Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guia de Estudio 3°1° CENS POCITO
Uploaded by
Rociio CabreraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guia de Estudio 3°1° CENS POCITO
Uploaded by
Rociio CabreraCopyright:
Available Formats
GUÍA DE ESTUDIO- CENS POCITO- 3° 1°
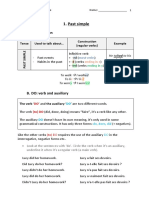
PAST SIMPLE (VERB TO BE)
El pasado del Verbo “TO BE” se utiliza para decir “estaba” o “era” (es lo mismo que el
verbo TO BE en presente, que quiere decir “Estar” o “Ser”, pero en su forma en pasado)
Para aprenderlo es importante saber que existen dos formas “WAS” y “WERE”, las
cuales significan lo mismo, “estaba” o “era”. La única diferencia que existe entre ellas es
los SUJETOS con las que se utilizan.
WAS → I, HE, SHE IT WERE→ WE, YOU, THEY
ORACIONES AFIRMATIVAS:
SUJETO + WAS/ WERE + ...
Ejemplos:
*She was my classmate at school.
*My friends were happy yesterday.
ORACIONES NEGATIVAS:
SUJETO + WASN’T/ WEREN’T + ...
Ejemplos:
*She wasn’t my classmate at school.
*My friends weren’t happy yesterday.
ORACIONES INTERROGATIVAS:
WAS/WERE + SUJETO + ...?
Ejemplos:
*Was she my classmate at school?
*Were my friends happy yesterday?
Short answers
• Afirmativas: Yes, (sujeto) + was / were
Ej: Yes, she was. = Yes, Mary was.
Yes, they were. = Yes, my friends were.
• Negativas: No, (sujeto) + wasn’t / weren’t
Ej: No, she wasn’t. = No, Mary wasn’t.
No, they weren’t. = No, my friends weren’t.
GUÍA DE ESTUDIO- CENS POCITO- 3° 1°
1. Choose the correct words.
Valentina Treshkova 1 was/ were the first
woman in space in 1963. Valentina’s
parents 2 wasn’t/ weren’t Russian; they
3 was/ were from Belarus. But their
daughter 4 was/ were born in Russia in
1937. Today, most cosmonauts are
scientists, but Valentina 5 wasn’t/
weren’t a scientist. Four hundred
women 6 was/ were candidates for the
special mission, but Valentina 7 was/
were the lucky one.
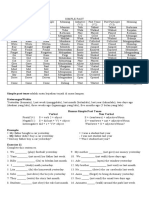
2. Complete the sentences with the correct past simple forms of the verb BE.
a. Harry and Sam ___________ at the football match on Saturday. (✓)
b. On Friday, Mia ___________ at home. ()
c. Holly ___________ at the cinema last night. (✓)
d. My parents ___________ angry. ( )
e. The weather ___________ very good. ()
f. We ___________ on holiday last week. (✓)
3. Write sentences with the past simple forms of the verb BE.
a. I / at home last night.
I was at home last night.
b. My friends / not at the concert on Saturday.
____________________________________________
c. Nadia / not tired after the match.
____________________________________________
d. We / worried before the exam.
____________________________________________
e. My dad / not at work yesterday.
____________________________________________
f. They / in Australia last summer.
____________________________________________
4. Re- write the sentences from exercise 3 in their interrogative forms.
a. Was I at home last night?
GUÍA DE ESTUDIO- CENS POCITO- 3° 1°
b. ________________________________________
c. ________________________________________
d. ________________________________________
e. ________________________________________
f. ________________________________________
5. Choose “wasn’t” and “weren’t” to complete the following sentences.
a. She ___________ at the café on Monday.
b. Alfredo and Sam ___________ in the museum on Tuesday afternoon.
c. My cousin ___________ at the cinema yesterday.
d. Some classmates ___________ late last Friday.
e. My friends ___________ happy with the results.
f. I ___________ in Bariloche last year.
g. We ___________ at the restaurant last night.
h. Last month Patrick and I ___________ very busy.
i. They ___________ at the party last weekend.
