Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Specialised Animal Cells - Living Organisms - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC Bitesize
Uploaded by
sparkle.comic-0kOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Specialised Animal Cells - Living Organisms - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC Bitesize
Uploaded by
sparkle.comic-0kCopyright:
Available Formats
Sign in Home News Sport Reel Worklife Tr)vel Future
BITESIZE Ch)nge l)ngu)ge
Home Le)rn Support C)reers My Bitesize All Bitesize
KS3
Speci)lised )nim)l cells
P:rt of Biology Living org)nisms
Add to My Bitesize
Jump to
Key points
Key points
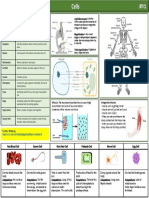
Speci:lised :nim:l cells h:ve components th:t :llow them to complete :
Video - Wh)t )re specific purpose.
speci)lised )nim)l Speci:lised :nim:l cells include red blood cells, sperm, eggs, nerve cells,
cells?
muscle cells, cili:ted cells, :nd villi.
Red blood cells
Sperm cells
Egg cell
Nerve cells Video - Wh)t )re speci)lised )nim)l cells?
Muscle cells
Video - Underst)nding
muscle cells
Cili)ted cells
Villi
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
Video Transcript
C:n you :nswer these questions b:sed on the video?
1. Wh)t )re the three m)in components of )nim)l cells?
2. How m)ny )nim)l cells could fit )cross the width of ) full stop?
Show more
Most cells sh:re fe:tures such :s h:ving : nucleus, : cell membr:ne,
cytopl:sm :nd mitochondri:.
E:ch type of cell h:s its own job to do. These cells h:ve speci:l fe:tures th:t
:llow them to perform their functions effectively.
Red blood cells
Red blood cells c:rry oxygen :round the body, which is needed for
respir)tion. They :re well suited to this function bec:use:
They cont:in h)emoglobin , which c:rries oxygen molecules.
They don't h:ve : nucleus, :llowing more sp:ce to c:rry oxygen.
They :re : fl:t disc sh:pe with dips on both sides (biconc:ve). This gives
them : l:rge surf:ce :re:, :nd the best ch:nce of :bsorbing :s much
oxygen :s they c:n in the lungs.
Sperm cells
Sperm :re the m:le sex cell. They :re m:de in the testes :Ner puberty . They
join with :n egg cell during fertilis)tion to form :n embryo which c:n then
develop into : new life. The following fe:tures m:ke them well suited to this
function:
A t:il moves them tow:rds :n egg cell.
M:ny mitochondri) rele:se energy for movement.
P:rt of the tip of the he:d of the sperm, c:lled the :crosome, rele:ses
enzymes to digest the egg membr:ne to :llow fertilis:tion to t:ke pl:ce.
The h)ploid nucleus cont:ins the genetic m:teri:l for fertilis:tion.
Sperm :re produced in l:rge numbers to incre:se the ch:nce of
fertilis:tion.
Egg cell
Eggs :re the fem:le sex cell. They :re m:de in the ov:ries before birth.
Usu:lly, one egg is rele:sed e:ch month during the menstru:l cycle, but
sometimes this number m:y be higher. They join with : sperm cell during
fertilis:tion to form :n embryo which c:n then develop into : new life. They
:re well suited to this function bec:use:
The egg cell’s cytopl:sm cont:ins nutrients for the growth of the e:rly
embryo.
The h:ploid nucleus cont:ins genetic m:teri:l for fertilis:tion.
The cell membr)ne ch:nges :Ner fertilis:tion by : single sperm so th:t no
more sperm c:n enter.
Nerve cells
Nerve cells tr:nsmit electric:l sign:ls in the nervous system . They :re well
suited to their function bec:use:
They :re thin, :nd c:n be more th:n one metre long in your spin:l cord.
This me:ns they c:n c:rry mess:ges up :nd down the body over l:rge
dist:nces very quickly.
Nerve cells h:ve br:nched connections :t e:ch end. These join to other
nerve cells, :llowing them to p:ss mess:ges :round the body.
