Professional Documents
Culture Documents
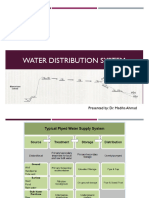
Water Supply System
Uploaded by
Kechan ShenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Water Supply System
Uploaded by
Kechan ShenCopyright:
Available Formats
12.
4 WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS
Water supply systems are networks whose edges and nodes are pressure pipes and either pipe junctions, water sources or
end-users, respectively. Their function is to provide end-users with potable water with a sufficient pressure level.
What are the types of water supply systems?
The water distributed via municipal water supply systems should reach the end-user with sufficient pressure and flow
rates. In order to achieve this, four main water distribution system types are used:
GRID IRON SYSTEMS
In grid iron systems, the main water supply line goes through the central part of the area, while sub mains branch out
perpendicular to the main line. This system has no dead-ends, as all of the individual pipes are interconnected. This type
of water supply system is great for cities that have a rectangular layout that resembles a gridiron.
RING SYSTEMS
Circular or ring systems feature a supply main that forms a circle or ring around the area of distribution. In this system,
the branches are cross-connected to the supply mains and each other. This type of system has similar advantages and
disadvantages to gridiron systems and is suitable for towns and cities with well-planned roads and streets.
RADIAL SYSTEMS
In radial systems, the distribution area is divided into different distribution districts or zones. Each zone has an elevated
distribution reservoir in the middle from which supply lines run in a radial pattern towards the distribution district
periphery. Radial systems offer swift distribution and allow for simpler design calculations.
DEAD-END SYSTEMS / TREE SYSTEMS
Dead-end water supply systems are the best choice for cities and towns without definite road patterns. In this type of
system, there is one main line that runs through the town or city with sub-mains branching off from left and right. These
sub-mains then divide into a number of branch lines that provide service connections.
Two major water supply system in houses/buildings.
DIRECT SYSTEM
A direct water supply system is one where the raising main feeds directly the cold water taps and a multi-point water
heater. The mains water comes in via a rising main and directly feeds all the cold taps and a multi-point water heater - so
all the taps and other water feeds are at mains water pressure.
INDIRECT SYSTEM
Water enters house from the rising main. After entering, it is branched off into kitchen sink and towards storage tank.
Storage tank is first filled and then water is supplied to appliances from same. The location of storage tank should be at
some height so that water flows down easily under gravity without any external pressure. Only Kitchen sink has portable
water available. All other appliances have stored tank water. Indirect water supply system is flexible because when mains
run out of water, stored water is a benefit till mains flow return.
What are the components of a water supply system?
A municipal water supply system is made up of pipelines, pumps, water storage facilities, and other distribution
accessories. The main components include:
WATER SOURCE: The sources of drinking water can come from groundwater, lakes, reservoirs, rivers, canals,
rainwater, and saltwater.
WATER PURIFICATION & TREATMENT FACILITIES: Different treatment systems are used depending on the
source of the water.
TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS: The treated water is transported from the source via water mains
and sub-mains to the end-users.
STORAGE SYSTEMS: these may include water tanks, reservoirs, and water towers. In smaller systems, pressure vessels
and cisterns may be used.
PUMPING STATIONS: in order to maintain optimal water pressure, additional pressurizing components, called
pumping stations, are often used.
ACCESSORIES: these may include support components such as valves, service lines, generators, meters, fire hydrants,
and other accessories needed to ensure a smoothly running system.
COMMUNITY SYSTEMS
Community water supply systems are public or private entities that install and provide a central supply of water to a
neighbourhood, city or special district. They are government owned, as in most cities, or privately owned, such as in a
rural housing development where the builder or real estate developer develops the water system. The water for these
systems may have been obtained from any of the water sources discussed previously.
For example: Part of the water may be taken from a river or reservoir, and it may be supplemented by deep wells.
WATER METERS are required in all community system that charge for water usage or in systems where water
consumption must be monitored.
PRIVATE SYSTEMS - Private, or individual, water systems are composed of private ground water residential wells,
cisterns, and larger private water systems that serve more than one residence.
Private ground water wells usually supply water to an individual residence.
Private water systems are those that serve no more than 25 people at least 60 days of the year and have no more than 15
service connections (varies by state). Each building serviced by the same private water system is considered to be a
service connection for that system. Most private water systems use ground water wells.
WHAT IS THE WELLS SYSTEM?
A modern well system consists of a well, a motor-driven pump, and a storage tank. In most systems, the pump draws
water from the well where it is stored in a storage tank. A switch activated by water pressure controls the pump.
WHAT’S IN WELL WATER?
