Professional Documents
Culture Documents
06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
alexander.tarakanovOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
alexander.tarakanovCopyright:
Available Formats
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
Q Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
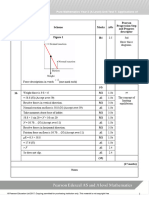
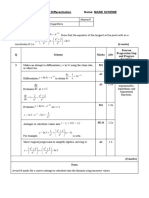
1 Makes an attempt to substitute any of n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 into M1 1.1b 5th
Complete proofs
by exhaustion.
A1 1.1b
Successfully substitutes n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 into
Draws the conclusion that as the statement is true for all B1 2.4
numbers from 1 to 6 inclusive, it has been proved by
exhaustion.
(3 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 1
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
2 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
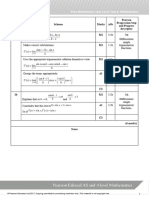
(a) M1 2.1 6th
Understand
Shows that small-angle
approximations
M1 1.1b for sin, cos and
Shows that tan (angle in
radians).
Shows M1 2.1
A1 1.1b
Recognises that
(4)
(b) A1 1.1b 7th
When θ is small, Use small-angle
approximations to
solve problems.
(1)
(5 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 2
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
3 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
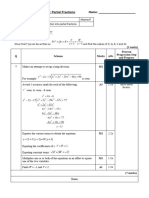
(a) Interprets the stone hitting the ground as when M1 3.4 8th
Use parametric
equations in
Makes an attempt to use the quadratic formula to find t. M1 2.2a modelling in a
variety of
contexts.
For example, is seen.
Finds M1 1.1b
A1 3.2a
Deduces m. Accept awrt 24.6
(4)
(b) M1 2.2a 8th
Finds Use parametric
equations in
Demonstrates an understanding that the greatest height will M1 3.1a modelling in a
variety of
contexts.
occur when . For example,
M1 1.1b
Solves to find
Makes an attempt to find the greatest height by substituting M1 ft 3.2a
into
For example,
A1 ft 1.1b
Finds y = =13.265… m. Accept awrt 13.3 m.
(5)
(9 marks)
Notes
(b) can also be found using . This is an acceptable method.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 3
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
(b) Award ft marks for correct sketch using incorrect values from earlier in part b.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 4
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
4 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
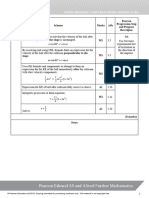
(a) Differentiates to obtain M1 1.1b 6th
Differentiate
reciprocal and
inverse
trigonometric
A1 1.1b functions.
Writes
(2)
(b) Use the identity to write M1 2.2a 6th
Differentiate
reciprocal and
inverse
M1 2.2a
Attempts to substitute and into trigonometric
functions.
A1 1.1b
Correctly substitutes to find and states
(3)
(5 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 5
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
5 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
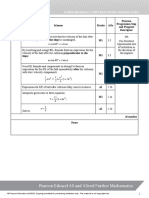
(a) A1 1.1b 5th
Clearly states that
Integrate
Makes an attempt to integrate the remaining two terms. Raising M1 1.1b
a power by 1 would constitute an attempt.
A1 1.1b
States the fully correct answer
(3)
(b) Makes an attempt to substitute the limits into the expression. M1 1.1b 5th
For example, is Integrate
seen.
Begins to simplify this expression. For example, M1 1.1b
is seen.
A1 1.1b
States the fully correct answer or states
, n = 6 and
Also accept or equivalent.
(3)
(6 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 6
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
6 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
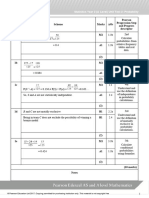
(a) States the range is or B1 3.2b 5th
Find the domain
and range for a
variety of familiar
functions.
(1)
(b) M1 2.2a 7th
Solve problems
Recognises that and involving the
modulus function
in unfamiliar
contexts.
Makes an attempt to solve both of these equations. M1 1.1b
A1 1.1b
Correctly states . Equivalent version is acceptable.
A1 1.1b
Correctly states . Equivalent version is acceptable.
Makes an attempt to substitute one equation into the other in an M1 ft 2.2a
effort to solve for k. For example, and
is seen.
A1 ft 1.1b
Correctly solves to find
B1 3.2b
States the correct range for k.
(7)
(8 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 7
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 8
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Notes
(b) Award ft marks for a correct method using an incorrect answer from earlier in the question.