They h:ve : f:tty (myelin) she:th th:t surrounds them. The f:tty she:th
incre:ses the speed :t which the mess:ge c:n tr:vel.
Muscle cells
Muscles cells :re found in bundles which m:ke up our muscles. These cells
:re :ble to contr:ct (get shorter) :nd rel:x (return to origin:l length). There
:re different types of muscle cell, e:ch perfectly :d:pted to its function:
C:rdi:c (he:rt) muscle cells contr:ct :nd rel:x to pump blood :round our
bodies for our entire lives. They never get tired.
Smooth muscle cells m:ke up thin sheets of muscle, such :s the stom:ch
lining. They c:n :lso be :rr:nged in bundles, or rings, like th:t in the :nus.
Skelet:l muscle is joined to bones. Its cells contr:ct to m:ke bones move
:nd joints bend.
Video - Underst)nding muscle cells
Find out how : sports ther:pist uses his knowledge of speci:lised cells to help his clients
Video Transcript
Cili)ted cells
Cili:ted cells :re found in the
:irw:ys. They h:ve tiny h:irs
on their tops c:lled cili)
which be:t in : rhythm.
These h:irs move mucus
cont:ining dust :nd other
p:rticles upw:rds :nd out of
the :irw:ys. Cili:ted cells :re
:lso found in the oviducts .
Here the tiny h:irs be:t to
move the egg from the ov:ries to the uterus .
Villi
Villi :re structures :bout one
millimetre long in the sm)ll
:nd l)rge intestines .
Millions of them poke out to
:bsorb digested food :nd
w:ter into the blood. They
:re well suited to this
function bec:use:
They h:ve : l:rge surf:ce
:re:.
They h:ve thin w:lls which
:re only one cell thick.
The cells of the lining h:ve tiny h:irs to :bsorb more food :nd w:ter.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
GI
F
Specialised animal cells
Test your knowledge in this multiple-choice quiz.
Start
Some of your information will be collected when you play this quiz.
Terms & Conditions
Test questions
Wh)t )re the )d)pt)tions of red blood cells?
Show )nswer
Wh)t )re the )d)pt)tions of nerve cells?
Show )nswer
Atomic L)bs g)me
Try out pr:ctic:l experiments in this KS3 science g:me
Living org)nisms
Build on your knowledge with these guides.
You're here
Speci)lised )nim)l Speci)lised pl)nt cells The four components
Anim)l )nd pl)nt cells
cells of the blood
1 of 15 2 of 15 3 of 15 4 of 15
Up next
Speci:lised pl:nt cells
Explore the BBC
Home News Sport Reel Worklife Tr)vel
Future Culture TV We)ther Sounds
Terms of Use About the BBC Priv:cy Policy Cookies Accessibility Help P:rent:l Guid:nce Cont:ct the BBC BBC em:ils for you
Advertise with us
Copyright © 2023 BBC. The BBC is not responsible for the content of extern:l sites. Re)d )bout our )ppro)ch to extern)l linking.
