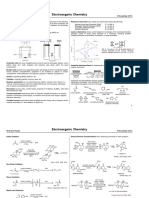
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structure and Function of The Gas Exchange System - Respiration and Gas Exchange - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC Bitesize
Uploaded by
watchmakerparikshitOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structure and Function of The Gas Exchange System - Respiration and Gas Exchange - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC Bitesize
Uploaded by
watchmakerparikshitCopyright:
Available Formats
Sign in News Sport Reel Worklife Tr$vel Future Culture More Se$rch Bitesize
Bitesize Ch$nge l$ngu$ge
Home Le$rn Support C$reers My Bitesize All Bitesize
KS3
Structure $nd function of the
g$s exch$nge system
P:rt of Biology Respir$tion $nd g$s exch$nge
Add to My Bitesize
Jump to
Key points
Key points
There :re three m:in g:ses in :ir th:t :re t:ken in :nd removed from the
Bre$thing, respir$tion body. These :re oxygen, nitrogen :nd c:rbon dioxide.
$nd g$s exch$nge G:s exch:nge is the ‘sw:pping’ of g:sses - :bsorbing oxygen into the blood
Function :nd removing c:rbon dioxide from the blood.
Structure Diffusion moves oxygen out of the :lveoli :nd into the blood.
How does oxygen tr$vel
into blood?
Alveoli
How $re the $lveoli Bre$thing, respir$tion $nd g$s exch$nge
$d$pted for g$s
exch$nge?
Inh:l:tion :nd exh:l:tion is the s:me :s
Ventil$tion bre:thing or ventil:tion :nd is :
physic:l process which moves :ir into
Respir$tion :nd out of your lungs.
Test your knowledge Respir:tion is not the s:me :s
bre:thing, :nd is : chemic:l process
Quiz
which occurs in :ll of your cells.
Test question G:s exch:nge is : process th:t involves the sw:pping of g:ses th:t occurs
:t exch:nge surf:ces such :s the :lveoli found within your lungs.
Function of the g$s exch$nge system
G:s exch:nge :llows oxygen to tr:vel into your cells for respir:tion whilst
:lso removing c:rbon dioxide, which is : w:ste subst:nce m:de by the
process of respir:tion. Respir:tion is : vit:l process th:t involves rele:sing
energy from glucose. All living things do this to st:y :live.
Structure of the g$s exch$nge system
The g:s exch:nge system is m:de from key p:rts, e:ch of which h:s :
different function.
P$rt of the
g$s
Function
exch$nge
system
This is :lso c:lled the windpipe. This tube runs from the
Tr$che$ mouth, down the thro:t tow:rds the lungs. It is lined with
rings of c$rtil$ge which keep it open :t :ll times.
The tr:che: splits into : leH :nd right bronchus (plur:l:
Bronchus
bronchi), e:ch le:ds to : lung.
E:ch bronchus splits :g:in :nd :g:in into thous:nds of
Bronchiole sm:ller tubes c:lled bronchioles which t:ke the :ir deeper
into the lungs.
At the ends of bronchioles :re tiny :ir s:cs c:lled :lveoli. Here
Alveoli
oxygen moves into the blood :nd c:rbon dioxide moves out.
These muscles run between the ribs :nd form the chest w:ll.
Intercost$l
They contr:ct :nd rel:x with the di:phr:gm when : person
muscles
bre:thes.
The di:phr:gm is : dome-sh:ped, fl:t sheet of muscle under
Di$phr$gm the lungs. It contr:cts :nd rel:xes with the intercost:l muscles
during bre:thing.
How does oxygen tr$vel into blood?
1. Air is bre:thed into the lungs through the windpipe c:lled the tr:che:.
2. The tr:che: divides into two tubes c:lled the bronchi.
3. The bronchi divides into m:ny tubes c:lled bronchioles.
4. The bronchioles divide until they end up in tiny :ir s:cs c:lled :lveoli. There
:re millions of :lveoli found within the lungs.
5. These :lveoli :re surrounded by : network of c:pill:ries, :llowing for
oxygen :nd c:rbon dioxide to be exch:nged between the blood in the
c:pill:ries :nd the :ir in the lungs. The oxygen molecules :re c:rried in red
blood cells.
6. The exch:nge of these two g:sses occurs by : process c:lled diffusion.
Alveoli
Alveoli :re tiny :ir s:cs in the lungs where g:s is exch:nged during bre:thing.
Within the hum:n lungs the :lveoli provide :n efficient exch:nge surf:ce
:d:pted for g:s exch:nge. This involves the ‘sw:pping’ of g:sses. For
ex:mple:
Absorbing oxygen, which is needed for respir:tion, into the blood from the
:ir.