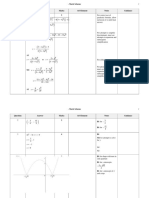
Alternative Method
Student draws the line with gradient passing through the vertex and calculates that , so answer is
M1: States the x-coordinate of the vertex of the graph is 4
M1: States the y-coordinate of the vertex of the graph is −5
M1: Writes down the gradient of or implies it later in the question.
M1: Attempts to use with and
A1: Finds o.e.
B1: States the correct range for k:
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 9
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
7 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
Makes an attempt to set up a long division. M1 2.2a 5th
Decompose
algebraic
For example: is seen. fractions into
The ‘0x’ being seen is not necessary to award the mark. partial fractions −
two linear factors.
Long division completed so that a ‘1’ is seen in the quotient and M1 1.1b
a remainder of 25x + 32 is also seen.
States M1 1.1b
Equates the various terms. M1 2.2a
Equating the coefficients of x:
Equating constant terms:
Multiplies one or both of the equations in an effort to equate one M1 1.1b
of the two variables.
A1 1.1b
Finds
A1 1.1b
Finds
(7 marks)
Notes
Alternative method
Writes as
States
Substitutes to obtain:
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 10
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Substitutes to obtain:
Equating the coefficients of x2:
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 11
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
8 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) States the recurrence relation. Choice of variable is not M1 3.1a 5th
important. or Work with
sequences defined
M1 3.1a by simple
Defines the first value. Accept either use of or . or recurrence
relations.
(2)
(b) M1 3.1a 5th
Makes an attempt to find the height, for example is
seen. Work with the nth
term formula for
States that the maximum height would be 13.445… cm. Accept A1 1.1b geometric
awrt 13.4 sequences.
(2)
(c) Attempts to make use of the sum to infinity. For example, M1 3.1a 6th
Use geometric
or is seen. sequences and
series in context.
Understands that the ball travels upwards and then downwards, M1 3.1a
so multiplies by 2. or is seen.
Recognises that when the ball is dropped, it initially only M1 3.1a
travels downwards. Either or
is seen or implied.
A1 1.1b
States a fully correct answer of cm. Accept awrt 453.3
cm.
(4)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 12
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
(d) ‘It is very unlikely that the ball will not bounce vertically’ or B1 3.5 6th
‘This model assumes the ball will continue to bounce forever’.
Understand
convergent
geometric series
and the sum to
infinity.
(1)
(9 marks)
Notes
(c) Award first method mark for an understanding that the sum to infinity formula is required.
Award second method mark for an understanding that the sum to infinity formula will need adjusting, i.e. the
ball goes down and then up.
Award third method mark for an understanding that the ball only goes down initially as it is dropped.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 13
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
9 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
Uses the double-angle formulae to write: M1 2.2a 6th
Use the
double-angle
M1 1.1b formulae for sin,
cos and tan.
Uses the fact that and to write:
M1 1.1b
Simplifies this expression to
Correctly solves to find A1 1.1b
(4 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 14
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
Q Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
10 Begins the proof by assuming the opposite is true. B1 3.1 7th
Complete proofs
using proof by
‘Assumption: there exists a rational number such that is the
contradiction.
greatest positive rational number.’
Makes an attempt to consider a number that is clearly greater M1 2.2a
than :
‘Consider the number , which must be greater than ’
M1 1.1b
Simplifies and concludes that this is a rational number.
By definition, is a rational number.
Makes a valid conclusion. B1 2.4
This contradicts the assumption that there exists a greatest
positive rational number, so we can conclude that there is not a
greatest positive rational number.
(4 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 15
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
11 Scheme Marks AOs Pearson
Progression Step
and Progress
descriptor
(a) M1 2.2a 6th
Understand the
Writes as binomial theorem
for rational n.
M1 1.1b
Expands
Simplifies: M1 1.1b
Award mark even if x2 term is not seen.
A1 1.1b
Uses to write a = 64.
A1 1.1b
Uses to write b = –6.
(5)
(b) B1 ft 3.2b 6th
States expansion is valid for Understand the
conditions for
A1 ft 1.1b validity of the
binomial theorem
Solves to state for rational n.
(2)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 16
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
(c) M1 ft 1.1b 6th
Understand the
Substitutes a = 64 and b = –6 into binomial theorem
for rational n.
A1 ft 1.1b
Finds
(2)
(9 marks)
Notes
(a) Note x2 term is not necessary to answer part a, so is not required. Will be needed to answer part c.
(b) Award marks for a correct conclusion using incorrect values of a and b from part a.
