Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study (Captopril)
Uploaded by
Baji ۦۦ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageDrug Study (Captopril)
Uploaded by
Baji ۦۦCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
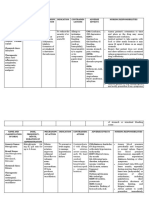
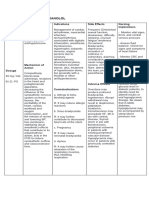
DRUG NAME
(Generic/Brand Name/ MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING
Classification/Dosage/ ACTION RESPONSIBILITIES/PRECAUTION
Frequency)
Angiotensin-converting Alone or with other Contraindicated in CNS: dizziness, fatigue, Watch for signs of angioedema,
CAPTOPRIL enzyme (ACE) inhibitors agents in the patients who are headache, insomnia. including rashes, raised patches of red
Therapeutic: block the conversion of management of hypertensive to this or white skin (welts), burning/itching
antihypertensives angiotensin I to the hypertension. product or any other Resp: cough, skin, swelling in the face, and difficulty
Pharmacologic: ACE vasoconstrictor Management of heart angiotensin-converting breathing. Notify physician
inhibitors angiotensin II. ACE failure. Reduction of enzyme inhibitor. CV: hypotension, chest immediately of these signs.
25mg inhibitors also prevent risk of death, heart Avoid in neonates, in pain, palpitations,
1 Tab SL the degradation of failure–related volume depletion and tachycardia. Assess blood pressure periodically and
bradykinin and other
hospitalizations, and renovascular disease. compare to normal values (See
vasodilatory
development of overt GI: taste disturbances, Appendix F) to help determine
prostaglandins. ACE
heart failure following abdominal pain, antihypertensive effects. Report low
inhibitors also increase
plasma renin levels and myocardial infarction. anorexia, constipation, blood pressure (hypotension),
reduce aldosterone Treatment of diabetic diarrhea, nausea, especially if patient experiences
levels. Net result is nephropathy in vomiting. dizziness, fatigue, or syncope.
systemic vasodilation. patients with type 1
Therapeutic Effects: diabetes mellitus and GU: proteinuria, Assess signs and symptoms of CHF
Lowering of blood retinopathy. impaired renal (dyspnea, rales/crackles, peripheral
pressure in patients function. edema, jugular venous distention,
with hypertension. exercise intolerance) to help
Improved survival and Derm: ANGIOEDEMA, document whether drug therapy is
reduced symptoms in rashes, pruritus. F and effective in reducing these symptoms.
patients with heart E: hyperkalemia.
failure. Improved Assess dizziness that might affect gait,
survival and reduced Hemat: balance, and other functional
development of overt AGRANULOCYTOSIS, activities (See Appendix C). Report
heart failure after neutropenia. balance problems and functional
myocardial infarction. limitations to the physician, and
Decreased progression Misc: fever. caution the patient and
of diabetic nephropathy
family/caregivers to guard against falls
with decreased need for
and trauma.
transplantation or
dialysis.
You might also like
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Oxylog Ve300Document134 pagesOxylog Ve300davidNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-1st BatchDocument27 pagesDRUG STUDY-1st BatchCanny CańasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Ate Mitch HN DRUG STUDYDocument23 pagesAte Mitch HN DRUG STUDYMarice VenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HypertensionDocument2 pagesDrug Study HypertensionFryd Ryxx GarciaNo ratings yet
- Centralloy G4852 Micro R (Cast Austenitic Stainless Steel)Document2 pagesCentralloy G4852 Micro R (Cast Austenitic Stainless Steel)Anonymous w6TIxI0G8lNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLester Paul SivilaNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)Document7 pagesNCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)MARIA KAWILANNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2 Valsartan, Furosemida, HydralineDocument4 pagesDrug Study 2 Valsartan, Furosemida, HydralineLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- 1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONDocument4 pages1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONEdmon SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study D InsipidusDocument7 pagesDrug Study D InsipidusAisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine-Drug Study 2BSN3Document3 pagesNifedipine-Drug Study 2BSN3Nichole DancelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 pagesHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Medications TemplateDocument5 pagesCardiac Medications TemplateErinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyPantaleon PacisNo ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument2 pagesTelmisartanRea LynNo ratings yet
- TAMBALDocument4 pagesTAMBALVianca Kate MarquezNo ratings yet
- HYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)Document1 pageHYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)wen_pilNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) Drug Study: Submitted By: Daryl S. AbrahamDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) Drug Study: Submitted By: Daryl S. AbrahamBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Trade Name: Isoket Generic Name: Isosorbide Dinitrate/ MononitrateDocument3 pagesTrade Name: Isoket Generic Name: Isosorbide Dinitrate/ MononitrateKhenz AkatpunkzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRea LynNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Med LopressorDocument2 pagesMed LopressorDeanna Lang ThibodauxNo ratings yet
- Sweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyDocument9 pagesSweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyRon OpulenciaNo ratings yet
- Captopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyDocument4 pagesCaptopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyKsksksksNo ratings yet
