Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hopkins Power Standards For 2nd Grade Mathematics Standard Benchmark Number and Operations
Uploaded by
tae hyungOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hopkins Power Standards For 2nd Grade Mathematics Standard Benchmark Number and Operations
Uploaded by
tae hyungCopyright:
Available Formats
Hopkins Power Standards for 2nd grade mathematics
Standard Benchmark
Number and Operations
Compare and represent whole numbers up to 1000 2.1.1.1 Read, write and represent whole numbers up to 1000.
with an emphasis on place value and equality. Representations may include numerals, addition, subtraction,
multiplication, words, pictures, tally marks, number lines and
manipulatives, such as bundles of sticks and base 10 blocks.
2.1.1.2 Use place value to describe whole numbers between 10 and
1000 in terms of hundreds, tens and ones. Know that 100 is 10 tens,
and 1000 is 10 hundreds.
Demonstrate mastery of addition and subtraction 2.1.2.1 Use strategies to generate addition, subtraction and
basic facts; add and subtract one- and two-digit multiplication facts including making tens, fact families, doubles
numbers in real-world and mathematical problems. plus or minus one, counting on, counting back, and the
commutative and associative properties. Use the relationship
between addition and subtraction to generate basic facts. (H)
2.1.2.2 Demonstrate fluency with basic addition facts and related
subtraction facts to 18. (H)
Demonstrate fluency with multiplication facts involving 0’s, 1’s,
and 2’s. (H)
2.1.2.5 Solve real-world and mathematical addition and subtraction
problems involving whole numbers using 2-digit whole numbers.
(H)
Solve simple real-world multiplication and division problems. (H)
Algebra
Recognize, create, describe, and use patterns and 2.2.1.1 Understand how to interpret number sentences involving
rules to solve real-world and mathematical addition, subtraction and unknowns represented by letters. Use
problems. objects and number lines and create real-world situations to
represent number sentences.
Geometry and Measurement
Identify, describe and compare basic shapes 2.3.1.2 Identify and name basic two- and three-dimensional shapes,
according to their geometric attributes. such as squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, trapezoids, hexagons,
cubes, rectangular prisms, cones, cylinders and spheres.
Understand length as a measurable attribute; use 2.3.2.2 Demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between
tools to measure length. length and the numbers on a ruler by using a ruler to measure
lengths to the nearest centimeter or inch.
Use time and money in real-world and mathematical 2.3.3.1 Tell time to 5 minutes and distinguish between a.m. and
situations. p.m. (H)
2.3.3.2 Identify pennies, nickels, dimes and quarters. Find the value
of a group of coins and determine combinations of coins that equal
a given amount.
Draft 4/12/10
You might also like
- 1 18Document3 pages1 18Brittany Ann Moliver50% (6)
- Adding and Subtracting Integers Word Problems WorksheetDocument2 pagesAdding and Subtracting Integers Word Problems Worksheetapi-23888000860% (10)
- Finding Areas of Compound ShapesDocument2 pagesFinding Areas of Compound Shapestae hyung0% (1)
- Jinkun Liu - Intelligent Control Design and MatLab Simulation (2018, Springer)Document294 pagesJinkun Liu - Intelligent Control Design and MatLab Simulation (2018, Springer)snri0da9100% (1)
- 2nd Math OasDocument2 pages2nd Math Oasapi-411338120No ratings yet
- MN Elementary Math StandardsDocument9 pagesMN Elementary Math Standardsapi-322018148No ratings yet
- Mathematics StandardsDocument4 pagesMathematics Standardsapi-369625583No ratings yet
- Mathstandards2007 005247 Reposted 92815Document3 pagesMathstandards2007 005247 Reposted 92815api-369626876No ratings yet
- Whole Number OperationsDocument2 pagesWhole Number Operationsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Ma 2Document2 pagesMa 2api-335623629No ratings yet
- 2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionDocument27 pages2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionElaine EricksonNo ratings yet
- Arizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsDocument8 pagesArizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsJessie OrrettNo ratings yet
- Math and Learning 2020-21Document7 pagesMath and Learning 2020-21madeehaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 2 - Q2 - W6-9-26-22Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 2 - Q2 - W6-9-26-22Evelyn DEL ROSARIONo ratings yet
