Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bab 6
Bab 6
Uploaded by
mdazrilomar08Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bab 6
Bab 6
Uploaded by
mdazrilomar08Copyright:
Available Formats
Jawapan Bab 6
Bab 6 Elektrik dan Kemagnetan Soalan / Questions:
Electricity and Magnetism Paparan arus terus menunjukkan garis lurus
manakala paparan arus ulang-alik menunjukkan
6.1 Penjanaan Tenaga Elektrik garis lengkung.
Generation of Electricity The direct current displays a straight line while the alternating current
displays a curved line.
1. (a) (ii) 7.
(b) (i)
(c) (ii) Persamaan
Similarity
2. (a), (c), (d)
3. Kedua-duanya boleh digunakan untuk pemanasan dan
(a) Stesen jana kuasa hidroelektrik
Hydroelectric power station pencahayaan
Both can be used in heating and lighting
(b) Stesen jana kuasa terma
Thermal power station
Perbezaan
Differences
(c) Stesen jana kuasa nuklear Arus terus Aspek Arus ulang-alik
Nuclear power station Direct current Aspect Alternating current
(d) Stesen jana kuasa biojisim Arah aliran
Biomass power station Satu arah elektron Sentiasa berubah
One way The direction of Alway changes
4. (a) (ii), (v) electron flow
(b) (iii), (vi) Kebolehan
(c) (i), (iv) voltan
5. Pemerhatian / Observation Tidak boleh diubah oleh Boleh
Cannot transformer Can
Jarum Lampu The ability of the
Langkah galvanometer voltage changed by
Step Galvanometer
LED the transformer
LED light
needle
Bateri, sel suria dan Penjana arus
Magnet bar digerakkan ke penjana arus terus Sumber ulang-alik
Terpesong Menyala Dry cell, solar cell and direct Source Alternating current
dalam gegelung Deflected Lights up
Bar magnet moved into the wire coil current generator generator
8. Jawapan murid
Magnet bar digerakkan Terpesong Student’s answer
Menyala
keluar dari gegelung Deflected Lights up
Bar magnet moved out of the wire coil
6.2 Transformer
Soalan / Questions Transformer
(a) magnet 1. (a) Mengubah voltan/ menaikkan atau
magnetic menurunkan voltan bagi arus ulang-alik
(b) magnet, aruhan (Va.c).
magnet, induction To change the voltage/ increase or decrease the voltage of an
(c) pegun, teraruh, dipotong alternating current (Va.c )
at rest, induced, cut (b) (i) Gegelung primer
Primary coil
6. Pemerhatian / Observation
(ii) Teras besi lembut berlamina
Laminated soft iron core
(iii) Gegelung sekunder
Secondary coil
(c) (i) Voltan yang dibekalkan oleh bekalan
kuasa
Arus terus (a.t) Arus ulang-alik (a.u) The voltage supplied by the power supply
Direct current (d.c) Alternating current (a.c)
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. J20
Sains Tingkatan 3 Jawapan
(ii) Voltan yang telah diubah oleh The number of the turns of primary coil for transformer J
is more than secondary coil while the number of turns of
transformer primary coil for transformer K is less than secondary coil.
The voltage that has been changed by the transformer
(ii) Transformer J menurunkan voltan
2. (a) (i) Transformer injak turun
Step-down transformer manakala transformer K menaikkan
(ii) Transformer injak naik voltan.
Step-up transformer Transformer J decreases the voltage while transformer K
increases the voltage.
(b) (i) Bilangan lilitan gegelung primer bagi
(iii) Voltan sekunder transformer K lebih
transformer J lebih banyak daripada
tinggi berbanding dengan transformer J.
bilangan lilitan gegelung sekunder Secondary voltage for transformer K is higher than
manakala bilangan lilitan gegelung transformer J.
primer bagi transformer K kurang (c) Arus ulang-alik
daripada bilangan lilitan gegelung Alternating current
sekunder.
