Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stats
Stats
Uploaded by
aprilvee12220 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
stats
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesStats
Stats
Uploaded by
aprilvee1222Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
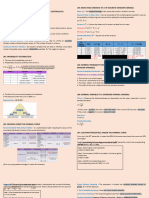
STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY X
Random Variable - it represents a random variable
- a set of possible values from a random Z-Score
experiment
- it measures how many standard deviation a
Sample Space given value is above or below the mean
- the set of all possible outcomes of an Positive Z-Score
experiment
- it indicates that the score is above the mean
Random Experiment
Negative Z-Score
- a process by which we observe something
- it indicates that the score is below the mean
uncertain
P (z > a)
Outcome
- it denotes the probability that z-score is
- a result of a random experiment
greater than a
Probability Distribution
Percentile
- a table, graph or formula that describes values
- a measure of relative standing
a random variable can take on, and its
corresponding probability Population
Mean - it consists of all elements considered in a study
- it is also called the expected value of the Sampling Distribution
discrete random variable
- the probability of distribution of a statistic
Standard Deviation
Sample
- the square root of the variance
- it is the small group that are observed
Normal Curve
- it provides a graphical representation of
statistical values that are needed in describing
the characteristics of population as well in
making decisions
- the mean of a standard normal curve
- the symbol for mean
Z-Table
- the table of areas under the normal curve
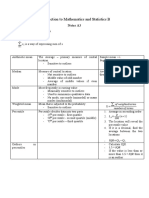
II.
1. The probability of each value of the
random variable must be between or
equal to 0 and 1 -T
2. An event is a particular performance of
a random experiment - F
3. The sum of all the probabilities of the
random variable must be equal to 10 - F
4. If the mean of a random variable is 55,
then its expected value is also 55 - T
5. Z-scores are not useful in comparing
observed values - F
6. If a z-score is equal to 0, then it is on
the mean - T
7. If a z-score is equal to 1, then it is 1
standard deviation below the mean - F
8. The normal curve is bell-shaped - T
9. Every statistic is a random variable - T
10. Random sampling is a method of
choosing an equally distributed subset
from a larger population - T
You might also like
- SPECIAL REPORT: Identifying Sources Key To Detailed Troubleshooting of Amine FoamingDocument9 pagesSPECIAL REPORT: Identifying Sources Key To Detailed Troubleshooting of Amine FoamingAbhishek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Bravo's Pantorouter - by BRAVOGOLFTANGO at LumberJocks - Com Woodworking CommunityDocument67 pagesBravo's Pantorouter - by BRAVOGOLFTANGO at LumberJocks - Com Woodworking CommunitySlamet Matematika88% (8)
- Key Ingredients To Inferential StatisticsDocument4 pagesKey Ingredients To Inferential Statisticseloisa dalmacioNo ratings yet
- STATSDocument4 pagesSTATSdennisalejaga08No ratings yet
- SP ReviewerDocument4 pagesSP ReviewerMalayao, Philip Jude M.No ratings yet
- PSYCH STATS CHAPTER 7aDocument3 pagesPSYCH STATS CHAPTER 7aNicole Rose Crave DagaleaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Statistics For Data Science - IIDocument60 pagesLesson 6 - Statistics For Data Science - IIrimbrahimNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution or Normal CurveDocument6 pagesNormal Distribution or Normal CurveJhun francis BisaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Quick Reference - 2Document16 pagesHypothesis Testing Quick Reference - 2Swathi MithaiNo ratings yet
- Z, T, and F Tests: Making Inferences From Experimental Sample To Population Using Statistical TestsDocument19 pagesZ, T, and F Tests: Making Inferences From Experimental Sample To Population Using Statistical TestsBaoz PingNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Finals ReviewerDocument2 pagesStatistics and Probability Finals ReviewerJanelle ArañaNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob - Q3 Week 5 - Mod5Document17 pagesStat and Prob - Q3 Week 5 - Mod5JessicaNo ratings yet
- Fand TtestsDocument19 pagesFand TtestsHamsaveni ArulNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes, FormulasDocument79 pagesLecture Notes, FormulasLourence Kate TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- Math 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Document3 pagesMath 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Jirish RiveraNo ratings yet
- MethDocument6 pagesMethdelinftwNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestDocument10 pagesHypothesis Testउज्जवल आनंदNo ratings yet