You might also like
- Human Body WorkbookDocument25 pagesHuman Body Workbookjk centralNo ratings yet
- Cell Notes Class 9Document18 pagesCell Notes Class 9Anshu DashNo ratings yet
- Cell To BiosphereDocument38 pagesCell To BiospherezaiNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: LG4: Understand Cells' Role in Living Things and HeredityDocument43 pagesCell Division: LG4: Understand Cells' Role in Living Things and HeredityBayne ReyesNo ratings yet
- CLASS 9 SCIENCE HANDWRITTEN NOTES Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument30 pagesCLASS 9 SCIENCE HANDWRITTEN NOTES Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Lifeaaravarora301050% (2)
- The Evolution of ManDocument695 pagesThe Evolution of ManJeanJames KöningNo ratings yet
- Tema 1 Natural ScienceDocument7 pagesTema 1 Natural ScienceCristina TorrenoNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 1 - Cell TheoryDocument22 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 1 - Cell TheoryEmer PerezNo ratings yet
- The Kidney - Hansel Et Al. - 1 Ed. (2016) - enDocument218 pagesThe Kidney - Hansel Et Al. - 1 Ed. (2016) - enDuda EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic SystemDocument86 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic Systemahmed elsebaeyNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Resources Natural Science 5Document120 pagesTeacher's Resources Natural Science 5nostrabubu57% (7)
- Cell Division: How Do You Grow From A Where Do TheDocument32 pagesCell Division: How Do You Grow From A Where Do Theaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Cell Division Fall 2022Document11 pagesLab 2 Cell Division Fall 2022Paridhi TiwariNo ratings yet
- IntroducingStemCellsFINAL Jan2012Document34 pagesIntroducingStemCellsFINAL Jan2012realalinorouziNo ratings yet
- Ficha 5 SM InglesDocument69 pagesFicha 5 SM InglesCarmenMartinNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Reproduction 1 ParteDocument13 pagesUnit3 Reproduction 1 ParteBegoña García AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 Flatworms NoblanksDocument27 pagesLecture6 Flatworms NoblanksRen StudyNo ratings yet
- C Ell Divis IonDocument38 pagesC Ell Divis IonPeter ChristianNo ratings yet
- Cell SpecialisationDocument2 pagesCell SpecialisationJenice WhiteNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Tumbuhan 02-DikonversiDocument49 pagesFisiologi Tumbuhan 02-DikonversiRatih AyuNo ratings yet
- Biology (Topic 1) PowerpointDocument23 pagesBiology (Topic 1) Powerpoint18hollickmNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1Azeem FaizalNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Science (E) CellDocument5 pagesGrade 10 - Science (E) Cellchamath p.s.a.d amakaraNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDocument30 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosischristian josh magtarayoNo ratings yet
- Specialised Animal Cells - Living Organisms - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC BitesizeDocument8 pagesSpecialised Animal Cells - Living Organisms - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC BitesizeMonica AdamoNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Class IxDocument46 pagesAnimal Tissues: Class IxDHARSHAN BOOPALANNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Cell TheoryDocument38 pages1 1 Cell TheorySaiam ShahNo ratings yet
- Biology CellsDocument1 pageBiology CellsJo PatrickNo ratings yet
- Scientist Behind The Cell TheoryDocument20 pagesScientist Behind The Cell TheoryBERNA MAE TAMAYONo ratings yet
- S1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationDocument19 pagesS1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationANGELA HO SHU YEANNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Living UnitsDocument49 pagesCells: The Living UnitsaranNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Zoology-Qb-Ch-3-Structural Organisation-NavasDocument9 pagesHsslive-Xi-Zoology-Qb-Ch-3-Structural Organisation-Navasashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- S4en Biology Chapter 1Document59 pagesS4en Biology Chapter 1MeharNo ratings yet
- Mitosis-And-Meiosis-Ppt 7781Document30 pagesMitosis-And-Meiosis-Ppt 7781zhao YingingNo ratings yet
- Biology - Human ReproductionDocument21 pagesBiology - Human Reproductionsgw67No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument6 pagesGeneral BiologywellingtotakeNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Gas Exchange System - Respiration and Gas Exchange - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC BitesizeDocument1 pageStructure and Function of The Gas Exchange System - Respiration and Gas Exchange - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC BitesizewatchmakerparikshitNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis1Document45 pagesCell Division Mitosis1Rafael LabradorNo ratings yet
- BTEC Exam Revision BookletsDocument21 pagesBTEC Exam Revision BookletsMahmoud FawzyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeTownship TownshipNo ratings yet
- Set 4 SBL100 Stems Cells 15nov2023Document65 pagesSet 4 SBL100 Stems Cells 15nov2023dandotiya.yash73No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction ReviewDocument12 pagesHuman Reproduction ReviewMokYikLamNo ratings yet
