Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Condition
Uploaded by
one engOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Condition
Uploaded by
one engCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction: Heating and cooling systems play a crucial role in maintaining
comfortable indoor environments, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
Among these systems, air conditioning stands out as a cornerstone technology for
cooling indoor spaces, providing relief from heat stress and improving overall comfort
levels. This report aims to delve into various aspects of heating and cooling systems,
with a particular emphasis on air conditioning technology.
1. Overview of Heating and Cooling Systems: Heating and cooling systems are
designed to regulate indoor temperatures, ensuring thermal comfort for occupants.
These systems encompass a wide range of technologies, including furnaces, boilers, heat
pumps, and air conditioning units. They operate based on principles of heat transfer,
utilizing different mechanisms to either generate or remove heat as required.
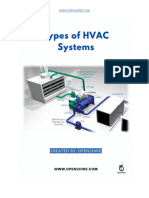
2. Types of Air Conditioning Systems: Air conditioning systems come in various types,
each suited to different applications and environments:
Central Air Conditioning: This type of system utilizes ductwork to distribute
cooled air throughout a building. It's commonly used in larger residential and
commercial buildings.
Split Air Conditioning: Split systems have components both inside and outside
the building. They're versatile and can be used for individual rooms or zones.
Window Air Conditioning: These units are self-contained and installed directly
in windows or through walls. They're typically used for cooling individual rooms
or small spaces.
Portable Air Conditioning: Portable units are versatile and can be moved from
room to room. They're suitable for temporary cooling or spaces where
permanent installation is impractical.
3. Working Principles of Air Conditioning: Air conditioning systems operate on the
principles of refrigeration, which involve the transfer of heat from one area to another.
The basic components of an air conditioning system include a compressor, condenser,
expansion valve, and evaporator. Refrigerant circulates through these components,
undergoing phase changes to absorb heat from indoor air and release it outdoors,
thereby cooling the indoor environment.
4. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact: Energy efficiency is a significant
consideration in the design and operation of air conditioning systems. Energy-efficient
models incorporate advanced technologies such as variable-speed compressors,
programmable thermostats, and smart controls to optimize performance and reduce
energy consumption. Additionally, the choice of refrigerants is crucial, with a shift
towards environmentally friendly alternatives such as hydrofluorocarbon (HFC)-free
refrigerants to mitigate the environmental impact of air conditioning systems.
5. Innovations and Future Trends: The air conditioning industry continues to innovate,
driven by advancements in technology and growing concerns about energy
consumption and environmental sustainability. Some notable trends and innovations
include:
Development of next-generation refrigerants with low global warming potential
(GWP) and zero ozone depletion potential (ODP).
Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies for remote monitoring,
control, and predictive maintenance of air conditioning systems.
Adoption of heat pump technology for both heating and cooling purposes,
offering greater efficiency and versatility.
Exploration of alternative cooling methods such as evaporative cooling and
radiant cooling for specific applications and climates.
Conclusion: Air conditioning technology plays a vital role in maintaining comfortable
indoor environments, especially in regions with hot and humid climates. Understanding
the principles, types, and innovations in air conditioning systems is essential for
optimizing their performance, energy efficiency, and environmental impact. As the
industry continues to evolve, embracing sustainable practices and innovative
technologies will be crucial in shaping the future of heating and cooling systems.
Introduction: Heating and cooling systems are integral to modern living, ensuring
thermal comfort and indoor air quality in various environments. This report provides a
detailed overview of heating and cooling technologies, including air conditioning, shofaj
systems, ducted systems, radiators, and Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems. Each
system has unique characteristics, applications, and considerations for design and
implementation.
1. Air Conditioning Systems: Air conditioning is a cornerstone technology in modern
buildings, providing cooling and dehumidification to maintain comfortable indoor
environments. Key components include compressors, condensers, evaporators, and
refrigerants. Air conditioning systems can be categorized into central, split, window, and
portable types, each suitable for different applications and building sizes.
2. Shofaj Systems: Shofaj systems, also known as evaporative cooling systems, utilize
the principle of evaporative cooling to lower air temperatures. They are particularly
effective in dry climates and can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to
traditional air conditioning systems. Shofaj systems work by passing air through wetted
pads, causing water to evaporate and cool the air before circulating it indoors.