Well water is more likely to be hard water, meaning that it contains minerals like calcium and magnesium. Water
containing minerals can be a good thing. Still, too many minerals can create build-up in pipes and heating systems,
leading to costly repairs. Hard water also performs poorly with soaps and detergents, leaving spots on dishes, shower
doors, and generally not cleaning things as well as soft water.
THERE ARE THREE COMMON TYPES OF WATER WELLS.
DUG WELLS are shallow wells, generally not more Than 25 ft (7.6 m) deep, and typically 3 to 6 ft (1 to 2 m) in diameter.
They are typically made by excavation with a backhoe or excavator but can be hand shovelled, as this was the method
typically used for hundreds of years.
DRIVEN WELLS also referred to as sand point wells. Consist of lengths of 11⁄4 to 2 in (32 to 50 mm) diameter pipe that
is driven into the ground. In driving this type of well, a sharp well Point and drive cap are attached to a pipe.
DRILLED/BORED Drilling or boring methods are used for Deep wells. A well-drilling rig is used to create the well hole.
Drilled wells have the holes formed by using rotary bits. Bored Wells have the holes formed by using an auger and
covered with a casing. Only the drilling method is effective in cutting through hard rock.
Classification Depth Construction Method
Shallow Less than 25 ft Dug, driven, and shallow bored
(7.6 m) in depth
Deep 25 ft (7.6 m) or Drilled and bored
More in depth
OTHER TYPES OF WELL PUMPS
A water well pump is a pump that is used in extracting water from a water well. They include different kinds of pumps,
most of them submersible pumps: Hand pump, manually operated. Injector, a jet-driven pump. Mechanical or rotary lobe
pump requiring mechanical parts to pump water.
A well tank works in conjunction with a well pump, a pressure switch, and a check valve to keep the water pressure in a
safe and comfortable range. Inside the tank is a rubber bladder, similar to a tire inner tube, which holds pressurized air to
force the water out of the tank and into your pipes.
WATER TOWERS AND ELEVATED STORAGE TANKS
A water tower must be tall enough to deliver adequate pressure to all of the houses and businesses in the area of the
tower. Each foot of water height provides 0.433 psi (pounds per square inch) of pressure. (This is discussed in Chapter
13.) A typical community water supply maintains pressures between 50 and 100 psi (344 and 688 kPa), whereas plumbing
fixtures require 8 psi (55 kPa) to 30 psi (206 kPa).
Elevated water storage tanks serve buildings that are too tall to rely on street water pressure. Water is pumped to a
storage tank located on top of the building. An elevated storage tank that is 30 to 35ft (10 to 12 m) above the highest
plumbing fixture being served is generally required. Elevated water storage tanks are sized to hold one to two days of
water supply plus a reserve for firefighting. An alternative to an elevated storage tank in tall buildings is a pressurized
tank a storage tank that is pressurized to the appropriate pressure.
You might also like
- Diy Body Care Gifts Made SimpleDocument51 pagesDiy Body Care Gifts Made Simplenurifauziyah100% (1)
- Domestic Water Supply - Group WorkDocument57 pagesDomestic Water Supply - Group Worksarah abdulrhmanNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemDocument53 pagesWater Distribution SystemChristy Mae LabajoNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemDocument57 pagesWater Distribution Systemamber1999588% (8)
- The Plumbing SystemDocument58 pagesThe Plumbing SystemJemina Piccio100% (1)
- Water Supply AppurtenancesDocument26 pagesWater Supply AppurtenancesPrashna Shrestha100% (1)
- Water Supply and Drainage in BuildingDocument21 pagesWater Supply and Drainage in BuildingAnu KpNo ratings yet
- Building UtilitiesDocument41 pagesBuilding UtilitiesJara Mi SerinoNo ratings yet
- Iso 3758 2012Document30 pagesIso 3758 2012aminNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: Medical HandwashingDocument4 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: Medical HandwashingRosh Hashana Louisse MatbaganNo ratings yet
- Gerunds Vs Paticiples 2022Document19 pagesGerunds Vs Paticiples 2022Ee DeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Sanitary/Plumbing Design: Engineering Utilities IiDocument22 pagesBasic Principles of Sanitary/Plumbing Design: Engineering Utilities IiKarl Cristian DaquilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Plumbing Terminology PDFDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - Plumbing Terminology PDFsachinkarape4844No ratings yet
