Professional Documents
Culture Documents
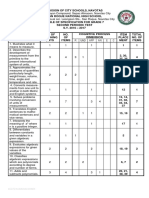
(377636) Year 2 Maths Curriculum
(377636) Year 2 Maths Curriculum
Uploaded by
Mkufunzi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
[377636]Year_2_Maths_Curriculum
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pages(377636) Year 2 Maths Curriculum
(377636) Year 2 Maths Curriculum
Uploaded by
MkufunziCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
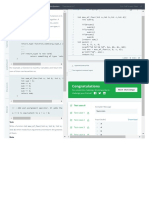
Year 2 Maths Curriculum Year 2 Should be taught to:
Number Sense Additive Reasoning Multiplicative Reasoning Geometric Reasoning
count in steps of 2, 3 and 5 from 0 and in count in steps of 2, 3 and 5 from 0 and count in steps of 2, 3 and 5 from 0 recognise, find, name and write
tens from any number, forward and backward in tens from any number, forward and and in tens from any number, fractions 1∕3, ¼, 2∕4 and ¾ of a length,
2.1, 2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12, backward 2.1, 2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, forward and backward 2.1, 2.2, 2.4, shape, set of objects or quantity 2.13,
2.13 2.8, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12, 2.13 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12, 2.13 2.14
recognise the place value of each digit in a write simple fractions for example ½
recognise the place value of each digit recall and use multiplication and
two-digit number (tens, ones) 2.1, 2.2, 2.4, division facts for the 2, 5 and 10 of 6 = 3 and recognise the
in a two-digit number (tens, ones) 2.1,
2.5, 2.8, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12
2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.8, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12 multiplication tables, including equivalence of 2∕4 and ½ 2.13, 2.14
identify, represent and estimate numbers
use place value and number facts to recognising odd and even numbers identify and describe the properties of
using different representations, including the 2.6, 2.7, 2.13
solve problems 2.1, 2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.8, 2-D shapes, including the number of
number line 2.1, 2.4, 2.8, 2.11
2.9, 2.11, 2.12 calculate mathematical statements for sides and line symmetry in a vertical
compare and order numbers from 0 up to line 2.3, 2.10, 2.14
solve problems with addition and multiplication and division within the
100; use >, < and = signs 2.1, 2.4, 2.8, 2.11
subtraction: multiplication tables and write them identify and describe the properties of
read and write numbers to at least 100 in 3-D shapes, including the number of
numerals and in words 2.1, 2.4, 2.8, 2.11 using concrete objects and pictorial using the multiplication (3), division
representations, including those (4) and equals (5) signs 2.7, 2.13 edges, vertices and faces 2.3, 2.10,
use place value and number facts to solve 2.14
involving numbers, quantities and show that multiplication of two
problems 2.1, 2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.8, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12
measures 2.2, 2.5, 2.9, 2.12 numbers can be done in any order identify 2-D shapes on the surface
compare and order lengths, mass, volume of 3-D shapes, [for example, a circle
/ capacity and record the results using >, applying their increasing knowledge (commutative) and division of one
of mental methods and written number by another cannot 2.7, 2.13 on a cylinder and a triangle on a
< and = 2.1, 2.4, 2.8, 2.11 pyramid] 2.3, 2.10, 2.14
methods 2.2, 2.5, 2.9, 2.12 solve problems involving
compare and sequence intervals of time 2.1, compare and sort common 2-D and
recall and use addition and subtraction multiplication and division, using
2.4, 2.8, 2.11 3-D shapes and everyday objects 2.3,
facts to 20 fluently, and derive and use materials, arrays, repeated addition,
recall and use multiplication and division related facts up to 100 2.2, 2.5, 2.9, 2.12 mental methods, and multiplication 2.10, 2.14
facts for the 2, 5 and 10 multiplication