6. Correct the mistakes in the sentences.
a. Were Tom not the oldest brother?
b. The car weren’t very expensive.
c. Was we at the library yesterday?
d. Her car broke down so she were late for the appointment.
e. It were a not very funny movie.
7. Circle the correct answer.
GUÍA DE ESTUDIO- CENS POCITO- 3° 1°
8. Complete the questions with WAS or WERE. Then write short answers.
a) ___Were_ you at home last night? ✓ Yes, I was
b) _________ Oliver happy yesterday? _____________
c) _________ your and Ted at the cinema together? ✓ _____________
d) _________ all your friends at the party? _____________
e) _________ I the fastest in the race? _____________
f) _________ Katy at school last Friday? ✓ _____________
PAST SIMPLE
Utilizamos el pasado simple para referirnos a hechos ocurridos en el pasado, para
alguna acción que fue completada en el pasado.
Para aprender este tema es IMPORTANTE ESTUDIAR LOS VERBOS REGULARES
(Verbos que se conjugan agregando “-ed” a su terminación) Y LOS IRREGULARES
(No siguen un patrón típico de conjugación).
Las estructuras para formar oraciones son las siguientes:
ORACIONES AFIRMATIVAS:
SUJETO + VERBO (REGULAR/ IRREGULAR) + ……
Ejemplos:
• We saw a great film at the cinema last night.
• He helped his mother to prepare a cake.
ORACIONES NEGATIVAS:
SUJETO + DIDN’T + VERBO (INF)+…….
Ejemplos:
• We didn’t see a great film at the cinema last night.
• He didn’t help his mother to prepare a cake.
ORACIONES INTERROGATIVAS:
DID + SUJETO + VERBO (INF) +……..?
Ejemplos:
• Did we see a great film at the cinema last night?
GUÍA DE ESTUDIO- CENS POCITO- 3° 1°
• Did he help his mother to prepare a cake?
Short answers
• Afirmativas: Yes, (sujeto) + (did)
Ej: Yes, she did.
• Negativas: No, (sujeto) + (didn’t )
Ej: No, she didn’t.
REGLAS PARA VERBOS REGULARES
Regla general → A todos los verbos se les agrega “-ED” al final.
Play – Played Start - Started
Cook – Cooked Walk – Walked
Si el verbo termina con la vocal -e, se le agrega solamente la letra -d al
final.
Live – Lived Dance – Danced
Para las palabras que terminan en -y, se sustituye la última letra por -i y
se le agrega -ed.
Study – Studied Cry – Cried
En el caso de los verbos monosílabos o aquellos que se acentúan en la
última sílaba y que terminan en vocal + consonante, se repite la consonante
antes de la terminación -ed.
Stop – Stopped Cancel - Cancelled
GUÍA DE ESTUDIO- CENS POCITO- 3° 1°
INFINITIVE SIMPLE PAST PAST PARTICIPLE
Be (Ser o estar) Was / Were Been
Become (convertirse) Became Become
Begin (empezar) Began Begun
Break (romper) Broke Broken
Build (construir) Built Built
Buy (comprar) Bought Bought
Choose (elegir) Chose Chosen
Come (venir) Came Come
Cut (cortar) Cut Cut
Do (hacer) Did Done
Draw (dibujar) Drew Drawn
Drink (tomar) Drank Drunk
Drive (conducer) Drove Driven
Eat (comer) Ate Eaten
Feel (sentir) Felt Felt
Find (encontrar) Found Found
Forget (olvidar) Forgot Forgotten
Get (conseguir/obtener…) Got Got
Give (dar) Gave Given
Go (ir) Went Gone
Have (tener…) Had Had
Hear (escuchar) Heard Heard
Know (saber) Knew Known
Leave (salir…) Left Left
Make (hacer…) Made Made
Meet (conocer…) Met Met
Pay (pagar) Paid Paid
Read (leer) Read Read
Run (corer) Ran Run
Say (decir) Said Said
See (mirar) Saw Seen
Show (mostrar…) Showed Showed
Sing (cantar) Sang Sung
Sleep (dormir) Slept Slept
Speak (hablar) Spoke Spoken
