Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 3 (Behavior of Gases) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)
Uploaded by
cherrymaeregalario2001Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 3 (Behavior of Gases) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)
Uploaded by
cherrymaeregalario2001Copyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE 10
Name: __________________________________________ Grade & Section: _________________________ Date: _______________
BEHAVIOR OF GASES
What’s In
Let’s Do it
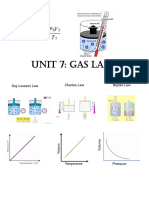
The volume of a gas is directly related to its temperature at Instruction: Convert the given measurements to the new units
constant pressure specified.
The pressure of a gas is directly related to its temperature at
constant temperature Conversion of Volume
The volume of a gas is inversely related to its pressure at constant 1. 22 mL = ___________ cm3
temperature 2. 18 dm3= ___________ L
The amount of a gas in amole is directly related to its volume at 3. 13 m3 = ____________ 1000 L
constant pressure and temperature 4. 3 mL = ____________ dm3
5. 5 dm3 = ___________ mL
The properties of gases can be varied. The relationship of these
properties can be quantified experimentally with the aid of the Conversion of Pressure
different laboratory apparatus or by using the different gas laws as 1. 2.5 atm = ___________ mm Hg
follows: 2. 5 atm = ___________ cm Hg
3. 7 atm = ____________ torr
4. 2 atm = ____________ Pa
5. 12 atm = ___________ psi
Conversion of Temperature
Commonly Used Units for Volume and Pressure
Not all gases behave ideally. Most of the gases found in nature
conform to the principles of Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law, Gay-Lussac’s
Law, Avogadro’s Law and Combines Gas Law
The following conversion factors are useful in solving gas law related
problems:
Volume units and their equivalents:
1 mL = 1cm3 1L = 1dm3 1 m3= 1000 L
Pressure units and their equivalents:
1 atm = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 101325 Pa
1 atm = 76 cm Hg 1 atm = 14.6956 psi
1 atm = 760 torr
Temperature units and their equivalents:
-End-
You might also like
- Gas Laws LabDocument4 pagesGas Laws LabBrady DeNioNo ratings yet
- Gases by Rymond ChangDocument20 pagesGases by Rymond Changمركز نونNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Gases StudentDocument6 pagesStudy Guide Gases StudentnicoNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Study Guide Gases Student EditableDocument6 pagesStudy Guide Gases Student EditableRicki HanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment Directions: Answer The Following Questions Below About Volume-Pressure Relationship and Write Your Answer inDocument2 pagesPre-Assessment Directions: Answer The Following Questions Below About Volume-Pressure Relationship and Write Your Answer inMa'am MercadoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarFrom EverandCarbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Unit 10 Packet 1 AnswersDocument26 pagesAP Chemistry Unit 10 Packet 1 AnswersBrandon BaxterNo ratings yet
- (A) Chapter 13 OutlineDocument10 pages(A) Chapter 13 Outlineabdelrahmanadelm2008No ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- LAS SCI10 4QTR WK1.2 RevisedDocument3 pagesLAS SCI10 4QTR WK1.2 RevisedCurt Andrie T PotenciaNo ratings yet
- Api MPMS 14.5Document8 pagesApi MPMS 14.5JorgeTunNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Calculation of Natural Gas Liquid Quantities: MPMS, The MeterDocument6 pagesCalculation of Natural Gas Liquid Quantities: MPMS, The MeterremsorNo ratings yet
- (Q1) MODULE 10 - Gas Stoichiometry PDFDocument18 pages(Q1) MODULE 10 - Gas Stoichiometry PDFJewel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Unit Review Part 2 2022Document3 pagesUnit Review Part 2 2022tjqxqpxzx5No ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument12 pagesIdeal GassteveislaryNo ratings yet
- Exp 15 Molecular Weight Determination of Vapor PDFDocument7 pagesExp 15 Molecular Weight Determination of Vapor PDFLisette Joyce LolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-13 Assessment Gases Student EditableDocument5 pagesChapter-13 Assessment Gases Student EditableFabricio FernandezNo ratings yet
- CHEM301 - Experiment 1 - Manual - P-V and P-T Relationships of Ideal and Real Gases - Fall2021Document9 pagesCHEM301 - Experiment 1 - Manual - P-V and P-T Relationships of Ideal and Real Gases - Fall2021FULL DİAMOND SET HONEYBADGERNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument3 pagesCharles Lawsarausos.zoe08No ratings yet
- Chem QuestionsDocument2 pagesChem QuestionsJullia Lyn Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Handout - 2 - Physical States of MatterDocument12 pagesHandout - 2 - Physical States of MatterHarun ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Avogadro Handout 8Document2 pagesAvogadro Handout 8cassandranguyen0702No ratings yet