add and subtract numbers and division facts, including order and arrange combinations of
tables, including recognising odd and even mathematical objects in patterns and
using concrete objects, pictorial problems in contexts 2.7, 2.13
numbers 2.6, 2.7, 2.13 sequences 2.3, 2.10, 2.14
representations, and mentally, recognise and use symbols for
choose and use appropriate standard use mathematical vocabulary to
including: pounds (£) and pence (p); combine
units to estimate and measure length / describe position, direction and
a two-digit number and ones amounts to make a particular value
height in any direction (m / cm); mass (kg movement, including movement in a
a two-digit number and tens 2.5, 2.7, 2.9
/ g); temperature (°C); capacity (litres / ml) straight line and distinguishing
to the nearest appropriate unit; using two two-digit numbers find different combinations of coins to
equal the same amounts of money between rotation as a turn and in
rulers, scales, thermometers and adding three one-digit numbers 2.2, 2.5,
2.5, 2.7, 2.9 terms of right angles for quarter, half
measuring vessels 2.8, 2.11 2.9, 2.12
tell and write the time to five minutes, and three-quarter turns (clockwise and
interpret and construct simple pictograms, show that addition of two numbers can
including quarter past/to the hour and anti-clockwise) 2.3, 2.10, 2.14
tally charts, block diagrams and simple be done in any order (commutative) and
subtraction of one number from another draw the hands on a clock face to
tables 2.6, 2.11
show these times 2.7, 2.13
ask and answer simple questions by cannot 2.5, 2.9, 2.12
counting the number of objects in each recognise and use the inverse know the number of minutes in an
hour and the number of hours in a day
category and sorting the categories by relationship between addition and
2.7, 2.13
quantity 2.1, 2.4, 2.6, 2.11 subtraction and use this to check
recognise, find, name and write
calculations and solve missing number
fractions 1∕3, ¼, 2∕4 and ¾ of a length,
problems 2.5, 2.9, 2.12
shape, set of objects or quantity 2.13,
recognise and use symbols for pounds
2.14
(£) and pence (p); combine amounts to
write simple fractions for example, ½
make a particular value 2.5, 2.7, 2.9
of 6 5 3 and recognise the
find different combinations of coins to
equal the same amounts of money 2.5, equivalence of
2.7, 2.9 2∕4 and ½ 2.13, 2.14
solve simple problems in a practical
context involving addition and
subtraction of money of the same unit,
including giving change 2.2, 2.5, 2.9
ask and answer questions about totalling
and comparing categorical data 2.2, 2.5,
2.9, 2.12
Year 2 Maths Curriculum Year 2 Should be taught to:
You might also like
- Service Manual Supplement (2002) : Isuzu Commercial Truck Forward TiltmasterDocument172 pagesService Manual Supplement (2002) : Isuzu Commercial Truck Forward Tiltmasterrolly67% (3)
- Lesson Observation FormDocument12 pagesLesson Observation FormBurst ShakurNo ratings yet
- Arena Codex Scientia PDFDocument162 pagesArena Codex Scientia PDFМаксим Дьяконенко100% (1)
- Ryobi RYi3500ES - 090930321 - 175 - RPL - R - 01Document7 pagesRyobi RYi3500ES - 090930321 - 175 - RPL - R - 01digitaltextNo ratings yet
- Fastiron 08070 L2guide 2Document353 pagesFastiron 08070 L2guide 2Suresh VNNo ratings yet
- Mathematics RevisionDocument184 pagesMathematics RevisionTrep Chiru100% (1)
- Math g7 Second Periodic Test 2016-17-1Document6 pagesMath g7 Second Periodic Test 2016-17-1Karizza Cruz100% (1)
- Math Starters: 5- to 10-Minute Activities Aligned with the Common Core Math Standards, Grades 6-12From EverandMath Starters: 5- to 10-Minute Activities Aligned with the Common Core Math Standards, Grades 6-12No ratings yet
- NCM 109 CMC at Risk PrelimDocument19 pagesNCM 109 CMC at Risk PrelimBeche May Lumantas100% (1)
- 1 PDFDocument4 pages1 PDFVishal BawaneNo ratings yet
- Computer Control: Control Processor UC Control Processor TVDocument23 pagesComputer Control: Control Processor UC Control Processor TVmaxxiss50% (2)
- A Simulation of Roll Wear in Hot Rolling ProcessesDocument336 pagesA Simulation of Roll Wear in Hot Rolling ProcessesVinay Rajput100% (1)