(c) Award marks for a correct answer using incorrect values of a and b from part a.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 17
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
12 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
M1 3.1a 6th
Finds via M
Solve geometric
problems using
vectors in 3
dimensions.
M1 3.1a
Finds via N
Finds M1 3.1a
Finds M1 3.1a
Equates the two ways of moving from O to P. M1 2.2a
M1 2.2a
Equates coefficients of a:
Equates coefficients of b. OR equates coefficients of c. M1 1.1b
A1 1.1b
Solves to find
Concludes that at this value the lines intersect. B1 2.1
Concludes that the lines must bisect one another as B1 2.1
and
(10 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 18
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
13 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) M1 3.3 8th
States Solve differential
equations in a
M1 2.2a range of contexts.
Separates the variables
Finds A1 1.1b
A1 2.1
Shows clearly progression to state
For example, is seen. May also explain the
where is a constant.
(4)
(b) M1 3.3 8th
States Solve differential
equations in a
M1 2.2a range of contexts.
Simplifies the expression by cancelling and then taking the
natural log of both sides
A1 1.1b
States that
(3)
(c) M1 3.3 8th
States Solve differential
equations in a
M1 2.2a range of contexts.
Simplifies the expression by cancelling and then taking the
natural log of both sides
Finds t = 18.613… years. Accept 18.6 years. A1 1.1b
(3)
(10 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 19
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 20
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
14 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) States that the local maximum occurs when B1 3.1a 7th
Use numerical
Makes an attempt to differentiate p(t) M1 2.2a methods to solve
problems in
A1 1.1b context.
Correctly finds
Finds and M1 1.1b
A1 2.4
Change of sign and continuous function in the interval
Therefore the gradient goes from positive to negative and so the
function has reached a maximum.
(5)
(b) States that the local minimum occurs when B1 3.1a 7th
Use numerical
Makes an attempt to differentiate M1 2.2a methods to solve
problems in
A1 1.1b context.
Correctly finds
Finds and M1 1.1b
M1 1.1b
Attempts to find
A1 1.1b
Finds
(6)
(11 marks)
Notes
(a) Minimum required is that answer states there is a sign change in the interval and that this implies a root in
the given interval.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 21
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 6 mark scheme
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 22
You might also like
- 01b A Level Mathematics Practice Paper A - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument17 pages01b A Level Mathematics Practice Paper A - Pure Mathematics Mark Schemejotpalak5No ratings yet
- 07 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 7 Mark SchemeDocument18 pages07 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 7 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry MSDocument8 pagesTrigonometry MSBashar RoveziNo ratings yet
- 03 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 3 Mark SchemeDocument21 pages03 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 3 Mark SchemeFox HendersonNo ratings yet
- Integration 1 MSDocument9 pagesIntegration 1 MSnppptry4kmNo ratings yet
- A Level Pure Unit 6 Trigonometry MSDocument8 pagesA Level Pure Unit 6 Trigonometry MSTahmid FarhanNo ratings yet
- MS Binomial Expansion WSDocument4 pagesMS Binomial Expansion WS11178No ratings yet
- AL Maths Pure Unit 1 MSDocument11 pagesAL Maths Pure Unit 1 MSjim0% (1)
- A Level Pure Maths Unit Test 4 Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesA Level Pure Maths Unit Test 4 Mark Schemelauren50% (2)
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A B1 M1Document10 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A B1 M1Nasser ElmanzalawyNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 B1Document10 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 B1Nasser ElmanzalawyNo ratings yet
- A Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument17 pagesA Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeZaka AhmedNo ratings yet
- Applications of Forces MSDocument7 pagesApplications of Forces MSjunkthingsandspamandstuffNo ratings yet
- Alevel Ut m1 U8 MarkschemeDocument6 pagesAlevel Ut m1 U8 Markschemeiwan.fothergillNo ratings yet
- Differentiation 1 MSDocument10 pagesDifferentiation 1 MS7rdtbdns6zNo ratings yet
