Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UCC 103 Chapter 10 - Word Processing Application
Uploaded by
millychebet93Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UCC 103 Chapter 10 - Word Processing Application
Uploaded by
millychebet93Copyright:
Available Formats
UCU 103 – PRINCIPLES OF COMPUTING
Chapter 10: Word Processing
At the end of the chapter the learner shall be able to;
Explain the different word processing terms
Creating new documents and open existing ones
Type and edit text
Use Save and Save As
Perform spelling and grammar check after typing a document
Apply formatting to text and page
Print preview a document and print it
Follow the mail Merging wizard to mail merge a document
10.1. Introduction
Word processors are programs that enable you to Create, Edit and Format documents such letters, memos
and reports. Examples of word processors are, Microsoft Word, Word perfect, Word star.
10.1.1 Features of a good word
Word processors vary considerably, but all word processors support the following basic features:
1) Allow adding, inserting and deleting of text anywhere in the document.
2) Allows copy, cut and paste:
Allows you to remove (cut) a section of text from one place in a document and insert (paste)
it somewhere else.
Copy: Allows you to duplicate a section of text.
3) Allows multiple formatting of text e.g. bold, italics, font style, bullets and numbering.
4) Allows you to define various page sizes and margins, and the word processor will automatically
readjust the text so that it fits.
5) Allows you to direct the word processor to search for a particular word or phrase. You can also
direct the word processor to replace one group of characters with another everywhere that the first
group appears.
6) Provide graphical features such as pictures, graphs, and arts.
7) The word processor automatically moves to the next line when you have filled one line with text,
and it will readjust text if you change the margins – feature called word wrapping.
8) Allows you to send a document to a printer to get hardcopy.
9) Allows access to different documents simultaneously.
10.2. Microsoft Word (MS-WORD 2007 / 2010)
10.2.1 Loading Ms-Word
Click start button at the task bar
Point at programs
Click at Microsoft word
Loading can also be achieved by clicking the Ms Word icon on the Microsoft shortcut bar (only if it is
available)
10.2.2. The Word Application Window
The Word application window contains tools you'll use to work with documents. In the application
window, you display and edit a document, and use various features to enhance the appearance of your
document.
The Ms Word screen contains various features. The common ones are:
The word Screen and the Ribbon
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 1
The Word Application Window
The Word application window contains tools you'll use to work with documents. In the application
window, you display and edit a document, and use various features to enhance the appearance of your
document.
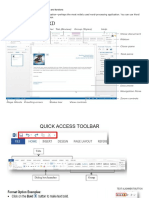
Title Bar
Office Button Ruler
Menu Bar
Quick Access
Tool Bar Clipboard Font Tool Bar Paragraph Tool Bar Styles Toolbar
Tool Bar
Status Bar Document Area Scroll Bar Zoom tool
Component Description
Quick Access Located in the uppermost left of the window. The Quick Access Toolbar provides one-
Toolbar click access to core commands such as Save, Undo, and Redo. It can also be customized
to include additional commands based on user preference.
Title bar Located along the top of the window. The title bar displays the name of the current
document.
Ribbon Located directly below the title bar. The ribbon contains common commands and
features used to create and edit documents.
Document area The main portion of the window. The document area is where you display documents.
Scroll bars Located to the right of and directly under the document area. The scroll bars allow you to
navigate a document vertically or horizontally.
Status bar Located along the bottom of the window. The status bar shows information about the
current document, such as the number of pages or words.
Zoom Tool Used to change the Sizes of documents
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 2
Quick Access Tool
1) Located in the uppermost left of the window. The Quick Access Toolbar provides one-click access to
core commands such as Save, Undo, and Redo. It can also be customized to include additional
commands based on user preference.
2) More command icons can be displayed on the Quick Access toolbar by selecting from the Customized
quick Access Toolbar
The Ribbon
10.3. The Ribbon
The ribbon is a graphical menu panel that appears at the top of the application window. It was designed to
provide a central location for accessing various functions of the environment without having to navigate
the user interface extensively. From the ribbon, you can access most, if not all, of the commands that you
will need to use in the application.
The ribbon is made up of two parts: the tabs and the command groups that make up each tab. Each tab has
an organizational title that references the specific functions that the command groups within that tab
provide. Each command group also has an organizational title, with the specific commands within each
group associated with a specific task in the application environment. You can customize the ribbon by
adding, removing, or rearranging tabs, groups, and commands.
