Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Managment Mids
Uploaded by
Huzair NadeemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Network Managment Mids
Uploaded by
Huzair NadeemCopyright:
Available Formats
DNS: NETWORK MANAGEMENT:
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is a decentralized Network management involves the administration, monitoring,
naming system for computers, services, or any resource and optimization of computer networks to ensure efficient
connected to the internet or a private network. operation, security, and reliability.
DNS translates easily memorable domain names, like It includes tasks such as device configuration, performance
"example.com," into the numerical IP addresses that monitoring, troubleshooting, security management, and resource
computers use to identify each other on the network. allocation.
The DNS system works like a distributed database, with Network management systems (NMS) utilize software tools and
multiple servers worldwide that store and manage domain protocols to manage and control network devices, analyze network
name records. traffic, and provide insights into network performance.
Root DNS Servers:
These are the highest level of DNS servers in the hierarchy NETWORK TYPES:
and maintain information about top-level domain (TLD) LAN (Local Area Network):
names, such as .com, .net, .org, etc. A network that connects devices within a limited geographic area,
TLD DNS Servers: such as a home, office, or campus.
These servers are responsible for maintaining information WAN (Wide Area Network):
about domain names under specific top-level domains, such A network that spans over a large geographical area, connecting
as .com, .net, .org, etc. multiple LANs or other networks. The internet is the largest WAN.
Authoritative DNS Servers: WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network):
These servers store and provide information about specific A type of LAN that uses wireless technology (Wi-Fi) for
domain names. They are responsible for maintaining the connectivity, allowing devices to connect without physical cables.
actual DNS records, such as IP addresses, associated with MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
domain names. A network that covers a larger geographic area than a LAN but
Recursive DNS Servers (Resolver): smaller than a WAN, typically serving a city or metropolitan area.
These are the DNS servers that most devices use to look up VPN (Virtual Private Network):
domain names. They perform the actual work of querying A secure network that extends a private network across a public
other DNS servers to resolve domain names. network like the internet, enabling users to access resources
securely from remote locations.
ACTIVE LIFE SERVICE:
Active live services in network management refer to the NETWORK PROTOCOLS:
continuous monitoring and management of network services TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol):
and resources in real-time. These services involve proactive The fundamental protocol suite of the internet, responsible for
measures to ensure optimal performance, availability, and data transmission and routing across networks.
security of the network infrastructure. Here are some key HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol):
components of active live services in network management: A protocol used for transferring web pages and other resources
on the World Wide Web.
Real-time Monitoring: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure):
This involves continuously collecting and analyzing data on An extension of HTTP that adds encryption and security features,
network traffic, performance metrics, and device status to commonly used for secure communication over the internet.
identify any issues or anomalies promptly. FTP (File Transfer Protocol):
Performance Optimization: A protocol used for transferring files between a client and a server
Network management actively optimizes network on a network.
performance by identifying and resolving bottlenecks, SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol):
congestion, and other performance-related issues. A protocol used for sending email messages between servers over
Fault Detection and Troubleshooting: a network.
This includes identifying connectivity issues, device failures, or DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol):
configuration errors and taking appropriate actions to restore A protocol used for automatically assigning IP addresses and other
service and minimize downtime. network configuration parameters to devices on a network.
Security Monitoring:
Network management actively monitors for security threats
and vulnerabilities to prevent unauthorized access, data
breaches, or other cyber threats
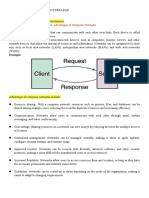
PROTOCOL ANALYZER:
A protocol analyzer, also known as a network protocol analyzer or packet sniffer, is a software
or hardware tool used to capture, analyze, and interpret network traffic in real-time. It
monitors the data packets transmitted over a network and provides insights into the
communication between devices, applications, and services. Protocol analyzers are commonly
used for troubleshooting network issues, optimizing performance, and ensuring security
compliance. They decode and display packet headers and payloads, allowing network
administrators to identify protocol violations, anomalies, and potential security threats.
