Professional Documents
Culture Documents
As (Complete) Formua Sheet
Uploaded by
AyeshaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
As (Complete) Formua Sheet
Uploaded by
AyeshaCopyright:
Available Formats
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
(UNIT &Physical Quantities ) Seven S.I Base quantities and units Chapter#1
Quantity Unit Symbol
Mass kilogram Kg
Distance Meter m
Time Second s
Current ampere A
Temperature Kelvin K
Amount mole mol
Light Intensity Candela Cd
Derived quantites with their base units
Quantity Unit base unit
Velocity meter / second m/s
Acceleration meter / squared second m/s2
Force newton(N) kg·m / s2
Pressure pascal(Pa) kg·m-1 s-2
Energy joule(J) kg⋅m2⋅s−2
Voltage volt(V) kg⋅m2⋅s−3⋅A−1
Power watt(W) kg⋅m2⋅s−3
Resistance ohm(Ω) kg⋅m2⋅s−3⋅A−2
Mathematical Prefixes
Name Symbol Scaling factor
Tera T 1012
Giga G 109
Mega M 106
Kilo k 103
Deci d 10-1
Centi c 10-2
Milli m 10-3
Micro µ 10-6
Nano n 10-9
Pico p 10-12
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
(Measurments) Chapter#2
Quantity Accuracy Instrument
1 cm Tape
Length 0.1 cm Ruler
0.01 cm Vernier caliper
0.001 cm Micrometer screw
gauge
1 cm3 Measuring cylinder
Volume 0.05 cm3 Pipette/burette
0.5o Protractor
Angle
1 min Clocks
Time 1.01 sec Stopwatch
1.02 x-axis scale Time base of c.r.o
o
1C Thermometer
o
Temperature 0.5 C Thermocouple
P.d. 0.01 V Voltmeter
0.01 A Ammeter
Current 0.000 Galvanometer
1A
Uncertainty calculations
Absolute, fractional and percentage uncertainty
We use ± to show an error in measurement
Assume we measure something to be (208 ± 1.0) mm in length...
1.0 mm is the absolute uncertainty
1/208 is the fractional uncertainty(0.0048)
0.48 % is the relative (percent)
uncertainty Combiningun certainties
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Rules To determine the uncertainty of a calculated value...
For addition and subtraction, add absolute uncertainties If U=X+Y then δU=δX + δY
If U =X-Y then δU=δX + δY
For multiplication and division add fractional uncertainties Similarly if
U=XY then δu/u = δx/x +δY/Y
Similarly if U=X/Y δu/u = δx/x +δY/Y
When using exponents, multiply the fractional uncertainty by the exponent
Similarly if U=Xn then δu/u=n δx/x
Rules for Uncertainty
Adding andSubtracting
add the absolute uncertainties e.g. (20.5 ± 0.1 cm) +( 7.2 ±0.2cm) = 27.7 ±0.3cm
Multiplying and Dividing
add the percentage uncertainty e.g. (3.2±3%) × (2.4 ±1%) = 7.7 ±4% = 7.7 ±0.3
Exponents
multiply the percentage uncertainty by the
exponente.g. (5.0 ±2%)3 = 125.0 ±6% = 125.0±7.5
Multiplying or dividing by a constant
multiply or divide the uncertainty by the constante.g.
10T = 18.2 ±0.3s; T = 1.82 ±0.03s
Multiplying or dividing by a constant does not change
The percentage uncertainty e.g.
