Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CA Classes-46-50
Uploaded by
SrinivasaRaoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CA Classes-46-50
Uploaded by
SrinivasaRaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Architecture Unit 2
Self Assessment Questions
11. Performance of the computer is improved by ___________________.
12. The ability of the servers to expand its processors and disks is known
as ____________________.
13. The main objective of ______________________ is to extend beyond
the instruction implementation to cut the total time taken to complete
the instruction series.
14. ____________________ declares that the item referred in the recent
times has potential to be accessed in the near future.
15. ____________________ states that the items nearby the location of
the recently used items may also be referred close together in time.
2.6 Power Consumption
Power consumption is another important design criterion that affects the
design of the modern computers. The power efficiency can normally be
dealt for performance or cost benefits. Recent processor designs put more
emphasis on the power efficiency. Also, in the upcoming world of totally
embedded computers, power efficiency has been the major concern of the
computer designers.
It is now widely accepted that power is the primary concern of the modern
microprocessors, rather it has become a constraint in most of the cases.
Power is a function of both static and dynamic power. Static Power is
proportional to the number of transistors, whereas Dynamic Power is
generally the product of the transistor switching and the switching rate.
Static power is generally the concern at the design stage, while when
operating, dynamic power is the dominant energy consumer.
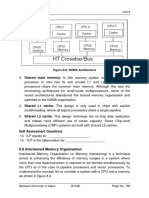
Technologists estimated the rough percentage of usage by each component
of the computer. This is represented in the following figure 2.9, which shows
CPUs only drawing about 5 percent of a PC's total power.
Manipal University Jaipur B1648 Page No. 46
Computer Architecture Unit 2
Figure 2.9: Pie Chart Showing Power Consumption Distribution
Most techniques used for improved performance, viz. multiprogramming and
multithreading, will of course increase the energy consumption. But the
question here is: Does it increase power consumption at a higher rate than
the increase in performance.
Unfortunately, the current techniques used by the programmers to improve
the performance are inefficient from the point of view of power consumption.
This occurs due to the following two characteristics:
1. Delivering multiple instructions earns some overhead in logic that
develops faster than the issue rate develops. Thus, without voltage
reductions to decrease power, it is probable to lead to lower rate of
performance per watt.
2. There has been observed a growing gap between high issue rates and
continual performance. The number of switching transistor rate is
proportional to the high issue rates and the performance is proportional
to the sustained performance. This causes a growing gap between both
of them leading to increased energy consumption per unit. This gap
arises from many issues.
For example, if we want to sustain four instructions per clock, we must
fetch more, issue more, and initiate execution on more than four
instructions. This will create the same situation of gap and such
techniques cannot improve the long-term power efficiency.
Manipal University Jaipur B1648 Page No. 47
Computer Architecture Unit 2
Self Assessment Questions
16. ____________________ can normally be dealt for performance or cost
benefits.
17. ____________________ is the product of the transistor switching and
the switching rate.
18. The number of switching transistor rate is proportional to ___________
and the performance is proportional to ______________.
2.7 Summary
Let us recapitulate the important concepts discussed in this unit:
There are two types of execution – concurrent and parallel.
Computer design is an activity that converts the architecture design of
the computer into a programming structure implementation of a
particular organisation.
Computer technology has made drastic changes in the past 60 years
when the first general-purpose computer was invented.
Desktop computers have the largest market in terms of costs. It varies
from low-end systems to very high-end heavily configured computer
systems.
The world’s first designer was Charles Baggage and is considered as
the father of computers.
Computer designer needs to determine the attributes that are necessary
for a new computer, then design a computer to maximise the
performance.
The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) is the part of the processor that is
visible to the programmer or compiler writer.
Performance of the computer is improved by taking advantage of
parallelism.
Focussing on the common case will work positively both for power and
resource allocation, thus, leading to advancement.
2.8 Glossary
CISC: Complex instruction set computer
Computer designer: A person who design CPUs or computers that are
actually built and are into considerable use and influence the further
development of computer designs.
Manipal University Jaipur B1648 Page No. 48
Computer Architecture Unit 2
Desktop computers: These are in the form of personal computers (also
known as PCs) and workstations.
