Professional Documents
Culture Documents
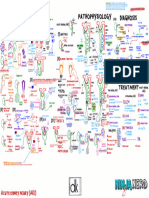
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Tin Myat SweCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Tin Myat SweCopyright:
Available Formats
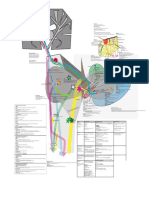
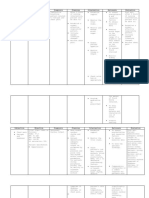
The pancreas is located in the back of the abdomen.
It is
Subtopic Anterior
approx 6 inches long. Pancreas
The effects of these hormones are the increase of your heart
rate, which also increases the amount of oxygen you take in, This layer is located in the centre of the gland, it makes Main topic
the increase of blood pressure, it increases your eyesight adrenaline and noradrenaline. These hormones are what Adrenal Medulla
temporarily, and it causes the liver to produce more glucose controls your "fight or flight" responses.
which provides more energy.
from JGA area of nephron (juxtaglomerular
Renin apparatus); converts the blood protein
Angiotensinogen to Angiotensin
C ortisol - This controls the glucose production in the liver
Subtopic
and protein breakdown in the muscles. Kidneys 7
Adrenal glands are 2 layer glands that sit on top of your
Increased reabsorption of water and
kidneys in the deepest part of the abdomen (the retro- Adrenal Angiotensin sodium into the bloodstream (less
Aldosterone - C ontrols blood pressure by the amount of fluid peritoneum).
urine, more blood plasma)
Subtopic that the body holds onto. This affects the heart and blood The C ortex is located on the outer layer and it creates 3
vessels. main hormones which help control the heart, kidneys, GI Adrenal C ortex
tract, bones, genitalia and the immune system.
Stimulates appetite; rises after weight loss
Stomach Ghrelin
Androgens and Estrogens - These are sex-hormones that (hard to stay on diets!) Role in obesity.
control the growth of the reproductive organs (testes &
ovaries) This also effects the development of the male and
female characteristics. Androgens control male growth and as fat accumulates, leptin levels rise &
Adipose
Estrogen for the female growth. Endocrine cells appetite is supressed; as fat decreases, so
Tissue (Body Leptin
found inside non- does blood leptin, and appetite increases.
Fat)
Paracrine Cells endocrine system Role in obesity: potential treatment?
organs, often with
local effect only.
Secreted after meals; appetite suppressant.
Small Intestine PYY
Failure of PYY system is a factor in obesity.
Protects embryo by suppressing
Human maternal immune cells; maintains
C horionic corpus luteum during pregnancy;
Estrogen is vital in the development of breast, the
Gonadotropin used in pregnancy tests; may
distribution of fat in the hips, legs, and breasts, and the
have role in tumor formation.
development of reproductive organs.
Placenta & Uterus 5
Makes pelvic ligaments more flexible,
Estrone (E1) -C onsidered a weaker type of estrogen. It is weakens pubic symphysis (centre of
Estrogen Relaxin
the main form of estrogen in menopausal women and is pelvis) for labour; in first trimester,
found in adipose tissues. increases blood flow & cardiac output.
Estradiol (E2) -Dominating estrogenic form in the female. The ovaries (the female gonads, label 4) are located
Produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands. Estradiol is at the ends of the fallopian tubes, on either side of
Types of Estrogen
considered the strongest and most active type of estrogen. ADH, or vasopressin, is a hormone created by the
the uterus (label 5) and they produce hormones hypothalamus and released by the pituitary gland. It mainly
that regulate the female sex organs. Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) effects the kidneys by increasing permeability of the
Estriol (E3) -A waste product of estradiol and is produced in colecting ducts to encourage water absorption into the blood.
the liver. When it binds to an estrogen receptor it prevents Without ADH water would flow out as urnine.
the effects of estradiol. Thus having both estrogenic and
antiestrogenic properties.
Ovaries C orticotropin is a hormone that has the main function of
controlling stress. It controls the release of the
adrenocorticotropic hormone from the pituitary gland. The
C orticotropin-releasing hormone (C RH) adrenal glands are then stimulated and will release cortisol,
the stress hormone. This hormone also helps the body
counter-act things such as appetite and can help highten
one's attention.