Tab Description
FILE Displays the Backstage View, where you can access commands that perform file-
related tasks, such as saving and printing. On the FILE tab, you can also get
information about a document, and configure Word customization options.
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 3
Tab Description
HOME Contains the frequently used commands you'll use to start working with a Word
document. The command groups on this tab include Clipboard, Font, Paragraph,
Styles, and Editing. They allow you to format and edit text.
INSERT Contains commands that insert different objects into your document, such as charts,
tables, and pictures. Groups on this tab include Pages, Tables, Illustrations, Links,
Header & Footer, Text, and Symbols.
PAGE Contains commands used to customize document pages, including controlling the
LAYOUT placement of text and graphics. Groups on this tab include Themes, Page Setup, Page
Background, Paragraph, and Arrange.
REFERENCES Contains commands to create references to the document content, such as footnotes and
indexes. Groups on this tab include Table of Contents, Footnotes, Citations &
Bibliography, Captions, Index, and Table of Authorities.
MAILINGS Contains commands to create mailing documents, such as faxes, letters, and emails.
Groups on this tab include Create, Start Mail Merge, Write & Insert Fields, Preview
Results, and Finish.
REVIEW Contains commands to review and edit the content in a document. Groups on this tab
include Proofing, Comments, Language, Tracking, Changes, Compare, and Protect.
VIEW Contains various commands to switch between different document views. Groups on
this tab include Document Views, Show, Zoom, Window, and Macros.
10.3.1. Types of Menus
A. File
Displays the Backstage View, where you can access commands that perform file-related tasks, such as
saving and printing. On the FILE tab, you can also get information about a document, and configure Word
customization options.
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 4
B. Home Menu
Contains the frequently used commands you'll use to start working with a Word document. The command
groups on this tab include Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Styles, and Editing. They allow you to format
and edit text.
Tools Bars
Sub-menus under this menu
1) Clipboard: Cut, Copy, Paste
2) Font – Font, Font size, Bold, Itallics, Underline, Strike out, subscript, Super Script, change case, text 3.
highlighting, font colour, etc.
3) Paragraph:- Bullets, Numbering, Multilevel list, Decrease & Increase Indent, Sort, Paragraph Align
Left, Center, Right & Justify, Line Spacing, Shading and Borders.
4) Styles Toolbar;- font style (heading style & Normal styles)
5) Editing Toolbar;- Find, Replace and Select tools
C. Insert Menu
Contains commands that insert different objects into your document, such as charts, tables, and pictures.
Groups on this tab include Pages, Tables, Illustrations, Links, Header & Footer, Text, and Symbols.
Sub-menus under this menu
1) Pages toolbar;- Cover page, Blank page & Page break
2) Tables Toolbar
3) Illustrations Tool bar; Picture, Clip Art, Shapes, Smart Art, Chart
4) Links; Hyperlink, Bookmarks, Cross-reference
5) Header & Footer Tool bar; Header toolbar, Footer Toolbar, Page numbering toolbar
6) Text Toolbar; Text Box toolbar, Quick Parts, Word Art, Drop Cap, Signature Line, Date & Time,
Object
7) Symbols; Equation, Symbol
D. Page Layout Menu
Contains commands used to customize document pages, including controlling the placement of text and
graphics. Groups on this tab include Themes, Page Setup, Page Background, Paragraph, and Arrange.
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 5
Sub-menus under this menu
1) Themes Toolbar; Themes, Colors, Fonts & Effects
2) Page Set-up; Margins, orientation, Size, Columns, Breaks, Line Numbering, Hyphenation
3) Page Background; watermark, page color, page borders
4) Paragraph; Indenting, Spacing
5) Arrange; position, bring to front, send to back, text wrapping, Align, rotate etc.
E. References Menu
Contains commands to create references to the document content, such as footnotes and indexes. Groups
on this tab include Table of Contents, Footnotes, Citations & Bibliography, Captions, Index, and
Table of Authorities.
Sub-menus under this menu
1) Table of content;
2) Footnotes;
3) Citation and Bibliography
4) Captions
5) Index
6) Table of Authority
F. Mailings Menu
Contains commands to create mailing documents, such as faxes, letters, and emails. Groups on this tab
include Create, Start Mail Merge, Write & Insert Fields, Preview Results, and Finish.
