Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trigo Notes
Uploaded by
Faith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIOOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigo Notes
Uploaded by
Faith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIOCopyright:
Available Formats
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
It means looking for the unknown parts These are formulas used to:
given at least 3 parts. One given part
A. Determine the value of the
must be a side for the triangle to have
a solution. trigonometric function, or
If three angles are given, there are an B. Determine the value of the angles,
infinite number of solutions. or
C. Prove identities
sin A cos A
tan A cot A
RIGHT TRIANGLES cos A sin A
One of the angles is 90 degrees sin 2 A cos2 A 1
The side opposite the 90 degree angle sec2 A 1 tan 2 A
is called hypotenuse
csc2 A 1 cot2 A
The following principles shall be used in the sin 2 A 2 sin A cos A
solution of right triangles:
cos 2 A cos2 A sin 2 A
1. The sum of the acute angles is
90 degrees.
cos 2 A 2 cos2 A 1
cos 2 A 1 2 sin 2 A
2. Pythagorean Theorem
sin( A B) sin A cos B cos A sin B
3. Trigonometric Functions
sin( A B) sin A cos B cos A sin B
Note: These principles are exclusive to right
cos(A B) cos A cos B sin A sin B
triangles.
cos(A B) cos A cos B sin A sin B
tan A tan B
tan( A B)
OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 1 tan A tan B
Generally, NO angle is 90 degrees
The principles use in solution of SPHERICAL TRIGONOMETRY
obliques can be used also in solving
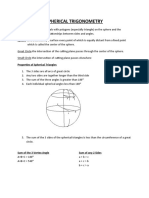
right triangles. Spherical Triangle
Triangles belonging to the oblique Any section made by a cutting
family are scalenes, equilaterals, and plane that passes through a sphere is
isosceles. circle. A great circle is formed when the
cutting plane passes through the center
The following principles shall be used in the of the sphere. Spherical triangle is a
solution of oblique triangles: triangle bounded by arc of great circles
of a sphere.
1. The sum of the all three angles
is 180 degrees.
2. Sine Law
3. Cosine Law
Note: These principles CAN BE USED in
right triangles.
Note : For spherical triangles, sides a, b,
and c are usually in angular units. And like
plane triangles, angles A, B, and C are
also in angular units.
Sum of interior angles of spherical triangle
The sum of the interior angles of a
spherical triangle is greater than 180° and less
than 540°.
Area of spherical triangle
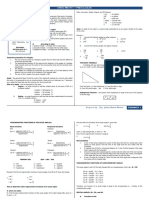
Napier’s Rules
The area of a spherical triangle on the
surface of the sphere of radius R is given by SIN-COOP Rule
the formula In the Napier’s circle, the sine of any
middle part is equal to product of the cosines
of its opposite parts.
where E is the spherical excess in degrees.
Spherical excess:
SIN-TAAD Rule
In the Napier’s circle, the sine of any
middle part is equal to the product of the
Notes: In spherical trigonometry, earth is tangents of its adjacent parts.
assumed to be a perfect sphere. One minute
(0° 1') of arc from the center of the earth has a
distance equivalent to one (1) nautical mile
(6080 feet) on the arc of great circle on the
surface of the earth.
1 minute of arc = 1 nautical mile
1 nautical mile = 6080 feet
1 statute mile = 5280 feet
1 knot = 1 nautical mile per hour
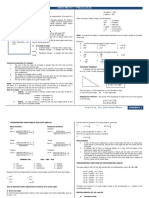
RIGHT SPHERICAL TRIGONOMETRY
Solve for the spherical triangle whose
Solution of right spherical triangle parts are a = 73°, b = 62°, and C = 90°.
With any two quantities given (three
quantities if the right angle is counted), any
right spherical triangle can be solved by
following the Napier’s rules. The rules are
aided with the Napier’s circle. In Napier’s circle,
the sides and angle of the triangle are written
in consecutive order (not including the right
angle), and complimentary angles are taken for
quantities opposite the right angle.