Embedded computer: A computer system designed to perform a
particular function or task.
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): A part of the processor that is
visible to the programmer or compiler writer.
Integrated circuits: An electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned
diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of
semiconductor material.
RISC: Reduced instruction set computer
Supercomputers: These are high-performance computers for scientific
computing.
VLIW: Very long instruction word
2.9 Terminal Questions
1. Describe the three types of computer markets.
2. Explain the characteristics of embedded computers.
3. Who is a computer designer? Explain the job of a computer designer.
4. What are the components of Instruction Set architecture? Discuss in
brief.
5. Explain the technology trends in computer design.
6. Discuss briefly the quantitative principles in computer design.
7. Elucidate Amdahl’s Law.
2.10 Answers
Self Assessment Questions
1. Microprocessor
2. Main-frame
3. True
4. Minimum cost
5. Charles Baggage
6. ISA
7. 16
8. Complex instruction set computer
9. False
10. Integrated circuits or microchips
Manipal University Jaipur B1648 Page No. 49
Computer Architecture Unit 2
11. Adopting parallelism
12. Scalability
13. Pipelining
14. Temporal Locality
15. Spatial Locality
16. Power efficiency
17. Dynamic Power
18. High issue rates, sustained performance
Terminal Questions
1. Desktop computers have the largest market in terms of costs. It varies
from low-end systems to very high-end heavily configured computer
systems. Refer Section 2.2.
2. An embedded system is a single purpose computer embedded in a
devise to control some particular function of that bigger devise. The
performance requirement of an embedded application is real-time
execution. Refer Section 2.2.
3. Computer Designer is a person who has designed CPUs or computers
that were actually built and came into considerable use and influenced
the further development of computer designs. Refer Section 2.3.
4. Architecture covers all three aspects of computer design – instruction
set architecture, organisation, and hardware. Refer Section 2.3.
5. Technology trends need to be studied on a regular basis in order to
cope with the dynamic and rapidly changing market. The instruction set
should be designed such to adapt the rapid changes of the technology.
Refer Section 2.4.
6. Quantitative principles in computer design are: Take Advantage of
Parallelism, Principle of Locality, Focus on the Common Case and
Amdahl’s Law. Refer Section 2.5.
7. Amdahl’s law states that the performance improvement to be gained
from using some faster mode of execution is limited by the fraction of
the time the faster mode can be used. Refer Section 2.5.
Manipal University Jaipur B1648 Page No. 50
You might also like
- CA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerDocument112 pagesCA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerOmprakash DNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-31-35Document5 pagesCA Classes-31-35SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-41-45Document5 pagesCA Classes-41-45SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Cse Viii Advanced Computer Architectures (06cs81) NotesDocument156 pagesCse Viii Advanced Computer Architectures (06cs81) NotesJupe JonesNo ratings yet
- RTSEC DocumentationDocument4 pagesRTSEC DocumentationMark JomaoasNo ratings yet
- ACA NotesDocument156 pagesACA NotesSharath MonappaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture & OrganizationDocument3 pagesComputer Architecture & OrganizationAlberto Jr. AguirreNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization: Virtual MemoryDocument26 pagesComputer Organization: Virtual Memorychuks felix michaelNo ratings yet
- 1.speed Synchronization of Multiple MotorsDocument89 pages1.speed Synchronization of Multiple MotorsBhanu TummalapalliNo ratings yet
- Multi-Core Processor PDFDocument6 pagesMulti-Core Processor PDFFaiqa mehboobNo ratings yet