- Housekeeping StepsDocument7 pagesHousekeeping StepsBanjo De Los Santos100% (1)
- Water Supply System - Minal PalveDocument51 pagesWater Supply System - Minal PalveminalNo ratings yet
- DESIGN 01 (General Residential) PDFDocument127 pagesDESIGN 01 (General Residential) PDFMar Jhon Paulo MojicaNo ratings yet
- 1,2,3 - Water Supply and DistributionDocument5 pages1,2,3 - Water Supply and DistributionKaren JohnsonNo ratings yet
- WS - Chap 1& 2&3Document28 pagesWS - Chap 1& 2&3Eng Bagaragaza RomualdNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Drainage NotesDocument41 pagesPlumbing Drainage NotesDinesh Kumar100% (2)
- Pioneer Beginners Tests Module 4Document3 pagesPioneer Beginners Tests Module 4Boglárka SzórádiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 2: Engr. Ervin John D. Melendres InstructorDocument24 pagesEngineering Utilities 2: Engr. Ervin John D. Melendres InstructorStephanie CanibanNo ratings yet
- PlumbingDocument7 pagesPlumbingMichaella Corine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 Water Distribution System16!02!24Document27 pagesLec-3 Water Distribution System16!02!24muhammadurafm.aliNo ratings yet
- Water Supply & Waste DisposalDocument22 pagesWater Supply & Waste DisposalRNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution: PipelinesDocument4 pagesWater Distribution: PipelinesYash DhabaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-2-3-WS&SE - semII-2023Document91 pagesChapter1-2-3-WS&SE - semII-2023Kunduwera MethodeNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemsDocument8 pagesWater Distribution SystemsCasao JonroeNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Systems-1Document13 pagesWater Supply Systems-1Godwin MasulaNo ratings yet
- Jet Pump Vs Submercible PumpDocument14 pagesJet Pump Vs Submercible PumpxiaoyaojacNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Eu1Document6 pagesActivity 1 Eu1bsnow5325No ratings yet
- Report Eu 2 J9 2Document40 pagesReport Eu 2 J9 2Joey Aguilar VelascoNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemDocument38 pagesWater Distribution SystemHarshita MittalNo ratings yet
- 18ar30 - Services RecapDocument40 pages18ar30 - Services RecapAsir kotawdekarNo ratings yet
- Share 12.4 and 12.5 ReportDocument26 pagesShare 12.4 and 12.5 ReportMichael Dominique Granada IINo ratings yet
- Building Services Unit 1Document8 pagesBuilding Services Unit 1Payal Yadav100% (1)
- MCW4 $$$$$$$$$Document9 pagesMCW4 $$$$$$$$$Epaphrodite NDAYISHIMIYENo ratings yet
- PAT205 Building Services 1 Plumbing & Sanitary: Distribution of Water ServicesDocument174 pagesPAT205 Building Services 1 Plumbing & Sanitary: Distribution of Water ServicesShudhan NambiarNo ratings yet
- Pid 7a Indicative Loc of Utilities Plumbing and Sanitary 20210424 174715Document127 pagesPid 7a Indicative Loc of Utilities Plumbing and Sanitary 20210424 174715Ani-me TanNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesBahasa Inggriscontoh ajaNo ratings yet
- Well PumpsDocument18 pagesWell PumpsGodwin MasulaNo ratings yet
- Acp 10 - PPT - Q3 - M1Document69 pagesAcp 10 - PPT - Q3 - M1Yeye VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Water Supply # Sources of WaterDocument27 pagesWater Supply # Sources of WaterArjun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Distribution MethodsDocument25 pagesWater Supply and Distribution MethodsNeha RaniNo ratings yet
- W.s.s.in B Ppt6Document17 pagesW.s.s.in B Ppt6Poii GNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Distribution SystemingDocument5 pagesWater Supply and Distribution SystemingMelissa GabayNo ratings yet
- Public Water SupplyDocument5 pagesPublic Water SupplycessNo ratings yet
- Types of Water ClosetDocument6 pagesTypes of Water ClosetLovelia Viloria AgorNo ratings yet
- h20 DistributionDocument38 pagesh20 DistributionUd BsecNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 DrainageDocument62 pagesUnit 2 DrainagekarunyaNo ratings yet
- Appurtenances in The Distribution System: - Valves - Fire Hydrants - Water Meters - PumpsDocument12 pagesAppurtenances in The Distribution System: - Valves - Fire Hydrants - Water Meters - PumpsPratyoosh MadhaviNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Collection ProcessDocument3 pagesWastewater Collection Processking21No ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemDocument15 pagesWater Distribution SystemSreyas E RNo ratings yet
- Adri WaterSuppy-Drainage NotesDocument9 pagesAdri WaterSuppy-Drainage NotesDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemDocument38 pagesWater Distribution SystemDoodlez AhangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 and 8-WS&SEDocument72 pagesChapter 7 and 8-WS&SEKunduwera MethodeNo ratings yet