Progesterone
This hormone stimulates the pituitary gland to release two
more hormones: follicle stimulating hormone and luteinising
Progesterone is imperative for the regulation of ovulation The hypothalamus is the link
hormone. The follicle stimulating hormone acts on the
and menstruation. Lack of progesterone can cause women to between the nervous ovaries and the testes to stimulate and maintain their
not have periods. system and the endocrine Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
reproductive function. The follicle stimulating hormone and
system. It controls the luteinising hormone both work together to regulate the
internal balance of the amount of hormones the two reproductive parts produce in
men and in women.
Hypothalamus body, which is also known
as homeostasis. The
hypothalamus (label 11) is I wonder what these hormones do. Hmm. Oh wait, I know!
located above the pituitary They stimulate the pituitary gland to release or inhibit growth
hormones into the bloodstream! Yay! Another name for the
gland and below the Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) growth hormone inhibiting hormone is Somatostatin. the
thalamus. Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) hypothalamus secretes this hormone in order to inhibit the
release of the growth hormone in the pituitary gland. The
This hormone is a androgenic hormone that controls the growth hormone releasing hormone also has some affects
growth and functions of the males reproductive organs. It on sleep, food intake among other things.
causes the development of the male characteristics during
puberty such as facial hair, deepening of the voice and
growth spurts. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control Oxytocin is secreted by the pituitary gland, controlled by the
the amount of testosterone that the testes produce. hypothalamus. It is most known in women as it is
Testosterone
Testosterone also provides the main stimulus for sperm responsible for contraction of the uterus and lactation.
Oxytocin
production. Oxytocin is also present in men, however, helping the
movement of sperm cells and the production of testosterone
in the testes.
Hypogonadism is a condition that ocurs when sex glands
produce little or no Testosterone. Hypogonadism is a
condition that you can be born with or it can develp from an These hormones are responsible for stimulating the
infection or injury. Primary Hypogonadism is when the Prolactin-releasing hormone (PRH) production of the hormone prolactin in the pituitary gland.
human body doesn't have enough sex hormones, the gonads Hypogonadism Prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH) Prolactin is shown to have over 300 functions in the human
are reciveing the message to produce hormones but are body and is located in places such as the breasts and uterus.
unable to do so. Some symptoms that occur in males are
loss of body hair, reduced growth of penis and testes, low
sex drive, infertility, and loss of muscle mass.
Endocrine System and Hormones
The Testes ( the male gonads, label 6) are
located behind the penis in a pouch of skin
called the scrotum. The Testes lie outside of the
body but are are still attachted to the body wall The adrenocorticotropic hormone is a polypeptide that
controls the nutrition and growth of the adrenal cortex. The
by a thin cord called the spermatic cord. They Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
hormone also stimulates the production of steroids in the
Testes produce hormones that regulate the male
reproductive organs.
cortex of the adrenal gland
The luteinizing Hormone stimulates ovulation in females and
Luteinizing Hormone the synthesis of androgen in males. It stimulates the testes
in males for production of testosterone
The Human Growth Hormone is a peptide hormone that
Human Growth Hormone stimulates growth and cell reproduction. When things goes
wrong here, it can cause gigantism or dwarfism
TSH promotes the growth of the thyroid gland in the neck
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Anterior Pituitary Gland and stimulates it to produce more thyroid hormones.
This hormone is essential to the development during
puberty and the function of the Testes. FHS acts on sertoli
cells in the Testes and promotes sperm production. This FSH have a different role for female and males. It regulates
hormone is regulated by levels of Testosterone and Inhibin. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone growth and development and also puberty. In females, it
The pituitary gland is the main endocrine gland, known as releases estrogen and in males, starts production of sperm
the master gland because it releases hormones that control
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) other glands and body functions. The pituitary is a pea-sized
Increased Levels of FSH can lead to Kallmann Syndrome
which can cause Testicular Failure. This is a genetic condition gland located in the center of the brain and is composed of 2 Prolactin prepares the breasts for production of milk when a
where the main symptom is a failure to start puberty or to parts, the posterior pituitary, and the anterior pituitary. female is pregnant. After birth, it is now responsible for
complete it. This condition affects the production of promoting milk production as long as the mother keeps
hormones that are responsible for sexual development.