- Observed of Deviation Dard S Expected Observed ZDocument5 pagesObserved of Deviation Dard S Expected Observed ZMarlon RoundtreeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5A - Tests Of: SignificanceDocument30 pagesChapter 5A - Tests Of: SignificanceAhmad AiNo ratings yet
- Z Test Lecture Examples 1 2 3 With 1Document4 pagesZ Test Lecture Examples 1 2 3 With 1Ralph Zedrick AbayonNo ratings yet
- Statistics RefresherDocument7 pagesStatistics RefresherJASMINE GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Stat Probability Pointers2reviewDocument1 pageStat Probability Pointers2reviewIrish Siagan AquinoNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions & Standard Error: Lesson 7Document20 pagesSampling Distributions & Standard Error: Lesson 7Lorena TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Project Locus Grade 11Document9 pagesProject Locus Grade 11hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Stats and Prob Reviewer, Q3 Jess Anch.Document8 pagesStats and Prob Reviewer, Q3 Jess Anch.JessicaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics and Probability Distribution: Random VariableDocument19 pagesDescriptive Statistics and Probability Distribution: Random VariableSamidhaSinghNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument2 pagesStatisticsCHAIM G.No ratings yet
- FS Summary of Book and VideosDocument13 pagesFS Summary of Book and VideosPrasanna KandavelNo ratings yet
- IL2-Describing Variation in DataDocument7 pagesIL2-Describing Variation in DataVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Probability Distribution: - Discrete - ContinuousDocument5 pagesProbability Distribution: - Discrete - ContinuousEavie OngNo ratings yet
- Stat Review NotesDocument8 pagesStat Review Notes안지연No ratings yet
- Fulgar - 9040 Standard Normal DistributionDocument29 pagesFulgar - 9040 Standard Normal Distributioneugene louie ibarraNo ratings yet
- Statistics Part 3Document4 pagesStatistics Part 3Emilia CassidyNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob Q3 Week 5 Mod5 Carla CatherineDocument20 pagesStat and Prob Q3 Week 5 Mod5 Carla CatherineCharlene Binasahan100% (2)
- Key Ingredients For Inferential StatisticsDocument65 pagesKey Ingredients For Inferential StatisticsJhunar John TauyNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Statistics and Probability ReviewerDocument42 pagesTerm 2 Statistics and Probability ReviewerBulbasaur NyaaNo ratings yet
- Write The Given Step 4: Critical Region: Z-TestDocument2 pagesWrite The Given Step 4: Critical Region: Z-TestRob FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in StatisticsDocument5 pagesReviewer in StatisticsGail LeslieNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Quarter 3 Week 4 PDFDocument26 pagesStatistics and Probability Quarter 3 Week 4 PDFSam OxfordNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Stats For Exam Cheat Sheet Stats For ExamDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet Stats For Exam Cheat Sheet Stats For ExamUrbi Roy BarmanNo ratings yet
- Things To Know PDFDocument56 pagesThings To Know PDFMolly McMillanNo ratings yet
- Instalinotes - PREVMED IIDocument24 pagesInstalinotes - PREVMED IIKenneth Cuballes100% (1)
- Alternative Hypothesis: Central Limit TheoremDocument3 pagesAlternative Hypothesis: Central Limit TheoremEunice C. LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Stat ProbDocument7 pagesStat Probvinceleony.reyes.sciNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in StatsDocument2 pagesReviewer in StatsKirsten IguetNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics and Analysis Course 2&3Document42 pagesBusiness Statistics and Analysis Course 2&3Mugdho HossainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematics and Statistics B: Notes A3Document4 pagesIntroduction To Mathematics and Statistics B: Notes A3Harawa WonaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetBlythe ButlerNo ratings yet
- Stat Hypothesis TestingDocument14 pagesStat Hypothesis TestingJosh DavidNo ratings yet
- Univariate StatisticsDocument7 pagesUnivariate StatisticsDebmalya DuttaNo ratings yet
- (Assignment) (Business) (International Analysis)Document4 pages(Assignment) (Business) (International Analysis)Sheraz Aslam SherazNo ratings yet
- Inferential Testing: Tests of DifferenceDocument7 pagesInferential Testing: Tests of DifferenceKezia MadeloNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability ReviewerDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability ReviewerClover BlythNo ratings yet
- Stats 4TH Quarter ReviewerDocument2 pagesStats 4TH Quarter ReviewerKhryzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Dealing With Skewed DataDocument7 pagesStatistics: Dealing With Skewed DataAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Interpret Standard Deviation Outlier Rule: Using Normalcdf and Invnorm (Calculator Tips)Document12 pagesInterpret Standard Deviation Outlier Rule: Using Normalcdf and Invnorm (Calculator Tips)maryrachel713No ratings yet