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 6
Sub-menus under this menu
1) Create mailing labels
2) Mail Merge
3) Write and Insert fields
4) Preview results
5) Finish & Merge
G. Review
Contains commands to review and edit the content in a document. Groups on this tab include Proofing,
Comments, Language, Tracking, Changes, Compare, and Protect.
Sub-menus under this menu
1) Proofing; Spelling & Grammar checking, Thesaurus, Word Count, Translate
2) Comments; insert, Delete, previous & next
3) Tracking;
4) Changes; Accept, Reject, Previous & Next etc
5) Compare
6) Document protection
H. View Menu
Contains various commands to switch between different document views. Groups on this tab include
Document Views, Show, Zoom, Window, and Macros.
Sub-menus under this menu
1) Document Views; print layout, Full Screen reading, Web layout, Outline, Draft etc
2) Show/Hide; Ruler, Gridlines, Document Map, Thumbnails
3) Zoom;
4) Window;
5) Switch Window
6) Macros
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 7
10.4. Creating, Saving and Closing Documents
10.4.1. Creating
Option 1
1. Click the Office button, click New then double click the Blank Document icon.
Option 2
2. On the standard tool bar click the ‘New’ (icon)
10.4.2. Scrolling through a document
a) On the right of the screen you have a vertical scroll bar; at the bottom of the screen you have a
horizontal scroll bar. At either end of the scroll bars are arrows pointing in opposite directions.
b) C licking on these arrows will scroll a document up or down, left or right, depending on which arrow you
select.
You also can scroll by positioning the mouse arrow on the scroll box itself, holding down the left
mouse button, and dragging the box in the scroll bar.
You can also scroll and position the cursor very precisely by using the arrow keypad on the keyboard
10.4.3. Saving a New Document
To save a new document
1) Click Office Button/file and choose Save As.
2) Type the file name on the File name box that appears.
3) Chose the location to save the file in the Save in box e.g. Hard disk(C), secondary storage such as
Flash Disk etc
4) Select the Save As Type format or accept the default (.docx for word 7 and above. Previous
version save as .doc)
5) Click the Save button.
10.4.4. Opening an Existing Word Document
1) Click Office Button/file and the Open menu
2) Select the location of the file in the secondary memory
3) Select the file
4) Click Open button
10.4.5. Closing or Exiting Document
1) Click Office Button/file
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 8
2) Either Click Close button to close the document BUT remain in Word
OR
Click Exit word to both close the file and exit word
10.5. Selecting Text/Block of Text
SELECT DO THIS
1) A word Drag over the word or Double click it
2) A graphic Click anywhere within the graphic
3) A line of text Drag over the text or Double click at the start of line
4) A sentence Hold Down Ctrl key and click anywhere in the Sentence
5) A paragraph Triple click anywhere in the paragraph to select
6) Entire document From Edit, click Select All or Ctr+A
10.6. Formatting
10.6.1. Formatting Text
a. To bold text
Select or highlight the text.
On the font menu click Bold button (B).
b. To Italicize text
Select or highlight the text.
On the font menu click Italics button (I).
c. To underline text
Select or highlight the text.
On the font menu click Italics button (U).
d. To change Font size and Font Type
Select or highlight the text.
On the font menu Select the font size OR the Font type by clicking he Down Arrow to the right
of the boxes
e. To change the font color
Select the text.
On the font menu select the font color by clicking the down arrow to the right of menu button
shown below.
Under color box, choose the color desired.
10.6.2. Formatting Paragraphs
Word displays text, as it will appear when printed.
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 9
a. Line Spacing
Line spacing determines the amount of vertical space between the lines and text. Word uses single line
spacing by default.
Inserting line spaces
In the paragraph menu.
Click the down arrow to the right of line spacing button and select the required line spacing
specification
b. Aligning text
Select or highlight the text.
In the paragraph menu, choose and click alignment desired i.e. left, center, right, justify
c. Creating drop caps
1) Place the cursor at the beginning of the line/paragraph you want to have a drop cap on.
2) In the format menu, click drop cap.
3) Under position in the dialogue box choose either Dropped or in margin.
4) In the lines to drop box specify the number
5) Click Ok.
Note: You can specify the distance from the text and type of the font for the drop cap.
d. Change case
1) Highlight or select the text.