Kallmann Syndrome Pituitary Prolactin
breast-feeding. When the mother stops breat-feeding,
Other common symptoms are infertility and hypothyroidism. dopamine is released sending a signal to the brain saying
People with Kallmann Syndrome also tend to a weak sense that milk is not needed anymore so production of it, stops.
of smell or none at all.
a-MSH is responsible for stimulating melanogenesis which
Alpha Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone
Decreased levels of FSH can lead to lack of sperm produces the pigmentation of skin and hair.
production which in turn causes infertilty, and can also
caause delayed puberty. FSH can be used to determine
wheather a couple can or can not become pregnant. They
can test both the male and females FSH levels to make sure Oxytocin is responsible for stimulating the contractions
that their sex organs are working properly. during birth and also for lactation when babies suckle on
Oxytocin mother. Oxytocin is also released when someone is
comfortable with someone, and is the feeling people
describe when they fall in love
Posterior Pituitary Gland
Vasopressin is a peptide hormone that stimulates capillary
Vasopressin muscles increasing blood pressure. Vasopressin also reduces
the flow of urine but increases its concentration.
Main topic
Endocrine System Diagram
You might also like
- Testosterone ScienceDocument49 pagesTestosterone ScienceMithlesh Rajak100% (3)
- Orthopedic Evaluation MedicalTemplateDocument3 pagesOrthopedic Evaluation MedicalTemplatee-MedTools50% (4)
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument1 pagePost-Traumatic Stress DisorderJoan MonzonesNo ratings yet
- Motivation and EmotionDocument6 pagesMotivation and EmotionnowellstanNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control MechanismsDocument4 pagesFeedback Control MechanismsJividan SasidranNo ratings yet
- Train Your Brain Build A Framework For Clear ThinkingDocument235 pagesTrain Your Brain Build A Framework For Clear ThinkingyashyiNo ratings yet
- Pranayama - 15 Step-by-Step Breathing Techniques To Relieve Stress and Calm Your Mind - (Pranayama and Breathwork, Breathing Practices, Body-Mind Management) (Pranayama, Breathing Pranayama)Document31 pagesPranayama - 15 Step-by-Step Breathing Techniques To Relieve Stress and Calm Your Mind - (Pranayama and Breathwork, Breathing Practices, Body-Mind Management) (Pranayama, Breathing Pranayama)Velpandian ManiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer - BAYLONDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer - BAYLONElijah Joaquin Payumo BaylonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemMesum Jutt100% (1)
- 9 - Toronto Notes 2011 - EndocrinologyDocument56 pages9 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Endocrinologyarcsan15100% (1)
- NeuroSuccess: Your Brain Retraining Guide to Wealth and AccomplishmentFrom EverandNeuroSuccess: Your Brain Retraining Guide to Wealth and AccomplishmentNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemshasagailNo ratings yet
- Psychology-for-BBA - First sems-Pokhara-UniversityDocument100 pagesPsychology-for-BBA - First sems-Pokhara-UniversitySundar Singh ThakuriNo ratings yet
- Lab Values 1Document30 pagesLab Values 1Ezekiel John GarciaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map PT 1Document1 pageConcept Map PT 1api-657741346No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonist MAPDocument1 pageAdrenergic Agonist MAPJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- CKD ModulDocument31 pagesCKD ModulOlan Adjalah KeknyaNo ratings yet
- Sedation in Neurocritical Patients: Is It Useful?: ReviewDocument7 pagesSedation in Neurocritical Patients: Is It Useful?: ReviewAditiaPLNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument1 pageDigestive SystemCHANON KIATKAWINWONGNo ratings yet
- Renal Pathology) 07 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) - KeyDocument1 pageRenal Pathology) 07 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Recommended Antiemetic Regimen For Single-Day ChemotherapyDocument1 pageRecommended Antiemetic Regimen For Single-Day ChemotherapyAhmed Abd El AzizNo ratings yet