Swim (nadar) Swam Swum
Take (tomar algo…) Took Taken
Teach (enseñar) Taught Taught
Tell (decir…) Told Told
Think (pensar) Thought Thought
Wake (despertar) Woke Woken
Win (ganar) Won Won
Write (escribir) Wrote Written
You might also like
- Double The: Simple Past Tense Regular Verbs - Verbs Ending in How? ExamplesDocument6 pagesDouble The: Simple Past Tense Regular Verbs - Verbs Ending in How? ExamplesLee ZieNo ratings yet
- Past Tense Explanations PracticeDocument10 pagesPast Tense Explanations PracticeBridge EnglishNo ratings yet
- The Aryan Debate PDFDocument8 pagesThe Aryan Debate PDFSreedhar Ranganathan100% (1)
- Atividade de Ingles Past Simple Regular and Irregular Verbs 9 AnoDocument2 pagesAtividade de Ingles Past Simple Regular and Irregular Verbs 9 AnoMarineusa Lopes100% (1)
- DLL On Oral Communication WEEK 14Document4 pagesDLL On Oral Communication WEEK 14Jane LegardoNo ratings yet
- Módulo 10: in Those DaysDocument34 pagesMódulo 10: in Those DaysEUDSONBRITONo ratings yet
- Atividade de Ingles Past Simple - Regular and Irregular Verbs 9 AnoDocument2 pagesAtividade de Ingles Past Simple - Regular and Irregular Verbs 9 AnoMelAdams100% (2)
- Unit2 Did:didn't CorrDocument12 pagesUnit2 Did:didn't CorrHélène lilaNo ratings yet
- Material InglésDocument13 pagesMaterial Ingléscristina molinaNo ratings yet
- Resumos TESTE INGLÊSDocument4 pagesResumos TESTE INGLÊSMariana castroNo ratings yet
- 3 Grammar 2 Present Continuous TenseDocument8 pages3 Grammar 2 Present Continuous TenseYeri Fe BrianNo ratings yet
- Simple Past - Past Continuous UseDocument14 pagesSimple Past - Past Continuous Usekeren Noelia Carranza SanchezNo ratings yet
- Unit 8.1Document2 pagesUnit 8.1Anh Nguyen DucNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 2 - S03.s1Document43 pagesENGLISH 2 - S03.s1Alberto SotoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 English Handout 1st Term 2023Document18 pagesGrade 10 English Handout 1st Term 2023D'Fátima Sementeira Jr.No ratings yet
- Simple Past - Exercises: I Talked To The Teacher. He Drank The CoffeeDocument5 pagesSimple Past - Exercises: I Talked To The Teacher. He Drank The CoffeeArnold YueNo ratings yet
- Inglês Módulo 05 Cbmerj: Past Tense in EnglishDocument6 pagesInglês Módulo 05 Cbmerj: Past Tense in EnglishVitor GreyNo ratings yet
- Công TH C Và Bài TâpDocument8 pagesCông TH C Và Bài TâpHuynh Thi Cam Van (K18 CT)No ratings yet
- English Booklet (5th Year) 2021Document54 pagesEnglish Booklet (5th Year) 2021Debora AzcurraNo ratings yet
- English PDFDocument25 pagesEnglish PDFMórmonLimaDosSantosNo ratings yet
- To Be Present Past Cont.Document13 pagesTo Be Present Past Cont.Natalia Bravo NegreteNo ratings yet
- Past Simple SamanthaChi-DeysiDuarteDocument11 pagesPast Simple SamanthaChi-DeysiDuarteDeysi DuarteNo ratings yet
- Ingles Tema 2Document28 pagesIngles Tema 2Vladimir Huamanvilca HuamaniNo ratings yet
- Módulo Inglés BásicoDocument39 pagesMódulo Inglés BásicoEducación CadesNo ratings yet
- 7 ANO OptimizedDocument30 pages7 ANO OptimizedNagatoro HayaseNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present ProgressiveDocument9 pagesSimple Present and Present Progressivemoj tokNo ratings yet
- Past Simple of Regular VerbsDocument2 pagesPast Simple of Regular VerbsOana MariaNo ratings yet
- 6 GrammarDocument18 pages6 Grammarzhenya.shigaeva1No ratings yet