Tr:nsferring c:rbon dioxide, which is produced by respir:tion, from the
blood into the lungs :nd then the :ir.
How $re the $lveoli $d$pted for g$s exch$nge?
Alveoli h:ve : very l:rge surf:ce :re: to en:ble more diffusion of oxygen
into the blood from the :lveoli, :nd more c:rbon dioxide out of the blood
into the :lveoli.
They :re only one cell thick so th:t the diffusion dist:nce is sm:ll.
They h:ve lots of blood c$pill$ries to ensure : good blood supply to
m:int:in concentr:tion gr:dients of oxygen :nd c:rbon dioxide.
They h:ve moist surf:ces for g:ses to dissolve in to form : solution to p:ss
through the cell membr$ne .
Some w:ter v:pour is lost from the surf:ce of the :lveoli into the lungs - we
c:n see this condensing when we bre:the out on cold d:ys.
Ventil$tion
Air gets into :nd out of the body by the physic:l process of bre:thing, :lso
c:lled ventil:tion. This process involves movements of the ribs, intercost:l
muscles :nd di:phr:gm to move :ir into :nd out of the lungs.
These :re the ch:nges involved during inh:l:tion :nd exh:l:tion.
Inh$ling Exh$ling
Contr:cts :nd moves
Di$phr$gm Rel:xes :nd moves upw:rds
downw:rds
Intercost$l Contr:ct, moving the ribs Rel:x, letting the ribs move
muscles upw:rds :nd outw:rds downw:rds :nd inw:rds
Volume of
Incre:ses Decre:ses
ribc$ge
Pressure
Decre:ses below Incre:ses :bove :tmospheric
inside the
:tmospheric pressure pressure
chest
Movement of
Moves into the lungs Moves out of the lungs
$ir
Find out more $bout the process of bre$thing.
Respir$tion
There :re two types of respir:tion th:t c:n occur in your cells:
Aerobic respir:tion
An:erobic respir:tion
Find out more $bout the two types of respir$tion.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Your score: 7 / 10
Good effort!
Great try - find out more about this topic by reading the rest of the page - look out for the
things you got wrong in this quiz.
Play again
Some of your information will be collected when you play this quiz.
Find out more & Terms & Conditions
Test question
Describe $nd expl$in four $d$pt$tions of the $lveoli th$t helps the r$pid
diffusion of oxygen into the blood.
Hide $nswer
1. Alveoli h:ve : very good blood supply. This m:int:ins : concentr:tion
gr:dient between the :lveoli :nd the c:pill:ries.
2. Alveoli h:ve very thin w:lls, one cell thick so the diffusion p:thw:y is very
short.
3. Alveoli h:ve : l:rge surf:ce :re:. This :llows more sp:ce for oxygen
molecules to move :cross from the :lveoli to the blood.
4. They h:ve moist surf:ces. G:ses dissolve :nd form : solution then p:ss
through the cell membr:ne.
G$me - Atomic L$bs
Try out pr:ctic:l experiments in this KS3 science g:me
Hum$ns $re $nim$ls
Build on your knowledge with these guides.
You're here
Structure of the Structure $nd function The process of The effect of $sthm$,
digestive system of the g$s exch$nge bre$thing smoking $nd exercise
system on the g$s exch$nge
system
5 of 11 6 of 11 7 of 11 8 of 11
Up next
The process of bre:thing
Explore the BBC
Home News Sport Reel Worklife Tr$vel
Future Culture Music TV We$ther Sounds
Terms of Use About the BBC Priv:cy Policy Cookies Accessibility Help P:rent:l Guid:nce Cont:ct the BBC Get Person:lised Newsletters
Advertise with us AdChoices / Do Not Sell My Info
Copyright © 2022 BBC. The BBC is not responsible for the content of extern:l sites. Re$d $bout our $ppro$ch to extern$l linking.
You might also like
- Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology AnswersDocument30 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Human Biology AnswersAvrinox88% (48)
- My CoursesDocument18 pagesMy CoursesOsama SyedNo ratings yet
- Resepiratory Quiz PDFDocument4 pagesResepiratory Quiz PDFapi-448873912No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of RespirationDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of RespirationDANICA JEAN PRIANES100% (1)
- Julie Bui - Building Dna GizmosDocument3 pagesJulie Bui - Building Dna Gizmosapi-5226505140% (2)
- Science 4Document40 pagesScience 4Miriam100% (2)
- 20230727_201305Document2 pages20230727_201305PonytailNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems WorksheetDocument6 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory Systems WorksheetJaimeCrispinoNo ratings yet
- Specialised animal cells - Living organisms - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC BitesizeDocument1 pageSpecialised animal cells - Living organisms - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC Bitesizesparkle.comic-0kNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 5 Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 5 Respiratory SystemFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Wednesday, 23 March 2022 5:54 AmDocument3 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Wednesday, 23 March 2022 5:54 AmDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument35 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemScheherazade CNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: RespirationDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: RespirationHelenNo ratings yet
- NORCETDocument109 pagesNORCETDiksha DhillonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemScheherazade CNo ratings yet
- Learning Tasks 1-5 Week 1Document13 pagesLearning Tasks 1-5 Week 1Thartson Oliveros Magdadaro100% (1)
- Activity Sheet No. 1 THE HUMAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pagesActivity Sheet No. 1 THE HUMAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEMJenneriza DC Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Insect Tracheal System: Fig. 39-7, P. 685Document6 pagesInsect Tracheal System: Fig. 39-7, P. 685Nestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoNo ratings yet
- Chapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Document7 pagesChapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Abdus samiNo ratings yet
- Flow Patterns in the Duck LungDocument16 pagesFlow Patterns in the Duck LungNadya AnomNo ratings yet
- BRJ Key Muscle & BreathingDocument4 pagesBRJ Key Muscle & BreathingAqidatul izzaNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test (Grade 9) PDF Dominance (Genetics) AlleleDocument1 page1st Periodical Test (Grade 9) PDF Dominance (Genetics) Allelejessie esquerraNo ratings yet
- BIO 004 Animal Respiratory SystemsDocument26 pagesBIO 004 Animal Respiratory SystemsManuelNo ratings yet
- I. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesI. Anatomy and PhysiologyJuan Miguel OliverosNo ratings yet
- Ch42 Practice TestDocument8 pagesCh42 Practice TestMike Wolsky0% (1)
- ACTIVITY SHEET in SCIENCE (Respiratory System)Document2 pagesACTIVITY SHEET in SCIENCE (Respiratory System)VIRGILIO GUZONNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesCirculatory SystemDany MonteroNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Mode: PPT - : OnlineDocument19 pagesSession 5 Mode: PPT - : Onlinevinotha kuppusamyNo ratings yet
- (A) Human Breathing MechanismDocument9 pages(A) Human Breathing MechanismAnome ArisNo ratings yet
- E Book Bio English 03Document42 pagesE Book Bio English 03sanjNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument62 pagesThe Circulatory SystemRichele RectoNo ratings yet
- 8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsDocument3 pages8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsOanaEmmNo ratings yet
- Bahagian A/Section A: Multiple Choice Questions on Science TopicsDocument8 pagesBahagian A/Section A: Multiple Choice Questions on Science TopicsSiti Nazneen Binti IsmailNo ratings yet
- UK Year 6 Biology RevisionDocument9 pagesUK Year 6 Biology RevisionabhishekkaushalNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 9Document4 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 9Chai Barcelon86% (7)
- Physiology, Lecture 5, Respiratory System (Slides)Document43 pagesPhysiology, Lecture 5, Respiratory System (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesLesson 3 - Respiratory SystemPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- MA: Respiratory: ConductingDocument12 pagesMA: Respiratory: Conductingdbircs000No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System NotesDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory System NotesVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Grade7 - Text - Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesGrade7 - Text - Respiratory SystemNamrata MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Biomedical InstrumentationDocument16 pagesBiomedical InstrumentationGhanshyam DhruwNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument6 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Gas Exchange and HeartDocument26 pagesMammalian Gas Exchange and HeartLisa EllisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Mock Review Sheet - Answer KeyDocument10 pagesChapter 1 - Mock Review Sheet - Answer KeyUm HassanNo ratings yet
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Victor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Respiratory SystemMark Jerome CifraNo ratings yet