2) In the font menu, click the down arrow to the right of the change case icon then select required
change case format.
e. Adding bullets and numbers
1) Select the items, which you want to add bullets or numbers.
2) In the paragraph menu section, click down arrow to the right of the bullets icon, then select the
required bullet type
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 10
3) For numbers.
4) In the paragraph menu section, click down arrow to the right of the Numbering icon, then select
the required numbering format
f. Remove bullets or numbering
1) Select the items, which you want to remove bullets or numbers.
2) On the paragraph menu click the respective format Icon (Bullets or numbering)
g. Page Break
1) Position the cursor where you want the page break to appear.
2) From the Page Layout menu, Click the down arrow to the right of Breaks command
h. Insert a picture
You can insert a clip art or a picture from the clip Gallery.
1) Position the insertion point (cursor) where you want to insert a clip art or a picture.
2) From the Insert menu, click the Picture command icon.
3) Click a clip art category then choose a clipart and click insert clip.
i. To resize the objects
1) Click inside the object i.e. clipart, word art or a drawing.
2) Position the mouse pointer in either of the placeholders.
3) Click and drag to the desired size.
4) Release the mouse button.
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 11
10.7. Editing Your Document
1) To undo mistakes
a) In the edit menu, click undo or click the Undo button on the standard toolbar.
2) To undo Specific actions
a) Click the down arrow to the right of the Undo Icon to display a list of the most recent actions.
b) Click the action you want to undo. If you don’t see the action, scroll through the list.
10.7.1. To insert page numbers, Footers and Headers
From the Insert menu, click the arrow at the bottom of each format Icon, then select the required style
Typically, footnotes and endnotes are used in printed documents to explain, comment on, or provide
references for text in a document. You can include both footnotes and endnotes in the same document. It
allows you to create appropriate notes and citations.
When you print the document, footnotes appear where you specified: either at the end of each page or
directly below the text. In the printed document, endnotes also appear where you specified: either at the
end of the document or at the end of each section.
Header
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 12
Footer
Page Numbers
Removing Page Numbers, Header and Footer
1) In the respective menu
2) Click remove header, footer or page number respectively
10.7.2. Indenting
Indenting refers to the situation where one line or several lines of a paragraph are set in from the rest of
the paragraph. This is accomplished in Word using the Indent Markers on the ruler at the top of the screen
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 13
There are three indent markers
1) First Line Indent marker on top,
2) Hanging Indent marker in the middle,
3) Left Indent marker below-- the small box on which the other margin markers sit). When you drag on
the small box (the Left Indent marker) all the markers move together.
Hanging Indents
The indent markers can also be set independently to achieve two types of indents.
First, there is the traditional indentation commonly used for the first line of paragraphs- where you set
the margin for the first line in a few spaces from the rest of the paragraph
Second, there is the indentation for lists such as bibliographies or itemized data-- where you set the
margin for the first line back a few spaces from the rest of the paragraph. Word refers to these
indents as "hanging indents," because the lines that follow look as if they are hanging off the first line.
Indenting the first line of paragraphs
Click at the beginning of the first line of the first paragraph of the Abstract page (on the next line
after the Abstract header) on page 1, hold down the Shift key and click again at the end of the
Abstract (to highlight all the Abstract text)
Now position the tip of the mouse arrow on the First Line Indent marker (the upper marker) on the
ruler at the top of the screen
10.8. Copying, Moving and Pasting Text
An existing piece of text may be required in a different document. Ms Word allows the user to copy this
text rather than retype then paste it to the required area. When text or graphic is copied or cut, it is stored
in the clipboard and can be pasted into as many documents as desired.
To copy and paste text
1) Select the text to copy.
2) From the Clipboard menu click Copy icon.
3) Position the cursor where the text is to be placed.
4) From the clipboard menu click bottom arrow to the right of the paste icon, then select the relevant past
type
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 14
Moving text
1) Select the text to move.
2) From the Clipboard menu click Cut icon.
3) Position the cursor where the text is to be placed.
4) From the clipboard menu click bottom arrow to the right of the paste icon, then select the relevant past
type
Note: When you cut, the text is completely removed from the original location.
10.9. Spell check, Find and Replace text
To spell check a Document
1) From the Review Menu
2) Click the Spelling & Grammar Icon
1) Follow the instructions as given to replace a word, ignore, edit etc
2) Click Ok button when spelling and grammar is complete.
To find text
1) On the edit menu, click Edit and choose Find.