3. Pemerhatian / Observation:
Bilangan lilitan
Aktiviti Number of turns Jenis transformer Kecerahan mentol
Activity Gegelung primer Gegelung sekunder Type of transformer The brightness of bulb
Primary coil (Np) Secondary coil (Ns)
Injak naik Cerah
A 30 60 Step-up Bright
Injak turun Malap
B 60 30
Step-down Dim
1. Membandingkan bilangan lilitan dalam VS 50
gegelung primer dan sekunder 7. =
50 100
Compare the number of turns in the primary and secondary coil
2. Semakin banyak bilangan lilitan gegelung 50 x 50
Vs = = 25 V
sekunder, semakin cerah mentol. 100
The higher the number of turns of coil in the secondary coil, the 60 V 1
brighter the bulb. 8. = S =
3. Menambah bilangan lilitan gegelung 240 VP 4
sekunder Nisbah lilitan Np : Ns = 4 : 1
Increase the number of turns in the secondary coil Ratio of number of turns of Np : Ns = 4 : 1
4. Transformer hanya berfungsi untuk menaik
dan menurunkan arus ulang-alik. Sel kering 6.3 Penghantaran dan Pengagihan Tenaga Elektrik
Transmission and Distribution of Electricity
membekalkan arus terus.
The transformer only works to increase or decrease the alternating
current. Dry cells supply direct current. 1. (a)
Kehilangan tenaga elektrik dalam bentuk
5. (a) Mengawal voltan yang dibekalkan tenaga haba.
Control the supplied voltage The loss of electrical energy in the form of heat energy.
(b) Voltan yang dibekalkan adalah terlalu besar (b) (ii), (iv)
untuk mentol yang digunakan iaitu 240 V. 2. (a) (i) Stesen transformer / Transformer station
The voltage supplied is too big for the bulb used which is 240 V . (ii) Lapangan suis / Switch zone
6. (a) Akan meletup / terbakar kerana bekalan (iii) Pencawang bahagian / Branch substation
voltan di Malaysia lebih tinggi iaitu 240 V. (iv) Pencawang masuk utama / Main substation
Will explode / burn because the supplied voltage in Malaysia is
higher which is 240 V. (b) P: Transformer injak naik
Step-up transformer
(b) Alatan di Malaysia beroperasi pada voltan
Q: Transformer injak turun
240 V manakala voltan yang dibekalkan di Step-down transformer
Thailand ialah 110 V. Oleh itu, kipas itu gagal R: Transformer injak turun
beroperasi dengan baik kerana kurang Step-down transformer
bekalan voltan. (c) (i) elektrik / Electrical
The Malaysian electrical appliances operate using 240 V while (ii) stesen jana kuasa / power stations
the voltage supplied in Thailand is 110 V. Therefore, the fan
cannot function well due to less voltage supply. (iii) Rangkaian Grid Nasional
National Grid Network
(iv) tenaga haba / heat energy
(v) injak naik / step-up
J21 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Sains Tingkatan 3 Jawapan
(vi) meninggikan / increase
Litar kuasa Membekalkan arus elektrik kepada semua
(vii) diturunkan / decreased Power circuit soket
(viii) injak turun / step-down Supplies electric current to all sockets
(d) Keperluan tenaga yang berbeza untuk
kawasan perindustrian dan perumahan. Litar Membekalkan arus elektrik kepada semua
Different energy requirements for industrial areas and residential pencahayaan lampu
areas. Light circuit Supplies electric current to all lamps
(e) (i) ✓ Dawai bumi Membawa arus bocor ke bumi
(iv) ✓ Earth wire Carries leakage current to the earth
3. Pemutus litar Mengasing litar elektrik ke peralatan
Pernyataan Fasa tunggal Tiga fasa
Statement Single-phase Three-phase MCB elektrik yang lain
Miniature Circuit Segregate the electrical circuit to the other electrical
Breaker appliances
(a) ✓
(b) ✓ (e) 240 V
(f ) Arus ulang-alik
(c) ✓ Alternating current
(g) Sistem pendawaian satu fasa
(d) ✓ Single-phase wiring system
4. (a) 5. (a) (i) Palam 3-pin / 3-pin plug
(ii) Seterika, cerek / Iron, kettle
Nama Kod warna antarabangsa
Name International colour code (iii) Palam 2-pin / 2-pin plug
X: Dawai hidup Perang (iv) Pengering rambut, pengisar / Hair dryer,
Live wire Brown blender
Y: Dawai (b) (i) Dawai hidup
Biru Live wire
neutral Blue
Neutral wire (ii) Dawai neutral
Neutral wire
Z: Dawai bumi Jalur kuning berbelang hijau
