Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carpenter Class 3 Section B
Uploaded by
Aaron MushunjeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carpenter Class 3 Section B
Uploaded by
Aaron MushunjeCopyright:
Available Formats
Class three section b carpenter
1. With reference to temporary construction, define the following terms:
Formwork, shoring, centering. (6)
- Formwork is a temporary mould to save as a system into which wet
concrete and steel reinforcement is cast and compacted to form the
required shape.
- Shoring is a form of temporary support to building structures
which is defective and likely to collapse when alterations are being
made to buildings.
- Centering is used to support the brickwork in the construction of
arches and ensures for a smooth finished curve of the arch.
2. Define each of the following roof work terms:
Truss, gable end. (4)
- Truss is a two or more members joined together in a triangular
pattern to form a sturdy frame to carry roof covering.
- A gable end is the external brick work built to the slope of the
rafters taking the same slope or shape as roof.
3. Discuss water proofing material under the following headings:
(Liquid coating); characteristics, properties, application and fixing.
(4)
- It takes the shape of area or object it is applied to
- Liquid coatings serves as water-proofing sealants
- The area where the coatings will be applied must be clean, dry and
smooth
- Liquid coatings are applied with a cloth or a brush
4. List three water proofing materials used on roofs to seal off joints,
openings and cracks. (3)
- Mastic
- Acrylic
- Asphalt
- Plastic
5. A building is not fit to be used by humans if it does not have a roof.
Give the purpose and function of a roof.(3)
- To protect the occupants of the house in the building
- To cover the interior of the building
- To provide shelter against weather
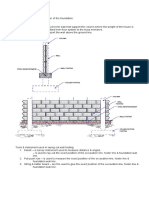
6. Explain under which conditions piled foundations will be used.(3)
- Natural low bearing capacity of soil.
- High water table.
- Subsoil – subjected to movement e.g. expansion and contraction of shrinkable
clay soil.
- Subsoil – subjected to high moisture content. Recently placed filling materials
which are not sufficiently compacted.
7 Briefly explain another method to finish off the joint between two gypsum
boards. (2)
- Before painting, the joints between the gypsum boards can be
closed and finished off with Rhinolite or cretestone.
8 Timber for roof trusses must be treated. Give three reasons why it must be treated. (3)
- To protect it against water and rot
- To protect it against attack from fungi
- To protect it against attack from insects such as beetles
- To protect it against attack from wood borers
9. Describe how a steel roof truss can be protected from corrosion. (3)
- Painted
- Galvanised
- Powder coated
- Electroplating
10. Choose an item from column B that matches a description in column A.
(5)
Column A Column B
i. Has a slight slope a. Gable roof
ii. Has vertical end on two sides b. Conical roof
iii. Found on most round c. Hip roof
buildings d. Flat roof
iv. Commonly used on the side of e. Monopitch roof
a larger building
v. Has all roof end sloping
- (i) – D
- (ii) – A
- (iii) – B
- (iv) – E
- (v) – C
-
Carpenter class three sec b
1 Briefly explain what working drawings are in construction work.(3)
- Working drawings are the main documentation prepared by an
architect from which the quantity surveyor prepares some bill of
quantities.
- It should have some descriptive notes and supplemented by
details.
- These are the drawings which the contractor uses to construct the
work on site.
2 State two uses of the water level during setting out process of a
building. (2)
- The water level is used to determine the difference in height
between two or more points
- It is used to transfer levels from one level point to another point.
3 Indicate three methods of securing purlins to rafters. (3)
- By means of hurricane clips
- By means of wire clips and nails
- Using combination of wire and nails
- By using combination of nails and hoop iron
4 Briefly explain how trusses are permanently fixed to the wall
structure. (3)
- Nail the truss from both sides with 100mm nails into the wall
plate.
- Strap hoop iron firmly over the truss and nail securely.
- Ensure that the hoop iron is long enough to tie down both the wall
plate and the truss.
5. Briefly explain the following terms in construction work.
i. Easing and striking in centering (2)
ii. A kicker in formwork. (2)
- Easing and striking means the slackening or slightly lowering and
the removal of wedges, posts and centres.