- Unit Task Cardiovascular ChangesDocument3 pagesUnit Task Cardiovascular ChangesCamille MactalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Y.LDocument11 pagesDrug Study Y.LZhij ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Y.LDocument11 pagesDrug Study Y.LZhij ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Trade Name: Isoket Generic Name: Isosorbide Dinitrate/ MononitrateDocument3 pagesTrade Name: Isoket Generic Name: Isosorbide Dinitrate/ MononitrateMarky Mendoza FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Document5 pagesAngiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Isabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskev mondaNo ratings yet
- Johnlevy, ENDODocument3 pagesJohnlevy, ENDOAERONH JOHN PURIFICANDONo ratings yet
- Propranolol Drug StudyDocument1 pagePropranolol Drug Studycarbon.mariaauroraisabel.cNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine DSDocument2 pagesHydralazine DSAntoniette Jane Martin PathayNo ratings yet
- Atenolol2Document1 pageAtenolol2Christine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- AGE DrugDocument5 pagesAGE DrugLA GomezNo ratings yet
- Categorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionDocument3 pagesCategorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionMicah LatosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Stury NS3Document2 pagesDrug Stury NS3Mikaela Ysabel CañaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Task 2Document94 pagesDrug Study Task 2ClaireNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteRamsam UayanNo ratings yet
- ARCHEDERA (Drug Study #10&11)Document2 pagesARCHEDERA (Drug Study #10&11)SHIELA MAE ARCHEDERANo ratings yet
- Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesDrug Study LosartanQueenie Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument6 pagesPharmacology Drug StudyShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AtorvastatinReyes MarinellaNo ratings yet
- IV. Medications and Treatment BN/GN Dosage/ Frequency/ Route Indication/ CI Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesIV. Medications and Treatment BN/GN Dosage/ Frequency/ Route Indication/ CI Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesStephy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Drug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYDocument71 pagesDrug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYJay MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drugs 2Document6 pagesDrugs 2Elyse Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Llarenas, Kimberly Kaye P.Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Llarenas, Kimberly Kaye P.Kimberly Kaye LlarenasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study StaDocument3 pagesDrug Study StaarjeighNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- DLP L05 - Challenges in AdolescenceDocument3 pagesDLP L05 - Challenges in AdolescenceSora YamazakiNo ratings yet
- Arahan Dan Soalan Tugasan Jkp513e417e Sa 20222023Document4 pagesArahan Dan Soalan Tugasan Jkp513e417e Sa 20222023skblueNo ratings yet
- Phys172 S20 Lab07 FinalDocument8 pagesPhys172 S20 Lab07 FinalZhuowen YaoNo ratings yet
- THE 3RD INDONESIA EBTKE CONEX 2014 (4-6 June'14) PDFDocument10 pagesTHE 3RD INDONESIA EBTKE CONEX 2014 (4-6 June'14) PDFArik AprilliyantoNo ratings yet
- Civic Ass JolaxDocument3 pagesCivic Ass JolaxEyob TeferaNo ratings yet
- Pps Overview BrochureDocument15 pagesPps Overview BrochureizzybjNo ratings yet
- TranscriptDocument1 pageTranscriptGursharanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- (E) Chapter 1 - Origin of Soil and Grain SizeDocument23 pages(E) Chapter 1 - Origin of Soil and Grain SizeLynas Beh TahanNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan IMRAD StructureDocument2 pagesPenjelasan IMRAD Structureaji bondesNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy (DISE)Document4 pagesDrug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy (DISE)Luis De jesus SolanoNo ratings yet
- A Sensorless Direct Torque Control Scheme Suitable For Electric VehiclesDocument9 pagesA Sensorless Direct Torque Control Scheme Suitable For Electric VehiclesSidahmed LarbaouiNo ratings yet
- Analog Devices - LVDT Signal Conditioner AD598Document16 pagesAnalog Devices - LVDT Signal Conditioner AD598maguschNo ratings yet
- Assignment (60%) : ECS312 Counselling in SchoolsDocument6 pagesAssignment (60%) : ECS312 Counselling in SchoolsJelebu Charity RunNo ratings yet
- 02 - Thank You Maam Square Task CardsDocument8 pages02 - Thank You Maam Square Task CardsMaria Evelyn Won100% (1)
- 6.1 Mean Median Mode and RangeDocument21 pages6.1 Mean Median Mode and RangeGilbert Guzman TurarayNo ratings yet
- Imran Index 1Document11 pagesImran Index 1api-387022302No ratings yet
- Srijana BahadurDocument13 pagesSrijana Bahadurkhadija khanNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Series 7Document44 pagesUser Manual: Series 7Roniel ManjaresNo ratings yet
- A View From Elkab The Tomb and Statues oDocument87 pagesA View From Elkab The Tomb and Statues oBeatriz FélixNo ratings yet
- 344W11MidTermExamI Solution PDFDocument22 pages344W11MidTermExamI Solution PDFTrường TùngNo ratings yet
- 4 AMcKayCatalogDocument10 pages4 AMcKayCatalogManuelNo ratings yet
- 2CSE60E14: Artificial Intelligence (3 0 4 3 2) : Learning OutcomesDocument2 pages2CSE60E14: Artificial Intelligence (3 0 4 3 2) : Learning OutcomesB. Srini VasanNo ratings yet
- Formal Language and Automata TheoryDocument18 pagesFormal Language and Automata TheoryAyan DuttaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Rizal Morga Lifestyle: LifestyleDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Rizal Morga Lifestyle: LifestyleMarjorie GawalaNo ratings yet
- 805-Article Text-3656-1-10-20220310Document16 pages805-Article Text-3656-1-10-20220310abolfazlshamsNo ratings yet
- 4194-Article Text-11162-1-10-20190903Document6 pages4194-Article Text-11162-1-10-20190903Akhsana SantosoNo ratings yet