Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 5 Respiratory System
Uploaded by
FLANTAMOCKOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 5 Respiratory System
Uploaded by
FLANTAMOCKCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.
com/
Respiratory System
Synopsis —
The energy released during respiration is stored as chemical energy in the form of
ATP — adenosine tri-phosphate.
Aerobic respiration —
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP
Anaerobic respiration —
During vigorous exercise, the cells respire anaerobically and form lactic acid which
accumulate in the muscle cells causing fatigue and pain.
om
The respiration in humans occur in three phases:
.c
1. Breathing
ns
2. Gaseous Transport
3. Cellular respiration
io
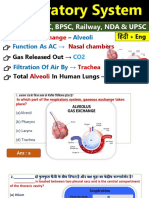
The oxygen inhaled in combines with haemoglobin present in the red blood cells
t
lu
forming an unstable compound called oxyhaemoglobin.
so
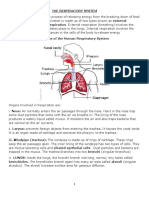
The nasal chamber has got hairy lining to prevent dust particles from reaching the
k
lungs. The lining also has mucous to trap germs and dust.
oo
The common passage for the food and air is the pharynx.
rtb
Trachea is also called the wind pipe.
The voice box or the Adam’s apple is the larynx which contains ligamentous folds
ce
called vocal cords.
.n
Incomplete closure of epiglottis during swallowing causes coughing.
w
The trachea is formed of incomplete C-shaped cartilaginous rings which keep
w
them permanently distended.
//w
The lungs are protected outside by the two membranes
called outer and inner pleura.
s:
Left lung is slightly smaller than the right lung.
tp
Left lung has two lobes while the right lung has three lobes.
ht
Breathing is an involuntary act.
Even after maximum forced expiration, some air is left in the lungs called residual
volume.
In normal adults, the breathing rate is 12-18/minute while a newborn breathes at
about 60 breaths per minute.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Asphyxiation is a condition in which blood becomes venous by the accumulation
of excess carbon dioxide and the oxygen supply is diminished.
The gas composition in artifical respiration is 95% oxygen, 5% carbon-di-oxide.
Snoring: Vibration of soft palate during breathing when mouth is kept open while
sleeping.
Sneezing: It is a protective mechanism through which a foreign irritant particle is
thrown out of the lungs suddenly and forcefully.
Hiccups: Jerky incomplete inspiration due to blockage of the respiratory tract.
Review Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
om
1. Put a tick (✓) against the most appropriate alternative in the following
.c
statements.
ns
(i) In humans, taken in of the air through nostrils into the nasal cavity is called
io
(a) Inhalation
t
lu
(b) Exhalation so
(b) Cellular respiration
(d) Internal respiration
k
oo
rtb
(ii) The front opening of the wind pipe is guarded by —
(a) Glottis
ce
(b) Exoglottis
.n
(c) Epiglottis
w
(d) Trachea
w
//w
(iii) The process during which food is oxidised and energy is released is called
s:
(a) Cellular respiration
tp
(b) Excretion
(c) Digestion
ht
(d) Transpiration
Short Answer Questions
1. Answer briefly the following:
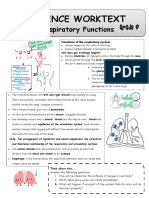
1. Why do our body cells require oxygen ?
Ans. Body cells require oxygen for the break down of glucose and release energy
for carrying out various life functions.
2. What is the difference between breathing and respiration?
Ans. Breathing is a simple physical process of drawing in air through the nostrils
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
and expelling it out.
Respiration is a chemical process which involves the breakdown of food and
release energy.
3. Name the by-product formed during the oxidation of food.
Ans. The by- products formed are
1. carbon-di-oxide
2. water
4. Name the agency which transports oxygen to all parts of the body.
Ans. Blood .
5. What is the role of epiglottis during swallowing ?
Ans. Epiglottis closes the wind pipe at the time of swallowing.
Question 2.
Describe in brief the function of ribs and diaphragm in breathing.
om
Answer:
.c
ns
1. Ribs muscles—During inhalation, the ribs muscles contract and push the ribs
upward and outward.
io
During exhalation these relax and cause the ribs to return to original position.
t
lu
2. Diaphragm: During inhalation it becomes flattened while during exhalation it
so
relaxes and moves up and back into convex (dome) shape.
k
oo
Question 3.
rtb
Name the gas which is expelled out during expiration. Where is it originally produced in
our body ?
ce
Answer:
.n
The gas which is expelled during expiration is carbon-di¬oxide. It is produced as a result
w
of oxidation of glucose in the tissues. (Cellular respiration)
w
//w
Question 4.
s:
Name the following:
tp
ht
1. Respiratory process
2. in which oxygen is not utilized.