- Statistics Year 2 (A Level) Unit Test 1: Regression and Correlation Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesStatistics Year 2 (A Level) Unit Test 1: Regression and Correlation Mark SchemeRory SimkinsNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A B1 B1 (2) 1B M1 M1Document6 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A B1 B1 (2) 1B M1 M1TM100% (1)
- Unit 8 AnswersDocument8 pagesUnit 8 Answerspyropop3No ratings yet
- Al Maths Pure Unit 6 MsDocument8 pagesAl Maths Pure Unit 6 MsHacjer EiNSTi3NNo ratings yet
- Regression and Correlation MSDocument10 pagesRegression and Correlation MSifrahshazad123No ratings yet
- Factor Theorem and Proof - Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesFactor Theorem and Proof - Mark SchemeAlex MoneyNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 M1Document11 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 M1Khadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution MSDocument7 pagesThe Normal Distribution MSManav MaistryNo ratings yet
- Further Mechanics 1 Unit Test 5 Elastic Strings and Springs and Elastic Energy Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesFurther Mechanics 1 Unit Test 5 Elastic Strings and Springs and Elastic Energy Mark SchemeGavin Man100% (4)
- Further Mechanics 1 Unit Test 6 Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions Mark Schemedocx PDF FreeDocument9 pagesFurther Mechanics 1 Unit Test 6 Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions Mark Schemedocx PDF FreeAB IVNo ratings yet
- Further Mechanics 1 Unit Test 6 Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesFurther Mechanics 1 Unit Test 6 Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions Mark SchemeGavin Man63% (8)
- 02.unit-Test 8b MSDocument1 page02.unit-Test 8b MS185359No ratings yet
- 01.unit-Test 2 MSDocument2 pages01.unit-Test 2 MS185359No ratings yet
- Alevel Pure Math 123456789Document15 pagesAlevel Pure Math 123456789Sophy ThweNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper C MsDocument17 pagesPractice Paper C MsKostas KostaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 21Document5 pages9709 w16 Ms 21yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 M1Document9 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 M1sara jaimeNo ratings yet
- As Maths Pure Unit 4 MSDocument10 pagesAs Maths Pure Unit 4 MSArthur LongwardNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Mechanics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 7: Kinematics 1 (Constant Acceleration)Document6 pagesMark Scheme: Mechanics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 7: Kinematics 1 (Constant Acceleration)Huzaifah100% (2)
- Probability 1 MSDocument8 pagesProbability 1 MSvdaiNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Practice Feb 2Document5 pagesMark Scheme Practice Feb 2Owin Nolan GunawanNo ratings yet
- A Level Statitics Unit 1 Mark SchemeDocument10 pagesA Level Statitics Unit 1 Mark SchemeTheNo ratings yet
- CRW 6. Equations, Inequalities and Graphs MarkSchemeDocument8 pagesCRW 6. Equations, Inequalities and Graphs MarkSchemeMahdi TasninNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument8 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelBassem Khalid YasseenNo ratings yet
- Trial Work2 MSDocument6 pagesTrial Work2 MSAblerh Paul LawerhNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Statistics Unit 1 MSDocument8 pagesAS Maths Statistics Unit 1 MS11110000No ratings yet
- CRW 5. Factors and Polynomials MarkSchemeDocument8 pagesCRW 5. Factors and Polynomials MarkSchemeMahdi TasninNo ratings yet
- CRW 2. Simultaneous Equations MarkSchemeDocument10 pagesCRW 2. Simultaneous Equations MarkSchemeMahdi TasninNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper1Document124 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper1ishaanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A M1Document7 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A M1Arthur LongwardNo ratings yet
- As Further Mechanics 1 June 2022 Shadow Paper MS WordDocument5 pagesAs Further Mechanics 1 June 2022 Shadow Paper MS WordMr DudeeNo ratings yet
- Further Mechanics 1 Unit Test 4 Momentum and Impulse (Part 2) Mark SchemeDocument2 pagesFurther Mechanics 1 Unit Test 4 Momentum and Impulse (Part 2) Mark SchemeGavin Man100% (1)
- Quality of Tests MsDocument8 pagesQuality of Tests MsKrishan LalNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Pure 1 Revision Worksheet 1Document13 pagesYear 12 Pure 1 Revision Worksheet 1JohnNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1ADocument8 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1AMohamed Elamin100% (1)
