Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat It Up
Heat It Up
Uploaded by
christinaslavenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat It Up
Heat It Up
Uploaded by
christinaslavenCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Christina Slaven
Heat it Up!
INTRODUCTION
In class, you have already taken a look at states of matter. You have learned
that if temperature increases, so does the motion of the particles that are heated.
Today, you will put it into practice using an online simulation that will use Neon,
Water, Oxygen and Argon. You will see how each change from one state to another.
Procedure
1. Click on the “solid, liquid, gas” box on the left
2. Start off with solids of each substance at the right
3. Change the temperature up or down by adding fire or ice
4. Record what happens in the chart provided, i.e., what are the particles doing?
Observations
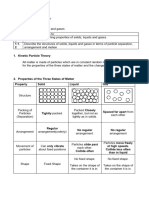
Title here: The Effect of Temperature on Substances as Solids.
Substance Increasing Temp. Decreasing Temp
Neon Particles disperse and The vibration of
move fast losing their particles lessens, and
fixed shape. the shape becomes
firmer.
Argon Particles disperse and Particles slowly stop
speed up but at a slower vibrating and keeps its
rate than Neon. shape more stable.
Oxygen Particles disperse but Particles become closely
stick together for a packed together.
while then move
separately.
Water Particles cluster closer Vibration lessens.
together but no fixed
shape.
“Heat it Up” 1 Created by Doug Spicher
Procedure:
Use the simulation to complete the following chart for temperatures of the
different states of each substance
Title here: The Temperature of Substances in Different States.
Substance Solid Temp Liquid Temp Gas Temp
Argon 43K 86K 189K
Neon 14K 28K 56K
Oxygen 27K 57K 113K
Water 146K 286K 430K
Going Further
On the same page, click on the “Phase Changes” tab at the top left. What is
the relationship between pressure, temperature, and the state of matter?
Temperature and Pressure are directly proportional: as the temperature increases
so does the pressure. The state of matter turns into gas or remains the same.
Questions
1. What happened to the speed of the particles in this lab as you increased the
temperature? The particles started to move faster.
2. Do your findings agree with the behavior of particles in the solid, liquid and
gas phases? Explain. Yes. Temperature is a major factor on how
particles of a substance react and move no matter what state they are in.
3. So, based on the results of this activity, what are two differences between the
states of solids, liquids and gasses? Particle motion/formation and
room temperature.
“Heat it Up” 2 Created by Doug Spicher
You might also like
- Do You Want A Penis? or A Sword! by Moses DavidDocument6 pagesDo You Want A Penis? or A Sword! by Moses DavidsirjsslutNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- HYDRO-GUARD® Water-Based Drilling Fluid Delivering Stable Wellbore ThroughDocument1 pageHYDRO-GUARD® Water-Based Drilling Fluid Delivering Stable Wellbore ThroughFauzan Rahman HaqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 0620 NotesDocument192 pagesChemistry 0620 Notesmohammed mahdyNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)Document28 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)salma salNo ratings yet
- An Early Morning Trader StrategyDocument3 pagesAn Early Morning Trader StrategySasikumar ThangaveluNo ratings yet
- SEO Report TemplateDocument6 pagesSEO Report TemplateAllan Charles BradburyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundingsshashi kumar sinhaNo ratings yet
- Personal Statement Guide by Doctor Laska PDFDocument3 pagesPersonal Statement Guide by Doctor Laska PDFSteve JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect ExplanationsDocument2 pagesPast Perfect ExplanationsHuma RiazNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory & Thermal Properties Notes IGCSE AVGDocument12 pagesKinetic Theory & Thermal Properties Notes IGCSE AVGWeteach100% (3)
- L4 Motion of Particles PDFDocument53 pagesL4 Motion of Particles PDFcheezykimbapNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v3Document21 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v3Adenekan Therhophic Orlanshilay100% (2)
- Kinetic Theory, Phase Changes, Brownian MotionDocument10 pagesKinetic Theory, Phase Changes, Brownian MotionRamesh GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Sah-Lab: Clinical LaboratoryDocument4 pagesSah-Lab: Clinical LaboratoryRazel Ann ElagioNo ratings yet
- 2-Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pages2-Thermal PhysicsSamah Hafez100% (1)
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- 17 4 Probability - Tree DiagramsDocument5 pages17 4 Probability - Tree Diagramsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- 03 GUL Interoperability Troubleshooting (Drive Test) V1.0Document34 pages03 GUL Interoperability Troubleshooting (Drive Test) V1.0Sangwani Nyirenda100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument6 pagesStates of MatterchristinaslavenNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 1-Module 3Document31 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 1-Module 3Niño Edrianne NimoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Core g9Document62 pagesChemistry Core g9YahyaNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Chapter 2 - State of MatterDocument13 pagesCHEM-Chapter 2 - State of Mattersecag45630No ratings yet
- Simulation On States of MatterDocument3 pagesSimulation On States of MatterlalabalakishiliNo ratings yet
- Computerlabstatesofmatter Amalia and DanielaDocument5 pagesComputerlabstatesofmatter Amalia and Danielaapi-348325291No ratings yet
- 2.3 Changing States & Water CycleDocument65 pages2.3 Changing States & Water CycleJohn Michael DitchonNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- Solids: Notes 1 Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter Solids, Liquids and GasesDocument7 pagesSolids: Notes 1 Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter Solids, Liquids and GasesQfkjfksNo ratings yet
- Pravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225511125526807058Document228 pagesPravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225511125526807058jkNo ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - 1Document37 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - 1AbdullaahNo ratings yet
- Revision Plan 2023-24 O Level ChemistryDocument14 pagesRevision Plan 2023-24 O Level ChemistryFarah LangrialNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument34 pagesMatterAngelica NeritNo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet 1 PDFDocument8 pagesLearning Worksheet 1 PDFMAZYRIELLOISE TOLENTINONo ratings yet
- Phase Changes of MatterDocument36 pagesPhase Changes of MatterCherry GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Thermal ExpansionDocument5 pagesThermal ExpansiongospakopaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Experiment 4Document5 pagesPHYSICS Experiment 4Moana BerbonNo ratings yet
- Why Can The Smell of Durians Be Detected Even Very Far Away ?Document38 pagesWhy Can The Smell of Durians Be Detected Even Very Far Away ?Kavitha ThayagarajanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocument25 pagesKinetic Model of MatterHafiza JaweriaNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Changes of StatesDocument39 pagesChanges of StatesSalemah MeshalNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocument15 pagesKinetic Model of MatterMuqarram FaisalNo ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table BelowDocument8 pagesSolids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table BelowAmelia AuclairNo ratings yet
- StatesDocument5 pagesStatesoffenberg1No ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademyDocument14 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument5 pagesStates of MatterMichaela JohanntgesNo ratings yet
- ExploreDocument3 pagesExploreLourdes Joy LibradoNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of Chemistry 19Document196 pages1 Principles of Chemistry 19LaziNo ratings yet
- Ss1 Chemistry Note Third TermDocument65 pagesSs1 Chemistry Note Third Termabejideseyi12No ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- ASMR 2.1 Heating and Cooling CurveDocument3 pagesASMR 2.1 Heating and Cooling CurveKathlein SiscarNo ratings yet
- G7 Matter & Its StatesDocument44 pagesG7 Matter & Its Statesgabrielle.nathan.naomiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KineticsDocument4 pagesChemistry KineticsmayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1dowanahamidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 - States of Matter and Mixtures - Student NotesDocument20 pagesUnit 1.1 - States of Matter and Mixtures - Student Notesjaniel2027No ratings yet
- Particle Arrangement and MovementDocument4 pagesParticle Arrangement and Movementshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics (Kinetic Particle Model of Matter) - Particle ModelDocument1 pageThermal Physics (Kinetic Particle Model of Matter) - Particle ModelTamilore AdegbonmireNo ratings yet
- Entropy and Gibbs Free EnergyDocument3 pagesEntropy and Gibbs Free EnergyFAB 5No ratings yet
- Laboratoy Activity 2Document10 pagesLaboratoy Activity 2Jasper BarlisNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- 01 Structure of Matter 2009Document6 pages01 Structure of Matter 2009api-27085921No ratings yet
- Pa-Shun Hawkins PhET - States of Matter - Lab 3 (1) - 2Document8 pagesPa-Shun Hawkins PhET - States of Matter - Lab 3 (1) - 2Parris HawkinsNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument8 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- Matter States & ChangesDocument4 pagesMatter States & Changesallysyngaskins7No ratings yet
- Uas Praktek Thermodinamika Laksmana Andika PK 2 ADocument6 pagesUas Praktek Thermodinamika Laksmana Andika PK 2 AAngga Prayoga ManopoNo ratings yet
- 08 - Particles and PurificationDocument20 pages08 - Particles and PurificationDaniel IciousNo ratings yet
- 19 TeeDocument12 pages19 TeeamitNo ratings yet
- PKK Kanak-Kanak Berkeperluan KhasDocument11 pagesPKK Kanak-Kanak Berkeperluan Khassyisyirararoro100% (1)
- Cellonics Technology Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesCellonics Technology Seminar Reportnm gunasekharNo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength Test of Hydraulic Cement MortarDocument2 pagesCompressive Strength Test of Hydraulic Cement MortarJersey Mae PerlasNo ratings yet
- Maseno University Grand Child Insurance: Name Adm NumberDocument4 pagesMaseno University Grand Child Insurance: Name Adm NumberEugeneNo ratings yet
- 34-Digital Marketing Assignment BriefDocument3 pages34-Digital Marketing Assignment BriefNabeel hassanNo ratings yet
- Salesforce1 User GuideDocument8 pagesSalesforce1 User GuideastinetNo ratings yet
- Nhóm-10 VTBHK - TMAE33112 2 - 2021CLC 1-2Document22 pagesNhóm-10 VTBHK - TMAE33112 2 - 2021CLC 1-2Irene Quỳnh AnhNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement For Allegory of The CaveDocument4 pagesThesis Statement For Allegory of The Cavejacquelinethomascleveland100% (3)
- Deutz Fahr AGROTRON TTV 1160 Tractor Service Repair ManualDocument20 pagesDeutz Fahr AGROTRON TTV 1160 Tractor Service Repair ManuallaopaodunNo ratings yet
- PGDID Project Report GuidelinesDocument5 pagesPGDID Project Report GuidelinesLakshya gamers RajputNo ratings yet
- Profile 2021 EngDocument162 pagesProfile 2021 EngMohammad Ahbab HasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-22 Prolonged PregnancyDocument24 pagesLecture-22 Prolonged PregnancyMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- 2018-19 SDUHSD Math 1 Honors Module 3H SEDocument27 pages2018-19 SDUHSD Math 1 Honors Module 3H SEBlake LilleyNo ratings yet
- ACCT2511 Topic 1 PASS Question Answers 2023 T1Document3 pagesACCT2511 Topic 1 PASS Question Answers 2023 T1KJSAdNo ratings yet
- Vol 4Document738 pagesVol 4Yurley LUNANo ratings yet
- Steps in Project ManagementDocument12 pagesSteps in Project ManagementHimani SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 12 Reasons To Save The National LanguageDocument2 pages12 Reasons To Save The National LanguagepatdavinciNo ratings yet
- Piers Unit IVDocument36 pagesPiers Unit IVSuryaNo ratings yet
- Saving Private RyanDocument16 pagesSaving Private Ryanbertincruz658100% (1)
- Sistema Centry KTA 38Document12 pagesSistema Centry KTA 38Ian RodríguezNo ratings yet