- Captura de Pantalla 2023-05-15 A La(s) 21.40.59Document82 pagesCaptura de Pantalla 2023-05-15 A La(s) 21.40.59Valeria MorenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Skletal SisitemDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Skletal SisitemAnis PuadahNo ratings yet
- S1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationDocument21 pagesS1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationANGELA HO SHU YEANNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Life Science Remote Learning BookletDocument57 pagesTerm 3 Life Science Remote Learning BookletAgrarianNo ratings yet
- Sci Nervous and Endocrine RVWRDocument5 pagesSci Nervous and Endocrine RVWRNhovie Claire FlorencioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5ingridvirginia2006No ratings yet
- 2 Boore - The Human CellDocument27 pages2 Boore - The Human Cellمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Unit 7A Cells: The Body's Building Bricks: Name: .Document15 pagesUnit 7A Cells: The Body's Building Bricks: Name: .irene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis 02152018Document31 pagesMitosis and Meiosis 02152018Marta SzczykutowiczNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesAKSHAJ AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System WorksheetDocument7 pagesSkeletal System Worksheet마스러버No ratings yet
- ResPaper ICSE BIOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESDocument24 pagesResPaper ICSE BIOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESBharati GulajkarNo ratings yet
- 14 1 Cell TheoryDocument12 pages14 1 Cell TheorycinsssNo ratings yet
- Cells Revision L02 HLDocument17 pagesCells Revision L02 HLJhanvi ParekhNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis SheetDocument4 pagesMitosis & Meiosis SheetJoly Ann GesmanNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@glia 23643Document13 pages10 1002@glia 23643rishabh sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 IB Cell TheoryDocument32 pages1.1 IB Cell TheoryVenya NaiduNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide Introduction To BodyDocument3 pagesLearning Guide Introduction To BodyAutumn ReadNo ratings yet
- Relab Term 3Document57 pagesRelab Term 3Nqobile NjokoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal & Postnatal GrowthDocument85 pagesPrenatal & Postnatal GrowthShreyaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science IVellesig navaretteNo ratings yet
- Frog ALL SYSTEMS-1Document85 pagesFrog ALL SYSTEMS-1Ranjeet PandeyNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz 2Document4 pagesScience Quiz 2xandra joy abadezaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument91 pagesConnective TissueSamuel ArikodNo ratings yet
- Large Leaves Have A Large Surface Area, Which Would Allow Them To AbsorbDocument5 pagesLarge Leaves Have A Large Surface Area, Which Would Allow Them To AbsorbKeziah VenturaNo ratings yet
- BAMS First YearDocument19 pagesBAMS First Yearsahajanand ThakorNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument18 pagesHistologyGlavinorNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy Using CTDocument39 pagesCardiac Anatomy Using CTDyah KumalasariNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument41 pagesMuscular SystemGem Rose UretaNo ratings yet
- ST Joseph's Institution (Senior School) IBDP1 HL Biology PracticalDocument5 pagesST Joseph's Institution (Senior School) IBDP1 HL Biology PracticalSean NgNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Muscular SystemYOPO KITZ ANGELONo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22Document5 pagesHISTOLOGY 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22Anas HanifNo ratings yet
- Development of Male Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesDevelopment of Male Reproductive SystemOgunsusi DamilolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology Week 8 Lesson 2 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Biology Week 8 Lesson 2 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsAva HoNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemsDocument3 pagesPlant Tissue Systemselizabeth shaw gonzalez100% (1)
- Permanent TissuesDocument16 pagesPermanent TissuesRiyashika RNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System 101 Guided Notes 2Document3 pagesCardiovascular System 101 Guided Notes 2airihatsune21No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesLecture 5 The Respiratory Systemmido_20067581No ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Manual Semester 4Document2 pagesPharmacognosy Manual Semester 4Xee JayNo ratings yet
- Unit 3, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument27 pagesUnit 3, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell Pharmadeekshigowda07No ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument36 pagesConnective TissueSalman NaseebNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology LAB REPORT XDocument5 pagesPlant Physiology LAB REPORT XBoyd benson kayomboNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY Trans PELVIS POST ABDOMINAL WALL PERINEUMDocument8 pagesANATOMY Trans PELVIS POST ABDOMINAL WALL PERINEUMSan LapuhapuNo ratings yet
- Development of VoiceDocument11 pagesDevelopment of Voiceprathamesh patilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Transport in Vascular PlantDocument35 pagesChapter 11 - Transport in Vascular PlantMASYITAH MOHD PADZILNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesMale Reproductive System金 Abigail RodriguezNo ratings yet