- Boyle's Law Computer ActivityDocument3 pagesBoyle's Law Computer ActivityAnonymous 52Z8ZFkv0% (1)
- Science 10 - Week 28Document4 pagesScience 10 - Week 28Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument12 pagesIdeal GasJasminSutkovicNo ratings yet
- Avogadro's LawDocument5 pagesAvogadro's LawHeng Pris100% (1)
- Unit 7 Gas Laws Packet 2021Document40 pagesUnit 7 Gas Laws Packet 2021Alberto Laborte Jr.No ratings yet
- Dos and Donts in FlowDocument19 pagesDos and Donts in FlowPatricia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Test ReviewDocument2 pagesGas Laws Test ReviewXzyle1213No ratings yet
- Gases, Vapors, Liquids and Solids: Basic Principle II Second Class Dr. Arkan Jasim HadiDocument13 pagesGases, Vapors, Liquids and Solids: Basic Principle II Second Class Dr. Arkan Jasim Hadiالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 The Ideal Gasq PDFDocument4 pagesLesson 3 The Ideal Gasq PDFireneNo ratings yet
- CH 01 - 06Document132 pagesCH 01 - 06sara_g6r100% (2)
- Gas Laws Exam: Escribe Tu Nombre CompletoDocument4 pagesGas Laws Exam: Escribe Tu Nombre CompletoEver MendezNo ratings yet
- Basic Gas Law Notes 2017Document14 pagesBasic Gas Law Notes 2017Sreeja TipirneniNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics: Fluid Dynamics, Leon Liebenberg, 2019Document4 pagesFluid Statics: Fluid Dynamics, Leon Liebenberg, 2019wtkafeNo ratings yet
- SMCH 1Document7 pagesSMCH 1Eng MohammedNo ratings yet
- Pressure Review and PracticeDocument2 pagesPressure Review and PracticeVixenNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - GasesDocument13 pagesModule 1 - GasesRuth AquinoNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Guide: Episode 901 Name - : Chemistry: A Study of MatterDocument7 pagesNote Taking Guide: Episode 901 Name - : Chemistry: A Study of MatterKaya SNo ratings yet
- Exp 8 Ideal Gas LawDocument7 pagesExp 8 Ideal Gas LawEzat Rahman0% (1)
- AvocadoDocument8 pagesAvocadoKaye GelieNo ratings yet
- 9th+class Gas+laws Chmistry+material+ (CMD)Document11 pages9th+class Gas+laws Chmistry+material+ (CMD)Karthik NNo ratings yet
- 02-Experiment # 2 Measurement of Densities and Specific Gravities (7-11) PDFDocument5 pages02-Experiment # 2 Measurement of Densities and Specific Gravities (7-11) PDFKristina DavidNo ratings yet
- 6 02 Experiment 2 Measurement of Densities and - 230823 - 172120Document7 pages6 02 Experiment 2 Measurement of Densities and - 230823 - 172120Joshua Joseph LlamasNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity of GasesDocument9 pagesHeat Capacity of Gasesismail100% (1)
- Science 10 - Week 27Document3 pagesScience 10 - Week 27Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Calculations Involving GasesDocument2 pages1.4 Calculations Involving GasesLaurenNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 TestDocument2 pagesUnit 8 TestmamazookeeprNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 PGE381Document58 pagesChapter2 PGE381leeNo ratings yet
- There Are Two Ways To Measure The Density 1. Hydrometers 2. Baknometers A Stopper Capillary: A Hydrometer Is AnDocument21 pagesThere Are Two Ways To Measure The Density 1. Hydrometers 2. Baknometers A Stopper Capillary: A Hydrometer Is AnAmmar YasserNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Phase Behaviour of Hydrocarbons: Hrishikesh Chavan Hrishikesh - Chavan@mitpune - Edu.inDocument66 pagesUnit 2: Phase Behaviour of Hydrocarbons: Hrishikesh Chavan Hrishikesh - Chavan@mitpune - Edu.inSuvishal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Topic 05 - States of Matter - TutorsDocument17 pagesTopic 05 - States of Matter - TutorsTran Nhat ThangNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument1 pageScriptcherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Boyle's LawDocument4 pagesBoyle's Lawcherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Script 2Document2 pagesScript 2cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 4 (Boyle's Law) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)Document2 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 4 (Boyle's Law) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 14 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document6 pagesModule 14 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Rosario Trino RagosNo ratings yet