2) In the find what box, type the word/text being sought
3) Click find next button
4) To close the dialogue box, click cancel button
To Replace Text
You can find and replace text at the same time
1) On the edit menu, click edit and choose replace
2) In the find what box type word / text as above
3) In replace with box type the word/ text to replace the sought word / text
4) Click replace all button
5) To close the dialogue box click cancel button
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 15
10.10. Changing Page Setup
Depending on the size of the paper required and / or paper orientation and layout, Ms –word will allow
changing of the defaults to users requirement.
To change page setup
1) Click Page Layout Menu
2) Click Icon for the required page format
Margins
Select & click the relevant page setup template
OR
Click Custom Margins
Orientation
Click the required page orientation Icon.
10.11. Creating Table of Content
Word uses the headings in your document to build an automatic table of contents that can be updated
when you change the heading text, sequence, or level.
The text to appear in the Table of content should be of the style “Heading”
Steps
1) Go to a blank page where the table of content is to be placed – usually at the beginning of the
document and after the title page
2) Select the references menu
3) Select/Click Table of content
4) Select the preferred style and Click
10.12. Working with Tables
A table is made up of rows and columns that can be filled with text and graphics. You can sort and perform
calculations on them. Tables make it easy to read information that would otherwise have to be written in a
representative and lengthy fashion. Use tables to organize information and create interesting page layouts
with side-by-side columns of text and graphics.
10.12.1.Table Menus (Accessed when a table is selected)
Menu has two sub-menus
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 16
Design
Layout
Design Menu
Table styles options, table styles, draw borders
Layout Menu
1) Table; Select, View Gridlines, properties
2) Rows and Columns; Delete, Insert (top, bottom, right & left
3) Merge; Merge cells, Split cells, Split table
4) Cell size
5) Alignment
6) Data; sort, repeat header, convert to text etc.
10.12.2. Inserting a simple table:
1) Select Insert Menu
2) Select the Table menu
3) Click Insert
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 17
4) In the no. of columns box enter the number of columns.
5) In the no of rows box enter the number of rows.
6) Click Ok.
10.12.3.Merging cells in a tab
1) Select the cells to be merged.
2) From the table menu choose Layout menu
3) Click merge cells.
10.12.4. Splitting the cells
1. Select cell to be split
2. From the table menu Choose the Layout menu
3. Choose split cells
4. Type the number of columns and rows each cell is to be cell split
10.12.5.To delete rows and columns in a table
1. Select the row or the column to be deleted
2. From the Table Layout menu click the down arrow at the bottom of the delete command icon
3. Select the required delete option
10.12.6.Adjusting column width
1) Position the mouse pointer over the column boundary until it changes shape
2) Drag the column boundary to the right or left
10.12.7.Adding rows to a table
1) Select the Table Layout menu
2) Select the required insert row option
10.12.8.To delete cells in a table
1) Select the Table Layout Menu
2) Click the down arrow at the bottom of the delete command icon
3) Select delete cell option.
10.12.9. Sorting
Information in the table can be sorted in either ascending or descending order
1. Click any cell in the table
2. From the Table Layout menu choose sort
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 18
3. Select the appropriate sort parameters
4. Click Ok to sort
10.12.10. Performing calculations in a table
1. Click the cell in which you want the result to appear.
2. On the Table Layout menu, click Formula.
3. Enter the formula OR Select the function to from the Paste Function field
4. Click OK
10.13. Columns
Newspaper style columns
You can format text into multiple newspaper style columns. This is best applied when creating documents
like newspaper, newsletters or brochures.
Option 1
Using the column button on the standard toolbar
1. Highlight the text to be columned.
2. From the Page Layout, on the page set-up menu, click Columns Icon
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 19
3. Select the required columns options.
10.14. Templates
A template is a document that contains predefined settings. The use of templates ensures that there is
consistency between documents.
1. Click the File menu
2. Select New
3. Select the template that you want to use.
10.15. To Print a Document
You can print the active document by clicking the print icon on the standard toolbar. This will not give you
the option of choosing a variety of commands.
1) Click the File menu
2) Click print.
3) Select Print View to view how the document will print
4) Select Print to open the printer dialog box
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 20
a) In the Printer name box select a printer.
b) Choose an option for the number of pages to be printed i.e.