You might also like
- Trigonometry (Principles)Document56 pagesTrigonometry (Principles)JLS 04No ratings yet
- Trigonometry PDFDocument12 pagesTrigonometry PDFSantosh SinghNo ratings yet
- L2 Trigonometry of Right TrianglesDocument13 pagesL2 Trigonometry of Right TrianglesRyan Jhay YangNo ratings yet
- BSED MATH 3 Plane Trigo Module 2 1Document15 pagesBSED MATH 3 Plane Trigo Module 2 1Jhanes Kent FatNo ratings yet
- MAT 1100 Transcendental Functions - 2020Document41 pagesMAT 1100 Transcendental Functions - 2020Nathan MulunguNo ratings yet
- Review in TrigoDocument5 pagesReview in TrigoJohnMichaelM.ManaloNo ratings yet
- (ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 2Document28 pages(ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 2Jaxon Riego100% (1)
- Trigonometry Plane&Solid Geometry: By: Engr. Roy Andrew GarciaDocument50 pagesTrigonometry Plane&Solid Geometry: By: Engr. Roy Andrew GarciaEraAlmen100% (1)
- (ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 2Document34 pages(ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 2Johnny Siason100% (1)
- Sine, Cosine and Area RulesDocument42 pagesSine, Cosine and Area Ruleslwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Trigono Ratios&IdentitiesDocument38 pagesTrigono Ratios&Identitiesopbinod7702No ratings yet
- Math12-1 - Lesson 9 - Spherical TrigonometryDocument15 pagesMath12-1 - Lesson 9 - Spherical TrigonometryKobe MartinezNo ratings yet
- Spherical TrigonometryDocument19 pagesSpherical Trigonometryjohn tanNo ratings yet
- G09 Week 1 - Q4 - Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument72 pagesG09 Week 1 - Q4 - Six Trigonometric RatiosGladje Fran JerezNo ratings yet
- Csec Maths Revision SheetDocument7 pagesCsec Maths Revision SheetAlayna ChauharjasinghNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry: Spherical Trigonometry - It Concerns With Important Propositions of Spherical TriangleDocument3 pagesSpherical Trigonometry: Spherical Trigonometry - It Concerns With Important Propositions of Spherical TriangleZairah Ann BorjaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1.1 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument28 pagesTOPIC 1.1 - Trigonometric FunctionsAnne Canlyn ManlutacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 09 - 17 PagesDocument17 pagesLesson 09 - 17 Pagesjonel rabongaNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument26 pagesTrigonometryJohn Allen EstillomoNo ratings yet
- 4 4 App Trig To TRDocument14 pages4 4 App Trig To TRAudrey LeeNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths Key Notes CH 08 Introduction To TrigonometryDocument2 pages10 Maths Key Notes CH 08 Introduction To TrigonometryShafeequ RahmanNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry Lecture SummaryDocument3 pagesSpherical Trigonometry Lecture SummaryRenderizzah FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Document18 pagesChapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Angel Angel100% (1)
- Lesson 2: Trigonometry of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument13 pagesLesson 2: Trigonometry of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Spherical TrigonometryDocument2 pagesSpherical TrigonometryArvin LazoNo ratings yet
- Sine Cosine Area Rules-Gr11Document42 pagesSine Cosine Area Rules-Gr11KingX SandileNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 NotesDocument15 pagesUnit 6 NotesÉva HuszárNo ratings yet
- 1-Basic Mathematics-01-TheoryDocument37 pages1-Basic Mathematics-01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic - 14 TrigonometryDocument22 pagesTopic - 14 TrigonometryJorifNo ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pagesSolution of TrianglesnathanNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Applicatn Trignmetry To Triangles PDFDocument12 pages4 4 Applicatn Trignmetry To Triangles PDFAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- GRade 8 Triangles DemoDocument60 pagesGRade 8 Triangles DemoJoxel GallerNo ratings yet
- Math 9 q4 Week 1Document6 pagesMath 9 q4 Week 1Millet Castillo100% (1)
- ENGG MATH 1 - Precalculus: Lesson FiveDocument3 pagesENGG MATH 1 - Precalculus: Lesson FiveJan Leynard ParraNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem: C A B Leg LegDocument93 pagesPythagorean Theorem: C A B Leg LegMa. Edilyn ChiaoNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument29 pagesTrigonometryAileen Grace Delima100% (11)
- Module 1 in MfeDocument9 pagesModule 1 in Mfevantae SmithNo ratings yet
- 10.6 Sine RuleDocument6 pages10.6 Sine RuleMateu ChanganoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 EXISTINGDocument6 pagesWeek 1 EXISTINGJea TaladroNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RevisionDocument4 pagesTrigonometry RevisionKin Wai CheahNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 2Document9 pagesTrigonometry 2learningarabic1238No ratings yet
- Short Notes For Geometry - PrintDocument8 pagesShort Notes For Geometry - PrintAvinash GudainiyanNo ratings yet
- Spherical Lec JowDocument37 pagesSpherical Lec JowWassan IdreesNo ratings yet
- Triangle Formula 1 22Document10 pagesTriangle Formula 1 22Harsh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Chapter 5Document30 pagesTrigonometry Chapter 5Luisa Mae N. MahenerNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Kinds of AnglesDocument8 pagesTrigonometry: Kinds of AnglesRandom User100% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument20 pagesTrigonometryGary NugasNo ratings yet
- Eng Math Lesson 3Document3 pagesEng Math Lesson 3Kyla Jynell SaquitonNo ratings yet
- I DunnoDocument71 pagesI DunnoJulius Patrick MallanaoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 TrigonometryDocument36 pagesUnit 3 TrigonometryHanif AshranNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- Finals ModuleDocument22 pagesFinals ModuleTin MhudzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Preliminary Concepts in TrigonometryDocument6 pagesLesson 1 Preliminary Concepts in TrigonometryMARIA ELIZA LOMUNTADNo ratings yet
- Theory of TrigonometryDocument26 pagesTheory of Trigonometrysyerry_179No ratings yet
- Right-Triangle-Trigonometry 2023 2024Document24 pagesRight-Triangle-Trigonometry 2023 2024Ashlie JaneNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument0 pagesTrigonometrysanjivtisNo ratings yet
- PHYS2614 Year 2023Document243 pagesPHYS2614 Year 2023Lesego MogoaneNo ratings yet
- 30 Aug 2023 - Introduction & Characteristics of EarthquakesDocument25 pages30 Aug 2023 - Introduction & Characteristics of EarthquakesFaith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIONo ratings yet
- APPENDIX B - Load Calculation According NSCP2015Document12 pagesAPPENDIX B - Load Calculation According NSCP2015Faith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIONo ratings yet
- The Seminar On Transportation Engineering Free Software Was Held Last FridayDocument1 pageThe Seminar On Transportation Engineering Free Software Was Held Last FridayFaith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIONo ratings yet
- Geometric GradientDocument7 pagesGeometric GradientFaith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIONo ratings yet
- Fun With Fourier SeriesDocument84 pagesFun With Fourier SeriesJuanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 MathsDocument174 pagesCBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Mathskuldeep123qwNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Mid Term Form 1Document4 pagesPaper 1 Mid Term Form 1Aziela OthmanNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Algebraic Expressions CYUDocument4 pages1-1 Algebraic Expressions CYUvNo ratings yet
- P1 - Algebra: Past Papers QuestionsDocument50 pagesP1 - Algebra: Past Papers QuestionsJumanaAsimNo ratings yet
- Intso Education: Mathematics Talent Search Olympiad (Mtso) 2015 - 2016Document4 pagesIntso Education: Mathematics Talent Search Olympiad (Mtso) 2015 - 2016Vasa LakshmipathiraoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Triangle CongruenceDocument2 pagesApplications of Triangle CongruenceDane Hern'zNo ratings yet
- Techiez Online: C Programming Questions & Answers For Placements Basic To AdvancedDocument54 pagesTechiez Online: C Programming Questions & Answers For Placements Basic To AdvancedRahul TrikotiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: 1 InformationDocument7 pagesAssignment 1: 1 InformationassyNo ratings yet
- Vieta's Formulas HandoutDocument14 pagesVieta's Formulas HandoutVardayineeNo ratings yet
- Test 2BDocument10 pagesTest 2BJasmina Angelevska KostadinoskaNo ratings yet
- Whole Numbers and The Four Operations: ReteachDocument10 pagesWhole Numbers and The Four Operations: ReteachLaura Marcela Noguera RiveraNo ratings yet
- Mat 251Document40 pagesMat 251khaleedmogajiNo ratings yet
- MathDocument3 pagesMathKea April TomoNo ratings yet
- 6.6 NotesDocument19 pages6.6 NotesRheey CastroNo ratings yet
- Alaminos City National High School Summative Assessment in General MathematicsDocument3 pagesAlaminos City National High School Summative Assessment in General MathematicsAbby Gayle NacinoNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers and PropertiesDocument22 pagesRational Numbers and PropertiesRingle JobNo ratings yet
- Ntse Mathematics SynopsisDocument32 pagesNtse Mathematics SynopsissrilathaNo ratings yet
- BS 4500-2009 îºÍÅäºÏ.× ÐÎÅäºÏÏ Í ºÍ ÓC 13 1500, È Ó6mm 630mmö СÓÚ ÈÓÚ500mm Ä× ÐÎ Ä Îï ÍDocument50 pagesBS 4500-2009 îºÍÅäºÏ.× ÐÎÅäºÏÏ Í ºÍ ÓC 13 1500, È Ó6mm 630mmö СÓÚ ÈÓÚ500mm Ä× ÐÎ Ä Îï Ísaj_ash82No ratings yet
- Maths - Race#057Document2 pagesMaths - Race#057PkrNo ratings yet
- Worksheet BrevetDocument5 pagesWorksheet Brevetcaroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- Combinatorics:, - . - , A A, A A, - . - , ADocument26 pagesCombinatorics:, - . - , A A, A A, - . - , ASilviuNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Passage To Abstract Mathematics by Watkins PDFDocument14 pagesSolution Manual For Passage To Abstract Mathematics by Watkins PDFa857548274100% (1)
- GENED Math-DrillsDocument2 pagesGENED Math-DrillsCharles Kenn MantillaNo ratings yet
- LP4 - de Moivre's TheoremDocument7 pagesLP4 - de Moivre's TheoremNoraisa MacabaasNo ratings yet
- 2Document458 pages2Dunareanu AvraamNo ratings yet
- Home Connectiones Answer Key PDF Multiplication Elementary MathematicsDocument1 pageHome Connectiones Answer Key PDF Multiplication Elementary MathematicsAnisaNo ratings yet
- Day 1.2 GCF Common Monomial FactorDocument19 pagesDay 1.2 GCF Common Monomial FactorLea Jane RafalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Trigonometry Mathongo PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 Trigonometry Mathongo PDFNagireddy KalluriNo ratings yet
- College Algebra5Document25 pagesCollege Algebra5AbchoNo ratings yet