interval adjustments are based on area under
the curve (AUC)-guided or trough-guided serum concentration monitoring. Refer to the UpToDate topic on vancomycin dosing
for sample nomogram and discussion of vancomycin monitoring.
◊ The approach to pediatric vancomycin dosing is generally determined at the institutional level. A typical dose is 15
mg/kg/dose IV every 6 to 8 hours (use every 6-hour interval for serious infections; maximum dose: 4 g/day), however other
dosing strategies (eg, AUC-guided approach) may be used. Refer to UpToDate content on invasive staphylococcal infections in
children for details of trough-guided and AUC-guided vancomycin dosing.
§ Oral step-down therapy is appropriate for certain clinical syndromes (eg, abscess in the absence of bacteremia). However, we
favor continuing initial intravenous therapy for endovascular infections (eg, bacteremia, endocarditis) as well as other severe or
difficult to treat syndromes.
¥ Dosing is based on the amoxicillin component for the amoxicillin:clavulanate 7:1 formulations (eg, amoxicillin-clavulanate 200
mg/28.5 mg, 400 mg/57 mg, or 875 mg/125 mg). Not all products are interchangeable; using a product with the incorrect
amoxicillin:clavulanate ratio could result in subtherapeutic clavulanic acid concentrations or adverse effects (eg, severe
diarrhea). For dosing for other amoxicillin-clavulanate formulations, refer to the Lexicomp drug monograph.
‡ Although ciprofloxacin is not routinely used in children, it is a reasonable alternative when no other oral options are available.
Graphic 139420 Version 2.0
© 2024 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
- Page 2 of 2 -
You might also like
- Antibiotic ConversionDocument9 pagesAntibiotic ConversionfabianNo ratings yet
- Paediatric DosesDocument2 pagesPaediatric DosesMichael AdjeiNo ratings yet
- Homeo Drug CompenDocument6 pagesHomeo Drug CompenSittie Nadia MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Treatment of Infection Due To Vibrio Vulnificus - UpToDateDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Treatment of Infection Due To Vibrio Vulnificus - UpToDateKevo VillagranNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Antibiotic DosingDocument7 pagesPediatric Antibiotic DosingAnonymous mm1yTelKNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosages in PediatricsDocument4 pagesDrug Dosages in Pediatricsmarry.as2012No ratings yet
- Dr. Ave - Anti ParasitesDocument44 pagesDr. Ave - Anti ParasitesDeanGrestamaNo ratings yet
- Finasteride: Analgesics (Non-Opioid) & AntipyreticsDocument5 pagesFinasteride: Analgesics (Non-Opioid) & AntipyreticsSarah Michelle NiduaNo ratings yet
- Nidua's Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNidua's Drug ChartSarah Michelle NiduaNo ratings yet
- Articol Engleza-1Document7 pagesArticol Engleza-1Miruna MiulescuNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DosesDocument5 pagesPediatric Dosesa2r91No ratings yet
- Degracia, John Noeh D. Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDegracia, John Noeh D. Drug StudyLenie DegraciaNo ratings yet
- Ivf: Therapeutics: Anti-Pyretics: PenicillinsDocument6 pagesIvf: Therapeutics: Anti-Pyretics: PenicillinsJenny CiNo ratings yet
- FormularyDocument5 pagesFormularyMichelle WongNo ratings yet
- Calpol Tablets Oral Suspension and Paediatric DropsDocument15 pagesCalpol Tablets Oral Suspension and Paediatric DropsAndrew PartridgeNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument5 pagesFormulaEloiseBalasbasNo ratings yet
- Measles PHIDSPILDocument5 pagesMeasles PHIDSPILriczen mae vilaNo ratings yet
- Theraputic Agent in NeonateDocument7 pagesTheraputic Agent in Neonateد. محمد فريد الغنامNo ratings yet
- Analgesik/Pire Tik Dosis Sediaan Obat DOA OOA Drug Interaction Paracetamol IVDocument9 pagesAnalgesik/Pire Tik Dosis Sediaan Obat DOA OOA Drug Interaction Paracetamol IVNicole NgoNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin 250 MG Capsules-Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument65 pagesAmoxicillin 250 MG Capsules-Summary of Product CharacteristicsBrown and Burk UK Ltd100% (1)
- Route/Dosage: Concentration: Not To Exceed 10 Mg/ml. Do NotDocument2 pagesRoute/Dosage: Concentration: Not To Exceed 10 Mg/ml. Do NotMaria MargaritaNo ratings yet
- 05 Pharmacology PLE 2019 RatioDocument50 pages05 Pharmacology PLE 2019 RatioPatricia VillegasNo ratings yet
