Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week7 Ch5
Uploaded by
bestniaz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pageswewe a dad
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentwewe a dad
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesWeek7 Ch5
Uploaded by
bestniazwewe a dad
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Lec 13
Ch 5: Bernoulli and Energy Equations
The Bernoulli Equation
It is an approximate relation between pressure, velocity, and elevation.
It is valid in regions of steady, incompressible flow where net frictional
forces are negligible.
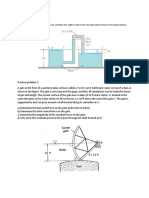
A piezometer and a Pitot tube are tapped into a horizontal water pipe,
to measure static and stagnation (static 1 dynamic) pressures. For the
indicated water column heights, determine the velocity at the center of
the pipe.
GENERAL ENERGY EQUATION
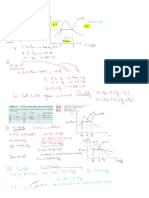
The tank shown in the figiure is being filled with water by two one-
dimensional inlets. Air is trapped at the top of the tank. The water height
is h. (a) Find an expression for the change in water height dh/dt. (b)
Compute dh/dt if D1 = 1 cm, D2 = 3 cm, V1 = 1 m/s, V2 = 2 m/s, and At = 1
m2, assuming water at 20°C.
You might also like
- Mechanical Behavior and Fracture of Engineering Materials PDFDocument253 pagesMechanical Behavior and Fracture of Engineering Materials PDFbestniaz100% (3)
- Mechanical Behavior and Fracture of Engineering Materials PDFDocument253 pagesMechanical Behavior and Fracture of Engineering Materials PDFbestniaz100% (3)
- Physics Investigatory Project: Bernoulli'S TheoremDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Bernoulli'S TheoremSriram JNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 11Document18 pagesPhysics Project Class 11Aarya Rajesh71% (55)
- Chapter 7 Permeability Hydraulic ConductivityDocument73 pagesChapter 7 Permeability Hydraulic Conductivityjoemer cabayaoNo ratings yet
- Flow of Water Through SoilsDocument11 pagesFlow of Water Through SoilsRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Steel Mils in PakistanDocument9 pagesSteel Mils in Pakistanbestniaz100% (3)
- Experiment 1 - Friction Losses in Pipes-ReportDocument41 pagesExperiment 1 - Friction Losses in Pipes-ReportKhairil Ikram68% (53)
- Chapter 2 Inviscid Flow and Bernoulli Equation - StudentsDocument35 pagesChapter 2 Inviscid Flow and Bernoulli Equation - StudentsMERSYA NABILA100% (1)
- Hydraulic CalculationsDocument18 pagesHydraulic Calculationsnike_y2k100% (1)
- Fluid Dynamics1Document34 pagesFluid Dynamics1Buddhi Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- BernoulliDocument27 pagesBernoulliAcademic Cell - OLC CIPET AhmedabadNo ratings yet
- Giambattista Real FluidsDocument20 pagesGiambattista Real FluidscalmyourmindwithmusicNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics, Pumps & Water SuppliesDocument170 pagesHydraulics, Pumps & Water Suppliesmokshaq7No ratings yet
- Demonstration of Bernoulli's EquationDocument27 pagesDemonstration of Bernoulli's Equationmahbub1332100% (5)
- Transient Mass Transfer: Lecture T1Document12 pagesTransient Mass Transfer: Lecture T1Jimmy GranjaNo ratings yet
- Handout Minggu 14 PBGN 611 Mektan - Flow NetDocument56 pagesHandout Minggu 14 PBGN 611 Mektan - Flow NetIkeNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Pressure DWFSOM147Document4 pagesHydraulics Pressure DWFSOM147p kishorNo ratings yet
- Ewert 2018Document23 pagesEwert 2018wily784No ratings yet
- Fund of Hydr - PressureDocument4 pagesFund of Hydr - PressuresantoshNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics ExerciseDocument5 pagesFluid Statics ExercisechitooNo ratings yet
- Project Festus 2Document17 pagesProject Festus 2samuelhmar170No ratings yet
- Cve 305 - 5,6Document22 pagesCve 305 - 5,6mohammed adoNo ratings yet
- Topic Time Frame: 9 Hours: Learning ModuleDocument13 pagesTopic Time Frame: 9 Hours: Learning ModuleJea Escabal MosenabreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document6 pagesLecture 10Muhammad Sameer NawazNo ratings yet
- Notes Part A - Pipes and Pipe SystemsDocument44 pagesNotes Part A - Pipes and Pipe SystemsProfessor GobozaNo ratings yet
- Law of FlowDocument7 pagesLaw of FlowYasir AliNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lect 5 Fall 2023Document27 pagesFluid Mechanics Lect 5 Fall 2023Dr.Ebrahim AboueleynanNo ratings yet
- Fluid 1Document40 pagesFluid 1NateNo ratings yet
- Research No 2Document14 pagesResearch No 2Mahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- 8 Internal Flow-Forced Convection PDFDocument52 pages8 Internal Flow-Forced Convection PDFNavarre LatchmanNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Chapter 3 PDFDocument45 pagesBernoulli Chapter 3 PDFMirrovshan Sagdullaev100% (1)