- Mercedes 230sl. Fuel Injection Linkage Adjustment and Idle Adjustment ProceduresDocument15 pagesMercedes 230sl. Fuel Injection Linkage Adjustment and Idle Adjustment ProceduresLockie Owens0% (1)
- PT - Math 4 - q1 With TosDocument5 pagesPT - Math 4 - q1 With TosLovella AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in - MATHEMATICS 5 With TOSDocument7 pagesSecond Periodical Test in - MATHEMATICS 5 With TOSGeraldine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Audio-Lingual Method (Assignment)Document13 pagesAudio-Lingual Method (Assignment)Lisa Kwan100% (12)
- Contoh Proposal Bahasa InggrisDocument35 pagesContoh Proposal Bahasa InggrisRinni Rinnis88% (25)
- Whole Number OperationsDocument2 pagesWhole Number Operationsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- New PUMA Mathematics Mastery Curriculum Maps 1Document31 pagesNew PUMA Mathematics Mastery Curriculum Maps 1kayani.bushraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Math OasDocument2 pages2nd Math Oasapi-411338120No ratings yet
- 2TOSDocument3 pages2TOSRito MontalbanNo ratings yet
- Hopkins Power Standards For 2nd Grade Mathematics Standard Benchmark Number and OperationsDocument1 pageHopkins Power Standards For 2nd Grade Mathematics Standard Benchmark Number and Operationstae hyungNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 5 - q2 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesPT - Mathematics 5 - q2 2nd QuarterMarife Canayong JacintoNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 5 - Q2Document8 pagesPT - Mathematics 5 - Q2Shaun BarsolascoNo ratings yet
- PT Mathematics-5 Q2Document8 pagesPT Mathematics-5 Q2jannegabriellemataNo ratings yet
- Mathematics StandardsDocument4 pagesMathematics Standardsapi-369625583No ratings yet
- Lesson No. Objectives: Table of Specification Second Grading Period (Mathematics 5) SY 2016-2017Document5 pagesLesson No. Objectives: Table of Specification Second Grading Period (Mathematics 5) SY 2016-2017Gizelle Yarcia HuligangaNo ratings yet
- Second Quarterly Examination in Math 5Document9 pagesSecond Quarterly Examination in Math 5Carla Calma RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification End of Term 2 2024Document6 pagesTable of Specification End of Term 2 2024Melissa MorrisNo ratings yet
- Tos MathematicsDocument2 pagesTos MathematicsRochelle Pasaan Nala100% (1)
- Mathstandards2007 005247 Reposted 92815Document3 pagesMathstandards2007 005247 Reposted 92815api-369626876No ratings yet
- Arch2017 Maths GR 8 Final Exam PaperDocument10 pagesArch2017 Maths GR 8 Final Exam Papervutshilaashton52No ratings yet
- PT Mathematics 5 q2Document6 pagesPT Mathematics 5 q2Krystel Monica Manalo100% (3)
- PT Mathematics-5 Q2Document7 pagesPT Mathematics-5 Q2Diosa JimenezNo ratings yet
- TOS and Test Papers ?Document3 pagesTOS and Test Papers ?Ruth CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Stage 2 - tcm142-354104Document3 pagesMathematics Stage 2 - tcm142-354104hildebrandokNo ratings yet
- 2021 GRADE 9 MATHEMATICS NOV 2021 TEST Final Mod - 211110 - 085100 - 112432Document11 pages2021 GRADE 9 MATHEMATICS NOV 2021 TEST Final Mod - 211110 - 085100 - 112432thabinonkululekoNo ratings yet
- 1st Grade Math Year at A GlanceDocument1 page1st Grade Math Year at A GlanceJosé Andrade GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Number Systems: ObjectivesDocument25 pagesNumber Systems: ObjectivesKhanh HungNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers and Indices Rubric 2022Document2 pagesReal Numbers and Indices Rubric 2022nd1319610No ratings yet
- Grade 6 4th Math Learning CompetenciesDocument3 pagesGrade 6 4th Math Learning CompetenciesMelinda RafaelNo ratings yet
- Sample Format TOS ALS AssessmentDocument5 pagesSample Format TOS ALS AssessmentMARY GAYLE LEYSANo ratings yet
- ALC MasterDocument113 pagesALC MasterShubhamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 - Q2 - PTDocument6 pagesMathematics 4 - Q2 - PTHECTOR RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 5 - Q2Document6 pagesPT - Mathematics 5 - Q2Shazell VaronaNo ratings yet