- Module 12 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document10 pagesModule 12 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Regalario, CM.R - M5 - Prof. Ed 16Document6 pagesRegalario, CM.R - M5 - Prof. Ed 16cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 13 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document5 pagesModule 13 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 10 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document5 pagesModule 10 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 8 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document7 pagesModule 8 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Regalario, CM.R - M3 - Prof. Ed 13Document4 pagesRegalario, CM.R - M3 - Prof. Ed 13cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Regalario, CM.R - M4 - Prof. Ed 16Document4 pagesRegalario, CM.R - M4 - Prof. Ed 16cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- TOS For Science 10 - 3rd Periodic ExamDocument1 pageTOS For Science 10 - 3rd Periodic Examcherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- The Roles of Hormones - DLP 10Document7 pagesThe Roles of Hormones - DLP 10cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- De Cuong On Thi HK2 Tieng Anh 10Document5 pagesDe Cuong On Thi HK2 Tieng Anh 10hoangtouri2512No ratings yet
- Computer Typing History of TypingDocument9 pagesComputer Typing History of TypingRamNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Pressure Equipment Safety: PurposeDocument9 pagesProcedure: Pressure Equipment Safety: PurposeChegwe CorneliusNo ratings yet
- Aitkensmethod 170829115234Document17 pagesAitkensmethod 170829115234Yumi koshaNo ratings yet
- Practicality and Efficiency: Presented By: Grace EscabasDocument11 pagesPracticality and Efficiency: Presented By: Grace EscabasMiaeNo ratings yet
- Connecting Your Database and Auto Generate ID Using VB - Net 2008 and MySQL DatabaseDocument1 pageConnecting Your Database and Auto Generate ID Using VB - Net 2008 and MySQL DatabaseAgusWibowoNo ratings yet
- Balanced Cable Measurement Using The 4-Port ENADocument9 pagesBalanced Cable Measurement Using The 4-Port ENAA. VillaNo ratings yet
- Khairro SanfordDocument2 pagesKhairro SanfordJezreel SabadoNo ratings yet
- TSS Training Package Implementation Guidefinal 0Document18 pagesTSS Training Package Implementation Guidefinal 0hanabbecharaNo ratings yet
- Complete-Crp SPC Shamli r01-1562323540Document291 pagesComplete-Crp SPC Shamli r01-1562323540p nandyNo ratings yet
- Laboratorios RoeDocument11 pagesLaboratorios RoeVioleta CubaNo ratings yet
- Qüestionari KPSI.: ActivitiesDocument2 pagesQüestionari KPSI.: ActivitiesfrancisNo ratings yet
- AYLS Annual Report 2019 LampDocument136 pagesAYLS Annual Report 2019 LampHigh FourNo ratings yet
- English Is The Window To The World. MimieDocument2 pagesEnglish Is The Window To The World. MimieFARAH NADIANo ratings yet
- Purchasing Process Models Inspiration For Teac 2019 Journal of Purchasing ADocument11 pagesPurchasing Process Models Inspiration For Teac 2019 Journal of Purchasing ASunita ChayalNo ratings yet
- Iso 6336 5 2016Document54 pagesIso 6336 5 2016Кирилл100% (2)
- Wind Load On StructuesDocument14 pagesWind Load On StructuesNasri Ahmed mohammedNo ratings yet
- Eurotuner February 2010 PDFDocument1 pageEurotuner February 2010 PDFJenniferNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractJignesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Ratio GCSE WorksheetDocument11 pagesThird Space Learning Ratio GCSE WorksheetDrichy Obi-EmelonyeNo ratings yet
- Bianca Premo - The Enlightenment On Trial - Ordinary Litigants and Colonialism in The Spanish Empire-Oxford University Press (2017)Document385 pagesBianca Premo - The Enlightenment On Trial - Ordinary Litigants and Colonialism in The Spanish Empire-Oxford University Press (2017)David Quintero100% (2)
- 1 Conformity Asch StudyDocument31 pages1 Conformity Asch StudyjasbruNo ratings yet
- (English) Time and The Brain - The Illusion of Now - Hinze Hogendoorn - TEDxUtrechtUniversity (DownSub - Com)Document14 pages(English) Time and The Brain - The Illusion of Now - Hinze Hogendoorn - TEDxUtrechtUniversity (DownSub - Com)Диана ТатарчукNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills For Effective LeadershipDocument12 pagesCommunication Skills For Effective LeadershipKovaNo ratings yet
- Thing in Itself Kantian: AnstoßDocument1 pageThing in Itself Kantian: Anstoßwhynotbequiet23No ratings yet
- Design Data 610 3450 9.5 1650 2 3300 2 1650 120Document3 pagesDesign Data 610 3450 9.5 1650 2 3300 2 1650 120miteshpatel191100% (1)
- Kids 2: INSTITUTO CAMBRIDGE de Cultura Inglesa - EXÁMENES 2019Document2 pagesKids 2: INSTITUTO CAMBRIDGE de Cultura Inglesa - EXÁMENES 2019Evaluna MoidalNo ratings yet
- Survey 2 Module 2Document76 pagesSurvey 2 Module 2veereshNo ratings yet
- 14.ergonomic Workstation Design For Science Laboratory (Norhafizah Rosman) PP 93-102Document10 pages14.ergonomic Workstation Design For Science Laboratory (Norhafizah Rosman) PP 93-102upenapahangNo ratings yet
- Basic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYDocument17 pagesBasic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet