Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 10 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Don Remver Loyola0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Science 10 reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesScience 10 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Don Remver LoyolaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
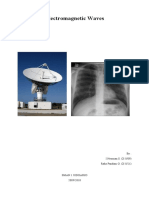
Science 10 reviewer History of Electromagnetic Wave Theory
Electromagnetic waves are produced by a Ancient measures were taken to understand
charge that changes its direction or speed. atmospheric electricity, specifically
An electromagnetic wave contains an lightning.
electric field and a magnetic field. James Clerk Maxwell developed a scientific
Electromagnetic waves are transverse theory to better explain electromagnetic
waves. waves.
They travel at the speed of light, denoted as Heinrich Hertz applied Maxwell's theories to
c, which is 3 times 10 raised to the 8th the production and reception of radio waves.
power meters per second. Michael Faraday contributed to the
electromagnetic theory of light.
Properties of Electromagnetic Waves Andre Marie Ampere made the
revolutionary discovery that a wire carrying
Produced by accelerated or oscillating electric current can attract or repel another
charge. wire next to it that's also carrying electric
Do not require any material or medium for current.
propagation. Hans Christian Orsted discovered that the
Travel in free space at the speed of 3 times electric current in a wire can deflect a
10 raised to the 8th power meters per magnetized compass needle.
second. Experts compiled all the discoveries of these
scientists to form the basic principles of the
Components of Electromagnetic Waves electromagnetic wave theory.
Made up of an electric field and a magnetic Electromagnetic waves
field positioned at right angles to each other
and to the direction of motion of the wave. Comprise of an electric field and a magnetic
Electric and magnetic fields are the regions field at right angles to each other and to the
through which the push or pull of charged direction of the motion of the wave.
particles and magnets is exerted. Travel at the same speed in a vacuum, which
Changing magnetic field produces an is 3 times 10 raised to the 8th power meters
electric field and changing electric field per second.
produces a magnetic field. Are often arranged in the order of
wavelength and frequency in what is known
Production and Transmission of as the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electromagnetic Waves Are described by their physical wave
features: amplitude, wavelength, and
frequency.
Electromagnetic waves are produced by a
charge that changes its direction or speed.
Charged particles such as electrons must Characteristics of electromagnetic waves
move to create the vibrating electric and
magnetic fields. Amplitude is the maximum field strength of
Electromagnetic waves can travel in a the electric and magnetic fields.
vacuum where there is no matter. Frequency describes how many waves per
Light can be transmitted with a medium as second a wavelength produces.
through the atmosphere or without a Wavelength measures the length of an
medium as through space. individual wave in meters.
Electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum at
the speed of 3 times 10 raised to the 8th
power meters per second.
Electromagnetic spectrum
Waves are often arranged in the order of
wavelength and frequency in what is known
as the electromagnetic spectrum.
Waves with the longest wavelengths have
the lowest frequencies while waves with the
shortest wavelengths have the highest
frequencies.
The electromagnetic spectrum includes:
o Radio waves
o Microwaves
o Infrared
o Visible light
o Ultraviolet rays
o X-rays
o Gamma rays
Different types of electromagnetic waves are
defined by the amount of energy carried by
their photons.
Radio waves own photons with the lowest
energies while gamma rays carry photons of
high energies.
Gamma rays, x-rays, and high ultraviolet
rays are classified as ionizing radiation
while radio waves, microwaves, infrared
rays, and visible light are classified as non-
ionizing radiation.
Wave speed, frequency, and wavelength
The wave speed, frequency, and wavelength
are related by the equation: v equals lambda
f.
The unit for frequency is hertz, which is also
cycles per second.
All electromagnetic waves can travel
through a medium, but they can also travel
in a vacuum or empty space.
You might also like
- Lesson 1 Q2Document33 pagesLesson 1 Q2odnimernNo ratings yet
- Common Properties of Light Renzej - 20240309 - 201256 - 0000Document52 pagesCommon Properties of Light Renzej - 20240309 - 201256 - 0000Lidelyn Jane CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Ste Q2-Sci 10 W1-4Document24 pagesSte Q2-Sci 10 W1-4MARK NEIL ARPON100% (1)
- Q2-M1 Electromagnetic WavesDocument58 pagesQ2-M1 Electromagnetic WavesJaycob Sedrick TaboNo ratings yet
- Christine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIDocument82 pagesChristine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIRyuji ReyesNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document4 pagesWeek 1jia aganaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves PresentationDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Waves PresentationCyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Nature of Electromagnetic WavesDocument24 pagesNature of Electromagnetic WavesEivol Kimoy ÖNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Radio WavesDocument26 pagesLesson 10 - Radio WavesJerick Sapa100% (1)
- Science Quarter 2-Module 2 Electricity and MagnetismDocument81 pagesScience Quarter 2-Module 2 Electricity and MagnetismJazelle Kaye Azupardo100% (2)
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentDivina BacaniNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic WavesRalph AntonioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateDocument8 pagesAnatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateBhaskarKhersaNo ratings yet
- Q1SCIL1Document4 pagesQ1SCIL1Jiann AguilarNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 - Arellano University - Prepared by Sir - Andro RomanoDocument31 pagesGeneral Physics 2 - Arellano University - Prepared by Sir - Andro RomanoKesia AlmodalNo ratings yet
- 8.EMW14 NotesDocument7 pages8.EMW14 NotesMohitha Reddy CNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: y Z y ZDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: y Z y Zmaruthi cyber19No ratings yet
- General Physics 2 4.1 Maxwell'S EquationsDocument6 pagesGeneral Physics 2 4.1 Maxwell'S EquationsNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document13 pagesPhysics 1bort kortNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETICDocument48 pagesELECTROMAGNETICMichelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: By: I Nyoman S. (X-8/09) Raka Pandam G. (X-8/21)Document11 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: By: I Nyoman S. (X-8/09) Raka Pandam G. (X-8/21)Nyoman SuryadinataNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationSundayNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave TheoryDocument75 pagesElectromagnetic Wave TheoryLen Cardona Bagunas100% (1)
- Chapter 24Document47 pagesChapter 24sairahhannahNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 1Document38 pagesQ2 Module 1aaronscimdtNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (B - MARCH 2022Document40 pagesUnit-1 (B - MARCH 2022Vibin SimonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWShaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument50 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMisty Vito100% (1)
- Science Reviewer 1Document15 pagesScience Reviewer 1Symon MarianoNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Assignment 1Document9 pagesApplied Physics Assignment 1areejNo ratings yet
- Grade10 Q2 SLM1Document18 pagesGrade10 Q2 SLM1Archie Caba100% (1)
- 1 Electromagnetic Waves Theory (Week 1)Document32 pages1 Electromagnetic Waves Theory (Week 1)Christa Gabrielle BosingNo ratings yet
- Scientific Journal: Electromagneti C FieldDocument15 pagesScientific Journal: Electromagneti C FieldAgustine AcelajadoNo ratings yet
- EM WaveDocument47 pagesEM WaveKia LeighNo ratings yet
- What Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarDocument18 pagesWhat Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarAndrei Cojanu100% (1)
- Displacement CurrentDocument10 pagesDisplacement Currentojhamunesh388No ratings yet
- Elec RAdDocument26 pagesElec RAdariba khanNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument54 pagesThesisJeon ManobanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum - ScienceDocument19 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum - ScienceChar- MatoNo ratings yet
- Ss3 First Term Physics NoteDocument64 pagesSs3 First Term Physics NoteAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- EM Waves - UPHDocument20 pagesEM Waves - UPHSHIVA THAVANI100% (1)
- 8 Electromagnetic WavesDocument7 pages8 Electromagnetic WavesPreethiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves (EM Waves)Document17 pagesElectromagnetic Waves (EM Waves)Joshdave cuambotNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight Chapter Eight: Physics Group PR OjectDocument24 pagesChapter Eight Chapter Eight: Physics Group PR OjectSyeda haniNo ratings yet
- Class 12 TH PDF 2nd Term For Share FileDocument108 pagesClass 12 TH PDF 2nd Term For Share FileDeepak singh SengarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 - EM WavesDocument8 pagesLecture 2.1 - EM WavesAPPLE CAGUNGUN-BELGICANo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument7 pagesPHYSICSSurya A S100% (1)
- What Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismDocument23 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismUma Venkata SumanthNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument74 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJohnNo ratings yet
- Fundamental To Electromagnetic WavesDocument9 pagesFundamental To Electromagnetic WavesResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesScience Notes - 2nd QuarterRanz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 3 4Document9 pagesModule 2 Week 3 4LeiRne Jo KBahingawan TanGuidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Electromagnetic WavesDocument45 pagesLesson 4 Electromagnetic WavesErica QuirobNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EM WavesDocument9 pagesModule 1 EM WavesALTHEA ANN TUPASNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 (Assignment)Document6 pagesChapter 8 (Assignment)asmaaysha121No ratings yet
- Physics Project 2022-23Document28 pagesPhysics Project 2022-23ZedS1yzNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesScience Notes - 2nd QuarterRanz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: Description: Electromagnetic Waves Are Formed When An Electric Field ComesDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: Description: Electromagnetic Waves Are Formed When An Electric Field Comesj_sachin09No ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsK. KurokawaNo ratings yet
- Solar-Powered Atmospheric Water GeneratorDocument2 pagesSolar-Powered Atmospheric Water GeneratorAbdelrhman TarekNo ratings yet
- You Are Writing A Research Paper On Energy Policy in The United StatesDocument9 pagesYou Are Writing A Research Paper On Energy Policy in The United Statesgvzrg8jy100% (1)
- National Portal for Rooftop Solar - Ministry of New and Renewable EnergyDocument10 pagesNational Portal for Rooftop Solar - Ministry of New and Renewable Energysudhir7220No ratings yet
- Xel 014palDocument2 pagesXel 014palPp YotamNo ratings yet
- STULZ CyberAir 3PRO CW Brochure 2001 ENDocument20 pagesSTULZ CyberAir 3PRO CW Brochure 2001 ENIvan Rudolf De FretesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Circuit A Fact Sheet 2Document3 pagesA Simple Circuit A Fact Sheet 2LADY ANN GRACE LAGASNo ratings yet
- Askari TowerDocument49 pagesAskari TowerIQRA ASGHARNo ratings yet
- EWS 3 User Guide C BDocument4 pagesEWS 3 User Guide C Bchn_rakesh3120No ratings yet
- Smoke Damper RuskinDocument4 pagesSmoke Damper RuskinWinda Risqi NurainiNo ratings yet
- Design Manual Triol AK06Document27 pagesDesign Manual Triol AK06napo3tNo ratings yet
- De On Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi Lop 9 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019 2020 So 2Document10 pagesDe On Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi Lop 9 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019 2020 So 2trần phương uyênNo ratings yet
- 6areva GBSQSSHVDCFACTSDocument38 pages6areva GBSQSSHVDCFACTSSampath KumarNo ratings yet
- Laurent BussonDocument20 pagesLaurent BussonJavier PairazamanNo ratings yet
- Bonding JumpersDocument7 pagesBonding Jumpersvladimir rosas ayalaNo ratings yet
- Anti Corona 8001Document3 pagesAnti Corona 8001김범석No ratings yet
- Efficiency Testing Methods For Centrifugal PumpsDocument16 pagesEfficiency Testing Methods For Centrifugal PumpsAfnian SariNo ratings yet
- FSAE Rules 2022 V21Document138 pagesFSAE Rules 2022 V21Antonio TešićNo ratings yet
- EHS-WI.005 Lockout-Tagout Program (Eng Ver0)Document14 pagesEHS-WI.005 Lockout-Tagout Program (Eng Ver0)Aldrien CabinteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Industry and ManufacturingDocument36 pagesChapter 11 - Industry and ManufacturingNolan NelsonNo ratings yet
- 13-SAMSS-003 2017 General Purpose Gear UnitsDocument7 pages13-SAMSS-003 2017 General Purpose Gear UnitsWHWENNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Filter Separator: Key BenefitsDocument2 pagesHorizontal Filter Separator: Key Benefitsadewunmi olufemiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols GuideDocument13 pagesElectrical Symbols GuideGEENo ratings yet
- Project DescriptionDocument17 pagesProject DescriptionCullen MoralesNo ratings yet
- Fe Review Fall 9232020 LecturewithannotationsDocument56 pagesFe Review Fall 9232020 Lecturewithannotationsfem mece3381No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences GR 11 Exam Guidelines 2024 EngDocument28 pagesPhysical Sciences GR 11 Exam Guidelines 2024 Engnthabisengmemory258No ratings yet
- Well Intervention - Systems & MethodesDocument19 pagesWell Intervention - Systems & MethodesJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Sarmad SadiqNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs MCQ June 21 EngDocument92 pagesCurrent Affairs MCQ June 21 EngPradeep PradeepaNo ratings yet
- Power System Stability: Prof. M Venkateswara RaoDocument56 pagesPower System Stability: Prof. M Venkateswara RaochinnaNo ratings yet
- Breathe Brick: Done By: Aleena Vinoji Valliyam ThadathilDocument9 pagesBreathe Brick: Done By: Aleena Vinoji Valliyam ThadathilViNo ratings yet