Earth wire Yellow with green strip (iii) Dawai bumi
Earth wire
(b) Dawai hidup membekalkan tenaga elektrik (iv) Fius
ke rumah manakala dawai neutral membawa Fuse
tenaga elektrik ke luar rumah 6. Pemerhatian / Observation:
Live wire transmits the electrical energy into the house while the
neutral wire transmits the electrical energy out of the house. Pemerhatian
(c) Memudahkan meter dibaca oleh pembaca Langkah Observation
meter Step Fius Mentol
To ease the meter to be read by the meter reader Fuse Bulb
(d)
Sebelum menyambungkan Tiada
Komponen Fungsi Menyala
dawai kuprum yang tebal perubahan Lights up
Component Function Before connecting the thick copper wire No change
Fius utama Mengawal jumlah arus yang dibekalkan Selepas menyambungkan Fius Tidak
Main fuse ke rumah dawai kuprum yang tebal melebur menyala
Controls the amount of electrical energy supplied to the After connecting the thick copper wire Fuse melts Does not light up
house
(a) Untuk mengurangkan rintangan dan boleh
Meter elektrik Menyukat jumlah unit tenaga elektrik
Electric meter membawa lebih arus.
yang digunakan To reduce the resistance and hence can carry more current.
Measures the total unit of electricity used
(b) Litar pintas / Short circuit
Suis utama Mengawal jumlah arus yang mengalir (c) Dawai kuprum yang tebal mempunyai
Main switch melalui Iitar di dalam rumah rintangan yang lebih rendah berbanding
Controls the amount of current that flows through the circuit dengan mentol dan dawai penyambung
in the house
yang nipis.
Pemutus litar Memutuskan semua litar dalam rumah The thick copper wire has lower resistance than the bulb and the
thin connecting wires.
ELCB jika arus yang dibekalkan berlebihan
Earth Leakage Break all the circuits in the house if current is supplied (d) Terlalu banyak arus mengalir melalui litar.
Circuit Breaker excessively. Hal ini menyebabkan suhu meningkat dan
fius melebur.
Too much current flow through the circuit. This causes the
temperature to rise and the fuse melts.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. J22
Sains Tingkatan 3 Jawapan
(e) Fius memutuskan litar apabila arus yang Gunakan apabila cuaca betul-betul
terlalu banyak mengalir melalui litar itu. panas / Jangan laraskan pada suhu
The fuse breaks the circuit when too much current flows through Penyaman
the circuit. udara paling rendah / Matikan suis apabila
7. (a) (i) Fius kartrij Air tidak diperlukan.
Cartridge fuse conditioner Use when the weather is really hot / Do not
(ii) Fius wayar boleh ganti adjust at the lowest temperature / Turn off the
Replaceable wire fuse switch when not needed
(b) Pemanas Matikan aliran air ketika tidak
Nilai fius air digunakan
Value of fuse
(i) 10 A (ii) 2 A (iii) 1 A (iv) 3 A Water heater Stop the water flow when not in use
8. Jawapan murid/ Student’s answer 5. (a) = 156 kWj × RM0.218 / 156 kWh × RM0.218
9. Jawapan murid/ Student’s answer = RM34.008
(b) (i) 42 258.3 kWj / kWh
6.4 Pengiraan Kos Penggunaan Elektrik (ii) 42 558.2 kWj / kWh
Calculate the Cost of Electricity Consumption (iii) 299.9 kWj / kWh
1. (a) Kecekapan tenaga merujuk peratus tenaga 6. Kos tenaga elektrik / Cost of electrical energy
input yang ditukarkan kepada tenaga output = Kuasa (kW) × Masa penggunaan (j) × Kadar per
yang berfaedah. unit
Energy efficiency refers to the percentage of energy input that is Power (kW) × Time usage (h) × Rate per unit
converted to useful energy output. = 2 kW × 5 j / h × RM0.20
100 – 80 = RM2.00
(b) Kecekapan tenaga laptop = × 100%
Energy efficiency of laptop 100 7. Kos tenaga elektrik
= 20% Cost of electrical energy
(c) (i) PALSU / FALSE = Kuasa (kW) × Masa penggunaan (j) × Kadar per
(ii) BENAR / TRUE unit
Power (kW) × Time usage (h) × Rate per unit
(iii) PALSU / FALSE
= 0.5 kW × 2 j / h × 30 hari / day × RM0.20
(iv) BENAR / TRUE
= RM6.00
2. (a) P>Q>R
(b) R / Lampu LED, kerana tenaga input yang 8. Jawapan murid/ Student’s answer
ditukarkan kepada tenaga cahaya paling
Praktis Masteri 6
tinggi (90%) dengan hanya kehilangan 10%
Bahagian A
tenaga haba.