- Jerry Leung - Enhancing Transfusable Platelets Using mRNA Therapy To Produce Exogenous ProteinsDocument1 pageJerry Leung - Enhancing Transfusable Platelets Using mRNA Therapy To Produce Exogenous ProteinsCBR UBCNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Ana Lec 2Document53 pagesNervous System Ana Lec 2hey lolNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument230 pagesUntitledSilvana RoccoNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument22 pagesBlood VesselsEulanda DelenNo ratings yet
- Lect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFDocument11 pagesLect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFBinisha KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Managing Microbes Poster AIF 00612Document1 pageManaging Microbes Poster AIF 00612Devina Sari PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Neu.2017.5599 - NICE PaperDocument61 pagesNeu.2017.5599 - NICE PaperGregory MillánNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Sym&Parasym DrugsDocument2 pagesMind Map Sym&Parasym Drugsjitpinun.sNo ratings yet
- Basalog One PiDocument2 pagesBasalog One Pipratibha.turitoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation On Strength and Balance in Patients After Coronary Artery Bypass GraftDocument5 pagesEffect of Cardiac Rehabilitation On Strength and Balance in Patients After Coronary Artery Bypass GraftJulenda CintarinovaNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Penyakit Paru Obstruksi Kronik (PPOK) : Tinjauan PustakaDocument10 pagesFarmakoterapi Penyakit Paru Obstruksi Kronik (PPOK) : Tinjauan PustakaLilisNo ratings yet
- Patient Data - 100Document1 pagePatient Data - 100pavankn0402No ratings yet
- The Effect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityJassim AlsabtNo ratings yet
- Microanatomy PracticalsDocument1 pageMicroanatomy Practicalsaferdita xhepaNo ratings yet
- Von Willebrand Factor Antigen - 0020002300: Limitations/interfering SubstancesDocument3 pagesVon Willebrand Factor Antigen - 0020002300: Limitations/interfering Substances28850No ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument10 pagesCell Structureadhit46No ratings yet
- 2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Document63 pages2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Taif SalimNo ratings yet
- CUP Strong Evidence MatrixDocument1 pageCUP Strong Evidence Matrixmajetan212No ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument1 pageCEREBELLUMOscar Orengo AlbertorioNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Analysis in Plasma-Serum and Urine Brochure en 4Document6 pagesAmino Acid Analysis in Plasma-Serum and Urine Brochure en 4yousrazeidan1979No ratings yet
- Pituitary Diseases: Pituitary Gland Pituitary GlandDocument6 pagesPituitary Diseases: Pituitary Gland Pituitary Glandمحمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Optimal Control Applied To Disease ModelsDocument37 pagesAn Introduction To Optimal Control Applied To Disease ModelsMohammad Umar RehmanNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Atrial-TachycardiaDocument1 pageConcept Map Atrial-TachycardiaBea Mae DeocampoNo ratings yet
- DUF of July 2022Document22 pagesDUF of July 2022Alexandra RenneNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesHomeostasis and Endocrine SystemsiewyonglimNo ratings yet
- 2-The Digestive ProcessDocument8 pages2-The Digestive ProcessYo1No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FluidDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 FluidShaz NagaNo ratings yet
- Online Edition - Digital AccessDocument1 pageOnline Edition - Digital Access18aw2708No ratings yet
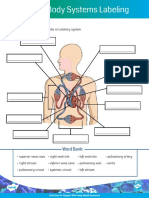
- Human Body Systems Labeling Activity DigitalDocument7 pagesHuman Body Systems Labeling Activity Digitalmoony mohammedNo ratings yet
- Level of Organisation QPDocument10 pagesLevel of Organisation QPApdiweli AliNo ratings yet
- Subjective Objective Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesSubjective Objective Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlethen Janine SagunNo ratings yet
- Andrew J. Cutler - Valbenazine and DeutetrabenazineDocument1 pageAndrew J. Cutler - Valbenazine and DeutetrabenazineSanty P Vásconez CalderónNo ratings yet
- Excretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17Document8 pagesExcretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17edeceNo ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff Tendonitis/Impingement Rehabilitation Protocol: Laith M. Jazrawi, MDDocument3 pagesRotator Cuff Tendonitis/Impingement Rehabilitation Protocol: Laith M. Jazrawi, MDLéo ToaldoNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Tumors SummaryDocument1 pageGynecological Tumors SummaryZahid iqbalNo ratings yet
- Urinary Sys@completeDocument48 pagesUrinary Sys@completeGhina MengalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Summary Notes For Topics Listed in DescriptionDocument1 pageIGCSE Biology Summary Notes For Topics Listed in DescriptionskyeNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in PregnancyDocument3 pagesDiabetes in Pregnancyspatel15072002No ratings yet
- Comparison Between Orthonasal and Retronasal Flavour Perception at Different ConcentrationsDocument6 pagesComparison Between Orthonasal and Retronasal Flavour Perception at Different ConcentrationsFarhan RahmadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 7 - Autonomic Nervous Systemmichael3vo-1No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal: High-Yield SystemsDocument13 pagesGastrointestinal: High-Yield SystemsMohammad DarkhabaniNo ratings yet
- Compare Vivix With Noni Xango MonavieDocument1 pageCompare Vivix With Noni Xango MonaviecustomhealthNo ratings yet
- Judo Is The BestDocument1 pageJudo Is The BestAnkit MohantaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Overview - AMBOSSDocument1 pageAnatomy Overview - AMBOSSxogk.agsavvasNo ratings yet
- Neurodynamic TechniquesDocument2 pagesNeurodynamic Techniquestara deviNo ratings yet
- All Charts Final Exam 1 PDFDocument294 pagesAll Charts Final Exam 1 PDFYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- ICU RehabilitationDocument10 pagesICU RehabilitationKarina Saldivia TecaNo ratings yet
- Pituitary DisordersDocument42 pagesPituitary DisordersDudy HumaediNo ratings yet
- Ncm116 Cop Compiled Notes 1Document27 pagesNcm116 Cop Compiled Notes 1Krizzia LaturnasNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesAssignment For Endocrine SystemMoheeddin KababNo ratings yet
- Every Day Science Part 2 PDFDocument68 pagesEvery Day Science Part 2 PDFSadam GillalNo ratings yet
- A&PII Test 1Document14 pagesA&PII Test 1Alyssa BattcockNo ratings yet
- ABT Endocrine PPDocument39 pagesABT Endocrine PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- ScienceSLM G10 Q3 M3 the-Nervous-System - Docx-1Document31 pagesScienceSLM G10 Q3 M3 the-Nervous-System - Docx-1John100% (1)
- Module 5Document9 pagesModule 5CamilleCalmaLenonNo ratings yet
- Hormone NotesDocument2 pagesHormone Notesapi-188978784100% (1)
- Effects of Steroid Hormones On Brain: GlossaryDocument6 pagesEffects of Steroid Hormones On Brain: GlossaryAnonymous droqJBqu6No ratings yet
- Hormones and Behavior: Basic Concepts: R. J. Nelson, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USADocument9 pagesHormones and Behavior: Basic Concepts: R. J. Nelson, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USAapabooksNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument27 pagesBiology Projectravifact0% (2)
- MSC Yoga Syllabus PDFDocument50 pagesMSC Yoga Syllabus PDFsankuj5354No ratings yet
- Obesity A Review of Pathophysiology and Classific - 2023 - Mayo Clinic ProceediDocument16 pagesObesity A Review of Pathophysiology and Classific - 2023 - Mayo Clinic Proceedialerta.bfcmNo ratings yet
- Agya Chakra and Your PersonalityDocument7 pagesAgya Chakra and Your PersonalityDrGarima Saxena MehtaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Case StudyDocument3 pagesEndocrine Case StudyJenny ViNo ratings yet
- Bruxism Affects Stress Responses in Stressed RatsDocument8 pagesBruxism Affects Stress Responses in Stressed RatsJonathan GIraldo MartinezNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Endocrine System: EquilibriumDocument20 pagesFunctions of The Endocrine System: EquilibriumKumah WisdomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Motivation and EmotionDocument34 pagesChapter 9 Motivation and EmotionChehekNo ratings yet
- The Maternal BrainDocument358 pagesThe Maternal BrainCarlos VargasNo ratings yet
- Physiology Handouts Topics (42-64)Document67 pagesPhysiology Handouts Topics (42-64)bc200411046No ratings yet