Ans. Cellular respiration
3. Respiratory process in which oxygen is utilized.
Ans. Gaseous transport
4. The microscopic air-sacs of the lungs.
Ans. Alveoli
5. The two membranes which protect the lungs.
Ans. Outer pleura, inner pleura
Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Why is a respiratory system necessary ?
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Answer:
Respiratory system is very important for the body. Respiration in human beings is
divided into two distinct parts. The first part involves taking in oxygen from the air or
what we commonly call breathing. The respiratory system is responsible for breathing in
and out of air, and exchange of gases. The main parts of the respiratory system consist
of the nostrils, trachea or wind pipe and lungs.
The blood, then, transports the oxygen to the individual cell where it is used for the
chemical process of respiration. This is known as cellular respiration.The second part
involves taking out carbon dioxide, which is a waste product of cellular function.
Question 2.
What factors are most likely to affect the breathing rate ?
Answer:
om
Breathing is a necessary function for human beings. It supplies oxygen for a process
called cellular respiration, which is how cells manufacture the energy they need for their
.c
life functions.
ns
There are lots of things that can affect the rate of breathing in humans and they
io
are:
t
lu
1. Exercise is one of those things, particularly aerobic exercise. Aerobic exercise is
so
any exercise that causes the person to breathe more, such as running jogging,
k
playing basketball, football, running track, or playing soccer.
oo
2. Even Breathing rate also changes while the person is sleeping, sitting at rest or
rtb
even after climbing the stairs.
3. Another factor that can influence breathing rate is allergic reactions to stimuli from
ce
the environment, such as pollen. This can inflame the passageways leading to the
.n
lungs, making them smaller, requiring more air.
w
4. Smoking is a habit that can influence the development of lung cancer, which in
w
turn influences the rate a person breathes.
//w
5. Nervous conditions and reactions to stimuli also influence the breathing rate, such
s:
as the fumed “fight or flight” syndrome.
tp
ht
Question 3.
What happens to the energy liberated during respiration?
Answer:
The energy liberated during respiration is utilised for carrying out various life processes.
Some of the energy liberated during the breakdown of the glucose molecule, is in the
form of heat, but a large part of it is converted into chemical energy called Adenosine
Triphosphate (ATP). Any activity inside the cell is carried out by the energy released by
these ATP molecules.
Question 4.
What do you understand by inhalation and exhalation ? How are they different from
each other ?
Answer:
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
The physical process, by which the air containing oxygen is drawn into the lungs and air
containing carbon dioxide is forced out from lungs is called breathing. Breathing
involves two steps, inhalation (inspiration) and exhalation (expiration).
Inhalation (Inspiration)
1. Ribs move upwardsand outwards.
2. Diaphragm is pushed downwards and flattens.
3. Volume of chest cavity increases.
4. Lungs expand, air pressure becomes low.
5. Atmospheric air at higher pressure rushes into the lungs
om
Exhalation (Expiration)
.c
1. Ribs move downwards and inward.
ns
2. Diaphragm moves upwards and becomes dome shaped.
io
3. Volume of chest cavity decreases.
t
lu
4. Lung size reduces, air pressure becomes high.
so
5. Air rushes out of lungs as atmospheric air pressure is lower.
k
oo
Question 5.
What do you understand by the term respiratory diseases ? Name any three common
rtb
respiratory diseases.
ce
Answer:
Any of the diseases and disorders that affect human respiration are called Respiratory
.n
diseases. Diseases of the respiratory system may affect any of the structures and
w
organs that have to do with breathing, including the nasal cavities, the pharynx (or
w
throat), the larynx, the trachea (or windpipe), the bronchi and bronchioles, the tissues of
//w
the lungs, and the respiratory muscles of the chest cage.
s:
tp
1. Bronchitis — It is a respiratory infection in which the lining of the bronchi
ht
becomes inflamed. As this irritated membrane begins to swell, it narrows or shuts
off the bronchial passages, resulting in breathlessness and coughing spells.
2. Asthma — It is a chronic disease that also causes inflammation and swelling in
the airways. But this happens periodically. During an asthmatic attack, a patient
experiences tightness in the chest, shortness of breath and wheezing. This
condition improves considerably with medication.
3. Pneumonia — It is a respiratory infection caused by a bacteria. This bacteria
enters the air sacs, multiplies there and the air sacs may get filled with fluid. This
disease causes chest pain, chills and high fever.
Question 6.
State the cause and treatment for the following diseases
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
1. Tuberculosis
2. Pneumonia
3. Bronchitis
Answer:
1. Tuberculosis — Cause: Caused by bacteria that can spread by air, dust or
sputum.
Treatment: BCG vaccine, antibiotic — Streptomycin.
2. Pneumonia — Cause: Mainly caused by bacteria inhaled through air or by
contact.
Treatment: Antibiotics—Penicillin.
3. Bronchitis — Cause: This respiratory infection is mainly caused by a virus. Air
om
pollution and smoking can also cause bronchitis.
Treatment: Drinking plenty of fluids, following a well balanced diet, frequent hand
.c
washing and adequate rest can prevent and improve bronchitis.
ns
io
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
t
lu
so
A. Fill in the blanks.
k
oo
1. The respiration is of two types aerobic and anaerobic.
rtb
2. In human beings, exchange of gases takes place in lungs.
3. Bronchi divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles.
ce
4. Haemoglobin is present in the red blood cells and helps in the transport of
.n
oxygen.
w
5. Diaphragm is a muscular membrane present below the lungs.
w
6. Malpighian body consists of Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus.
//w
7. Sweat serves to excrete excess of water urea and salts.
s:
B. Write true or false for each statement. Rewrite the false statements correctly.
tp
ht
1. Respiration and breathing are two different processes.
True
2. Breathing is a chemical process.
False. Respiration is a chemical process.
3. The oxidation of food to release energy and water is called breathing.
False. The oxidation of food to release energy and water is called Respiration.
4. The exchange of gases through the skin is called cutaneous respiration.
True
5. The trachea branches into two tubes called bronchioles.
False. The trachea branches into two tubes called bronchi.
6. The microscopic air sacs present in the lungs are called bronchi.
False. The microscopic air sacs present in the lungs are called alveolar sacs.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
7. The walls of alveoli are richly supplied with veins.
False. The walls of alveoli are richly supplied with blood capillaries.
8. The mature roots and woody stems of certain trees have openings called lenticels.
True
C. Arrange the following organs in the correct order to show the path of air.
1. trachea, nose, bronchioles, bronchi, larynx, alveoli, pharynx, lungs
Answer:
nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, bronchioles.
D. Differentiate between
om
Question 1.
Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
.c
Answer:
ns
Aerobic Respiration
tio
lu
1. It takes place in the presence of oxygen. so
2. Complete oxidation of food takes place.
3. 38 molecules of ATP are produced by oxidation of one gram mole of glucose.
k
oo
4. CO2 and H2O are the end products.
rtb
Anaerobic Respiration
ce
.n
1. It takes place in the absence of oxygen.
w
2. In complete oxidation of food takes place.
w
3. 2 molecules of ATP are produced by oxidation of gram mole of glucose.
//w
4. Ethyl alcohol (C2H2 OH) and CO2are the end products.
s:
Question 2.
tp
bronchi and alveoli.
ht
Answer:
Bronchi
1. The two branching tube of trachea are called bronchi.
2. There are two bronchi
3. The walls of bronchi are not richly supplied with blood capillaries.
Alveoli
1. The out growths of microscopic air sacs are called alveoli.
2. There are millions of alveolar sacs.
3. The walls of the bronchioles are richly supplied with blood capillaries.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Question 3.
Breathing and Respiration.
Answer:
Breathing
1. It is a physical process.
2. Air containing oxygen is taken into the lungs and air loaded with carbondioxide is
given out.
3. Lungs are mainly involved.
Respiration
1. It is a catabolic process
om
2. Oxygen taken in is used in oxidizing glucose and energy is released.
3. Occurs in tissues and cells of the body.
.c
ns
Question 4.
io
Bowman’s capsule and alveolus.
t
lu
Answer: so
Bowman’s capsule
k
oo
1. It is a part of kidney i.e. a excretory unit.
2. It is cup shaped structure at the end of nephron.
rtb
3. It helps in filtration of blood
ce
.n
Alveolus
w
w
1. It is a part of using i.e.a respiratory unit.
//w
2. It is the outgrowth of air sacs (alveolar sacs).
3. It helps in exchange of gases (CO2 and O2).
s:
tp
ht
E. Find the odd one out. Give reasons for your choice.
1. ureter, kidney, urinary bladder, lung, urethra
Ans. lung, because all others are organs of excretory system and it is a
respiratory organ.
2. skin, heart, lung, liver, kidney
Ans. Heart because it helps to pump blood in our body and the rests help in
excretion.
3. tannin, urine, latex, resin
Ans. urine, because it is excretory product of animals and rests are excretory
products of plants.
F. Write short answers.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
1. Define respiration.
Ans. The process of conversion of glucose molecules in food into energy rich
molecules, carbondioxide and water with the help of oxygen is known as
respiration.
2. What is the full form of ATP ?
Ans. ATP is the energy currency of cell its full form is Adenosine Triphosphate.
3. Define cutaneous respiration ?
Ans. The exchange of gases through moist skin and blood capillaries underneath
is called cutaneous respiration.
4. What is the role of diaphragm in respiration in human beings ?
Ans. Diaphragm moves up and down and helps in the exchange of air between
the atmosphere and lung
G Answer in detail.
om
.c
Question 1.
How is the process of respiration different from breathing ?
ns
Answer:
io
Respiration
t
lu
so
1. It is a complex bio-chemical process which involves enzymes.
k
2. It involves oxidation of glucose in to CO2, water and energy.
oo
3. Energy is released and stored in the form of ATP.
rtb
4. It takes place inside the cell.
ce
Breathing
.n
w
1. It is a mechanical process without the involvement of enzymes.
w
2. It involves only the exchange of oxygen and CO2.
//w
3. No energy is released.
s:
4. It takes place outside the cell.
tp
ht
Question 2.
Explain the process of Cellular Respiration.
Answer:
Cellular Respiration is a biochemical process which involves the oxidation of glucose to
release energy, carbondioxide and water are released as by – products.
It involves a series of chemical reactions controlled by different enzymes. The energy
released in the process is stored in the form of energy rich substance called ATP
(Adenosine triphosphate). The ATP molecules are stored in the cells and later on can
be broken down to release energy for various metabolic activities. The entire process
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
takes place partially in the cytoplasm and partially in the mitochondria of our body cells.
The process of conversion of glucose molecules in food in to energy rich molecules,
CO2 and water with the help of oxygen is known as respiration
Question 3.
How is aerobic respiration different from anaerobic respiration ?
Answer:
Aerobic respiration
1. It occurs in the presence of oxygen
2. It occurs inside the mitochondria.
3. Complete oxidation of food takes place.
4. The end products are CO2 and water.
5. 38 ATP molecules are produced by oxidation of one gram mole of glucose.
om
.c
Anaerobic respiration
ns
1. It occurs in the absence of oxygen.
io
2. It occurs outside the mitochondria.
t
3. In complete oxidation of food takes place.
4. lu
Ethyl alcohal or lactic acid are the end products.
so
5. 2 ATP molecules are produced by oxidation of one gram mole of glucose.
k
oo
Question 4.
rtb
What happens to Oxygen after it enters the lungs?
ce
Answer:
Each lung contains millions of alveoli. The walls of the alveoli are richly supplied with
.n
blood capillaries. The air which reaches the alveoli after passing through trachea,
w
bronchi, bronchioles is rich in oxygen and contains very little CO 2 . The blood capillaries
w
of the alveoli contain blood that has more carbon dioxide and little oxygen. The oxygen
//w
diffuses from the thin walls of the capillaries in to the blood and combines with
hemoglobin in the red blood cells of blood thereby forming oxyhaemoglobin.
s:
Hemoglobin is a type of protein which contains iron. The blood carries oxygen to all the
tp
cells of the body. In the cells a series of chemical reactions, CO 2 , water and energy are
ht
released. The carbondioxide released combines with the hemoglobin to form
carbominohaemoglobin. Then the blood rich in carbominohaemoglobin leaves the cells
and reaches the alveoli where CO2 gas is released and is exhaled out through the nose.
Question 5.
Why is it better to breathe through your nose than your mouth?