6× 5.0 ±2% = 30.0 ±2%
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
(Kinematics)
Chapter # 3
For uniform motion of a body in a straight line with uniform acceleration
V= u+at
S = ut+1/2at2
v2 = u2 +2as
Vav = (u+v)/2 (Only for uniform velocity)
Vav = total displacement/total time( For any type of motion)
Projectile motion:
Summary of formulas:
Horizontal distance: Vertical distance:
dx = vx. t dy = ut +1/2gt2
Horizontal speed: Vertical Speed:
Vx=vcosθ vy=vsinθ
or
dx= vcosθ. t
Height of projectile:
H=u2sinθ2/2g
Time of flight:
T= 2usinθ/g( Time of flight)
T= usinθ/g( Time for maximum height)
Range of projectile:
R = u2sin2θ/g
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Dynamics Chapter #4
Force is the rate of change in momentum
F= ma =m(v-u)/t
Impulse= change in momentum = ∆P = Fxt
Collisions
m1u1+m2u2=m1v1+m2v2 When 2 objects collide and DON’T stick
m1u1+m2u2 =(m1+m2)v When 2 objects collide and stick together
mtotal utotal=m1v1+m2v2 When 1 object breaks into 2objects
Relative speed before collision = relative speed after collision
u1 -u2 = v2 –v1
For elastic collision
Momentum before Collision = Momentum after Collision
m1u1+m2u2=m1v1+m2v2
Kinetic energy before collision = kinetic energy after collision
1/2m1u12 + 1/2m2u22 = 1/2m1v12 +1/2m2v22
For inelastic collision
Kinetic energy beforecollision ≠ kinetic energy aftercollision
1/2m1u12+1/2m2u22 ≠ 1/2m1v12 +1/2m2v22
Momentum Momentum in one Dimension Momentum in 2-Dimension
P =mxv m1u1+m2u2=m1v1+m2v2
∆P = mv– mu (Same direction) m1u1+m2u2 =(m1+m2)v
∆P =mv + mu (Opposit direction) mtotal utotal=m1v1+m2v2
F = ∆P/t u1 -u2 = v2 –v1
In the x direction:
F = Density x Area x (Speed)2 1/2m1u12 + 1/2m2u22 = 1/2m1v12 +1/2m2v22 m1v1i = m1v1f cosθ + m2v2f cosφ
In the y direction:
0 = m1v1f sinθ - m2v2f sinφ
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Forces & vectors Chapter #5
Force on an Inclined Plane
mgsinϴ is the component of the weight pulling the mass down the ramp.
F = ma = mg sinθ , a = g sinθ
𝑚𝑔 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃−𝐹𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
F = ma = mg sinθ – Friction , 𝑎 𝑚
Horizontal Pulley Vertical pulley
The net force acting on the body A
Fnet = m1g – T , m1a = m1g – T ----(i)
The net force acting on the body B For m2
Fnet = T , m2a = T -------(ii) Fnet = W2 –T , m2a = m2g – T
By Solving eq (i) and (ii)
T = m2g – m2a
For m1
a Fnet = T-W , m1a = m1g – T
T = m1g – m1a
Resolving of Forces Horizontal component of forces
Vertical component of forces
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Moment Chapter # 6
Moment = force x displacement
Moment = FdSinɵ
Principle of Moment
Clockwise moment = Anticlock wise Moment
F1xd1 = F2xd2
Torque of a Couple
Conditions for equilibrium of a system
There are two conditions:
The sum of all moments equals = 0
The sum of all forces equals = 0
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
WORK, Energy, Power Chapter # 7
WORK:
Work = Force x displacement = F x d
Work = f.dCosɵ
Work done = ΔK = Change in kinetic energy = 1/2mv2 – 1/2mu2
Work done = P x ∆V = P x(V2 – V1)
Energy:
Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Elastic Store Energy
K.E = 1/2mv2 P.E = mgh Es = 1/2Kx2
Gases: k.e >p.e. K.E + P.E = ET
Liquids: k .e . ≈ p .e ∆K + ∆U = 0
Solids: k. e. < p.e. ∆K = -∆U
.