ALL: -Prints the entire document
CURRENT PAGE: -prints the current page
PAGE: -you can select certain pages within a document
c) In the number of copies box, specify the number of copies you want in each page.
d) Click Ok.
10.16. Mail Merging
If you had to type the same form letter 100 times, you know what boring and back breaking work it can be.
Never again, by setting up the form letter as a Ms Word merge documents, you need type the letter only
once.
STEP 1 Creating data Source
1) From the Mailing Menu
2) Click Select recipients, New Address List dialogue appear as shown below
3) Remove the fields not needed and / or create new field
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 21
1) Type in the details
2) Click OK. A Save dialogue box appears, so thatg you can save the documey,
3) Enter an appropriate Name, storing folder. Document is saved as Microsoft Office Address list
STEP 2
1. From the Mailing Menu
2. Click Start Mail Merge, the dialogue appear as shown below
3. Select Letters
Type the letter content
4. Click Select Recipients
Select type new List - to create a new list
Select Use Existing List - to open up an existing database
Select from Outlook contacts - to use your email contact list
5. Select Insert Merge File
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 22
Select the required fields and click insert button to paste the selected field into the document
Arrange them accordingly
6. Click Review Results to view the Mail merged document
UCC 103: Principles of Computing – Chapter 10 Word Processing Page 23
You might also like
- Theodore Metochites 1981 Greek Orthodox Theological ReviewDocument47 pagesTheodore Metochites 1981 Greek Orthodox Theological ReviewMatt BrielNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Basics2Document29 pagesMicrosoft Word Basics2Vidhyashree P SDM College of Education, UjireNo ratings yet
- Word ProcessorDocument35 pagesWord ProcessorNoelNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word: Instructor: Vikash RamrattanDocument29 pagesMicrosoft Word: Instructor: Vikash Ramrattanvik ramNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 (Introduction To MS Word)Document30 pagesLecture 02 (Introduction To MS Word)JavaidNo ratings yet
- Session 4: Features of Microsoft Word Application 2010Document26 pagesSession 4: Features of Microsoft Word Application 2010Nash KevinNo ratings yet
- PC Software Unit - 2Document102 pagesPC Software Unit - 2ppkritiNo ratings yet
- MS Word DetailsDocument28 pagesMS Word DetailsAllana Ruth P. AbudaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Parts and FunctionDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word Parts and FunctionKate OchaveNo ratings yet
- Form Two Notes 981313772Document108 pagesForm Two Notes 981313772Eddy OtienoNo ratings yet
- Word ProcessingDocument21 pagesWord ProcessingAlice Valiente100% (2)
- Microsoft WordDocument28 pagesMicrosoft WordMark Robert De JesusNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Word 2007: Introduction To Programming Electrical Engineering Department UET TaxilaDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Word 2007: Introduction To Programming Electrical Engineering Department UET TaxilaTanveer KhadimNo ratings yet
- Word ProcessorDocument4 pagesWord Processorwanguicynthia2005No ratings yet
- Practical 2Document41 pagesPractical 2ajay.k88No ratings yet
- Office Automation Using Ms-Office: Chapter-2Document85 pagesOffice Automation Using Ms-Office: Chapter-2sagar agrawalNo ratings yet
- Word 2007Document12 pagesWord 2007Abbas Ahsan100% (2)
- Microsoft Word Basics2Document25 pagesMicrosoft Word Basics2VidaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Basics2Document25 pagesMicrosoft Word Basics2Ayruhh DiNo ratings yet
- Iraqi Kurdistan RegionDocument12 pagesIraqi Kurdistan RegionYunis SalimNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 FoitDocument21 pagesUnit 2 Foitvarsha.j2177No ratings yet
- WORD 2010: Identify The Components of The Word InterfaceDocument6 pagesWORD 2010: Identify The Components of The Word InterfaceRavi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Word 2003 Tutorial 1Document17 pagesWord 2003 Tutorial 1Glenn100% (6)
