Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midpoint & Bridge Rectifier
Midpoint & Bridge Rectifier
Uploaded by
sushil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMidpoint & Bridge Rectifier
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMidpoint & Bridge Rectifier
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMidpoint & Bridge Rectifier
Midpoint & Bridge Rectifier
Uploaded by
sushilMidpoint & Bridge Rectifier
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
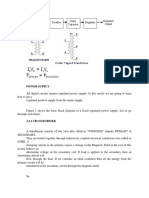
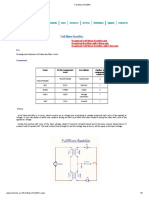
Factors Center tapped full wave rectifier Bridge rectifier
Center tapped rectifier as the name suggests
requires a center tapped transformer No center tapped transformer is required in a
Definition
(secondary winding). bridged rectifier.
Center tapped rectifier uses only two diodes
Number of diodes in its circuit. Bridge rectifier uses four diodes in its circuit.
The peak inverse voltage (PIV) of the diode
Peak inverse voltage PIV of the diode is equal
in the center tapped full wave rectifier is
to the transformer secondary voltage. Thus this
Peak inverse voltage twice the transformer secondary terminal
type of rectifier can be used for high voltage
voltage.
application.
Transformer The transformer utilization factor (TUF) is
The transformer utilization factor (TUF) is
Utilization Factor equal to 0.672
equal to 0.810 for the bridge rectifier.
(TUF)
Voltage drop across the two diodes of the The voltage drop across the 4 diodes of the
Voltage drop across
center tapped rectifier is less when bridge rectifier is more than the voltage drop
diodes
compared to bridge rectifier. across the center tapped rectifier.
The transformer required in the bridge
rectifier is smaller than that required in the The transformer required in the bridge rectifier
Size Of Transformer center tapped rectifier in terms of kVA is smaller than that required in the center
rating. tapped rectifier in terms of kVA rating.
Center tapped transformer is economically
efficient since it uses only two diodes in its Bridge rectifier is economically inefficient
Economic efficiency
circuit. since it uses four diodes in its circuit.
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Lecture On Power SupplyDocument81 pagesLecture On Power SupplyMATE0100% (2)
- Transducer and Their ResponseDocument53 pagesTransducer and Their Responseabuki bekriNo ratings yet
- Calculation 3DG-E34E General Information About Calculation On Electrical SystemDocument23 pagesCalculation 3DG-E34E General Information About Calculation On Electrical Systemmohammadkassar100% (1)
- DC Motor Direction Control Using Power TriacDocument7 pagesDC Motor Direction Control Using Power TriacAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Bridge RectifierDocument27 pagesBridge Rectifiergirishkumardarisi254100% (1)
- GPS Tracking System Project ReportDocument65 pagesGPS Tracking System Project Reportsumitsonkar199091% (23)
- 37 SENSOR KIT TUTORIAL FOR UNO AND MEGA v1.0 PDFDocument194 pages37 SENSOR KIT TUTORIAL FOR UNO AND MEGA v1.0 PDFChristian Bautista ChamorroNo ratings yet
- Level PresentationDocument38 pagesLevel PresentationFredrick Otieno100% (1)
- Full Wave Rectifier: AC Current DC Current DiodeDocument5 pagesFull Wave Rectifier: AC Current DC Current DiodeAlexo ManNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument17 pagesINTRODUCTIONPRASHANTNo ratings yet
- Bs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P1Document10 pagesBs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P1Bushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Fullwave RectifiersDocument27 pagesFullwave RectifiersSanjyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7-Fullwave RectifiersDocument27 pagesLecture 7-Fullwave RectifiersSanjyoti DasNo ratings yet
- VIVA Question-RectifierDocument3 pagesVIVA Question-RectifierMaheswariRVNo ratings yet
- 4 2 PDFDocument32 pages4 2 PDFAkoto BlessNo ratings yet
- PN Junction HW and FWDocument15 pagesPN Junction HW and FWSHIVANSH SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Half Wave & Full Wave RectifiersDocument19 pagesHalf Wave & Full Wave RectifiersRNKNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers: Alternating Current (AC) To Direct Current (DC)Document20 pagesRectifiers: Alternating Current (AC) To Direct Current (DC)Golu SinghNo ratings yet