- Ingles ComercialDocument41 pagesIngles ComercialSELVIN GARCIANo ratings yet
- The Simple Past TenseDocument8 pagesThe Simple Past Tensejana bojaNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect1otra A EntregarDocument7 pagesPast Perfect1otra A EntregarEsteban campazNo ratings yet
- Module No 2Document14 pagesModule No 2Hanelen DadaNo ratings yet
- Simple &progressive Past Explanation and ExercisesDocument6 pagesSimple &progressive Past Explanation and ExercisesKevin MonteroNo ratings yet
- Meeting Iv Past TenseDocument16 pagesMeeting Iv Past TenseCici FeroNo ratings yet
- Aula 13 - Simple PastDocument7 pagesAula 13 - Simple Pastgabrielfn.businessNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjt3b.ppsxDocument23 pagesPossessive Adjt3b.ppsxOlimzhon GanikhanovNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Past Continuous ADRIAN BARRERADocument9 pagesPast Simple and Past Continuous ADRIAN BARRERAAdrian BarreraNo ratings yet
- Teens 3 - Review For TEST B (Atual)Document41 pagesTeens 3 - Review For TEST B (Atual)Luciana AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- E Es e Ons Ez EntDocument22 pagesE Es e Ons Ez EntPushya ChhabriaNo ratings yet
- Forming The Past Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesForming The Past Perfect TenseKenia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Past Simpleand Past ContinuousDocument6 pagesPast Simpleand Past Continuousmalwina.wenskaNo ratings yet
- English ClassDocument6 pagesEnglish Classenzompoli7No ratings yet
- Past Tense F2 2022Document4 pagesPast Tense F2 2022Michael SchnetzerNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Hazman Rubi Farhani Iqbal Faturrohman Rasmita GintingDocument43 pagesGroup 1: Hazman Rubi Farhani Iqbal Faturrohman Rasmita Gintingtubagus ade rachmat hidayatNo ratings yet
- The Perfect TenseDocument11 pagesThe Perfect TenseMarissa ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Irregulares InglesesDocument10 pagesLista de Verbos Irregulares InglesesVerónica Martín GonzálezNo ratings yet
- List of Regular Verbs: Forma Simples Passado Forma Simples PassadoDocument3 pagesList of Regular Verbs: Forma Simples Passado Forma Simples PassadoRicardo MartinsNo ratings yet
- Your Name: - : Passive VoiceDocument9 pagesYour Name: - : Passive VoiceKhôi Nguyên ĐặngNo ratings yet
- French TheoryDocument13 pagesFrench TheoryKudzai TaruwonaNo ratings yet
- Mandar InglessssDocument14 pagesMandar InglessssJosi Llanes GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense Adalah Suatu Kejadian Terjadi Di Masa Lampau. KeteranganwaktuDocument2 pagesSimple Past Tense Adalah Suatu Kejadian Terjadi Di Masa Lampau. KeteranganwaktuAstri Rosdemak SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Workbook Kids Level 6Document8 pagesWorkbook Kids Level 6karenr.melgarlazaroNo ratings yet
- CBSE-X English - Chap-G1 (Complete Grammar)Document10 pagesCBSE-X English - Chap-G1 (Complete Grammar)parijatislam0No ratings yet
- Resumos de InglesDocument4 pagesResumos de InglesiloveasiandoramasNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument9 pagesPresent TenseRahiq HatemNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocument13 pagesPast Simple and Past ContinuousAntónio PereiraNo ratings yet
- SUPAnglDocument30 pagesSUPAngllebete100% (1)