- SK TAMAN KLANG UTAMA YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICS (DUAL LANGUAGE PROGRAMME) KSSR YEAR 3 2019Document14 pagesSK TAMAN KLANG UTAMA YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICS (DUAL LANGUAGE PROGRAMME) KSSR YEAR 3 2019amybabynotNo ratings yet
- 2 NdgrademathcurriculummapDocument4 pages2 Ndgrademathcurriculummapapi-318489536No ratings yet
- Standard 4 TERM 1,2,3Document81 pagesStandard 4 TERM 1,2,3Candice NunesNo ratings yet
- SISD 1st Grade Math Curriculum CalendarDocument1 pageSISD 1st Grade Math Curriculum CalendarJosé Andrade GarcíaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 2 - Q2 - W6Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 2 - Q2 - W6Kaiser Vim Dollaga100% (1)
- SK AYER KEROH, MELAKA YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICS (DUAL LANGUAGE PROGRAMME) KSSR YEAR 3Document15 pagesSK AYER KEROH, MELAKA YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICS (DUAL LANGUAGE PROGRAMME) KSSR YEAR 3marina75% (4)
- 2 Nyc Scopeandsequence 5-130606Document3 pages2 Nyc Scopeandsequence 5-130606api-351301306No ratings yet
- Capitulo 1 Teks MiddleDocument13 pagesCapitulo 1 Teks MiddleFreddy Reyes FalckNo ratings yet
- Numbers and Operations Topics: Whole Numbers, Odd/Even, EstimationDocument18 pagesNumbers and Operations Topics: Whole Numbers, Odd/Even, EstimationSumathi RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Grade Three Math IndicatorsDocument46 pagesGrade Three Math IndicatorsNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Mathstandards k-1Document4 pagesMathstandards k-1api-369643865No ratings yet
- Maths - End of Year 5 Expectations New National Curriculum ObjectivesDocument2 pagesMaths - End of Year 5 Expectations New National Curriculum ObjectivesShaminaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Yearly Plan Y4Document14 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan Y4skppasirNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 2)Document5 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 2)cikgu F100% (1)
- RPT Math DLP Year 2 2022-2023Document15 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 2 2022-2023puva nesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 3)Document8 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 3)cikgu F50% (2)
- Whole Numbers, Money, Time, and LengthDocument3 pagesWhole Numbers, Money, Time, and LengthkelinahNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learning Competences ReferencesDocument4 pagesLessons Learning Competences ReferencesMA. LOWELLA BACOLANDONo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Maths 4sklpDocument8 pagesYearly Plan Maths 4sklpAfifa SafferNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 6 2023Document13 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 6 2023Ani HaniNo ratings yet
- GRADE 2 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus) - EnglishDocument116 pagesGRADE 2 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus) - EnglishnoviNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 MathDocument8 pagesYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 MathNAJIB MIRZANo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Mathematics Standards and Learning OutcomesDocument132 pagesGrade 1 Mathematics Standards and Learning OutcomesGrade Five- Blessed Christine of the Holy CrossNo ratings yet
- KSSM Form 1 Yearly Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesKSSM Form 1 Yearly Lesson PlandinNo ratings yet
- Maths S&S and Unit Plans Term 2Document27 pagesMaths S&S and Unit Plans Term 2Mahnoor RamshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Learning OutcomesDocument55 pagesGrade 9 - Learning OutcomesMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- First Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence MathDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence Mathapi-234156613No ratings yet
- Everyday Math GoalsDocument4 pagesEveryday Math Goalsapi-441762465No ratings yet
- Year 5 Math ObjectivesDocument2 pagesYear 5 Math ObjectivesApp BountyNo ratings yet
- RPT MATEMATIK DLP TAHUN 4Document20 pagesRPT MATEMATIK DLP TAHUN 4SARANYA A/P KALIAPPAN MoeNo ratings yet
- RPT 2020 Mathematics Year 4 KSSR SemakanDocument13 pagesRPT 2020 Mathematics Year 4 KSSR SemakanThulasi VasiNo ratings yet
- Year 4 MathsDocument21 pagesYear 4 MathsZul ZachNo ratings yet
- Commoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDDocument1 pageCommoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDapi-288064681No ratings yet
- Arizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsDocument8 pagesArizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsChino GarciaNo ratings yet
- Paper Pattern & Syllabus - GR 9 Final AssessmentDocument8 pagesPaper Pattern & Syllabus - GR 9 Final AssessmentUmmul BaneenNo ratings yet
- PYPMath Phase Map Y1Document5 pagesPYPMath Phase Map Y1UNICOSMOS Grade1No ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 2 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyDocument16 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 2 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyrphsekolahrendahNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 2020Document8 pagesYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 2020Noorleha Manan100% (3)
- Maths MTP Term 2 Final 3Document2 pagesMaths MTP Term 2 Final 3api-399175357No ratings yet
- RPT Mate DLP THN 3 2022-2023Document22 pagesRPT Mate DLP THN 3 2022-2023rashiden denNo ratings yet
- SMK Sunga Mathematics Form One Yearly Lesson Plan 2021Document17 pagesSMK Sunga Mathematics Form One Yearly Lesson Plan 2021Caroline JetanNo ratings yet
- MATHfourth Aldine ISDDocument10 pagesMATHfourth Aldine ISDFreddy Reyes FalckNo ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade2Document16 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade2Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Activity 4-Table of SpecificationDocument2 pagesActivity 4-Table of SpecificationEuniceNo ratings yet
- School Name: .......... School Address: . Teacher'S NameDocument13 pagesSchool Name: .......... School Address: . Teacher'S NameRAJA A/L POOBALAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map MATH 2 Edited PRINTED 1-4Document31 pagesCurriculum Map MATH 2 Edited PRINTED 1-4Jo MeiNo ratings yet
- GR 3 Term 4 English Maths Programme of AssessmentDocument3 pagesGR 3 Term 4 English Maths Programme of AssessmentMeddie Ya KatlegoNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Worksheet IVDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Math Worksheet IVtae hyungNo ratings yet
- Parallelogram HomeworkDocument2 pagesParallelogram Homeworktae hyungNo ratings yet
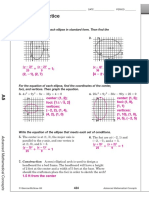
- Finding Quadratic Equations from Vertex & X-InterceptsDocument3 pagesFinding Quadratic Equations from Vertex & X-Interceptstae hyungNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Similar Triangle ApplicationsDocument12 pages6.5 Similar Triangle Applicationstae hyungNo ratings yet
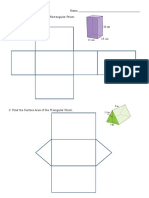
- Finding Surface Area With Nets CN and HDocument6 pagesFinding Surface Area With Nets CN and Htae hyungNo ratings yet
- 0688 Introduction To Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument39 pages0688 Introduction To Trigonometric Functions PDFkatia mariaNo ratings yet
- File Parallelogram Properties Worksheet 1 1620902105Document5 pagesFile Parallelogram Properties Worksheet 1 1620902105tae hyungNo ratings yet
- M-7-5-3 - Small Group Practice and KEYDocument5 pagesM-7-5-3 - Small Group Practice and KEYtae hyungNo ratings yet
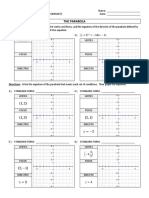
- Conic Sections - Parabolas WorksheetDocument2 pagesConic Sections - Parabolas Worksheettae hyungNo ratings yet
- Properties: Ab CD EF CD EF ABDocument4 pagesProperties: Ab CD EF CD EF ABtae hyungNo ratings yet
- 10.3 KeyDocument1 page10.3 Keytae hyungNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Math 9Document3 pages1st Periodic Test - Math 9Joy TanaleonNo ratings yet
- 1 - Q2 Bus MathDocument18 pages1 - Q2 Bus Mathtae hyungNo ratings yet
- Identify Proportional Relationships From GraphsDocument2 pagesIdentify Proportional Relationships From Graphstae hyungNo ratings yet
- Circles Conic Sections WorksheetDocument1 pageCircles Conic Sections Worksheettae hyungNo ratings yet
- Math Hs Reason EquationsDocument86 pagesMath Hs Reason Equationstae hyungNo ratings yet
- Module 03Document24 pagesModule 03tae hyungNo ratings yet
- Identify Proportional Relationships From TablesDocument2 pagesIdentify Proportional Relationships From Tablestae hyungNo ratings yet
- PressedDocument16 pagesPressedtae hyungNo ratings yet
- Identify The Constant of Proportionality From A GraphDocument2 pagesIdentify The Constant of Proportionality From A Graphtae hyung100% (1)
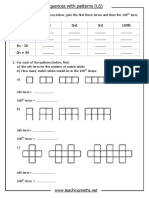
- Sequences With PatternsDocument1 pageSequences With Patternstae hyungNo ratings yet