R / LED lamp, because the input energy that is converted to light 1. B 2. D 3. A 4. B 5. A
energy is the highest (90%) with only 10% loss as heat energy. 6. D 7. B 8. B
P
3. (a) I = Bahagian B
V
= 910 W 1. (a) Gas asli
3
240 V Natural gas
= 3.80 A (b) Arang batu
(b) 910 W = 0.910 kW Coal
3
30 min = 0.5 j / h
Tenaga elektrik yang digunakan (b) (i) Tenaga solar / Solar energy
Electrical energy used (ii) Petroleum / Petroleum
= 0.910 kW × 0.5 j / h 2. (a) (i) PALSU / FALSE
= 0.455 kWj / kWh (ii) BENAR / TRUE
4. Jawapan murid (b)
(i) Fius kartrij
Student’s answer Cartridge fuse
(d)
(ii) Fius wayar boleh ganti
Alat Langkah-langkah penjimatan Replaceable wire fuse
Appliance Saving steps 3. (a) (i), (iii)
Mesin (b)
Gunakan dengan muatan penuh (i) Palam 3-pin
basuh 3-pin plug
Washing Use with a full load of laundry
machine (ii) Palam 2-pin
2-pin plug
J23 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Sains Tingkatan 3 Jawapan
Bahagian C (c) Konduktor kilat. Membumikan cas elektrik
1. (a) Transformer mengubah voltan arus ulang- yang dibawa oleh kilat. Mengelakkan
alik. Dalam rajah bateri yang menghasilkan kebakaran, kerosakan rumah dan peralatan
arus terus digunakan. elektrik.
Transformer converts the voltage of alternate current. In the Lightning conductor. To earth the electrical charge caused by the
diagram, battery cells which produce the direct current is used. lightning. Prevent fire, house and appliance damage.
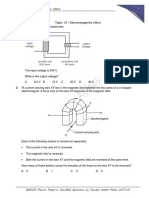
(b) (i)
Teras besi Fokus KBAT
Iron core
1. Pendawaian elektrik bawah tanah lebih selamat
jika berlaku kebocoran elektrik pada kabel.
Pendawaian ini mempunyai jangka hayat yang
Bekalan a.u. lebih lama dan tidak menjejaskan landskap.
Beban
a.c. supply Load Kelemahan jenis pendawaian ini ialah kos
pembinaan yang tinggi dan kesukaran kerja-kerja
pembaikan dan pertukaran kabel yang rosak.
Pendawaian elektrik di atas tanah pula lebih
Gegelung Gegelung
primer sekunder mudah untuk dibaiki jika berlaku kerosakan dan
Primary coil Secondary coil kos pembinaannya lebih murah. Kelemahan jenis
(iii) Persamaan / Similarity pendawaian ini termasuk boleh menjejaskan
Kedua-dua gegelung melilit pada teras landskap dan mudah berlaku kemalangan jika
besi yang sama. kabel terputus dan jatuh.