You might also like
- Topic 1 2 - NETWORK ADMINISTRATIONDocument7 pagesTopic 1 2 - NETWORK ADMINISTRATIONLanz CatamisanNo ratings yet
- FFFFFFFDocument7 pagesFFFFFFFSintayehu BedassaNo ratings yet
- ServersDocument5 pagesServersRahul KrNo ratings yet
- Prelim Topics: Sharing ResourcesDocument6 pagesPrelim Topics: Sharing ResourcesAimee Joy DaganiNo ratings yet
- 9APPENDIX 4 and 5Document4 pages9APPENDIX 4 and 5api-26570979No ratings yet
- Configure ServerDocument5 pagesConfigure ServerBikila SeketaNo ratings yet
- E Commerce (L5)Document24 pagesE Commerce (L5)Jawad AliNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Network Operating SystemDocument10 pagesTopic 9 Network Operating SystemsimonnjauNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3Document8 pagesAssignment #3Rogine CenizaNo ratings yet
- Networking 2: It 219: Lesson VDocument17 pagesNetworking 2: It 219: Lesson VKlim Hazel Racal LumansocNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Unit 1Document30 pagesComputer Networks Unit 1Sowmiya SowmiNo ratings yet
- Sage Glod Brush Stroke Watercolor A4 Blank Page BorderDocument34 pagesSage Glod Brush Stroke Watercolor A4 Blank Page BorderVashu TiwariNo ratings yet
- LAN (Local Area Network)Document3 pagesLAN (Local Area Network)Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Servers and WirelessDocument26 pagesServers and WirelessGraham L. PennerNo ratings yet
- SERVER AND ITS-WPS OfficeDocument13 pagesSERVER AND ITS-WPS OfficeGabriel ColcolNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1Document20 pagesInformation Sheet 1Archie May DegamonNo ratings yet
- Network Os and Distributed OsDocument3 pagesNetwork Os and Distributed OsNeetyam GutteeNo ratings yet
- NWEG5111 Ice Task 4Document2 pagesNWEG5111 Ice Task 4Yusuf BadatNo ratings yet
- Lan, Wan, Osi, DSLDocument8 pagesLan, Wan, Osi, DSLNaveen LohchabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ServerDocument5 pagesChapter 1 ServerLissa JusohNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument4 pagesNetworkingpkamal0111No ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworksDocument3 pagesIntroduction To NetworksMlondi DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Nma Unit I SolutionDocument4 pagesNma Unit I SolutionRutu BhattNo ratings yet
- SERVERS SoftwareDocument40 pagesSERVERS SoftwareMarbey Perez CastroNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking FundamentalsDocument21 pagesComputer Networking FundamentalsSreejith KSNo ratings yet
- WorkDocument45 pagesWork2019bakereNo ratings yet
- Network 1Document2 pagesNetwork 1Sukumar PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- H D R W ?: OW O Outers ORKDocument7 pagesH D R W ?: OW O Outers ORKNurhana HamdanNo ratings yet
- Linux & Windows Short DefinitionsDocument8 pagesLinux & Windows Short DefinitionsMohammad AzamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Network Administration: Structure Page NosDocument15 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Network Administration: Structure Page NosSanjay ManhasNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Document9 pages1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Mmichael123456789No ratings yet
- Puter NetworksDocument28 pagesPuter Networkswaleed.khaldNo ratings yet
- ICTNWK529 AT1 Install and Manage Complex Networks Noman BandiDocument8 pagesICTNWK529 AT1 Install and Manage Complex Networks Noman Bandishafe SPNo ratings yet
- Techinical DefinitionsDocument4 pagesTechinical DefinitionsYanixa Pérez Jimenez 8-7No ratings yet
- Act 1ST UnitDocument23 pagesAct 1ST Unit2211CS010355- MANKU HIMA BINDU REDDYNo ratings yet