Answer:
It is better to breathe through our nose than our mouth because our nasal cavity is lined
by hair. The air we breathe in contains fine dust particles. These particles get trapped in
the hair in the nasal cavity and are thereby prevented from reaching the lungs. The
inside of the nose is also covered by a sticky fluid called mucus. Dust and germs stick to
the muscles and thus, the air taken in is cleaned. The air is also warmed up by blood
vessels present in the nasal cavity
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
You might also like
- Barr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint: Kiernan, J. A Rajakumar, NagalingamDocument4 pagesBarr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint: Kiernan, J. A Rajakumar, NagalingamSaras Agrawal0% (1)
- Energy Producing & Distributing SystemsDocument40 pagesEnergy Producing & Distributing SystemsZerille Anne InsonNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen AdvantageDocument5 pagesThe Oxygen AdvantageJOHN0% (1)
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 5 Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 5 Respiratory Systemmangala kalaiselviNo ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Page No - 115Document5 pagesPage No - 115venfone byrappaNo ratings yet
- Respiration SystemDocument31 pagesRespiration SystemVikram SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Biology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabanDocument3 pagesBiology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabannoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Biology 2201 - Respiratory System Notes PDFDocument11 pagesBiology 2201 - Respiratory System Notes PDFVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Lesson 6Document3 pagesClass 7 Lesson 6gunjanrichaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Biology 11Document36 pagesChapter 11 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesNotebook Work Respiration in OrganismsachlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document24 pagesChapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Tauqeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- GRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewDocument9 pagesGRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewsabariqaNo ratings yet
- Asm 3789Document6 pagesAsm 3789Mohammad Farhan KhanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument9 pagesRespirationpriya.kesharwani0557No ratings yet
- Respiration G810FD6Document10 pagesRespiration G810FD6Tifa NassimNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exchange of GasesDocument9 pagesBreathing Exchange of Gasesravinderinst2No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesChapter 2 Tutorial 1Tanisa SaminNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsDocument5 pagesRespiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Matric Class NotesDocument38 pagesBiology Matric Class NotesNaveed Haroon BhachoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory Systemefe shanNo ratings yet
- 556Document3 pages556Nokutenda KachereNo ratings yet
- RWFMKNFKJSDFDSVDSDocument21 pagesRWFMKNFKJSDFDSVDSKEVIN JOSEMONNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.a FOR STUDENTDocument14 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.a FOR STUDENTErra PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 and Ch-12 Gas-Exchange in Humans and RespirationDocument12 pagesCh-11 and Ch-12 Gas-Exchange in Humans and Respirationdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 13 Respiratory SystemfrommeyerjamesNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10Document6 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10Ratnesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document8 pagesModule 10Jamille Nympha C. BalasiNo ratings yet
- Science 6 2nd Quarter W4Document13 pagesScience 6 2nd Quarter W4Leo Cereno100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Document5 pagesChapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Precious Aiverose EspinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersPooja AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinDocument14 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- Emergency Plan 1Document4 pagesEmergency Plan 1Iman Hassan Ahmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- IKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRDocument2 pagesIKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRikman nibosNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Breathing Mechanism 1.2 The Transport of Oxygen in The Human Body 1.3 The Importance of A Healthy Respiratory SystemDocument24 pages1.1 The Human Breathing Mechanism 1.2 The Transport of Oxygen in The Human Body 1.3 The Importance of A Healthy Respiratory SystemChang Yin YinNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument6 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Human Bio S1Q1 PDFDocument10 pagesHuman Bio S1Q1 PDFAngel MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Human Bio S1Q1Document10 pagesHuman Bio S1Q1Shaira BautistaNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesSUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - THE RESPIRATORY SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 14 - THE RESPIRATORY SystemNaveen Kumar PokalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Document7 pagesChapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Abdus samiNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Document10 pagesBiology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Âåřøhī MāhåjáňNo ratings yet
- Breathing & RespirationDocument11 pagesBreathing & RespirationU Than HanNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument4 pages11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesParimala deviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Document6 pagesChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925No ratings yet
- RTP Q1 G9 Science Module 1Document20 pagesRTP Q1 G9 Science Module 1Julie Ann Pineda BalichaNo ratings yet
- MCQs On Respiratory System - BiologyDocument12 pagesMCQs On Respiratory System - Biologysonia keniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- 6th Forms Science - Structure and Function of Body Systems - 2.2 Gas ExchangeDocument11 pages6th Forms Science - Structure and Function of Body Systems - 2.2 Gas ExchangeAs 54bdNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory Systemsouha kahilNo ratings yet
- PDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17FDocument15 pagesPDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17Fgandhitirth147No ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Document24 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- 0110232000210777Document4 pages0110232000210777alugayatri84No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 RespirationDocument2 pagesChapter 11 Respirationlock_jaw30No ratings yet
- Science 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDDocument7 pagesScience 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Breath Taking: The Power, Fragility, and Future of Our Extraordinary LungsFrom EverandBreath Taking: The Power, Fragility, and Future of Our Extraordinary LungsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 06 Decimal FractionsDocument12 pagesICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 06 Decimal FractionsFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 05 FractionsDocument15 pagesICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 05 FractionsFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 02 IntegersDocument12 pagesICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 02 IntegersFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 04 Factors and MultiplesDocument11 pagesICSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 04 Factors and MultiplesFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 6 Chapter 4 Elements, Compounds, Symbols and FormulaeDocument31 pagesSelina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 6 Chapter 4 Elements, Compounds, Symbols and FormulaeFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 MatterDocument27 pagesSelina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 MatterFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 Cell - The Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 Cell - The Structure and FunctionsFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 1 The LeafDocument20 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 1 The LeafFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 2 The FlowerDocument17 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 2 The FlowerFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 4 Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 4 Digestive SystemFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- HIST Harrapan Civilizatio NotesDocument5 pagesHIST Harrapan Civilizatio NotesFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Leeward Microbiology 130 DR - Kae Final ExamDocument164 pagesLeeward Microbiology 130 DR - Kae Final Examraymond theardNo ratings yet
- 5 Levels of Organization From Cells To OrganismDocument51 pages5 Levels of Organization From Cells To OrganismIan Alpa100% (1)
- Anaerobic Respiration: I CanDocument3 pagesAnaerobic Respiration: I CanZak RemtullaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Disturbance: Esraa Albaqqal 371230183 Banin Alshehab 381230590 Yaqin Alkhalaf 391230503 Ahoud Alzaid 391230645Document14 pagesSleep Disturbance: Esraa Albaqqal 371230183 Banin Alshehab 381230590 Yaqin Alkhalaf 391230503 Ahoud Alzaid 391230645Banin malekNo ratings yet
- Engle ZaDocument114 pagesEngle ZaAlexandra Calugar100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy and Physiology of AnimalDocument257 pagesClinical Anatomy and Physiology of Animalabdillah_syahida7524100% (3)
- Lab1 - RBCDocument4 pagesLab1 - RBCRamos, NicoleNo ratings yet
- Repiratory System: Presented by Group 3: Lacap, Lopez, Medina, MarceloDocument8 pagesRepiratory System: Presented by Group 3: Lacap, Lopez, Medina, MarceloAj LacapNo ratings yet
- Chart Showing The Classification of Human Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesChart Showing The Classification of Human Nervous Systemamala raviNo ratings yet
- ID Efektivitas Senam Jantung Sehat TerhadapDocument7 pagesID Efektivitas Senam Jantung Sehat TerhadapAisyah SyahidahNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesCirculatory SystemGlemarie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Kerry GomesDocument23 pagesKerry GomesAbegail IbañezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Joher B. Mendez, JR., R.N., M.DDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Joher B. Mendez, JR., R.N., M.DJoherNo ratings yet
- Management of Upper Airway DisorderDocument46 pagesManagement of Upper Airway DisorderSahana Rangarajan100% (1)
- Loeys - Dietz Syndrome and Sleep Disordered BreathingDocument44 pagesLoeys - Dietz Syndrome and Sleep Disordered BreathingAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Procedure AssessmentDocument3 pagesDeep Breathing Exercises: Procedure AssessmentJelly Jia100% (1)
- Sistem SarafDocument141 pagesSistem SarafPei YiingNo ratings yet
- Exocrine Glands-Endocrine GlandsDocument8 pagesExocrine Glands-Endocrine GlandsneerleoNo ratings yet
- Cognition in REM and NREM Sleep A ReviewDocument16 pagesCognition in REM and NREM Sleep A ReviewOlivier BenarrocheNo ratings yet
- Science Blood TransfusionsDocument10 pagesScience Blood Transfusionsapi-237866019No ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument32 pagesAnimal TissueIan Kerby Sollano100% (1)
- Nervous System QuizDocument8 pagesNervous System QuizGee ZNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - AnatomyDocument28 pagesRespiratory System - AnatomyDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sleep Deprivation On College Students' Academic PerformanceDocument11 pagesEffect of Sleep Deprivation On College Students' Academic PerformanceVirgil Viral Shah0% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesDigestive SystemMaika JimenezNo ratings yet
- 512 vPEP HC IFU PN 352rev07.1 Webview Version 1Document2 pages512 vPEP HC IFU PN 352rev07.1 Webview Version 1Nandhini SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hypovolemic ShockDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Hypovolemic ShockIan Rama100% (1)