Both coils wrap around the same iron core . The underground electrical wiring is much safer if there is a leakage
occurs at the cables. It has a longer life expectancy and does not deface
Perbezaan / Difference the landscape. The disadvantages of underground electrical wiring
Gegelung primer bersambung dengan include higher construction costs and the difficulty of repairing and
bekalan a.u manakala gegelung replacing broken cables. Overhead electrical wiring is less expensive to
build and easier to repair if it breaks. This type of wiring system has the
sekunder bersambung dengan beban. disadvantages of defacing the landscape and being prone to accidents
The primary coil is connected to the a.c supply whereas the if the cables break and fall.
secondary coil is connected to the load.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. J24
You might also like
- 14 TOEFL Reading Comprehension 2Document3 pages14 TOEFL Reading Comprehension 2Pou PouNo ratings yet
- Bab 4Document11 pagesBab 4Nicole LimNo ratings yet
- Symbols CircuitDocument1 pageSymbols CircuitignacioraffoortizNo ratings yet
- Quiz Electricity and Magnetism KSSM Form 3Document5 pagesQuiz Electricity and Magnetism KSSM Form 3Immy MaysmeekaNo ratings yet
- All Electric Circuit SymbolDocument1 pageAll Electric Circuit SymbolSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - StudentDocument7 pagesLesson 5 - StudentLộc SẹoNo ratings yet
- Minimum Level of Learning (For 60% Marks) : Subject - PhysicsDocument5 pagesMinimum Level of Learning (For 60% Marks) : Subject - PhysicsHasanNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETISMDocument11 pagesELECTROMAGNETISMSaiful NizamNo ratings yet
- Electric Current, Voltage, Resistance and Conductance: PHYS 121 Physics For Electrical EngineersDocument33 pagesElectric Current, Voltage, Resistance and Conductance: PHYS 121 Physics For Electrical EngineersDianne PañoNo ratings yet
- Sci NB Mod 6 LSN 2Document5 pagesSci NB Mod 6 LSN 2Ramses octavio Rodriguez ocanasNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism: Name - Date - ClassDocument3 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism: Name - Date - ClassFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- Workshop SymbolsDocument6 pagesWorkshop SymbolsYOUTUBE GAMERNo ratings yet
- STE - Week 3Document69 pagesSTE - Week 3Anonymous xf4o0AtOTFNo ratings yet
- Electric Machine (Chapter 1)Document11 pagesElectric Machine (Chapter 1)Habes NoraNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios ElectricidadDocument6 pagesEjercicios ElectricidadNICOLAS NAVAS SUASNAVASNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Transport: George G. Karady & Keith HolbertDocument41 pagesEnergy Conversion and Transport: George G. Karady & Keith HolbertMichael DarmstaedterNo ratings yet
- F3 Science Online Lesson 24 (B)Document20 pagesF3 Science Online Lesson 24 (B)Xavier KeeNo ratings yet
- Boost BoostDocument19 pagesBoost BoostnikitaNo ratings yet
- QP 22.8.23Document1 pageQP 22.8.23rkpost1703No ratings yet
- Chapter14 Electric CurrentDocument11 pagesChapter14 Electric CurrenteltytanNo ratings yet
- F.2 1st UT Scope of Assessment 2021-2022Document16 pagesF.2 1st UT Scope of Assessment 2021-2022Jason YipNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CHAPTER 5 240311 105505Document19 pagesMicrosoft Word - CHAPTER 5 240311 105505thivaa2703No ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Project SampleDocument13 pagesClass 12 Physics Project SampleUma MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Radioisotope Battery: STUDENT NAME: Tarun Gupta USN:1MJ17ME141Document24 pagesRadioisotope Battery: STUDENT NAME: Tarun Gupta USN:1MJ17ME141Tarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- XWJR 8 X 4 LxsgvbzpvdibtDocument24 pagesXWJR 8 X 4 LxsgvbzpvdibtRati SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Electricall Y Induced Vortical FlowsDocument391 pagesElectricall Y Induced Vortical FlowsTomas MullerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17Document16 