Effeciency = Energy output / Energy input
Power:
Power = workdone /time , P =W/t
Power =Force x velocity , power =F.V
Effeciency = Power out put / power input
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Pressure
Chapter#8
Pressure = Force/Area , P = F /A
Variation of pressure with depth , P = ρgh
Total Pressure
PT = Pa +ρgh, where Pa is atmospheric pressure
Up thrust = (P2-P1)A = ΔP.A = ρgh.A Since(A.h=Volume)
Up thrust = Vρg
Archimedes’ principal
For an object floating on liquid: weight = up thrust
F1/A1 = F2/A2
Total pressure of Manometer
Gas Pressure = Atmospheric Pressure + ρgh
Density:
Density = Mass / Volume , ρ = M/V
Alloys – a solid mixture of two or more metals
Mass of Alloy = ρAVA+ρBVB
Density of Alloy = ρAVA+ΡBVB / VTotal
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Deformation of solid Chapter#9
Hook’s Law: F = K.x
Springs in series and parallel Combinations:
Spring in Series combination Spring in Parallel combination
Total Extension XT = X1 + X2 Total Extension 1/ XT = 1/X1 + 1/ X2
Total Spring Constant 1/KT = 1/k1 + 1/k2 Total Spring Constant KT = k1 + k2
Extension: X X/2 2X 3X/2
Spring Constant: K 2K K/2 2K/3
Stress = force/area , σ = F/A
Strain = Change in length / original length , Strain = ∆L/L
Young Modulu’s = Stress/Strain , E = F/A x ∆L/L
Energy Stored = 1/2F.X = 1/2KX2
Energy Density = ½ Stress x Strain
Force & Extension Graph Stress & Strain Graph
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Electric field Chapter#10
Electric field strength is the force per unit charge , E = F/Q
The Electric field strength is given by , E = V/d
The potential difference is the work done per unit charge
P.D = Work/ Charge , V = W/Q
The kinetic energy of an electron having charge e, accelerated through a
potential difference V is
1/2mv2 = V.Q
An Electron –volt (ev) is the energy gained by an electron when it is being
accelerated through a potential difference of one electron.
1ev =1.6 x10-19J
Fundamental unit of charge, e = 1.6 x10-19C
An electron has charge –e and a proton has charge of +e
Work done = VxQ
Fxd = V x Q , mgxd = Vx Q
V/d = F/Q
F = QxV/d
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Current & Electricity
Chapter #11
Current = Charge/Time , I = Q/T
Current due to n’ no charge of particles: I = nq/t
Total current: I t = I + + I- , Total current = 2nQ/t
Drift speed: I = nAVQ so V = I/nAQ
Potential = work/ charge E.m.f = work/ charge
V = W/Q E.m.f = W/Q
Ohm’s Law: V = IR
𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝑅
Potential Divder: Vout = 𝑅 𝑅
Potential Divder: V1/V2 = R1/R2
Power
Input Power Power dissipated Power dissipated
P = V.I P= V2/R P = I2R
Effeciency = Poutput /powerinput
𝑃𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝐼 𝑅 𝑅
𝐸𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 (𝑛) ×1 %
𝑃𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 I (𝑅 𝑟) 𝑅 𝑟
Resistance =
Internal Resistance – the loss of potential difference per unit current in the source, when current
passes through the sourc
E.M.F(E) = IR + Ir
Kirchhoff’s Law:
1st Law
Current coming towards junction = Current away from junction
2nd Law
E.M.F = Sum of the Potential difference
E = V1 + V2 +V3
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
WAVES
Chapter#12
Speed, v = λ / T = (1 / T)λ = fλ
Intensity = Power/Area
Intensity α(amplitude)2.
Intensity α1/(Distance)2
Intensity α(Frequency)2
Phase Difference (ɸ):
for two sources that are IN PHASE:
if the P.D = nλ, where n = 0,1,2,3……then waves INTERFERE CONSTRUCTIVELY.
if the P.D = (n+ 1 /2)λ, where n = 0,1,2,3……then waves INTERFERE DESTRUCTIVELY
Equation relating x, λ,D, a:
Diffraction Grating d =1/N N= No of diffraction lines per mm
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Stationary Waveforms on a String
Stationary Waveforms in a Close Air Columns
Stationary Waveforms in an Open Air Columns
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Fundamental frequency for stretched strings:
Fundamental frequency for close pipes:
Fundamental frequency for open pipes:
The Doppler’s Equation
fo = fsv/v+vs (When source move away from observer)
fo = fsv/v-vs (When source move towards observer)
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Nuclear and Partical Physics
Chapter # 13,14
Alpha Decay:
Beta negative Decay :
Beta Positive Decay:
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
SALT
ACADEMY
AS LEVEL COMPLETE UPGRADED SYLLABUS FORMULA SHEET
Beta positive and negative decay
A-Level Physics with IRFAN YASIR 0300-6045447
You might also like
- Physics Manual Notes For CSEC and CAPEDocument114 pagesPhysics Manual Notes For CSEC and CAPEConnor England100% (1)
- EASA - Mechanical Repair FundamentalsDocument227 pagesEASA - Mechanical Repair Fundamentalsandres monedero100% (2)
- Physics Notes Section ADocument10 pagesPhysics Notes Section Astreaks1018100% (4)
- Every Second One in The World Drives Automatic!Document54 pagesEvery Second One in The World Drives Automatic!Kovács EndreNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningFrom EverandHandbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Units and Conversions PDFDocument33 pagesUnits and Conversions PDFiayamaeNo ratings yet
- SI Unit Conversion TableDocument4 pagesSI Unit Conversion TableGhazali ZuberiNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurements (3 Hours)Document55 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurements (3 Hours)Ahmad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsDocument49 pages1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsPunitha MarimuthooNo ratings yet
- Caie As Level: PHYSICS (9702)Document19 pagesCaie As Level: PHYSICS (9702)Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide BookDocument25 pagesPractical Guide BookEremu ThomasNo ratings yet
- Notes On Measurements1Document9 pagesNotes On Measurements1tmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Olevel Physics Revised Edition 2016Document426 pagesOlevel Physics Revised Edition 2016rasheedlukman9No ratings yet
- Membaca Skala Ukur Instrumen Lokal: Reading of Local Scale Measure InstrumentsDocument70 pagesMembaca Skala Ukur Instrumen Lokal: Reading of Local Scale Measure InstrumentsRirin WidianitaNo ratings yet
- 1 UHl 1 Z7 Xcov 77 Oag 5 HR7 Mi MLM 02 o 3 K5 KDocument140 pages1 UHl 1 Z7 Xcov 77 Oag 5 HR7 Mi MLM 02 o 3 K5 KSai AmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GamalDocument51 pagesChapter 1 Gamalkagwesamtulia372No ratings yet
- Combine ModuleDocument97 pagesCombine ModuleleahNo ratings yet
- Phy NotesDocument222 pagesPhy NotesNunu KheesNo ratings yet
- FSK 2024 Practical Manual StudentsDocument64 pagesFSK 2024 Practical Manual Studentsnapnom22No ratings yet
- Phy NotesDocument232 pagesPhy NotesTshegofatso LegadikoNo ratings yet
- International System of UnitsDocument2 pagesInternational System of UnitsHerbert Quinto SolisNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document28 pagesCH 1DanielNo ratings yet
- 2016 Bookmatter ThePhysicsOfLivingSystemsDocument11 pages2016 Bookmatter ThePhysicsOfLivingSystemsRihem and Soundosse wordsNo ratings yet
- Jhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1Document308 pagesJhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1Thoko SimbeyeNo ratings yet
- SI Units RulesDocument13 pagesSI Units RulesKarthikeyan GNo ratings yet