- Rectification by FilterDocument9 pagesRectification by Filteratta ul mominNo ratings yet
- What Is Half Wave Rectifier DeepuDocument15 pagesWhat Is Half Wave Rectifier Deepuharshvardhan singhNo ratings yet
- Psu PDFDocument75 pagesPsu PDFJhoanna DacatimbangNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument14 pagesHalf Wave RectifierSanjyoti DasNo ratings yet
- A Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentDocument9 pagesA Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentKaran SoniNo ratings yet
- Reectifiers ArjunDocument18 pagesReectifiers Arjunpragya gulatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Application of DiodesDocument35 pagesUnit 2-Application of DiodesradsradNo ratings yet
- Basic-Electronics (Rectifier) !Document30 pagesBasic-Electronics (Rectifier) !Rahim AnsariNo ratings yet
- Analog Module 2-Rectifiers PPTDocument35 pagesAnalog Module 2-Rectifiers PPTsanjit0907_982377739No ratings yet
- NAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034Document22 pagesNAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034BARUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Advantages, Disadvantages of Full Wave Center Tapped and Bridge RectifierDocument1 pageAdvantages, Disadvantages of Full Wave Center Tapped and Bridge RectifierSIAM AL MUJADDEDNo ratings yet
- RECTIFIERDocument15 pagesRECTIFIERAni AniNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave RectifierMurali Krishna GbNo ratings yet
- Tripura Institute of Technology: A Presentation OnDocument17 pagesTripura Institute of Technology: A Presentation OnsridharchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology: RectifiersDocument6 pagesElectrical Technology: RectifiersgefegNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers, Filters and RegulatoDocument12 pagesRectifiers, Filters and Regulatono.1slytherinprincessNo ratings yet
- Working of Pi filter (π-filter)Document11 pagesWorking of Pi filter (π-filter)Joseph B Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Welcome To My PresentationDocument19 pagesWelcome To My PresentationShaileshNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesRectifiers Questions and AnswersSuresh LNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument7 pagesFull Wave RectifierArun PratapNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument16 pagesRectifiersJaiom JoshiNo ratings yet
- Applications of Diode: Aditya Kumar CS-CDocument11 pagesApplications of Diode: Aditya Kumar CS-CsteelnervesNo ratings yet
- Elec 435 Electronics I: Rectifier CircuitsDocument14 pagesElec 435 Electronics I: Rectifier CircuitsRia HarshadNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Circuit With WorkingDocument8 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Circuit With WorkingKaran SoniNo ratings yet
- P N Junction DiodeDocument3 pagesP N Junction DiodeAsogwa ChinazaNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Analysis of Switching Performance of Boost ConverterDocument6 pagesInvestigation and Analysis of Switching Performance of Boost ConvertererpublicationNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifierutkarsh devNo ratings yet
- Subject: DC Machine & TransformerDocument48 pagesSubject: DC Machine & TransformerAngamuthu AnanthNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 and 10 - Half and Full Wave RectifiersDocument5 pagesLab 9 and 10 - Half and Full Wave RectifiershamzaNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument26 pagesRectifierhemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Bs-El-344 - Lecture-04 - P3Document14 pagesBs-El-344 - Lecture-04 - P3Bushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 4 Half Wave Rectifier Pre - Lab QuestionsDocument8 pagesExperiment - 4 Half Wave Rectifier Pre - Lab Questionsgautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Diode and Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument16 pagesDiode and Uncontrolled Rectifierssai krishnaNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument52 pagesRectifiersKALA H SNo ratings yet