pagesLecture 17ririnyuNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 8Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 8corazon philNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Harmonic Sources Magnetic Core SaturationDocument7 pagesModeling of Harmonic Sources Magnetic Core SaturationratheeshkumardNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Summary Notes Current Electricity - StuDocument13 pagesUnit 14 Summary Notes Current Electricity - StuWalter WhiteNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of PV Fed Two Stage DC/DC Converter For Home ApplicationsDocument6 pagesDesign and Implementation of PV Fed Two Stage DC/DC Converter For Home ApplicationsVishal KevatNo ratings yet
- Course Book - EnergyDocument3 pagesCourse Book - EnergyDr. Ghassan Nihad JawadNo ratings yet
- The Georgian Technical University The Department of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Simon NemsadzeDocument231 pagesThe Georgian Technical University The Department of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Simon Nemsadzepeter vanderNo ratings yet
- 2.RLC ElementsDocument34 pages2.RLC ElementsShivang LavaniaNo ratings yet
- C21 ElectromagnetismDocument12 pagesC21 ElectromagnetismJeketera ShadreckNo ratings yet
- 3 Stage / 2021-2022 University of Duhok: Dr. Hasan A. MohammedDocument19 pages3 Stage / 2021-2022 University of Duhok: Dr. Hasan A. MohammedlayaNo ratings yet
- Introduction-Electric DrivesDocument24 pagesIntroduction-Electric DrivesSarthakNo ratings yet
- Week 3 LabDocument2 pagesWeek 3 LabIvan SimonNo ratings yet
- 13.electromagnetic EffectsDocument14 pages13.electromagnetic EffectsAymen SenamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Electromagnetic InductionDocument18 pagesChapter 22 Electromagnetic InductionsonghannNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Power Device BasicsDocument4 pagesModule 1: Power Device BasicsAhmed IshaqNo ratings yet
- g10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetismDocument36 pagesg10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetismEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class Xii PhysicsDocument5 pagesHoliday Homework Class Xii PhysicsSoham ShawNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument2 pagesElectrical MachinesStephanie M. BernasNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics SyllabusDocument6 pagesClass 12 Physics SyllabusARAVIND SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Voltage Quality in Electric Arc Furnace With Matlab/SimulinkDocument11 pagesInvestigation of Voltage Quality in Electric Arc Furnace With Matlab/SimulinkerpublicationNo ratings yet
- 1Document32 pages1Mohit ChavdaNo ratings yet
- To Simulate, Design & Implementation of Maximum Power Harvesting of Solar Energy by Using DC-DC ConverterDocument6 pagesTo Simulate, Design & Implementation of Maximum Power Harvesting of Solar Energy by Using DC-DC Convertershrawani rajputNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Important Graphs: 1. Field Lines Due To Some Simple Charge ConfigurationsDocument19 pagesPhysics 12th Important Graphs: 1. Field Lines Due To Some Simple Charge ConfigurationsArjun PasrichaNo ratings yet
- OL P1 PhysicsDocument16 pagesOL P1 PhysicsWania KashifNo ratings yet
- A Novel Single Stage DC-AC Buck Boost Inverter For Solar Power ExtractionDocument6 pagesA Novel Single Stage DC-AC Buck Boost Inverter For Solar Power ExtractionsatheshkumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument65 pagesChapter1 PDFAugustine JR RobertNo ratings yet
- 2 StartersaDocument30 pages2 Startersaafiqah nasirNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument10 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversiondevie mohanNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Investigacion Maquinas CC.-1Document8 pagesTrabajo de Investigacion Maquinas CC.-1ßräyän Nðnð FichüNo ratings yet