- Ma 2Document2 pagesMa 2api-335623629No ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvDocument6 pagesTable of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvJaharaSalbayani100% (1)
- 13 J LZWSR VOVHT1 RT QF 4 K3 Eni 9 Nbu 7 HSHJDocument11 pages13 J LZWSR VOVHT1 RT QF 4 K3 Eni 9 Nbu 7 HSHJmdikwamihlaliiNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification Second Grading Period (Mathematics 5)Document6 pagesTable of Specification Second Grading Period (Mathematics 5)Marvin VillaquidanNo ratings yet
- 3RD Periodical Test MathDocument5 pages3RD Periodical Test MathRosendo LibresNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document32 pages2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Jwan DelawiNo ratings yet
- McDougal Littell - Algebra 1 Ch02Document68 pagesMcDougal Littell - Algebra 1 Ch02gsparksNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvDocument6 pagesTable of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvJoi EresehtNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Further Mathematics Specification Specification For First Teaching in 2018Document12 pagesLevel 2 Further Mathematics Specification Specification For First Teaching in 2018doesgraymatter13No ratings yet
- GR 12 WC Winelands District Maths P1 Sep 2020Document13 pagesGR 12 WC Winelands District Maths P1 Sep 2020kaleb12345No ratings yet
- Maths p1 Final Exams 2023Document7 pagesMaths p1 Final Exams 2023opholaonikaNo ratings yet
- PT MathematicsDocument6 pagesPT MathematicsKendisNo ratings yet
- Math5 Test 2ndDocument6 pagesMath5 Test 2ndEn CyNo ratings yet
- Q2tos 2022-2023Document2 pagesQ2tos 2022-2023Wenny TelenNo ratings yet
- GR 8 Edwardsmaths Test or Assignment Exponents, Numeric and Geometric Patterns T2 2022 EngDocument4 pagesGR 8 Edwardsmaths Test or Assignment Exponents, Numeric and Geometric Patterns T2 2022 EngntrhkxpvqfNo ratings yet
- PT in Mathematics 4 TosDocument2 pagesPT in Mathematics 4 TosEmmalyn Aquino FabroNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument361 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldHachi Mae LubaNo ratings yet
- Maths 2014-Gr-8-Nov-Vraestel-1-EngDocument8 pagesMaths 2014-Gr-8-Nov-Vraestel-1-EngEstelle EsterhuizenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2Document16 pagesMathematics P2AneeqahNo ratings yet
- Arch2018 Maths GR 8 Final ExamDocument9 pagesArch2018 Maths GR 8 Final Examvutshilaashton52No ratings yet
- Budget of Work in Mathematics ViDocument5 pagesBudget of Work in Mathematics ViJose Rene IlisacNo ratings yet
- Maths Common NotesDocument150 pagesMaths Common NotesV.V.S.SathvikNo ratings yet
- PT Mathematics 5 q2 With TosDocument7 pagesPT Mathematics 5 q2 With TosMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- RPT MATHDocument6 pagesRPT MATHyunayuniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 - Q2 - PTDocument6 pagesMathematics 4 - Q2 - PTMarlon CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Tos - Math 4 - Q1Document5 pagesTos - Math 4 - Q1sherley mercadoNo ratings yet
- 4FryFourth100Set PDFDocument23 pages4FryFourth100Set PDFMAANN SHARLA BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Leveled Title ListDocument26 pagesLeveled Title ListMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Fryeighth 100 SetDocument23 pagesFryeighth 100 Setapi-279479190No ratings yet
- Frysecond100set PDFDocument23 pagesFrysecond100set PDFMustika PungutNo ratings yet
- Fry's Sixth 100 WordsDocument23 pagesFry's Sixth 100 WordsMAANN SHARLA BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Fry's Tenth 100 Words PDFDocument23 pagesFry's Tenth 100 Words PDFNorsanah Abdulmorid SolaimanNo ratings yet
- Fry's Fifth 100 Words PDFDocument23 pagesFry's Fifth 100 Words PDFCathynen Grace VegaNo ratings yet
- School Nurse EvaluatonDocument5 pagesSchool Nurse EvaluatonMkufunziNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument2 pagesDifferentiationMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Scope and SequenceDocument15 pagesScope and SequenceMkufunziNo ratings yet