- GCSE Mathematics (1MA1) - Higher Tier Paper 2H October 2016 Mock Paper Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesGCSE Mathematics (1MA1) - Higher Tier Paper 2H October 2016 Mock Paper Mark SchemeSeb 14316No ratings yet
- CRW 3. Quadratic Functions MarkSchemeDocument12 pagesCRW 3. Quadratic Functions MarkSchemeMahdi TasninNo ratings yet
- Binomial Expansion Q'sDocument3 pagesBinomial Expansion Q'si.kirdar-smithNo ratings yet
- A Level Statistics Paper 1 MARK SCHEMEDocument7 pagesA Level Statistics Paper 1 MARK SCHEMEStefan AlbertNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: States Correct Answer: 5.3 (M S)Document7 pagesMark Scheme: States Correct Answer: 5.3 (M S)张婧雯0% (1)
- Markscheme Remedial Kls 12Document19 pagesMarkscheme Remedial Kls 12Digilib Cambridge TazkiaNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Statistics Unit 2 MSDocument9 pagesAS Maths Statistics Unit 2 MSPatryk Nionec33% (3)
- Mathematical Relations PDFDocument229 pagesMathematical Relations PDFmars100% (1)
- 1802 07880Document12 pages1802 07880Jack Ignacio NahmíasNo ratings yet
- P&C Division DistributionDocument3 pagesP&C Division DistributionAtharva Sheersh PandeyNo ratings yet
- 02-Integral, Semi-Empty Curves and Pure PDFDocument12 pages02-Integral, Semi-Empty Curves and Pure PDFLucius LunáticusNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Functions (Solved With Notes)Document21 pagesTransformation of Functions (Solved With Notes)cs23b1008No ratings yet
- Cobweb Con Matlab PDFDocument6 pagesCobweb Con Matlab PDFLea EleuteriNo ratings yet
- Question Most Important PYQs Sequences and Series Undefined Crash Course MathonGoDocument2 pagesQuestion Most Important PYQs Sequences and Series Undefined Crash Course MathonGoclass10th.pdfNo ratings yet
- Green's Theorem: Sin X 4 2 2Document2 pagesGreen's Theorem: Sin X 4 2 2kali1No ratings yet
- Important Question in VectorDocument7 pagesImportant Question in VectorBhakti Nath MishraNo ratings yet
- Matrices - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06)Document2 pagesMatrices - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06)Shambhavi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Cantor SetDocument4 pagesCantor SetNaveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- NA Assignment2 171465551 Sabbir Ahmed KIE180713Document30 pagesNA Assignment2 171465551 Sabbir Ahmed KIE180713Sabbir Ahmed NirobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 P1Document3 pagesChapter 1 P1Pavlos StavropoulosNo ratings yet
- Math 11 Derivative of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument12 pagesMath 11 Derivative of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsFranco Louis RomeroNo ratings yet
- Apostol Solutions Vol2Document142 pagesApostol Solutions Vol2Mário FilhoNo ratings yet
- Reteach: Solving Inequalities by Adding or SubtractingDocument4 pagesReteach: Solving Inequalities by Adding or SubtractingHala EidNo ratings yet
- Complex Number - Sheet - 2 Level-1Document5 pagesComplex Number - Sheet - 2 Level-1RdNo ratings yet
- Part-A: Note: in This Worksheet Symbols Used PDocument6 pagesPart-A: Note: in This Worksheet Symbols Used PKritikaNo ratings yet
- 2010-H2 Maths-Integration and Its Applications (Tut 3) - Int Applications Solutions)Document13 pages2010-H2 Maths-Integration and Its Applications (Tut 3) - Int Applications Solutions)Anita Yun Chu PengNo ratings yet
- DILE NO A LA PLANCHA (Kim Jhon Phatti Satto)Document6 pagesDILE NO A LA PLANCHA (Kim Jhon Phatti Satto)Kimsito Al TlvNo ratings yet
- 001 - Openfoam SSÇ ÀÚ ÁDocument189 pages001 - Openfoam SSÇ ÀÚ ÁAntonio Martín AlcántaraNo ratings yet
- Series Expansion Reciprocal GammaDocument23 pagesSeries Expansion Reciprocal GammalahlouhwissalNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra For Computational EngineeringDocument21 pagesLinear Algebra For Computational EngineeringCovenant AdeogoNo ratings yet
- Limit LawsDocument32 pagesLimit LawsGian Val Ensomo BorjaNo ratings yet
- Formulas EdDocument4 pagesFormulas EdCarlos Loler NavarroNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document13 pagesModule 1shaina sucgangNo ratings yet
- IB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument45 pagesIB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - Trigonometric FunctionsAnahiNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Control - A Lyapunov Based ApproachDocument4 pagesNonlinear Dynamical Systems and Control - A Lyapunov Based Approachosnarf706No ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument10 pagesMaths ProjectAnagha JayaramNo ratings yet
- Matrix and Determinants 2 PDFDocument4 pagesMatrix and Determinants 2 PDFkawther JassimNo ratings yet