- Low-Cost Current-Source 1-ph Photovoltaic Grid-Connected InverterDocument61 pagesLow-Cost Current-Source 1-ph Photovoltaic Grid-Connected InvertereliasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)Document4 pagesElectromagnetism - DPP 05 (Of Lec 06) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)pragnakrishnan5No ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Due To Current Carrying Conductor (MCQ) - Electrical Study ADocument10 pagesMagnetic Field Due To Current Carrying Conductor (MCQ) - Electrical Study Ajyotiranjan sahooNo ratings yet
- Obj Electrical 2002paper IIDocument13 pagesObj Electrical 2002paper IImuthusamyeeeNo ratings yet
- Two Electrical Models of The Lead Acid BDocument8 pagesTwo Electrical Models of The Lead Acid Bbouk omraNo ratings yet
- Power Factor CorrectionDocument28 pagesPower Factor CorrectionPaoloNo ratings yet
- Ceiling Concealed Chilled Water Fan Coil UnitDocument14 pagesCeiling Concealed Chilled Water Fan Coil UnitRodrigo Neira De FinoNo ratings yet
- 4611V002 - 08gb Piston Ring Groove Wear CurveDocument1 page4611V002 - 08gb Piston Ring Groove Wear CurveBertan ChirimNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Fcu-AhuDocument4 pagesChecklist of Fcu-AhuMoizuddin Khaja100% (1)
- Pre-Board Exam in Industrial and Power Plant Engineering: A. 4.71 HP BDocument6 pagesPre-Board Exam in Industrial and Power Plant Engineering: A. 4.71 HP BVon Eric DamirezNo ratings yet
- Iveco DailyDocument266 pagesIveco DailyJulianoDepetris100% (10)
- Allen Bradley 1485 PowertapDocument2 pagesAllen Bradley 1485 PowertapRAFAEL CARDOSONo ratings yet
- ZEECO PRODUCTS & INDUSTRIES - Burners - Boiler Burners PDFDocument2 pagesZEECO PRODUCTS & INDUSTRIES - Burners - Boiler Burners PDFKR PANo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Vs EntropyDocument28 pagesEnthalpy Vs Entropyanirbanpwd76100% (1)
- Classical Mechanics - CohenDocument221 pagesClassical Mechanics - CohenJames Maxwell100% (1)
- Acsr Conductors AccessoriesDocument7 pagesAcsr Conductors Accessoriesashok10577No ratings yet
- Vacuum Toilet EvacDocument7 pagesVacuum Toilet Evacdevendra singh100% (1)
- 03 WPS PQR For FCAWDocument3 pages03 WPS PQR For FCAWBrijesh Yadav100% (1)
- Activation Photochemical EnglishDocument1 pageActivation Photochemical EnglishplennyNo ratings yet
- Knut Schmidt-Nielsen, C. R. Taylor, Amiram Shkolnikf Department of Zoology, Duke University, Durham, N.CDocument20 pagesKnut Schmidt-Nielsen, C. R. Taylor, Amiram Shkolnikf Department of Zoology, Duke University, Durham, N.CRoscii RulezNo ratings yet
- Energomonitor CatalogDocument20 pagesEnergomonitor CatalogJesus MataNo ratings yet
- Smart Grids: PostgraduateDocument6 pagesSmart Grids: PostgraduateIarwaiNo ratings yet
- Bhushan Steels Or.Document189 pagesBhushan Steels Or.Naveen SinghNo ratings yet
- 03 K-90-2030 Cylinder 125lbsDocument1 page03 K-90-2030 Cylinder 125lbsKazuto KirigayaNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetJuan TiradoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument21 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsadvaithNo ratings yet
- Electric Equipment General Catalog: Leader in Electrics & AutomationDocument9 pagesElectric Equipment General Catalog: Leader in Electrics & AutomationNgười TốtNo ratings yet
- AquaFlex Offshore and Industrial HosesDocument28 pagesAquaFlex Offshore and Industrial HosesSetyohdWNo ratings yet
- TL10 Workshop-Manual enDocument165 pagesTL10 Workshop-Manual enJOEL APONTE ORTIZ100% (6)
- Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics: Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument104 pagesEngineering and Chemical Thermodynamics: Chapter 3 SolutionsIsabelHutterNo ratings yet
- Samsung Case Study 1 Samsung Case StudyDocument34 pagesSamsung Case Study 1 Samsung Case StudyMiller100% (1)
- Cthulhu Space 1889Document4 pagesCthulhu Space 1889Juan FranNo ratings yet
- Advance UnitDocument4 pagesAdvance Unitma.powersourceNo ratings yet
- Cartea PrestigeDocument73 pagesCartea PrestigeAndra DumitrescuNo ratings yet