- Network 1Document14 pagesNetwork 1jhn75070No ratings yet
- WIA1005 Network Technology Foundation: Application Layer and Build A Small NetworkDocument33 pagesWIA1005 Network Technology Foundation: Application Layer and Build A Small NetworkAina NajihahNo ratings yet
- The OSI Model: How Network Protocols WorkDocument5 pagesThe OSI Model: How Network Protocols WorkRafena MustaphaNo ratings yet
- 10 Data Communications Part 1Document20 pages10 Data Communications Part 1Emmanuel GumayagayNo ratings yet
- Mspc202 Topic4 Computernetworks June2022Document33 pagesMspc202 Topic4 Computernetworks June2022Anthony AyamdoohNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX 4 and 5Document5 pagesAPPENDIX 4 and 5api-26570979No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Network ManagementDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Network ManagementNik IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Information Security and Cyber Law: UNIT-1Document19 pagesInformation Security and Cyber Law: UNIT-1N ChandhuNo ratings yet
- Unit-1.2 Internet and World Wide WebDocument40 pagesUnit-1.2 Internet and World Wide Webco22352No ratings yet
- IT-401 Network Management and Administration: Bsit 1Document36 pagesIT-401 Network Management and Administration: Bsit 1Samiya NoorNo ratings yet
- Capture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsDocument38 pagesCapture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsCandy AngelNo ratings yet
- ServerDocument3 pagesServerJohn Rhino Estomagulang SantosNo ratings yet
- Application Layer Protocols in Computer Networks 17.01.2024Document8 pagesApplication Layer Protocols in Computer Networks 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- "Wireshark" Is A Ethereal, in May 2006 The Project Was Renamed Wireshark Due To Trademark IssuesDocument2 pages"Wireshark" Is A Ethereal, in May 2006 The Project Was Renamed Wireshark Due To Trademark IssuesBenhur DanielNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes DCNetwrk BCADocument21 pagesConcept Notes DCNetwrk BCAComputer Sc & BCA DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Network Operating SystemsDocument32 pagesNetwork Operating SystemsRieri RiezaNo ratings yet
- Network Administration AssignmentDocument5 pagesNetwork Administration AssignmentPapiNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Unit IDocument38 pagesComputer Networks - Unit IsreesajeshNo ratings yet
- ICT ProjectDocument25 pagesICT ProjectudaanthusaraNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 1 (Materi Ajar) EditedDocument43 pagesLampiran 1 (Materi Ajar) EditedMikel SantanaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument10 pagesComputer Networkruchisingh19No ratings yet
- Virtual Networks and PrivacyDocument3 pagesVirtual Networks and PrivacyAbdourahmane KaneNo ratings yet
- CNF152S - Introduction To NetworkingDocument54 pagesCNF152S - Introduction To NetworkingBenito KrielNo ratings yet
- Abdu Net Ass.t1Document5 pagesAbdu Net Ass.t1Ahmed KedirNo ratings yet
- Ispconfig How Install PDFDocument2 pagesIspconfig How Install PDFRaul Augusto RODAS HINOSTROZANo ratings yet
- Quick Installation Guide: 1. Connect The HardwareDocument2 pagesQuick Installation Guide: 1. Connect The HardwareJohnyNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Grievances Regarding Conduct of Mandatory Offline ExaminationDocument5 pagesGmail - Grievances Regarding Conduct of Mandatory Offline ExaminationshiviNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter TLE ICTDocument5 pages2nd Quarter TLE ICTJepoy Macasaet100% (1)
- 99 Ways To Speed Up Your Wordpress Website PDFDocument107 pages99 Ways To Speed Up Your Wordpress Website PDFjin0xNo ratings yet