- A kicker is a small upstand of concrete or timber, the same size as
plan of the column. To locate and secure the bottom of the form
box. It also prevents loss of concrete at the base of the column.
6. State three reasons or important functions of using shoring
during construction work. (3)
- To support a structure that show signs of weakness due to ground
subsidence or foundation sagging.
- To support a structure that has become defective and most
probably going to collapse
- To give support to an adjacent structure or building, where
extensive alterations are in operation
- To support the walls of a structure which tends to become bulgy
and full of cracks
7 Name three members that are directly involved in managing a
construction site. Also give one task performed by each member. (6)
- Structural and civil engineer – Designs the structural elements eg
beams and columns.
- Architect – appointed by the client to design the building and draw
up plans
- Building inspector – employed by the local authority to inspect the
building
- Quality surveyor – manages and controls building costs.
8 Briefly explain a datum peg (3)
- A datum peg is a temporary benchmarks expressed as the level or
elevation of any point as the vertical distance of the point above or
below a definite level. It is an imaginary level surface of the site.
9. During setting out operations of a building it is important to determine
and check the squareness of the building and its corners. Name three
methods used to perform this task. (3)
- 3.4.5 method
- Builders square
- Diagonal checks
- Optical square.
10. In formwork for columns yokes are used to keep the four sides together. Explain why the
distance between the yokes increases as one moves higher up the formwork. (2)
- The pressure exerted by the wet concrete at the bottom of the formwork is the greatest
and gradually decreases as the level rises to the top
CLASS three Section b
Test item one
Give TWO reasons why scaffolding must be inspected before it can be used. (2)
To ensure that the scaffolding is stable in all directions.
Must be able to carry the mass of the load.
Free of any defects.
Test item two
Name three materials that scaffolding can be made from. (3)
Steel
Wood
Bamboo
Aluminium.
Test item three
What is the maximum distance that a suspended scaffold may hang over the edge of the structure?
(2)
It can suspend- for 1,8m
Test item four
State the maximum height of a trestle scaffold? (2)
Maximum height of a trestle scaffolding is 3m
Test item five
Describe the first THREE steps that need to be considered when preparing timber before applying
preservatives. (3)
Sand the wood with surface with different grades of sand paper
Fill up all cracks and sand again until the surface is smooth
Remove all dust
Test item six
Differentiate between a conventional trap door and a hinged trap door in a ceiling in terms of the
way in which it opens. (4)
A convectional trap door consists of a panel that can be pushed up
A hinged trap door opens upwards or down wards by pivoting around the hinges
Test item seven
Name three parts of a conventional trapdoor. (3)
Timber frame
Board or panel
Cover strip
Test item eight
Describe four requirements that preservatives should comply with to be used effectively on timber.
(4)
Preservatives must:
Be poisonous enough to kill insects without being harmful to humans.
Be affordable.
Not smell unpleasant.
Not cause corrosion of metals in the wood.
Strengthen rather than weaken the wood.
Not spoil the appearance of the wood.
Not change the dimensions or the strength of the wood.
Test item nine
Name FOUR advantages of a water-based paint. (4)
Can be applied with brush
Enhances appearance of surfaces
Easy to apply
Dries quickly
Can be easily cleaned with water
Gives flexible resistance to cracking
TEST ITEM TEN
State four advantages of the curing of concrete. (4)
Increases strength
Decreases the permeability of concrete
Reduces cracks makes concrete more water tight
Provides volume stability
Class three sec b
Test item one
Explain THREE safety precautions to be adhered to when setting up a ladder to do maintenance work
at high levels in a building. (3)
- • Take note of overhead electrical cables and avoid contact with it.
- • Place the ladder so that its feet are a quarter of its length away from the object it is resting
against.
- • Unless the ladder is securely tied at the top, another person should hold it whilst in use.
- • Wherever possible, the ladder should protrude at least 900 mm above its support.
Test item two
Hand tools are an asset to any tradesman. Assume you are a tradesman. Explain how you will take
care of your hand tools to ensure that they serve you well in years to come. (4)
- • Only use the tool for its intended purpose.
- • Wet hands can cause ferrous metals to rust, try to make contact with these parts as little
as possible.
- • Remove rust from tools with steel wool only and thereafter apply a thin layer of oil or wax
over it.
- • Check tools regularly for defects.
- • Avoid stacking tools on top of each other.
- • Tools must not be left lying around, they must be returned to its proper storage place.
- • Cutting tools must be sharp and its edges protected with a covering
Test t item three
You are on site and a fellow worker is shocked by an electrical wire. Explain TWO precautionary
measures you will take to prevent further electrocution. (2)
- • Get the person away from the source of electricity.
- • Use a piece of timber or non-conductor to break the contact of electricity from the
person.
- • Switch off the power source.
Test item four
Describe FOUR requirements that materials used for formwork must meet. (4)
- • Should be strong enough to support the load of wet concrete.
- • It must not be able to deflect under the load of wet concrete.
- • It must be accurately set out.
- • It must have grout tight joints.
- • The design of the formwork unit should be such that it can be easily erected and
dismantled.
- • Formwork material must be of such a nature that it can be easily handled by hand or
mechanical lifting device.
- • The material must be re-usable.
Test item five
State FOUR factors that must be taken into account during the planning stage of a rib and block
floor. (4)
- • Pre-stressed units
- • Maximum span
- • In-situ concrete layer
- • Unit weight
- • Reinforcement requirements
- • Insulation characteristic
- • Fire resistance
- • Volume reduction
- • Sound insulation
- • Nature of struts
Test item six
Differentiate how mechanical and visual grading of timber is done.
- Visual grading is done visually/looking at it
- Whilst mechanical grading is done with testing equipment (machines).
Test item seven
Cement is an important material and has a limited shelf life. Explain how you will store cement for
use on a building site. (4)
- • Cement should be stored on a raised platform covered with waterproof material.
- • Should not be exposed to moisture.
- • Should be used as soon as possible.
- • Must be used in a cycle of first in first out.
- • Must be stacked away from the walls.
- • Do not store more than 12 bags on top of one another.
- • Do not stack more than two pallets on top of each other
Test item eight
What is the purpose of the guard rail of a scaffold in terms of safety? (3)
- • It prevents workers from falling off the scaffold.
- • It is used as a handrail.
- • It is used to strap on safety harnesses.
- • To protect the worker working on the scaffold.
Test item nine
Describe four safety precautions that must be adhered to when working on a scaffold. (4)
- • Do not throw any tools or materials from a scaffold.
- • Never jump on to and off a scaffold.
- • Never overload a scaffold.
- • Remove or cover sharp edges or corners.
- • Always attach free-standing scaffoldings to a building.
- • Use a ladder to get on and off a scaffold.
- • Keep free of waste or any other obstruction.
- • Never jump on a scaffold while working on it.
- • Responsible/qualified person must ensure that scaffolding is safe, rigid, stable and firm or
has no defects.
- • Scaffold must be supplied with guard rails/toe boards.
- • Scaffolds must be levelled on uneven ground.
- • Do not work on a scaffold in bad weather.
- • Wear a safety harness when working on scaffolding.
- • Do not throw tools on/off a scaffold.
Test item ten
Explain the purpose of painting. (3)
• The primary purpose of painting is to protect metals, wood and other material against corrosion
and decay.
• Provides a decorative/aesthetic appearance/finishing.
• Protects surfaces from moisture penetration.
• Protects surfaces from rust/uv rays.
You might also like
- Columns and Shear Walls Means Vertical Elements Form Work We Cane Remove After24 Hours But Slab Form Work Depend On Span Same Like ThisDocument16 pagesColumns and Shear Walls Means Vertical Elements Form Work We Cane Remove After24 Hours But Slab Form Work Depend On Span Same Like ThisImam ShakilNo ratings yet
- Formwork Is An Ancillary ConstructionDocument25 pagesFormwork Is An Ancillary ConstructionSarinNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Formwork Notes-1Document4 pages9.1 Formwork Notes-1RahulSinghRajput100% (1)
- Types of FormworkDocument12 pagesTypes of FormworkNino Celso AstilleroNo ratings yet
- Types of FormworkDocument12 pagesTypes of FormworkAnonymous LiddTaTaZTNo ratings yet
- Building Technology - FloorsDocument22 pagesBuilding Technology - FloorsSiegmund Kamau100% (5)
- Tutorial Kit (Building Tech 200 Level) - Vol. 2Document40 pagesTutorial Kit (Building Tech 200 Level) - Vol. 2Mustapha shehu100% (1)
- Internship ReportDocument17 pagesInternship ReportEBIN JACOB ANISH CE A 16-20No ratings yet
- BLD 204 Building Construction III Combined PDFDocument49 pagesBLD 204 Building Construction III Combined PDFdkaviti83% (30)
- 8-IWRE 416-Formwork and FalseworkDocument41 pages8-IWRE 416-Formwork and Falseworkally IsayaNo ratings yet
- Importat Question of Building ConstructionDocument19 pagesImportat Question of Building Constructionamol bardeNo ratings yet
- Slim Floor ConstructionDocument18 pagesSlim Floor ConstructionFrankie ChanNo ratings yet
- Crystal Metamfetamine PDFDocument3 pagesCrystal Metamfetamine PDFVia AnapiNo ratings yet
- Construction & Materials SolutionsDocument21 pagesConstruction & Materials SolutionsDeeksha PptNo ratings yet
- Building Construction 8: DR Nabil El-Sawalhi Associate Professor Engineering Projects ManagementDocument31 pagesBuilding Construction 8: DR Nabil El-Sawalhi Associate Professor Engineering Projects Management54 Nayeem ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- L6 - FormworkDocument3 pagesL6 - FormworkHntez ClarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Construction Materials: Question One (I)Document17 pagesChapter Three Construction Materials: Question One (I)OFOSU ANIMNo ratings yet
- RajatDocument23 pagesRajatShah PriyamNo ratings yet
- Formwork & Scafolding PDFDocument8 pagesFormwork & Scafolding PDFNilanjan TarafderNo ratings yet
- SSB CeDocument8 pagesSSB CeMalsawm ZualiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Building Construction 2008 UnprotectedDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Building Construction 2008 Unprotectedgabrieloduro318No ratings yet
- Waffle Slab - WikipediaDocument15 pagesWaffle Slab - WikipediaBryan PongaoNo ratings yet
- A Report On Reinforced Cement Concrete FloorsDocument7 pagesA Report On Reinforced Cement Concrete FloorsAshish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Shrinkage Strip Method Statment and Ther PDFDocument4 pagesShrinkage Strip Method Statment and Ther PDFhakim2020No ratings yet
- Quantity SurveyingDocument25 pagesQuantity Surveyingmercy atienoNo ratings yet
- 575.09.S01 Quantity Surveying ConstructionDocument6 pages575.09.S01 Quantity Surveying ConstructionMuchena Stephen GiftNo ratings yet
- 3 - Durability of Reinforced Concrete StructureDocument24 pages3 - Durability of Reinforced Concrete StructureyakaNo ratings yet
- Q1 - 2012 (Conference Hall)Document14 pagesQ1 - 2012 (Conference Hall)manishNo ratings yet
- Possible Solution To Past CM Examination Question: Question 1 - April 2012 Conference Hall and Exhibition GalleriesDocument61 pagesPossible Solution To Past CM Examination Question: Question 1 - April 2012 Conference Hall and Exhibition GalleriestfvnjyNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument27 pagesBuilding ConstructionSnigdha Dam100% (1)
- PfabDocument15 pagesPfabSudipto RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Construction Method in Reinforced ConcreteDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Construction Method in Reinforced Concretepritti_naa100% (1)
- Waffle Slab - WikipediaDocument15 pagesWaffle Slab - WikipediaDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology Assignment 2Document5 pagesConstruction Technology Assignment 2Otee IsaacNo ratings yet
- Managing The Technology of Modern and Traditional Construction WorksDocument24 pagesManaging The Technology of Modern and Traditional Construction WorksZlatin Kirov100% (1)
- q01 g3 Ahmad AmalludinDocument5 pagesq01 g3 Ahmad AmalludinAmal AmranNo ratings yet
- DPC Shoring Door NewDocument68 pagesDPC Shoring Door NewMARUFNo ratings yet
- TK/KW/15 - 7786 Third Semester B. Arch. (C.B.S.) ExaminationDocument3 pagesTK/KW/15 - 7786 Third Semester B. Arch. (C.B.S.) ExaminationAnkesh SinhaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-04-02 at 9.22.27 AMDocument44 pagesScreenshot 2023-04-02 at 9.22.27 AMGamal AbdelwahidNo ratings yet
- Conc. Folded SlabDocument17 pagesConc. Folded SlabBenedict CharlesNo ratings yet
- ARCH402 Nora Ahmd 21902492Document16 pagesARCH402 Nora Ahmd 2190249221902492No ratings yet
- Dundu 2011Document15 pagesDundu 2011fahmi aballiNo ratings yet
- SHORINGDocument10 pagesSHORINGIzzuddin ShahidanNo ratings yet
- Arghya Mohanta - Continuous Assessment 3Document10 pagesArghya Mohanta - Continuous Assessment 3Arghya MohantaNo ratings yet
- BLDG TechDocument2 pagesBLDG TechTrisha CieloNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument5 pagesCorrosionmyint phyoNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete: AI-Gadhib/CE 315/CE 323Document22 pagesReinforced Concrete: AI-Gadhib/CE 315/CE 323Thalia Arias GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Liquid Retaining StructureDocument37 pagesLiquid Retaining Structureshrikant kaleNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument84 pagesLectureYared AddisuNo ratings yet
- Laying Multi-Thickness Walls and PiersDocument14 pagesLaying Multi-Thickness Walls and PiersDawit Awash100% (6)
- The Properties of Roof TilesDocument9 pagesThe Properties of Roof TilesSingh is KingNo ratings yet
- Types of Formwork (Shuttering) For ConcreteDocument29 pagesTypes of Formwork (Shuttering) For Concretesaima BatoolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 RC TanksDocument18 pagesLecture 1 RC TanksAseel NajibNo ratings yet
- Formwork Nandja PDFDocument10 pagesFormwork Nandja PDFRadha PatelNo ratings yet
- Building Construction ReportDocument15 pagesBuilding Construction ReportDevendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- RCDAR - 02 - Reinforced Concrete V01Document19 pagesRCDAR - 02 - Reinforced Concrete V01Rom Reyes Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Final Group Work PDFDocument8 pagesFinal Group Work PDFTeddy MatiekaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II CTDocument58 pagesUNIT II CTDuraid FalihNo ratings yet
- TK/KW/15 - 7797 Sixth Semester B. Architecture Examination: Construction - V Paper - VDocument2 pagesTK/KW/15 - 7797 Sixth Semester B. Architecture Examination: Construction - V Paper - VShraddha 08No ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Facts On The Project ProgressDocument7 pagesFacts On The Project ProgressAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Statement of Changes in EquityDocument1 pageStatement of Changes in EquityAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Eco - Friendly Production and ProductsDocument31 pagesEco - Friendly Production and ProductsAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash FlowsDocument1 pageStatement of Cash FlowsAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Financial Management Group 8Document4 pagesEntrepreneurship and Financial Management Group 8Aaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Drain Laying Pipe SystemDocument19 pagesDrain Laying Pipe SystemAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Curriculum DesignDocument30 pagesDeterminants of Curriculum DesignAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Education Management Assignment Mr. MushunjeDocument8 pagesEducation Management Assignment Mr. MushunjeAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - 220920 - 120824Document2 pagesAssignment 2 - 220920 - 120824Aaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Ict Cover PageDocument1 pageIct Cover PageAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- The Role of Music in Promoting National Diversity - 094504Document6 pagesThe Role of Music in Promoting National Diversity - 094504Aaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Construction EquipmentDocument23 pagesConstruction EquipmentAaron Mushunje100% (1)
- Andragogy TheoryDocument1 pageAndragogy TheoryAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- OrganizedDocument34 pagesOrganizedMochammad Su'udNo ratings yet
- Submitted To The Department of Civil Engineering of CGC Technical Campus Jhanjeri, MohaliDocument46 pagesSubmitted To The Department of Civil Engineering of CGC Technical Campus Jhanjeri, MohaliBipinNo ratings yet
- Maps Showing Seismicity Regions: Appendix ADocument34 pagesMaps Showing Seismicity Regions: Appendix AcesarNo ratings yet
- Rev19Document14 pagesRev19quatudogonNo ratings yet
- LED LINEAR PROFILE LIGHTING CATALOGUE 18 19 Edited EditedDocument42 pagesLED LINEAR PROFILE LIGHTING CATALOGUE 18 19 Edited EditedKeshav SinghNo ratings yet
- Consultant FeeDocument15 pagesConsultant Feesadaqat181No ratings yet
- Aqe Reviewer PrintDocument20 pagesAqe Reviewer PrintFredmon Choy Fernandez NarvasaNo ratings yet
- Rynglok AB25 TF100-17Document8 pagesRynglok AB25 TF100-17cesarin2011No ratings yet
- Masonry 9Document5 pagesMasonry 9Shaina Freya Grantoza NasolNo ratings yet
- Soil Lateral Loads: Earthquake EngineeringDocument9 pagesSoil Lateral Loads: Earthquake EngineeringMelchor Jaramilla OronosNo ratings yet
- Zahra Kalantar - Properties of Bituminous Binders ModifiedDocument11 pagesZahra Kalantar - Properties of Bituminous Binders Modifiedzeidan111No ratings yet
- Assignment CE163 - RivetsDocument3 pagesAssignment CE163 - RivetsJems MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Cost Audit ProjectDocument23 pagesCost Audit ProjectHarshada SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Versitank® Versitank Is A Heavy Duty Plastic Tank ThatDocument10 pagesWhat Is Versitank® Versitank Is A Heavy Duty Plastic Tank ThatsreekanthchemiNo ratings yet
- Removal of Structures and Obstruction: Prepared By: Raymar B. CuerpoDocument9 pagesRemoval of Structures and Obstruction: Prepared By: Raymar B. Cuerporay cuerpoNo ratings yet
- En Domeo PDFDocument6 pagesEn Domeo PDFzainsarfarazNo ratings yet
- Hot Tapping in Tanks According To API 653 - ApiexamDocument9 pagesHot Tapping in Tanks According To API 653 - ApiexamHanindyo Ardhi100% (1)
- Seismic Analysis of Multi Storey Building On Sloping Ground and Flat Ground by Using ETABSDocument13 pagesSeismic Analysis of Multi Storey Building On Sloping Ground and Flat Ground by Using ETABSUttam ShresthaNo ratings yet
- GC6000-0-1-0 Principles of Bearing Selection and ApplicationDocument6 pagesGC6000-0-1-0 Principles of Bearing Selection and ApplicationFrancisco AlessandriNo ratings yet
- Inoxpa - ManualDocument93 pagesInoxpa - ManualnikitaNo ratings yet
- SAP2000 Viscous Fluid - Steel Structures PDFDocument16 pagesSAP2000 Viscous Fluid - Steel Structures PDFabelkrusnik02No ratings yet
- Earthquake IntroductionDocument5 pagesEarthquake IntroductionEr Harsh MahajanNo ratings yet
- BricklayingDocument20 pagesBricklayingJTNo ratings yet
- Simspon WallDocument3 pagesSimspon WallAlexandru Jora100% (1)
- Making Construction Simple, Transparent and Reliable Through Technology and ProcessesDocument17 pagesMaking Construction Simple, Transparent and Reliable Through Technology and ProcessesPulkit ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 - SolutionDocument7 pagesAssignment 7 - Solutiontajiw17001No ratings yet
- Criterios de Falla Vesic (1975)Document13 pagesCriterios de Falla Vesic (1975)ira0218No ratings yet
- Example Design 2 - 10 Terrace HomesDocument18 pagesExample Design 2 - 10 Terrace HomesJuan Fernando RestrepoNo ratings yet
- BN-S-UC001 Standard Checklist For Plant CompletionDocument3 pagesBN-S-UC001 Standard Checklist For Plant Completionwisnu_bayusaktiNo ratings yet
- Solid Hollow Plug PDFDocument3 pagesSolid Hollow Plug PDFSandra DevannyNo ratings yet