- Bridge RectifierDocument4 pagesBridge Rectifierropef82117No ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument36 pagesBasic Electronicswhatsapp status clipsNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument10 pagesRectifiersjipaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Full Wave TheoryDocument6 pagesFull Wave Theorypunjabe2004No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Fullwave RectifierDocument27 pagesLecture 2 Fullwave Rectifieryashrajsinghtomar918No ratings yet
- Diode ApproximationDocument35 pagesDiode ApproximationVimala ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument13 pagesFull Wave RectifierSundar RajanNo ratings yet
- Eet 06206 HandoutDocument40 pagesEet 06206 HandoutMohammed ShabanNo ratings yet
- ECE132: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Lab: Experiment 6Document24 pagesECE132: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Lab: Experiment 6Amit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-2:: AC-DC Single Phase ConvertersDocument41 pagesUnit-2:: AC-DC Single Phase ConvertersYendamuri ManjunadhNo ratings yet
- In-Process FormatDocument5 pagesIn-Process Formatsantosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Lighting Lighting: Ecofit Ledtubes T8Document4 pagesLighting Lighting: Ecofit Ledtubes T8Nestor Fortunato Lopez VargasNo ratings yet
- محاضرة فيزياء 1Document17 pagesمحاضرة فيزياء 1m26292391No ratings yet
- Service Manual: TFT LCD Monitor Model: L500BDocument37 pagesService Manual: TFT LCD Monitor Model: L500BcondejhonnyNo ratings yet
- Molded Case Circuit Breakers: FD 250A Frame Sentron SeriesDocument2 pagesMolded Case Circuit Breakers: FD 250A Frame Sentron Seriesabsolutvacio82No ratings yet
- Aditya-L1 Mission: S. Seetha and S. MegalaDocument3 pagesAditya-L1 Mission: S. Seetha and S. MegalaJyoti YadavNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument21 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentPankaj AttriNo ratings yet
- Led Canopy Light Generation 2 - VENAS-2022Document2 pagesLed Canopy Light Generation 2 - VENAS-2022Johana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Ata 33 LightsDocument141 pagesAta 33 LightsAvtech100% (1)
- Sychronous Type Overview 4 Pole Models: Basic - TypesDocument2 pagesSychronous Type Overview 4 Pole Models: Basic - TypesRichard Leo MoroniNo ratings yet
- Function of U1 CA555Document7 pagesFunction of U1 CA555sjnl100% (1)
- Symmetry & Space GroupsDocument49 pagesSymmetry & Space GroupsfaysaljamilNo ratings yet
- Handbook of II-VI Semiconductor-Based Sensors and Radiation DetectorsDocument527 pagesHandbook of II-VI Semiconductor-Based Sensors and Radiation DetectorsprvthesapNo ratings yet
- Product PS-p36: Multi-Crystalline ModuleDocument2 pagesProduct PS-p36: Multi-Crystalline ModuleAmmar Bany AtaNo ratings yet
- Table Kara New1Document3 pagesTable Kara New1mahmoud abd alazezNo ratings yet
- 2019-MC-01 Lab Report #1 (11 Files Merged)Document43 pages2019-MC-01 Lab Report #1 (11 Files Merged)Muhammad Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy LogicDocument9 pagesFuzzy LogicrakeshNo ratings yet
- TLWG Objective Type QnsDocument7 pagesTLWG Objective Type QnsDolianNo ratings yet
- B. Podor - Temperature Scaling in The Integer Quantum Hall Effect Regime: ExperimentsDocument9 pagesB. Podor - Temperature Scaling in The Integer Quantum Hall Effect Regime: ExperimentsGreamxxNo ratings yet
- Manual Switch de Flujo Duchas EmergenciaDocument4 pagesManual Switch de Flujo Duchas EmergenciaSantiago YánezNo ratings yet
- EEET2254 Lecture 2Document48 pagesEEET2254 Lecture 2Kashka Irani100% (1)
- 11 CSS Module Week 4Document8 pages11 CSS Module Week 4Alexander IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Auto Start Module With Can Bus J1939 Protocol - Smart-Can: FeaturesDocument2 pagesAuto Start Module With Can Bus J1939 Protocol - Smart-Can: FeaturesSimba WahyudiNo ratings yet
- JVC RXE 111 RSL Service ManualDocument54 pagesJVC RXE 111 RSL Service ManualPE TruNo ratings yet
- F864 LED Medium Intensity Obstruction Light - Datasheet - v202008v2Document2 pagesF864 LED Medium Intensity Obstruction Light - Datasheet - v202008v2REDDOT SIGNALNo ratings yet