- Google-Analytics DemoDocument45 pagesGoogle-Analytics DemoVishakhNo ratings yet
- Social Networking Privacy How To Be Safe, Secure and SocialDocument17 pagesSocial Networking Privacy How To Be Safe, Secure and SocialRafael AlemanNo ratings yet
- SAP Cloud Platform Identity Authentication ServiceDocument456 pagesSAP Cloud Platform Identity Authentication ServicefuzzynNo ratings yet
- Hypertext Is Text Displayed On A Computer Display or Other Electronic Devices With ReferencesDocument1 pageHypertext Is Text Displayed On A Computer Display or Other Electronic Devices With ReferencesenriquehraNo ratings yet
- L0Phtcrack: Made By:-Surabhi VarmaDocument21 pagesL0Phtcrack: Made By:-Surabhi VarmaSurabhi VarmaNo ratings yet
- 3rd G7 Lesson 4 Weekly Home Learning Plan in COMPUTERDocument5 pages3rd G7 Lesson 4 Weekly Home Learning Plan in COMPUTERHans Jhayson CuadraNo ratings yet
- Internet Social Media-Samia Saad PDFDocument13 pagesInternet Social Media-Samia Saad PDFapi-309074217No ratings yet
- 3DES - CBC - Sweet32 - Birthday Attacks On 64-Bit Block Ciphers in TLS and OpenVPN PDFDocument9 pages3DES - CBC - Sweet32 - Birthday Attacks On 64-Bit Block Ciphers in TLS and OpenVPN PDFsipteckNo ratings yet
- FAQ-Ibiz MuamalatDocument9 pagesFAQ-Ibiz MuamalatJob Zine'dineNo ratings yet
- Version - 2 CHECKLIST Industrial TrainingDocument3 pagesVersion - 2 CHECKLIST Industrial TrainingleonythamNo ratings yet
- IctDocument4 pagesIctJames Kirubakaran100% (1)
- Group 4 - Social Media ForensicsDocument6 pagesGroup 4 - Social Media ForensicsVasundhara100% (1)
- The Book of IRC PDFDocument351 pagesThe Book of IRC PDFchiquicikNo ratings yet
- Security Guide of UnionPay Card Personalization+Service+ProviderDocument41 pagesSecurity Guide of UnionPay Card Personalization+Service+ProviderVKM2013No ratings yet
- How To Delete A Course or Library in Open Edx: VersionDocument12 pagesHow To Delete A Course or Library in Open Edx: Versionzaki nygmaNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Affiliate Marketing Zalando Renault 4 12 2017 Marco Larocca Conoscente Cut 2017 12 04 14 36 14 PDFDocument53 pagesDigital Marketing Affiliate Marketing Zalando Renault 4 12 2017 Marco Larocca Conoscente Cut 2017 12 04 14 36 14 PDFAfshan AbdullayevaNo ratings yet
- Mis ReportDocument12 pagesMis Reportshazma khanNo ratings yet
- Untapped Traffic Sources in 2020 ThatDocument22 pagesUntapped Traffic Sources in 2020 Thathamza driouchNo ratings yet
- 4.2.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting EtherChannelDocument2 pages4.2.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting EtherChannelAndres RamosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Computer SecurityDocument5 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Computer SecuritykiriankiNo ratings yet
- Levelup0X Bug Bounty Hunting Training PDFDocument7 pagesLevelup0X Bug Bounty Hunting Training PDFMohamed saidNo ratings yet
- 2002 - Protecting Electronic Commerce From Distributed Denial-of-Service AttacksDocument9 pages2002 - Protecting Electronic Commerce From Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacksarifaliwasi2No ratings yet
- Cyber Security: Mohamed AdelDocument21 pagesCyber Security: Mohamed AdelMohamed Adel TahaNo ratings yet
- Internet Firewalls: BY T. Naveen KumarDocument11 pagesInternet Firewalls: BY T. Naveen KumarDarsh AntaniNo ratings yet
- Refresh Parent Grid After Sub-Grid Save in UI For ASP - NET MVC Grid - Telerik ForumsDocument3 pagesRefresh Parent Grid After Sub-Grid Save in UI For ASP - NET MVC Grid - Telerik ForumsAntony JosephNo ratings yet