- BuDocument2 pagesBuMARVEL SHOWSNo ratings yet
- Sanitary SystemDocument58 pagesSanitary Systemsuryaa ksNo ratings yet
- Chapter7-Plumbing system-WS&SEDocument30 pagesChapter7-Plumbing system-WS&SERwagatare civilcontractorsNo ratings yet
- Water Supply System For BuildingsDocument6 pagesWater Supply System For BuildingsPepper ChaeyoungNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and DistributinDocument37 pagesWater Supply and DistributinHello YouNo ratings yet
- Introduction - DoneDocument9 pagesIntroduction - DoneIr Fik TNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Hydraulic StructureDocument16 pagesWater Supply and Hydraulic Structurekenji belanizoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Final RequimentsDocument2 pagesDynamics Final RequimentsJoshua BacunawaNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemDocument43 pagesWater Distribution SystemPausePlay100% (1)
- Irrigation System ComponentsDocument7 pagesIrrigation System ComponentsanunayNo ratings yet
- Gravity - Flow Water Systems Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 DefinitionDocument4 pagesGravity - Flow Water Systems Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Definitionraju acharyaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing For BuildingsDocument24 pagesPlumbing For BuildingsMorshed Bin Alam FervvezNo ratings yet
- Business Plan LogoDocument2 pagesBusiness Plan LogoKechan ShenNo ratings yet
- Gloprt 2Document11 pagesGloprt 2Kechan ShenNo ratings yet
- Bron PogiDocument22 pagesBron PogiKechan ShenNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument7 pagesBusiness PlanKechan ShenNo ratings yet
- ANIMALSDocument17 pagesANIMALSKechan ShenNo ratings yet
- Jem 2 XDocument1 pageJem 2 XKechan ShenNo ratings yet
- LI L1 Unit Test 3BDocument2 pagesLI L1 Unit Test 3BRaquel Prado MarçalNo ratings yet
- Cube Living - Container Homes - KEA PDFDocument1 pageCube Living - Container Homes - KEA PDFoscar51No ratings yet
- 4.contoh Soal Chapter 4 Things in The Livingroom and BedroomDocument5 pages4.contoh Soal Chapter 4 Things in The Livingroom and Bedroompriyo cirebon100% (1)
- Cla FiltersDocument22 pagesCla FiltersAce Dynamics IndiaNo ratings yet
- WASH in Islam: Guide On Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) From An Islamic PerspectiveDocument49 pagesWASH in Islam: Guide On Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) From An Islamic PerspectiveMegan TariNo ratings yet
- Ritello Premium Edition Owner's Manual - ENGLISHDocument20 pagesRitello Premium Edition Owner's Manual - ENGLISHrenova chileNo ratings yet
- TNF Be Going To ExerciseDocument3 pagesTNF Be Going To ExerciseJonathan Charles Mendez GarnicaNo ratings yet
- Work Order: Bal Vidya Academy Near Mother Dairy, Sector 20, Rohini, Delhi 110086Document3 pagesWork Order: Bal Vidya Academy Near Mother Dairy, Sector 20, Rohini, Delhi 110086anshulNo ratings yet
- Final RecoverDocument17 pagesFinal RecoverDaypuyart Condez BernardNo ratings yet
- Caregiving Tools Equipment and ParaphernaliaDocument87 pagesCaregiving Tools Equipment and ParaphernaliaJorrel C LebaNo ratings yet
- Bag Technique Skills ChecklistsDocument10 pagesBag Technique Skills ChecklistsrobbyNo ratings yet
- Waterproofing QuoteDocument2 pagesWaterproofing QuoteSagar SamantNo ratings yet
- 02 BIE A2 2ED U6 Level1Document4 pages02 BIE A2 2ED U6 Level1Noelia ColomaNo ratings yet
- Specifications: Proposed 2-Storey ResidenceDocument6 pagesSpecifications: Proposed 2-Storey ResidenceFrancis John F. LopezNo ratings yet
- Tekno TDW 7000TIX UserManualDocument50 pagesTekno TDW 7000TIX UserManualOGMNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay OutlinesDocument3 pagesArgumentative Essay Outlinesajdegacaf100% (2)
- SE Catalogue (New Format) - Translation For Eng To FrenchDocument76 pagesSE Catalogue (New Format) - Translation For Eng To FrenchMukesh chopraNo ratings yet
- Contact Us: Add A Little Bit of Body TextDocument2 pagesContact Us: Add A Little Bit of Body Textdr.bashdphenomNo ratings yet
- Exploratory COOKERY Q1 M2Document16 pagesExploratory COOKERY Q1 M2RODELYN DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Seen Passage: Time 1 Hour 30 MinuteDocument2 pagesSeen Passage: Time 1 Hour 30 MinuteNadim MahamudNo ratings yet
- Opinion - Stop Using Toilet Paper - The New York TimesDocument2 pagesOpinion - Stop Using Toilet Paper - The New York TimesMartín Felipe CastagnetNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Word DocumentSunny SunNo ratings yet