3. Ducted Systems: Ducted heating and cooling systems use a network of ducts to
distribute conditioned air throughout a building. These systems are often centralised
and can incorporate both heating and cooling functions. Ducts can be made of various
materials such as sheet metal, fiberglass, or flexible plastic. Proper design and insulation
of ductwork are critical to ensure efficient operation and minimal energy loss.
4. Radiator Systems: Radiator systems are a common form of heating in residential and
commercial buildings, particularly in colder climates. They consist of a network of pipes
filled with hot water or steam, which radiate heat into the surrounding space. Radiators
can be integrated with boilers or other heat sources and offer precise control over
indoor temperatures through thermostatic valves.
5. Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems: VRF systems are advanced air
conditioning systems that offer precise control over cooling and heating capacities in
different zones of a building. They use refrigerant as the cooling/heating medium and
employ variable-speed compressors to modulate capacity based on demand. VRF
systems offer flexibility, energy efficiency, and zoning capabilities, making them ideal for
buildings with diverse thermal loads and occupancy patterns.
6. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Considerations: Energy efficiency is a critical
factor in the design and operation of heating and cooling systems. Advancements in
technology, such as high-efficiency compressors, intelligent controls, and heat recovery
systems, contribute to reduced energy consumption and operating costs. Additionally,
the choice of refrigerants and insulation materials plays a significant role in mitigating
environmental impact and complying with regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse
gas emissions.
Conclusion: Heating and cooling systems are essential for maintaining comfortable and
healthy indoor environments in buildings. Understanding the various technologies
available, including air conditioning, shofaj, ducted systems, radiators, and VRF systems,
is crucial for selecting the most suitable solution for specific applications. Energy
efficiency, environmental considerations, and ongoing technological advancements will
continue to shape the future of heating and cooling systems, driving towards more
sustainable and efficient solutions.
You might also like
- Project Report of HvacDocument56 pagesProject Report of HvacPrince Syed83% (59)
- Thermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesFrom EverandThermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument15 pagesAir Conditioning Systemshrikant100% (25)
- Steam Engineering TutorialsDocument7 pagesSteam Engineering Tutorialslanikhil100% (1)
- Tappi TIP 0404-63 PDFDocument25 pagesTappi TIP 0404-63 PDFmd ibrahim100% (1)
- ABB - E-Houses ConceptsDocument2 pagesABB - E-Houses ConceptsRafael Silva AnastacioNo ratings yet
- F. Mechanical System - HandoutDocument28 pagesF. Mechanical System - HandoutMIKI RULOMANo ratings yet
- TypesDocument9 pagesTypesKarlo MalenicaNo ratings yet
- ChillerDocument3 pagesChillermaburaNo ratings yet
- Hvac 160820181216Document33 pagesHvac 160820181216mani aroraNo ratings yet
- Review of Heating, Ventilating, Air Conditioning, and Refrigerating SystemsDocument76 pagesReview of Heating, Ventilating, Air Conditioning, and Refrigerating SystemsDatu JonathanNo ratings yet
- HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING AssignmentDocument14 pagesHEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING AssignmentGriffNo ratings yet
- HVAC Training ReportDocument47 pagesHVAC Training ReportM samirNo ratings yet
- Week 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalDocument90 pagesWeek 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalaimanfznnnNo ratings yet
- Classification of Mechnical and Electrical Services in A BuildingDocument18 pagesClassification of Mechnical and Electrical Services in A BuildingJeenu ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Final Report Mini ProjectDocument26 pagesFinal Report Mini ProjectAmirul HasanNo ratings yet
- Project On ACDocument82 pagesProject On ACMahesh DondapatiNo ratings yet
- M1 Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesM1 Air Conditioningsopan saNo ratings yet
- HvacDocument7 pagesHvacfaheem momdNo ratings yet
- Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Heating Cooling System For HospitalDocument23 pagesSustainable and Energy-Efficient Heating Cooling System For HospitalRISHAB KABDI JAINNo ratings yet
- Air Handlers FinalDocument8 pagesAir Handlers FinalHeber MarinNo ratings yet
- Services NotesDocument21 pagesServices NotesAkankshaNo ratings yet