- History Syllabus 1Document60 pagesHistory Syllabus 1MkufunziNo ratings yet
- Annual School Improvement Plan 2023Document14 pagesAnnual School Improvement Plan 2023MkufunziNo ratings yet
- Agenda - EADocument2 pagesAgenda - EAMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Updated 4TH Sept Timetable 2023Document10 pagesUpdated 4TH Sept Timetable 2023MkufunziNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Workshop MeetDocument1 pageDay 1 Workshop MeetMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Dean of Students OrganogramDocument1 pageDean of Students OrganogramMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and MineralsDocument57 pagesMicronutrients: Vitamins and MineralsMkufunziNo ratings yet
- End of Term ProgrammeDocument1 pageEnd of Term ProgrammeMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Schedule For Taking Staff Minutes January - April 2023Document1 pageSchedule For Taking Staff Minutes January - April 2023MkufunziNo ratings yet
- HOME SCIENCE - Form 1 - Term-IDocument8 pagesHOME SCIENCE - Form 1 - Term-IMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme 2016Document26 pagesMark Scheme 2016MkufunziNo ratings yet
- Blank Calendar LandscapeDocument1 pageBlank Calendar LandscapeMkufunziNo ratings yet
- Dorms Duty Rota - MKASS - Jan-March 2024-2Document2 pagesDorms Duty Rota - MKASS - Jan-March 2024-2MkufunziNo ratings yet
- 000 0648 - Scheme - of - Work - (For - Examination - From - 2020)Document76 pages000 0648 - Scheme - of - Work - (For - Examination - From - 2020)MkufunziNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Dimensional Analysis Similititude Modelling 1Document78 pagesTopic 4 Dimensional Analysis Similititude Modelling 1Riker SiNo ratings yet
- Heidelberg Intro Datasheet en 2016-05-14Document2 pagesHeidelberg Intro Datasheet en 2016-05-14johanes kharismaNo ratings yet
- IoT MCU Monitoring Using The AskSensors IoT PlatfoDocument8 pagesIoT MCU Monitoring Using The AskSensors IoT PlatfoAhmed MeddahNo ratings yet
- F.M.L. Thompson - The Cambridge Social History of Britain, 1750-1950, Vol. 01. Regions and CommunitiesDocument592 pagesF.M.L. Thompson - The Cambridge Social History of Britain, 1750-1950, Vol. 01. Regions and CommunitiesStevens DornNo ratings yet
- Class 2 - Parts of Speech PDFDocument10 pagesClass 2 - Parts of Speech PDFmahesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2007 Question PaperDocument8 pages9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2007 Question PapercheekybuoiNo ratings yet
- TardeTecnica Fevereiro2018 FricoDocument37 pagesTardeTecnica Fevereiro2018 FricoJoaquim MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Managing FP Side Effects and Complications: Prepared by Tsiyon. K Jimma Ethiopia JULY 2021Document59 pagesManaging FP Side Effects and Complications: Prepared by Tsiyon. K Jimma Ethiopia JULY 2021Yonas AbebeNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Orthodontic ProblemsDocument85 pagesEtiology of Orthodontic ProblemsShahid Hameed0% (1)
- Nectar Group 4 FinalDocument16 pagesNectar Group 4 FinalDevray ShankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13-pDocument9 pagesChapter 13-paravindkbNo ratings yet
- Functions in C - HackerRankDocument1 pageFunctions in C - HackerRankTeenie Weenie TitansNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Rev Asdaper TranslatingDocument7 pagesJurnal Rev Asdaper TranslatingIndra HedarNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - SuperelevationDocument24 pagesLec 1 - SuperelevationMohamedNo ratings yet
- Depp v. Heard CaseDocument6 pagesDepp v. Heard Casealve arantonNo ratings yet
- Lec 38drugs Used in AsthmaDocument19 pagesLec 38drugs Used in AsthmaAbdul MananNo ratings yet
- CRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument4 pagesCRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 1 - IntroductionMoke Fetane AmboNo ratings yet
- Test Equipment Price List - Issue 23Document4 pagesTest Equipment Price List - Issue 23Sundeer SunNo ratings yet