- Reconfigurable Computing: Architectures and Design MethodsDocument15 pagesReconfigurable Computing: Architectures and Design MethodsLuis Charrua FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- COA MidtermDocument13 pagesCOA MidtermAliaa TarekNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Power Consumption of Embedded System Processors Through Instruction-Set CompressionDocument4 pagesMinimizing Power Consumption of Embedded System Processors Through Instruction-Set CompressionMohamed HacamNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis On Multicore ProcessorsDocument9 pagesPerformance Analysis On Multicore ProcessorsJuan Carlos Álvarez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Compiler Technology For Future MicroprocessorsDocument52 pagesCompiler Technology For Future MicroprocessorsBiswajit DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 1 COALDocument24 pagesChapter # 1 COALShahzael MughalNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1 - Fundamental of Computer DesignDocument20 pagesKelompok 1 - Fundamental of Computer Design23206051025No ratings yet
- MICROCONTROLLERS AND MICROPROCESSORS SYSTEMS DESIGN - ChapterDocument12 pagesMICROCONTROLLERS AND MICROPROCESSORS SYSTEMS DESIGN - Chapteralice katenjeleNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Benchmarking of CPU Micro-Architecture: College of Engineering, Pune - 5Document5 pagesTechniques For Benchmarking of CPU Micro-Architecture: College of Engineering, Pune - 5Varad DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Ec6009 Advanced Computer Architecture Unit I Fundamentals of Computer Design 9Document15 pagesEc6009 Advanced Computer Architecture Unit I Fundamentals of Computer Design 9Anitha DenisNo ratings yet
- Aca Univ 2 Mark and 16 MarkDocument20 pagesAca Univ 2 Mark and 16 MarkmenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Frequency Locked Loop For DC MotorsDocument102 pagesFrequency Locked Loop For DC MotorsBhagya Sri100% (2)
- Experience of Teaching Embedded System Design Using Fpgas 1Document10 pagesExperience of Teaching Embedded System Design Using Fpgas 1Tharshninipriya RajasekarNo ratings yet
- Decisive Aspects in The Evolution of Microprocessors: Dezsö SimaDocument31 pagesDecisive Aspects in The Evolution of Microprocessors: Dezsö SimactorreshhNo ratings yet
- Cse-Vii-Advanced Computer Architectures (10cs74) - SolutionDocument111 pagesCse-Vii-Advanced Computer Architectures (10cs74) - SolutionShinu100% (1)
- Computer Performance Enhancing Techniques - Session-2Document36 pagesComputer Performance Enhancing Techniques - Session-2LathaNo ratings yet
- Course FileDocument36 pagesCourse FileElakkiya N.SNo ratings yet
- 5 2marksDocument22 pages5 2marksElakkiya N.SNo ratings yet
- CS6303 Computer Architecture ACT Notes b6608Document76 pagesCS6303 Computer Architecture ACT Notes b6608mightymkNo ratings yet
- Author Carson You PBP 5Document9 pagesAuthor Carson You PBP 5api-642869165No ratings yet
- An Efficient Wireless Noc With Congestion-Aware Routing For Multicore ChipsDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Wireless Noc With Congestion-Aware Routing For Multicore ChipsHimanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Wattch: Framework For Architectural-Level Power Analysis and OptimizationsDocument12 pagesWattch: Framework For Architectural-Level Power Analysis and OptimizationsUmekalsoomNo ratings yet
- The Landscape of Parallel Computing Research: A View From BerkeleyDocument56 pagesThe Landscape of Parallel Computing Research: A View From BerkeleyDima LitvinovNo ratings yet
- High Performance Computing in Power System ApplicationsDocument23 pagesHigh Performance Computing in Power System ApplicationsDjalma FalcãoNo ratings yet
- Using The AT89C2051 MCU As Virtual MachineDocument11 pagesUsing The AT89C2051 MCU As Virtual MachineplcmanaNo ratings yet
- ErtosDocument5 pagesErtossachinsomannaNo ratings yet
- Berkeley ViewDocument54 pagesBerkeley Viewshams43No ratings yet
- Compton Hauck RCOverview Paper 2002Document40 pagesCompton Hauck RCOverview Paper 2002PritKitNo ratings yet
- MPPT Using Sepic ConverterDocument109 pagesMPPT Using Sepic ConverterSandhya RevuriNo ratings yet
- Cse.m-ii-Advances in Computer Architecture (12scs23) - NotesDocument213 pagesCse.m-ii-Advances in Computer Architecture (12scs23) - NotesnbprNo ratings yet
- CA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerDocument109 pagesCA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerJagadeesh Mohan100% (1)
- IJREAMV01I12008Document5 pagesIJREAMV01I12008Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Design Techniques For Low Power Systems: Paul J.M. Havinga, Gerard J.M. SmitDocument20 pagesDesign Techniques For Low Power Systems: Paul J.M. Havinga, Gerard J.M. SmitChakita VamshiNo ratings yet