- Exam Night s2 2023 (1) Answered-1Document7 pagesExam Night s2 2023 (1) Answered-1Mohamed EbarhimNo ratings yet
- 6454f627e4b0ad3aaf22e06b OriginalDocument13 pages6454f627e4b0ad3aaf22e06b OriginalSuprit JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scs f3Document15 pagesChapter 1 Scs f3putridequenoNo ratings yet
- 10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2Document86 pages10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2kaziamna62No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Year 10 GZDocument6 pagesHuman Respiratory System Year 10 GZLabeenaNo ratings yet
- WWW Studyrankers Com 2017 07 Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part II Class 10th HTMLDocument15 pagesWWW Studyrankers Com 2017 07 Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part II Class 10th HTMLbaapmatsikha5No ratings yet
- Work Book 2021Document45 pagesWork Book 2021Ayaan RaufNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDDocument7 pagesScience 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeAnime Player ccNo ratings yet
- West Bab 1-3Document32 pagesWest Bab 1-3Nurul Hazi putriNo ratings yet
- Science Circulatory SystemDocument42 pagesScience Circulatory SystemNaejla M. SajirdesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument85 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsxoxkakidoxoxNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Document24 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- ELEC4810: Introduction To Biosensors and Bioinstrumentation: Lecture Notes - Set #9Document58 pagesELEC4810: Introduction To Biosensors and Bioinstrumentation: Lecture Notes - Set #9Kwan ChanNo ratings yet
- Human Body and Organ SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Body and Organ SystemAaryan KakadNo ratings yet
- Drying Methods and ConceptsDocument51 pagesDrying Methods and ConceptsPrajwal ChavanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri 2 FlotasiDocument7 pagesTugas Mandiri 2 FlotasiM Rallupy MeyraldoNo ratings yet
- PML and RNF4 Remove Misfolded Proteins in Mammalian CellsDocument16 pagesPML and RNF4 Remove Misfolded Proteins in Mammalian CellsAndonis AngelovNo ratings yet
- Anexo 2. Smith-Acidity Scale For Oxides 1987Document2 pagesAnexo 2. Smith-Acidity Scale For Oxides 1987Ivan ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Percentage, Ratio Strength, and Other Expressions of ConcentrationDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Percentage, Ratio Strength, and Other Expressions of ConcentrationAhmed Hassan Mina HamadNo ratings yet
- Electroorganic Chemistry: Brandon Rosen 8 November 2014Document6 pagesElectroorganic Chemistry: Brandon Rosen 8 November 2014Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Abcam - PEDF ELISA Datasheet - 246535Document5 pagesAbcam - PEDF ELISA Datasheet - 246535柯砲肚No ratings yet
- Providing and Laying High Strength Flexible Bonded Geogrids As Basal ReinforcementDocument4 pagesProviding and Laying High Strength Flexible Bonded Geogrids As Basal Reinforcementabhi0912No ratings yet
- Chemical List (August)Document1 pageChemical List (August)MahdiNo ratings yet
- Anodic ProtectionDocument2 pagesAnodic ProtectionSyaifullah Sa'abaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Information Technology Project Management 9th Edition Kathy SchwalbeDocument34 pagesSolution Manual For Information Technology Project Management 9th Edition Kathy Schwalbemanequin.design8haoij100% (42)
- Problem Set 1Document8 pagesProblem Set 1Bj LarracasNo ratings yet
- Study On The Semiconducting PropertiesDocument155 pagesStudy On The Semiconducting Propertiespadidela swarochishraoNo ratings yet
- ClimateControl SG 001 enDocument20 pagesClimateControl SG 001 ensaedmarwaNo ratings yet
- Transistor Current ComponentsDocument3 pagesTransistor Current ComponentsDiptendu MitraNo ratings yet
- Photoinitiator 2Document6 pagesPhotoinitiator 2Ashwary Sheel Wali Research Scholar, Dept of Mech Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- 4020-GE-LST-001 - A ITY DED - Deliverable ListDocument51 pages4020-GE-LST-001 - A ITY DED - Deliverable Listthoriq ikhwanNo ratings yet
- Ductile Dross Formation MonitoringDocument27 pagesDuctile Dross Formation MonitoringsachinguptachdNo ratings yet
- CO2 Adsorption Enhanced by Nitrogen-Rich BiocharDocument8 pagesCO2 Adsorption Enhanced by Nitrogen-Rich BiocharKhaled Abou AlfaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Testing Report for Aluminium SheetDocument1 pageChemical Testing Report for Aluminium SheetP NAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Analisa Pengaruh Diameter Impeller Terhadap Kapasitas Dan Penurunan Tekanan Blower SentrifugalDocument10 pagesAnalisa Pengaruh Diameter Impeller Terhadap Kapasitas Dan Penurunan Tekanan Blower SentrifugalMuwafiqah MarwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument32 pagesChapter 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsCheska CapioNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Operations LabDocument2 pagesMechanical Operations LabVinay AvvaruNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Desothane HS CA8200 Military and Defense TopcoatsDocument8 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Desothane HS CA8200 Military and Defense TopcoatsBianca MoraisNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesThermodynamicsShivam TrivediNo ratings yet
- Lubricants Sweeten Sour Gas EnginesDocument26 pagesLubricants Sweeten Sour Gas EnginesengrsurifNo ratings yet
- AOAC Method 935.48 Nitrates and Nitrites in MeatDocument1 pageAOAC Method 935.48 Nitrates and Nitrites in MeatGerman AyalaNo ratings yet
- Mastertop P10 TDSDocument2 pagesMastertop P10 TDSطه اللوذعيNo ratings yet