- Microsoft Word Basics2Document63 pagesMicrosoft Word Basics2Reymart de VeraNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Part 1 MS-WORDDocument26 pagesModule 3 Part 1 MS-WORDADITYA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Title Bar Ruler: What Is Word Processor?Document16 pagesTitle Bar Ruler: What Is Word Processor?Mehran KhanNo ratings yet
- ICT Productivity Tools 1. Word Processing Using MS Word ModuleDocument34 pagesICT Productivity Tools 1. Word Processing Using MS Word ModuleSanie BautistaNo ratings yet
- WWW - Chandansingh.co - In: Word ProcessingDocument25 pagesWWW - Chandansingh.co - In: Word ProcessingrharshaohmNo ratings yet
- Comp Report FileDocument33 pagesComp Report Filemanjula dangeNo ratings yet
- Ms Word Explained by Dr. Vatan SehrawatDocument62 pagesMs Word Explained by Dr. Vatan SehrawatVatan SehrawatNo ratings yet
- Word ProcessingDocument3 pagesWord ProcessingAdah EneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Word Processing Basics: Repeat Commands. You Can Add Other Commands ToDocument2 pagesLesson 1 Word Processing Basics: Repeat Commands. You Can Add Other Commands ToChristel ToledoNo ratings yet
- MS OfficeDocument16 pagesMS OfficeChristian JacobNo ratings yet
- MS Word EnvironmentDocument24 pagesMS Word EnvironmentRodulfo Capinig GabritoNo ratings yet
- Computer 6 Microsoft Word BasicDocument35 pagesComputer 6 Microsoft Word Basicleana marie ballesterosNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microsoft Word 2010Document151 pagesAdvanced Microsoft Word 2010Tina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Ms WordDocument24 pagesLab 2 Ms Wordbilal wadudNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document18 pagesLesson 1Sandy BasNo ratings yet
- Comp-Prog11 Q1 Mod1 MSword 16052021Document32 pagesComp-Prog11 Q1 Mod1 MSword 16052021Uary FebNo ratings yet
- Second Term Form One NoteDocument43 pagesSecond Term Form One NoteKafui AugustineNo ratings yet
- Word Processing SoftwareDocument18 pagesWord Processing SoftwareBeth Bauzon100% (1)
- Muhammad ZohaibDocument87 pagesMuhammad ZohaibZohaib JavedNo ratings yet
- Ict1 - Unit 3 - MswordDocument8 pagesIct1 - Unit 3 - MswordEverlyn D. BuglosaNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet: Word Processing Using MS Word Bcs 1 - NDocument17 pagesInformation Sheet: Word Processing Using MS Word Bcs 1 - NEricca AndradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 WordDocument9 pagesLesson 5 WordMutie MuthamaNo ratings yet
- End User Lesson 1Document10 pagesEnd User Lesson 1KonachanNo ratings yet
- Word Processing and Google DocsDocument28 pagesWord Processing and Google DocsRangika HerathNo ratings yet
- 1430209568MS Word Course - Reading Material (Limited)Document56 pages1430209568MS Word Course - Reading Material (Limited)r.kathirvel236No ratings yet
- Word Processing For Beginners, Part I: Techcenter - The Public Library of Cincinnati & Hamilton CountyDocument9 pagesWord Processing For Beginners, Part I: Techcenter - The Public Library of Cincinnati & Hamilton CountyObby-GiftMwambaKachecheNo ratings yet
- WORD Pamphlet PrintDocument27 pagesWORD Pamphlet Printabu yusif kargboNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word WindowDocument16 pagesMicrosoft Word WindowMary Jane Blanco FioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1DAVE SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- MS Office NotesDocument139 pagesMS Office NotesNoble Obeng-Ankamah100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Getting Started With DocumentDocument29 pagesQuarter 1 Getting Started With DocumentChezter Chaz HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Software Productivity - WordDocument36 pagesSoftware Productivity - WordJhan G CalateNo ratings yet
- Word Processing ApplicationDocument44 pagesWord Processing ApplicationRobert Jake CotonNo ratings yet