- MIPSDocument6 pagesMIPSsivakumarb92No ratings yet
- Khamis 2013Document8 pagesKhamis 2013Tung MaiNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Main Memory and Secondary MemoryDocument6 pagesDifference Between Main Memory and Secondary Memoryandrapradeshsse100% (1)
- Two Marks CADocument31 pagesTwo Marks CAMr.C.Makesh Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- The Case For The Reduced Instruction Set Computer: David A. PattersonDocument9 pagesThe Case For The Reduced Instruction Set Computer: David A. PattersonSudip Kumar DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Introduction To An Embedded System and ITs Design - Microcontrollers & Embedded SystemsDocument16 pagesChapter 6 - Introduction To An Embedded System and ITs Design - Microcontrollers & Embedded SystemsAmish VermaNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument83 pagesFinal ReportCallme PrinceNo ratings yet
- CCCCCC CDocument60 pagesCCCCCC CSanthan ManneNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation and Architecture AssignmentDocument6 pagesComputer Organisation and Architecture AssignmentLeonNo ratings yet
- Chameleon ChipDocument21 pagesChameleon ChipbiswalsantoshNo ratings yet
- Performance of A ComputerDocument83 pagesPerformance of A ComputerPrakherGuptaNo ratings yet
- Chameleon Chips PresentationDocument24 pagesChameleon Chips Presentationmanojreads100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingFrom EverandFundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient High Performance Processors: Recent Approaches for Designing Green High Performance ComputingFrom EverandEnergy Efficient High Performance Processors: Recent Approaches for Designing Green High Performance ComputingNo ratings yet
- Open-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsFrom EverandOpen-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- High Performance Parallelism Pearls Volume One: Multicore and Many-core Programming ApproachesFrom EverandHigh Performance Parallelism Pearls Volume One: Multicore and Many-core Programming ApproachesNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-236-240Document5 pagesCA Classes-236-240SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture AllClasses-OutlineDocument294 pagesComputer Architecture AllClasses-OutlineSrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-251-255Document5 pagesCA Classes-251-255SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture AllClasses-Outline-1-99Document99 pagesComputer Architecture AllClasses-Outline-1-99SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-261-265Document5 pagesCA Classes-261-265SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture AllClasses-Outline-100-198Document99 pagesComputer Architecture AllClasses-Outline-100-198SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-176-180Document5 pagesCA Classes-176-180SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-201-205Document5 pagesCA Classes-201-205SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-246-250Document5 pagesCA Classes-246-250SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-216-220Document5 pagesCA Classes-216-220SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-221-225Document5 pagesCA Classes-221-225SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-16-20Document5 pagesCA Classes-16-20SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-206-210Document5 pagesCA Classes-206-210SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-196-200Document5 pagesCA Classes-196-200SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-106-110Document5 pagesCA Classes-106-110SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-141-145Document5 pagesCA Classes-141-145SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-186-190Document5 pagesCA Classes-186-190SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-116-120Document5 pagesCA Classes-116-120SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-101-105Document5 pagesCA Classes-101-105SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-121-125Document5 pagesCA Classes-121-125SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-86-90Document5 pagesCA Classes-86-90SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-26-30Document5 pagesCA Classes-26-30SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-36-40Document5 pagesCA