- Bernoullie Theorm Lab ReportDocument5 pagesBernoullie Theorm Lab ReportBasant Sharma100% (1)
- Q Cie VZ1 ZN HAg Yx 08 P 365Document8 pagesQ Cie VZ1 ZN HAg Yx 08 P 365aavaathebestNo ratings yet
- City and Guilds 9210 UNIT 103 Hydraulics and Hydrology Level 6 Tutorial 1 - Pipe FlowDocument36 pagesCity and Guilds 9210 UNIT 103 Hydraulics and Hydrology Level 6 Tutorial 1 - Pipe Flowdipesh100% (1)
- Lab Guide - PipesDocument29 pagesLab Guide - PipesBonifacioNo ratings yet
- Modelling of HydroDocument9 pagesModelling of HydroMuhammad UzairNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 11Document18 pagesPhysics Project Class 11NhjghkkkNo ratings yet
- FRICTIONALDocument13 pagesFRICTIONALCleraNo ratings yet
- CE372 Midterm BlankDocument7 pagesCE372 Midterm BlankAsad YousafNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions DR YuanDocument5 pagesPractice Questions DR YuanSteven KuaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics, Bernoulli's Principle and Equation of ContinuityDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics, Bernoulli's Principle and Equation of ContinuitySheerin SulthanaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Chapter 3Document45 pagesBernoulli Chapter 3Izzudin HusseinNo ratings yet
- Density, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, and Specific GravityDocument11 pagesDensity, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, and Specific GravitycristyryeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Open Channel FlowDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Open Channel FlowJemelsonAlutNo ratings yet
- Objective of The ExperimentDocument3 pagesObjective of The ExperimentYousef SailiniNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law BasicsDocument13 pagesDarcy's Law BasicsHarsh BhattNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli ExperimentDocument7 pagesBernoulli ExperimentAbstergo KingslayNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument20 pagesFluid DynamicsMohammad Zunaied Bin Harun, Lecturer , CEENo ratings yet
- Hydraulic HeadDocument4 pagesHydraulic HeadJhansi Lakshmi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - HydrodynamicsDocument10 pagesAssignment 4 - HydrodynamicsluluNo ratings yet
- Water in SoilsDocument25 pagesWater in SoilsNicholas VineyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic RamDocument5 pagesHydraulic RamAbdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Ideal FlowDocument30 pagesIdeal FlowCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Ce 322-15 Module 7 - Permeability of SoilsDocument10 pagesCe 322-15 Module 7 - Permeability of SoilsBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- 流體力學Document30 pages流體力學sonkuas100% (1)
- Topic 3Document54 pagesTopic 3HCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Permeability Hydraulic ConductivityDocument65 pagesChapter 7 - Permeability Hydraulic ConductivityforsheeshuwuNo ratings yet
- Bernaulli's Theorem FullDocument17 pagesBernaulli's Theorem FullBart KwanNo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationGuilhem BourrieNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetbestniazNo ratings yet
- Fluid Ass2,3Document9 pagesFluid Ass2,3bestniazNo ratings yet
- Week7 - IDocument2 pagesWeek7 - IbestniazNo ratings yet
- Update On Community Service 7 Dec 2020Document28 pagesUpdate On Community Service 7 Dec 2020bestniazNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document5 pagesLec 4bestniazNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Thermodynamic TablesDocument1 pageAssignment 2 Thermodynamic TablesbestniazNo ratings yet
- ISVIV2020Document2 pagesISVIV2020bestniazNo ratings yet
- Assignment Using EES SoftwareDocument1 pageAssignment Using EES SoftwarebestniazNo ratings yet
- Personal Bond Refund FormDocument2 pagesPersonal Bond Refund FormbestniazNo ratings yet
- HEC Advance Countries ListDocument2 pagesHEC Advance Countries Listbestniaz100% (2)
- Construction Steel2017 BrochureDocument9 pagesConstruction Steel2017 BrochurebestniazNo ratings yet
- HEC Advance Countries ListDocument2 pagesHEC Advance Countries Listbestniaz100% (2)
- Riser VIV and Its Numerical Simulation: Kevin HuangDocument6 pagesRiser VIV and Its Numerical Simulation: Kevin HuangbestniazNo ratings yet
- Fluent Tutorial Sites GHGDocument1 pageFluent Tutorial Sites GHGbestniazNo ratings yet
- Journal of Management 2014 Gonzalez Mulé 0149206314535443Document16 pagesJournal of Management 2014 Gonzalez Mulé 0149206314535443bestniazNo ratings yet