- INGLES II 10MO Cuadernodetrabajo2 SEDUC TelebásicaDocument21 pagesINGLES II 10MO Cuadernodetrabajo2 SEDUC Telebásicavanessa bacaNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument37 pagesTenseasratnu_41155700No ratings yet
- Group4 Discussion 9-MarDocument18 pagesGroup4 Discussion 9-MarChan SyNo ratings yet
- Makalah-Simple Past-TenseDocument18 pagesMakalah-Simple Past-Tensemekarnet100% (1)
- SAP HANA Spatial Reference enDocument220 pagesSAP HANA Spatial Reference enrakeshNo ratings yet
- Homework Pro 7.8.2 Apk DownloadDocument8 pagesHomework Pro 7.8.2 Apk Downloadafeuqbmfv100% (1)
- Akshay Prakash Patil: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesAkshay Prakash Patil: ObjectiveNaveenJainNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Your Academic Writing PDFDocument24 pagesHow To Improve Your Academic Writing PDFipqtrNo ratings yet
- Guess Paper 2023Document4 pagesGuess Paper 2023Abdullah AftabNo ratings yet
- Trans JourDocument6 pagesTrans JourVanesa GalvisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming: SLIIT - Faculty of ComputingDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Programming: SLIIT - Faculty of ComputingRashmi SandeepaniNo ratings yet
- RSLogix 5000 - Using The GSV Instruction To Check Module StatusDocument6 pagesRSLogix 5000 - Using The GSV Instruction To Check Module StatusRafa ANo ratings yet
- Course Hand OutDocument70 pagesCourse Hand OutUdhaya SankarNo ratings yet
- Laravel Authentication Using Web3 - by Hafiq Iqmal - Geek Culture - Nov, 2021 - MediumDocument12 pagesLaravel Authentication Using Web3 - by Hafiq Iqmal - Geek Culture - Nov, 2021 - MediumvcazacuNo ratings yet
- Advanced - StudentsBook - Unit 1 PDFDocument10 pagesAdvanced - StudentsBook - Unit 1 PDFZandaNo ratings yet
- Cc1 TopicsDocument26 pagesCc1 TopicsVito ArgentoNo ratings yet
- Installing MSCorefontsin Linux SystemsDocument3 pagesInstalling MSCorefontsin Linux SystemsgreatsunNo ratings yet
- CH 1-4Document32 pagesCH 1-4onatbrossNo ratings yet
- PEL125Document12 pagesPEL125Rahul RajNo ratings yet
- Lab VIADocument6 pagesLab VIAJuby JohnsonNo ratings yet
- DS Combined All UnitsDocument66 pagesDS Combined All Units30. Suraj IngaleNo ratings yet
- Root Mean Square (RMS) and Overall LevelDocument20 pagesRoot Mean Square (RMS) and Overall LevelManoj SinghNo ratings yet
- Classroom Life Q PDFDocument11 pagesClassroom Life Q PDFAnca AnghelNo ratings yet
- 1 - Minutes of The Annual Dinner Meeting 2010Document2 pages1 - Minutes of The Annual Dinner Meeting 2010Mohamad Fuad50% (2)
- English 8 Q1 WK3Document15 pagesEnglish 8 Q1 WK3Ana Mary Joy PepeNo ratings yet
- RPP X 2Document55 pagesRPP X 2Fikri R. FauziNo ratings yet
- De Cuong Anh 8 - HK2Document8 pagesDe Cuong Anh 8 - HK2ducdm3bd20No ratings yet
- EDITED A Detailed Lesson Plan in English 4F 2 FDocument7 pagesEDITED A Detailed Lesson Plan in English 4F 2 FAtienza, Francheska Isabela C.100% (1)
- Note On The History of LogicDocument3 pagesNote On The History of Logicnabeel ahmedNo ratings yet
- Imagery Tone and MiscDocument20 pagesImagery Tone and Miscapi-240827612No ratings yet
- Graph Terminology PDFDocument9 pagesGraph Terminology PDFPeter BandaNo ratings yet
- English Language Teaching Methods: PPG215 Semester 1, 2014/2015Document41 pagesEnglish Language Teaching Methods: PPG215 Semester 1, 2014/2015mrajisNo ratings yet