- Simplified Ms WordDocument47 pagesSimplified Ms WordMac CayabanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word: What Is MS Word?Document4 pagesMicrosoft Word: What Is MS Word?mandeepNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Ms Word: Ict - 7 Self - Learning Material 1 Quarter 4: Week 1Document6 pagesParts and Function of Ms Word: Ict - 7 Self - Learning Material 1 Quarter 4: Week 1kxilxx_whoNo ratings yet
- Week005 - ModuleDocument12 pagesWeek005 - ModuleJohn Gabriel SambajonNo ratings yet
- Structure Fires Caused by Hot Work: Marty AhrensDocument14 pagesStructure Fires Caused by Hot Work: Marty AhrensBurgosg ValeryNo ratings yet
- Rod and Pump DataDocument11 pagesRod and Pump DataYoandri Stefania Guerrero CamargoNo ratings yet
- Program Orientation HandoutsDocument125 pagesProgram Orientation Handoutsapi-391214898No ratings yet
- Sow English Year 2 2023Document12 pagesSow English Year 2 2023Noramaliza GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Tripwire Is An Intrusion Detection SystemDocument28 pagesTripwire Is An Intrusion Detection SystempoornimaNo ratings yet
- 4 AMcKayCatalogDocument10 pages4 AMcKayCatalogManuelNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportyousufNo ratings yet
- A321 DIFFERENCE GUIDE From A320Document72 pagesA321 DIFFERENCE GUIDE From A320NigelNo ratings yet
- Verilog HDL: Special ClassesDocument11 pagesVerilog HDL: Special ClassesUnique ProNo ratings yet
- Facilities 2013 SG - Full Time, 2nd YearDocument49 pagesFacilities 2013 SG - Full Time, 2nd Yearsaifasad100% (2)
- Have To, Has To, Had To - Exercise 1 - Worksheet English GrammarDocument1 pageHave To, Has To, Had To - Exercise 1 - Worksheet English Grammarjonni jonsonNo ratings yet
- Pride&PrejudiceDocument88 pagesPride&PrejudiceMà Ř YãmNo ratings yet
- Cse205 Computer-Architecture-And-Organization TH 2.00 Ac26Document2 pagesCse205 Computer-Architecture-And-Organization TH 2.00 Ac26Ravi ThejaNo ratings yet
- ExcaDrill 45A DF560L DatasheetDocument2 pagesExcaDrill 45A DF560L DatasheetИгорь ИвановNo ratings yet
- Websdr PDFDocument11 pagesWebsdr PDFDoruNastaseNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Identifying Author's Bias For or Against: Quarter 3 Wk-1Document4 pagesLesson: Identifying Author's Bias For or Against: Quarter 3 Wk-1Mary Cris Navarro LiboonNo ratings yet
- Sky & Telescope - February 2016 (Gnv64)Document82 pagesSky & Telescope - February 2016 (Gnv64)bogarguz100% (1)
- BDU-BIT-Electromechanical Engineering Curriculum (Regular Program)Document187 pagesBDU-BIT-Electromechanical Engineering Curriculum (Regular Program)beselamu75% (4)
- Case Presentation: Placenta Previa: Crissa Marie D. PinedaDocument42 pagesCase Presentation: Placenta Previa: Crissa Marie D. PinedaCrissa PinedaNo ratings yet
- Jisicom - Smart System of Fast Internet Access Development Using Backbone Network MethodDocument9 pagesJisicom - Smart System of Fast Internet Access Development Using Backbone Network MethodVerdi YasinNo ratings yet
- 1 Scrum Master Skills m1 Slides PDFDocument66 pages1 Scrum Master Skills m1 Slides PDFSohaib Omer SalihNo ratings yet
- Novena To Our Lady Queen of PeaceDocument4 pagesNovena To Our Lady Queen of PeaceGraciedion MediaNo ratings yet
- Node Name Ping Status Community IP Address: CAPSTONE - IT Infrastructure Monitoring SNMP WalkDocument4 pagesNode Name Ping Status Community IP Address: CAPSTONE - IT Infrastructure Monitoring SNMP WalkSpartacus CaesarNo ratings yet
- Cosep v. People PDFDocument8 pagesCosep v. People PDFAlyssa Fatima Guinto SaliNo ratings yet
- Assignment (60%) : ECS312 Counselling in SchoolsDocument6 pagesAssignment (60%) : ECS312 Counselling in SchoolsJelebu Charity RunNo ratings yet
- Councillor Danny Thorpe: Leader, Royal Borough of GreenwichDocument2 pagesCouncillor Danny Thorpe: Leader, Royal Borough of GreenwichDr-Syed Ali TarekNo ratings yet
- SDS - Molykote 1000Document8 pagesSDS - Molykote 1000Zarni KyawNo ratings yet
- Steel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, For Pinions, Gears and Shafts For Reduction GearsDocument4 pagesSteel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, For Pinions, Gears and Shafts For Reduction Gearssharon blushteinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Língua Inglesa 7Document21 pagesLesson 2 - Língua Inglesa 7Shara Maria Venâncio SilvaNo ratings yet