Classes-36-40SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-126-130Document5 pagesCA Classes-126-130SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-111-115Document5 pagesCA Classes-111-115SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Programming in C - 161-180Document20 pagesProgramming in C - 161-180SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Programming in C - 216-220Document5 pagesProgramming in C - 216-220SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Programming in C - 21-40Document20 pagesProgramming in C - 21-40SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Programming in C - 121-140Document20 pagesProgramming in C - 121-140SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- Programming in C - 41-60Document20 pagesProgramming in C - 41-60SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- HP All in OneDocument9 pagesHP All in OneSudhir GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document51 pagesChapter 01Larson RogersNo ratings yet
- Arm BookDocument164 pagesArm BookSriramNaiduGorleNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessDocument31 pagesComputer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessADITYA KUMAR0% (2)
- As6installer-6 0 1703-Readme PDFDocument18 pagesAs6installer-6 0 1703-Readme PDFDmitriy GreenNo ratings yet
- COSC 1046 - Computer Science I: Hardware vs. SoftwareDocument10 pagesCOSC 1046 - Computer Science I: Hardware vs. SoftwarecoreyNo ratings yet
- Red Storm Rising Technical Supplement PDFDocument6 pagesRed Storm Rising Technical Supplement PDFMark BallingerNo ratings yet
- PIC16LF1454 5 9 14 20 Pin 8 Bit Flash USB Microcon-1903806Document404 pagesPIC16LF1454 5 9 14 20 Pin 8 Bit Flash USB Microcon-1903806Jalea TerroristaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Hardware Basics - PeripheralsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Hardware Basics - PeripheralsSasurika UchihaNo ratings yet
- Sharp MXM453N Error Codes Free DownloadsDocument8 pagesSharp MXM453N Error Codes Free DownloadsHarry TaNo ratings yet
- OS 2 Threads System CallsDocument9 pagesOS 2 Threads System CallsRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 8086 RegisterDocument3 pages8086 Registerdarwinvargas2011No ratings yet
- c6h Xoc Guide v05Document7 pagesc6h Xoc Guide v05jac1kNo ratings yet
- MP 160 Error CodesDocument2 pagesMP 160 Error CodesCOPIATOR BIZHUBNo ratings yet
- Stc8h1k7 enDocument1,177 pagesStc8h1k7 enGerman PascucciNo ratings yet
- DOC05 Dual Monitor Setup For Work - HP Store SingaporeDocument10 pagesDOC05 Dual Monitor Setup For Work - HP Store SingaporejoselionerNo ratings yet
- The Sparc ArchitectureDocument16 pagesThe Sparc ArchitectureAshwini PatilNo ratings yet
- Inside Computer NotesDocument16 pagesInside Computer NotesDeepali KadamNo ratings yet
- c02 En4442en00enDocument14 pagesc02 En4442en00enAgnes EcsekiNo ratings yet
- Dell PowerEdge 1650 Service ManualDocument83 pagesDell PowerEdge 1650 Service ManualJaviwin2011No ratings yet
- WR Workbench Ocd Ice Hardware Guide 2.3Document116 pagesWR Workbench Ocd Ice Hardware Guide 2.3sweden043No ratings yet
- 5 Cache and Main MemoryDocument15 pages5 Cache and Main MemoryAKASH PAL100% (1)
- Cyrix 6×86-P166+Gp 133Mhz 0.22 Gram Gold: Read MoreDocument3 pagesCyrix 6×86-P166+Gp 133Mhz 0.22 Gram Gold: Read Moretapas_kbNo ratings yet
- Define Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface ModulesDocument15 pagesDefine Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface ModulesSai RamNo ratings yet
- Tap Top.vDocument11 pagesTap Top.vpavithrNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Pixma Mp560Document80 pagesService Manual: Pixma Mp560Mar PopNo ratings yet
- Program Counter of SAP-1 (Computer Architecture and Organization)Document14 pagesProgram Counter of SAP-1 (Computer Architecture and Organization)Waqar TanveerNo ratings yet
- PowerElectronics Class6Document26 pagesPowerElectronics Class6Keyur PatelNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Dan Harga Desktop PC All in One Lenovo Lengkap Terbaru 2018Document2 pagesSpesifikasi Dan Harga Desktop PC All in One Lenovo Lengkap Terbaru 2018Ibe Tee Dua PeeNo ratings yet
- Office of Bids and Awards Committee (BAC) : Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP) Fy 2022Document2 pagesOffice of Bids and Awards Committee (BAC) : Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP) Fy 2022Jayson PalmaNo ratings yet