- INDICATIONS and ContraindicationsDocument2 pagesINDICATIONS and ContraindicationsKat SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Obat Dosis Obat: Pneumonia, Community-AcquiredDocument2 pagesObat Dosis Obat: Pneumonia, Community-Acquiredannisa shalihahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anati Purwakanthi, MSC Departemen Farmakologi Fkik UnjaDocument40 pagesDr. Anati Purwakanthi, MSC Departemen Farmakologi Fkik Unjaanes tiraNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Nama Obat Kisaran Dosis Dan Dosis Maksimal/Hari Dewasa Anak Oral (MG) Iv/ Im Oral (MG/KG) Iv/ImDocument2 pagesKlasifikasi Nama Obat Kisaran Dosis Dan Dosis Maksimal/Hari Dewasa Anak Oral (MG) Iv/ Im Oral (MG/KG) Iv/ImKhairul AlvaroNo ratings yet
- NICU Drugs GuideDocument49 pagesNICU Drugs GuideArhanNo ratings yet
- Id 397 TeicoplaninDocument2 pagesId 397 TeicoplaninStacey WoodsNo ratings yet
- MPC Antidote ChartDocument1 pageMPC Antidote Chartogodothomas51No ratings yet
- Drug Choice For OmaDocument1 pageDrug Choice For Omapriskilas911No ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFDocument15 pagesPediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFHuang Hasjim33% (9)
- Wound Infections: Common PathogensDocument1 pageWound Infections: Common PathogensAnonymous KGxzow5zxhNo ratings yet
- AntibiocardDocument25 pagesAntibiocardchildicuNo ratings yet
- Pediatic DosesDocument8 pagesPediatic Doseshailemariamgebrehiwot02No ratings yet
- Lampiran OM & FaringitisDocument6 pagesLampiran OM & FaringitisAdhinyDistiHelmiNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin 125 MG 250 MG 5 ML Oral SuspensionDocument16 pagesAmoxicillin 125 MG 250 MG 5 ML Oral SuspensionAshrafNo ratings yet
- Levetiracetam Brand Indication Dosage Form Cost/Packing: Adult and Adolescent 16 Years 500mg BIDDocument4 pagesLevetiracetam Brand Indication Dosage Form Cost/Packing: Adult and Adolescent 16 Years 500mg BIDMark PradsNo ratings yet
- Effect DoseDocument30 pagesEffect DoseXyprus Darina VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Recommended Doses of Medications To Treat Children With An Acute Asthma ExacerbaDocument3 pagesRecommended Doses of Medications To Treat Children With An Acute Asthma Exacerbaمعاذ الشريفNo ratings yet
- Tamiflu Epar Product Information - enDocument118 pagesTamiflu Epar Product Information - enUmar AliNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir (Systemic) - Pediatric Drug Information - UpToDate PDFDocument34 pagesAcyclovir (Systemic) - Pediatric Drug Information - UpToDate PDFAndreea LupuNo ratings yet
- Common Pediatric MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Pediatric MedicationsMilito KikamNo ratings yet
- Cilastati Imipenem Drug InfoDocument19 pagesCilastati Imipenem Drug InfoCosmina GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Daftar ObatDocument6 pagesKumpulan Daftar ObatZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- CLACIDODocument22 pagesCLACIDOSergel CapsuleNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument47 pagesAmoxicillin - Drug Information - UpToDateMikaela lNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease DrugsDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease DrugsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Dosage of Some Drugs-1Document45 pagesPaediatric Dosage of Some Drugs-1JaneNo ratings yet
- D-6-12 Sanaani, Mohammad Khaisar H. August 9, 2020: Bacterial VaginosisDocument4 pagesD-6-12 Sanaani, Mohammad Khaisar H. August 9, 2020: Bacterial VaginosisKenMNo ratings yet
- Gentamycin Case Notes by SDocument3 pagesGentamycin Case Notes by SSharan SahotaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guidelines For PediatricsDocument33 pagesAntibiotic Guidelines For PediatricsVarshini Tamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- CommedDocument3 pagesCommedFatee Kasim McrngnNo ratings yet
- Endometrialcarcinoma r0416 7941Document2 pagesEndometrialcarcinoma r0416 7941crisibarra911No ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTICSDocument51 pagesANTIBIOTICSamrharidi446No ratings yet
- Drugs For Paediatric UseDocument14 pagesDrugs For Paediatric Usefouza100% (1)
- Azithromycin Monograph - PaediatricDocument7 pagesAzithromycin Monograph - PaediatrictynNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Treatment of PCPDocument5 pagesDrugs For Treatment of PCPwennyoktavNo ratings yet