- Chapter 06 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 06 NotesLaurin KolbNo ratings yet
- Bioe Week 6Document11 pagesBioe Week 6Angeline LimNo ratings yet
- Block 4 MCO 3 Unit 2Document35 pagesBlock 4 MCO 3 Unit 2Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio StatisticsDocument13 pagesBio StatisticsMiguel Angel AcojedoNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument35 pagesNormal DistributioncealizcroftmacatangayNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greeks View of MatterDocument10 pagesAncient Greeks View of Matteraprilvee1222No ratings yet
- Module-1 Stat April2024Document5 pagesModule-1 Stat April2024aprilvee1222No ratings yet
- 18 Aos1715Document33 pages18 Aos1715aprilvee1222No ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignsDocument4 pagesQualitative Research Designsaprilvee1222No ratings yet
- Pe 2Document1 pagePe 2aprilvee1222No ratings yet
- UCSPDocument3 pagesUCSPaprilvee1222No ratings yet
- 17 - GT2011-45243-An Aerodynamic Design Methodology For Low Pressure Axial Fans WithDocument9 pages17 - GT2011-45243-An Aerodynamic Design Methodology For Low Pressure Axial Fans WithkcpatnaikNo ratings yet
- Pre Test I Science-10Document15 pagesPre Test I Science-10cristito inovalNo ratings yet
- African Explosives Limited - Report Student Name: Tazibana Moyo Module Coach: Underground ManagerDocument4 pagesAfrican Explosives Limited - Report Student Name: Tazibana Moyo Module Coach: Underground ManagertkubvosNo ratings yet
- TRS501&TRS601 - Project GuidelinesDocument3 pagesTRS501&TRS601 - Project GuidelinesHoang Trung Tin (K18 HCM)No ratings yet
- Speed Control of BLDC Motor Using DSP: 1 4 1 JNTUH Hyderabad, India 2 JNTUH Hyderabad, IndiaDocument5 pagesSpeed Control of BLDC Motor Using DSP: 1 4 1 JNTUH Hyderabad, India 2 JNTUH Hyderabad, IndiapravnkumarNo ratings yet
- Indak Kudong Cultural Dance Competition Forms 1Document7 pagesIndak Kudong Cultural Dance Competition Forms 1Mark Angelo BlasabasNo ratings yet
- Tech Specs Bwr6 ReactorDocument359 pagesTech Specs Bwr6 ReactorcagertonNo ratings yet
- Dry Run Observation Tool: Evident Not Evident Remarks During The Distribution of Learning Package)Document3 pagesDry Run Observation Tool: Evident Not Evident Remarks During The Distribution of Learning Package)WILLY C. DUMPITNo ratings yet
- HRM ZensarDocument8 pagesHRM ZensarJoydeep GoraiNo ratings yet
- All Out Line ReportsDocument72 pagesAll Out Line ReportsEinsidleNolalisanNo ratings yet
- 4 DeclarationDocument1 page4 DeclarationSonu YadavNo ratings yet
- Is Now Part ofDocument16 pagesIs Now Part ofAdan Pérez EchevarríaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Toyota"Fault Code"C1515 "Torque Sensor Zero Adjustment Is Not Complete" Operation MethodDocument8 pages2014 Toyota"Fault Code"C1515 "Torque Sensor Zero Adjustment Is Not Complete" Operation MethoddoudzoNo ratings yet
- Mass or Volume Air Flow InputDocument6 pagesMass or Volume Air Flow InputDaniel Mamani ParedezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Theoretical Background 3.1 Theory and AnalysisDocument37 pagesChapter Three: Theoretical Background 3.1 Theory and AnalysisNadish FatimaNo ratings yet
- Widgb4 - Test Unit 2 Group ADocument3 pagesWidgb4 - Test Unit 2 Group AYanina Garrido0% (1)
- ICE Attribute FormDocument15 pagesICE Attribute FormOlafNo ratings yet
- 1,4l 4AV (AHW+AKQ) 1Document10 pages1,4l 4AV (AHW+AKQ) 1ghitacrainic100% (1)
- PL3 PL4 Output Connection - v1.2Document5 pagesPL3 PL4 Output Connection - v1.2Victor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Discovery Early Career Researcher Award: Instructions To ApplicantsDocument39 pagesDiscovery Early Career Researcher Award: Instructions To ApplicantsvolhaNo ratings yet
- Letter From UtopiaDocument8 pagesLetter From UtopiaJohn SandhamNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 and 2Document14 pagesQuiz 1 and 2Nichole TumulakNo ratings yet
- Coercive Diplomacy (CD) : CDR Noorhakimi Bin Isa RMN CP 40 P127451Document15 pagesCoercive Diplomacy (CD) : CDR Noorhakimi Bin Isa RMN CP 40 P127451Ahmad AzrulNo ratings yet
- History of Civilizations of Central Asia vIIIDocument556 pagesHistory of Civilizations of Central Asia vIIIjaholubeck100% (4)
- Blower MotorsDocument42 pagesBlower MotorsRobNo ratings yet
- IDAB Assignment 3: 1. Explain SQL SubqueriesDocument6 pagesIDAB Assignment 3: 1. Explain SQL SubqueriesAayushi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Assignment Week 2Document2 pagesWeek 2 Assignment Week 2umaidkhalid2556No ratings yet
- CV Tegar PrajaksaDocument6 pagesCV Tegar PrajaksaijejejerryNo ratings yet