- Cie As Physics 9702 Theory v1Document18 pagesCie As Physics 9702 Theory v1Fasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Easurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: IDocument28 pagesEasurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: Ipankaj baviskarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Physical Quantities, Units & Dimensions 1.1 Physical QuantitiesDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Physical Quantities, Units & Dimensions 1.1 Physical QuantitiesAAAANo ratings yet
- Meaurement and Physical Quantities SPDocument14 pagesMeaurement and Physical Quantities SPsurabhiNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Prefixes and Numerical Values For SI Units Prefix Symbol Value ExampleDocument4 pagesCommonly Used Prefixes and Numerical Values For SI Units Prefix Symbol Value ExampleJilliane PascualNo ratings yet
- Units of Measurement ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnits of Measurement ObjectivesErienne IbanezNo ratings yet
- Unut Conversion 1Document1 pageUnut Conversion 1Vincent SangNo ratings yet
- Complete Mechanics o Level Notes 2023-24 SyllabusDocument19 pagesComplete Mechanics o Level Notes 2023-24 SyllabusAbsar KhaskheliNo ratings yet
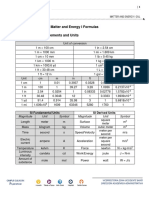
- Topic 2. Measurements and Units: Matter and Energy I FormulasDocument5 pagesTopic 2. Measurements and Units: Matter and Energy I FormulasGaelNo ratings yet
- Banner Data Tables PDFDocument11 pagesBanner Data Tables PDFpotNo ratings yet
- Physics Science (Lecture ExportDocument55 pagesPhysics Science (Lecture ExportSATYAM RATHOURNo ratings yet
- M2 ExperimentDocument13 pagesM2 ExperimenterickhadinataNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics Manual - 074634Document114 pagesCSEC Physics Manual - 074634Reyugi AisukaNo ratings yet
- The International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesThe International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsSamir ZaghloolNo ratings yet
- 1.1 & 1.3 Length & Time - Mass & Weight 2Document9 pages1.1 & 1.3 Length & Time - Mass & Weight 2Haniya NadeemNo ratings yet
- Holt 2210Document159 pagesHolt 2210Masoud AliNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditDocument19 pagesFundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditMohamad Radhahudin100% (1)
- 11 TH ExptsDocument5 pages11 TH ExptsViomnath SadatcharamourthyNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT-ForcedvibrationsDocument9 pagesLAB REPORT-Forcedvibrationsمصطفى سعيد سعد برغوث 201810526No ratings yet
- Physics Notes Form 5Document221 pagesPhysics Notes Form 5tonikay219No ratings yet
- 1.0 - Measurement 2020Document18 pages1.0 - Measurement 2020xw5xNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine LabDocument2 pagesFrancis Turbine LabLurking RogueNo ratings yet
- SSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessDocument6 pagesSSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessSubhajit DasNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFDocument6 pagesPhysical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFARAVINDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes: Physical Quantities, Units & MeasurementDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Notes: Physical Quantities, Units & MeasurementterrygohNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: SI Units: Rules About Writing UnitsDocument3 pagesAppendix A: SI Units: Rules About Writing UnitsLuis SanchezNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurmentsDocument6 pagesUnits and MeasurmentsShiva Sankar BeharaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudentDocument38 pagesChapter 1 StudentM HisyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ScienceBrandon LawNo ratings yet
- 1 - Physical Quantities & UnitsDocument9 pages1 - Physical Quantities & UnitsKaem ViottoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios: Ingeniería en PetroquímicaDocument7 pagesEjercicios: Ingeniería en PetroquímicaDiego FernandoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: Phys IDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction: Phys INiel A.No ratings yet
- Unit Conversion Tip Sheet v3.3 2016Document1 pageUnit Conversion Tip Sheet v3.3 2016McbeenNo ratings yet