- Complete These Sequences Fill in The GapsDocument1 pageComplete These Sequences Fill in The Gapstae hyungNo ratings yet
- Day 7 Properties and Matching Graphs PDFDocument3 pagesDay 7 Properties and Matching Graphs PDFMarivic LabuacNo ratings yet
- Working Out The Rule Dominos - Two AbilitiesDocument2 pagesWorking Out The Rule Dominos - Two Abilitiestae hyungNo ratings yet
- 4 Sequences AssessmentDocument1 page4 Sequences Assessmenttae hyungNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1Document23 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1tae hyungNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 13 Using Inductive or Deductive Reasoning in An ArgumentDocument19 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 13 Using Inductive or Deductive Reasoning in An Argumenttae hyungNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3Document25 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3Arnold A. Baladjay100% (3)
- WErbsen CourseworkDocument562 pagesWErbsen CourseworkRoberto Alexis Rodríguez TorresNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 2020Document32 pagesMathematics P2 2020uzilebanda30No ratings yet
- C. V. Raman: Albert EinsteinDocument3 pagesC. V. Raman: Albert EinsteinsatNo ratings yet
- Physics 72 EEE RecitationDocument2 pagesPhysics 72 EEE RecitationRalph EvidenteNo ratings yet
- Hive PPTDocument25 pagesHive PPTDavid JosephNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 7 : Line with inclined FV, HT and VTDocument4 pagesPROBLEM 7 : Line with inclined FV, HT and VTnishant dhimanNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Course OutlineDocument3 pagesData Mining Course Outlinevigneshwari_14985No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Mathematics Revision W/S - 2019-20 Fractions and Decimals ClassviiDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North Mathematics Revision W/S - 2019-20 Fractions and Decimals ClassviiVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Codes and CiphersDocument9 pagesCodes and CiphersMilk BrotherNo ratings yet
- QUANTIFIRESDocument3 pagesQUANTIFIRESEsther Martínez HerraizNo ratings yet
- Bio-Data (DR.P.K.sharMA) As On 13th June 2023Document34 pagesBio-Data (DR.P.K.sharMA) As On 13th June 2023Poonam Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Report Mat652 - 2021171741 - 2021119563Document6 pagesReport Mat652 - 2021171741 - 2021119563NUR DINI HUDANo ratings yet
- Excel Lab ExerciseDocument26 pagesExcel Lab ExerciseShrawan KumarNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument83 pagesDiffusionmohamedNo ratings yet
- Applying analytics to improve supply chain managementDocument1 pageApplying analytics to improve supply chain managementTushar PrasadNo ratings yet
- Practica 11 - Pascal LawDocument6 pagesPractica 11 - Pascal LawjuanNo ratings yet
- Entropy Measures For Plithogenic Sets and Applications in Multi-Attribute Decision MakingDocument17 pagesEntropy Measures For Plithogenic Sets and Applications in Multi-Attribute Decision MakingScience DirectNo ratings yet
- AFAQ SCIENCE SCHOOL AND COLLEGE SHAKARDARA MID TERM EXAM PAPERDocument3 pagesAFAQ SCIENCE SCHOOL AND COLLEGE SHAKARDARA MID TERM EXAM PAPERMuhammad Adil HussainNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Practice Papers 2Document13 pagesMechanics Practice Papers 2Sarvesh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Sop NilayDocument1 pageSop NilayNilayThakorNo ratings yet
- The Quantum Theory ofDocument121 pagesThe Quantum Theory ofBarata PrawiranegaraNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument38 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitsRamanjaneyulu Anji YadavNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Books OnlineDocument14 pagesCambridge Books OnlineAnonymous fVtXn0JfgsNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure Interaction (Ssi)Document16 pagesSoil Structure Interaction (Ssi)Asif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and DielectricsDocument22 pagesCapacitors and DielectricsVishal_93No ratings yet
- 0108-Staad - Pro 2006 Section Wizard Manual and Tutorial by Research Engineers InternationalDocument52 pages0108-Staad - Pro 2006 Section Wizard Manual and Tutorial by Research Engineers InternationalJule LobresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 20201030 (KBAT Question)Document3 pagesTutorial 20201030 (KBAT Question)jasonNo ratings yet
- The Biological Basis of Human LanguageDocument33 pagesThe Biological Basis of Human LanguagehalersNo ratings yet