- (According To Alphabetical Order) : Community Acquired Meningitis (CAM)Document69 pages(According To Alphabetical Order) : Community Acquired Meningitis (CAM)Nuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryFrom EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamFrom EverandPharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drugs Associated With Isolated ThrombocytopeniaDocument4 pagesDrugs Associated With Isolated ThrombocytopeniaKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Renal DoseDocument13 pagesAntibiotic Renal DoseKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- AntifungalDocument7 pagesAntifungalKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Consequences Different Perioperative Fluid Therapies in The Neonatal PeriodDocument6 pagesMetabolic Consequences Different Perioperative Fluid Therapies in The Neonatal PeriodKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- 501 1765 1 PBDocument7 pages501 1765 1 PBKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Practice Surveys On Parenteral Nutrition For Preterm InfantsDocument5 pagesA Systematic Review of Practice Surveys On Parenteral Nutrition For Preterm InfantsKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- 47 TPNDocument7 pages47 TPNKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside & VancomycinDocument10 pagesAminoglycoside & VancomycinKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- 430 FullDocument6 pages430 FullKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- FDA Approves First Gene Therapy, Betibeglogene Autotemcel (Zynteglo), For Beta-ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesFDA Approves First Gene Therapy, Betibeglogene Autotemcel (Zynteglo), For Beta-ThalassemiaGiorgi PopiashviliNo ratings yet
- German Atv-Dvwk Rules and StandardsDocument25 pagesGerman Atv-Dvwk Rules and StandardsMehmet Emre Bastopcu100% (1)
- Business Plan 3.3Document2 pagesBusiness Plan 3.3Rojin TingabngabNo ratings yet
- The Magic DrumDocument185 pagesThe Magic Drumtanishgiri2012No ratings yet
- Origami Oso HormigueroDocument9 pagesOrigami Oso HormigueroRogelio CerdaNo ratings yet
- SimovertDocument41 pagesSimovertRamez YassaNo ratings yet
- Broken BondsDocument20 pagesBroken Bondsapi-316744816No ratings yet
- UTP Student Industrial ReportDocument50 pagesUTP Student Industrial ReportAnwar HalimNo ratings yet
- Project Scheduling and TrackingDocument47 pagesProject Scheduling and TrackingArun VinodhNo ratings yet
- ME Eng 8 Q1 0101 - SG - African History and LiteratureDocument13 pagesME Eng 8 Q1 0101 - SG - African History and Literaturerosary bersanoNo ratings yet
- Appendix - Pcmc2Document8 pagesAppendix - Pcmc2Siva PNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument3 pagesReadmedhgdhdjhsNo ratings yet
- Project - New Restuarant Management System The Grill HouseDocument24 pagesProject - New Restuarant Management System The Grill HouseMayank Mahajan100% (3)
- Presentation 11Document14 pagesPresentation 11stellabrown535No ratings yet
- Objective & Scope of ProjectDocument8 pagesObjective & Scope of ProjectPraveen SehgalNo ratings yet
- PLC Laboratory Activity 2Document3 pagesPLC Laboratory Activity 2Kate AlindajaoNo ratings yet
- Ron Kangas - IoanDocument11 pagesRon Kangas - IoanBogdan SoptereanNo ratings yet
- Revenue and Expenditure AuditDocument38 pagesRevenue and Expenditure AuditPavitra MohanNo ratings yet
- Carriage RequirementsDocument63 pagesCarriage RequirementsFred GrosfilerNo ratings yet
- Rule 113 114Document7 pagesRule 113 114Shaila GonzalesNo ratings yet
- C C C C: "P P P P PDocument25 pagesC C C C: "P P P P PShalu Dua KatyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 16 - Monitoring, Review and Audit by Allan WatsonDocument29 pagesUnit 16 - Monitoring, Review and Audit by Allan WatsonLuqman OsmanNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument8 pagesTetralogy of FallotHillary Faye FernandezNo ratings yet
- g6 - AFA - Q1 - Module 6 - Week 6 FOR TEACHERDocument23 pagesg6 - AFA - Q1 - Module 6 - Week 6 FOR TEACHERPrincess Nicole LugtuNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: SV01-NHX40AX03-01E NHX4000 MSX-853 Axis Adjustment Procedure of Z-Axis Zero Return PositionDocument5 pagesService Manual: SV01-NHX40AX03-01E NHX4000 MSX-853 Axis Adjustment Procedure of Z-Axis Zero Return Positionmahdi elmay100% (3)
- Mcom Sem 4 Project FinalDocument70 pagesMcom Sem 4 Project Finallaxmi iyer75% (4)
- Ito Na Talaga Yung FinalDocument22 pagesIto Na Talaga Yung FinalJonas Gian Miguel MadarangNo ratings yet
- C - Amarjit Singh So Bhura SinghDocument5 pagesC - Amarjit Singh So Bhura SinghRohit JindalNo ratings yet
- B. Geoinformatics PDFDocument77 pagesB. Geoinformatics PDFmchakra720% (1)
- RSA - Brand - Guidelines - 2019 2Document79 pagesRSA - Brand - Guidelines - 2019 2Gigi's DelightNo ratings yet