- ASME Secc II D Si UnitsDocument3 pagesASME Secc II D Si UnitsCARLOS MARIONo ratings yet
- V. Dimensions and Units For Physical Quantities Mechanical UnitsDocument4 pagesV. Dimensions and Units For Physical Quantities Mechanical UnitsLei TolentinoNo ratings yet
- 99b SI UnitsDocument2 pages99b SI UnitscubanninjaNo ratings yet
- Fire Suppression Valve Series B0480 B04801218Document1 pageFire Suppression Valve Series B0480 B04801218Muhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- RDG405KN Room Thermostats With KNX CommunicationsDocument14 pagesRDG405KN Room Thermostats With KNX Communicationsdiogenes2012No ratings yet
- Power Prediction of A 15000 TEU Containership DeepDocument14 pagesPower Prediction of A 15000 TEU Containership DeepmhxdeeixfzfuaattrzNo ratings yet
- SAHIL ACHARYA (Water Wheel) - EnergyConversion - AsdDocument3 pagesSAHIL ACHARYA (Water Wheel) - EnergyConversion - AsdSahil AcharyaNo ratings yet
- AP Env Sci Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP Env Sci Cram Chart 2021高瑞韩No ratings yet
- Oeitker Swing Coupling Training BinderDocument66 pagesOeitker Swing Coupling Training BinderRubén César GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- High Flow NAMUR Valve G1/4" & G1/2": For Control of Pneumatic ActuatorsDocument20 pagesHigh Flow NAMUR Valve G1/4" & G1/2": For Control of Pneumatic ActuatorsIon FloareaNo ratings yet
- Sa-Csir, Sa-Cscr: Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument16 pagesSa-Csir, Sa-Cscr: Installation and Operating Instructionssushant moreyNo ratings yet
- FRB-8A New Model Service Training - 2 (Meter)Document57 pagesFRB-8A New Model Service Training - 2 (Meter)Pyae Phyoe AungNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineeringmohammadtaha labuanNo ratings yet
- PQT Chapter 2 - Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument25 pagesPQT Chapter 2 - Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingNguyễn Việt TiếnNo ratings yet
- Fe Review Fall 9232020 LecturewithannotationsDocument56 pagesFe Review Fall 9232020 Lecturewithannotationsfem mece3381No ratings yet
- Motores Ie3Document150 pagesMotores Ie3Pablo Andres Espin MartinNo ratings yet
- Ahu 9Document11 pagesAhu 9api-668834399No ratings yet
- (Worksheet) Paano Sasagipin Ang Mundo TranslationDocument2 pages(Worksheet) Paano Sasagipin Ang Mundo TranslationmorganNo ratings yet
- 06-fc1663 Catalyst Inlet Temperature Sensor Swapped With Outlet - Condition Exists.Document3 pages06-fc1663 Catalyst Inlet Temperature Sensor Swapped With Outlet - Condition Exists.SuryadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Chapter - ElectricityDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Chapter - Electricitykrish.meenaaaNo ratings yet
- Ns2-Dvn-2405 r7 Final PL of Misc BLR SH Spray Water System-Unit1-20200526Document33 pagesNs2-Dvn-2405 r7 Final PL of Misc BLR SH Spray Water System-Unit1-20200526PHAM PHI HUNGNo ratings yet
- Atys G M 4p Quick Start Guide 2018-12-542932 D enDocument2 pagesAtys G M 4p Quick Start Guide 2018-12-542932 D enfosterNo ratings yet
- MAN-Trouble Codes - EDC7 - 3737 A 3996Document22 pagesMAN-Trouble Codes - EDC7 - 3737 A 3996GastaoNo ratings yet
- Ifeolwapo: MoladeDocument6 pagesIfeolwapo: MoladeIfe KoladeNo ratings yet
- Battisti 2020Document31 pagesBattisti 2020soham kawaleNo ratings yet
- CV Dya Kurnelasari (Engineer - QS)Document4 pagesCV Dya Kurnelasari (Engineer - QS)rici kurniawanNo ratings yet
- E03-014 - Course DocumentDocument21 pagesE03-014 - Course DocumentFady MegalaNo ratings yet
- TC909A and B, TC910N and R, TC941A: Eclipse™ Series Intelligent ModulesDocument2 pagesTC909A and B, TC910N and R, TC941A: Eclipse™ Series Intelligent ModulessureshNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Webinar 12-01-2020Document44 pagesSustainability Webinar 12-01-2020prochemNo ratings yet
- VIP05.Displacement Vent PDFDocument8 pagesVIP05.Displacement Vent PDFSomaye KarimiNo ratings yet
- Deployable Oxygen Generation System (DOGS-M)Document1 pageDeployable Oxygen Generation System (DOGS-M)MIGUEL RONALDO RONCEROS AGÜERONo ratings yet