- CB, VAV, VRF, Fan Coils - A Comparison StudyDocument6 pagesCB, VAV, VRF, Fan Coils - A Comparison StudyprasathinusaNo ratings yet
- HVAC Course PDFDocument273 pagesHVAC Course PDFliliNo ratings yet
- Design Options For HVAC Distribution Systems R1Document68 pagesDesign Options For HVAC Distribution Systems R1ramon duldulaoNo ratings yet
- Advantage-Disadvantage VRFDocument13 pagesAdvantage-Disadvantage VRFRatnasariPurnadewi100% (3)
- Note 3Document2 pagesNote 3Deepankur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hvac AssignmentDocument8 pagesHvac AssignmentJospin MwemaNo ratings yet
- B037105018 PDFDocument14 pagesB037105018 PDFnavabnavab786No ratings yet
- Integration of Hvac SystemsDocument7 pagesIntegration of Hvac SystemsAnmol ChughNo ratings yet
- 05 Building Air Conditioning and Ventilation SystemDocument14 pages05 Building Air Conditioning and Ventilation SystemJocel SangalangNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning and Ventilation SystemDocument10 pagesAir Conditioning and Ventilation SystemMark justine david100% (2)
- Integration of HVAC SystemsDocument8 pagesIntegration of HVAC SystemsRiya Bansal0% (1)
- HVAC - Part-3Document55 pagesHVAC - Part-3ShubhaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning and Ventilation System: Batangas State UniversityDocument23 pagesAir Conditioning and Ventilation System: Batangas State UniversityRenee CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1. Role and Purpose of HVAC System in Everyday UseDocument6 pagesAssignment: 1. Role and Purpose of HVAC System in Everyday UseAswajith K BabuNo ratings yet
- RAC Blue Print ObjectivesDocument10 pagesRAC Blue Print Objectivesdawit solomonNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning IntroductionDocument347 pagesAir Conditioning IntroductionRathakrishnan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Mohammad Muawya Nouri HijaziNo ratings yet
- Climate Control ReportDocument9 pagesClimate Control ReportAbdul HannanNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Cooling SysDocument14 pagesHVAC - Cooling Sysknotship.comNo ratings yet
- Seminar On AC SystemDocument33 pagesSeminar On AC SystemJagadish SahuNo ratings yet
- Air Handling Unit: ComponentsDocument5 pagesAir Handling Unit: ComponentsHeber MarinNo ratings yet
- CTV046 HvacDocument21 pagesCTV046 Hvacbookslover1No ratings yet
- Types of Hvac SystemsDocument16 pagesTypes of Hvac SystemsVinita KumariNo ratings yet
- CTV003Document20 pagesCTV003Sujani MaarasingheNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning HistoryDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning HistoryJosue Carubio Ricalde Jr.No ratings yet
- Climate Control BuildingsDocument5 pagesClimate Control BuildingsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Seminar On AC System PDFDocument33 pagesSeminar On AC System PDFJagadish SahuNo ratings yet
- Air-Conditioning System DesignDocument42 pagesAir-Conditioning System DesignRaj Verma100% (2)
- Commercial HvacDocument118 pagesCommercial Hvacsasat1801No ratings yet
- Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning The Heart of Modern BuildingsDocument8 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air Conditioning The Heart of Modern Buildingsstynedale18No ratings yet
- Seminar On AC SystemDocument33 pagesSeminar On AC SystemHassan Elattar0% (1)
- Hvac and Air ConditioningDocument69 pagesHvac and Air ConditioningEtee AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Module1 - Basics of HVACDocument7 pagesModule1 - Basics of HVACanita shindeNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Ejectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid DynamicsFrom EverandEjectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Advances in Air Conditioning Technologies: Improving Energy EfficiencyFrom EverandAdvances in Air Conditioning Technologies: Improving Energy EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeFrom EverandSustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument2 pagesReviewone engNo ratings yet
- Ijiset V3 I7 61Document5 pagesIjiset V3 I7 61one engNo ratings yet
- Abstract 11111Document2 pagesAbstract 11111one engNo ratings yet
- 4 - Stability AnalysisDocument2 pages4 - Stability Analysisone engNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument12 pagesInternship Reportone engNo ratings yet
- Driven Piles in Sand: (Figure 10.7)Document5 pagesDriven Piles in Sand: (Figure 10.7)one engNo ratings yet
- Site InvestgationDocument11 pagesSite Investgationone engNo ratings yet
- 2 - Lateral Earth Pressure-2Document3 pages2 - Lateral Earth Pressure-2one engNo ratings yet
- 1 - Lateral Earth PressureDocument7 pages1 - Lateral Earth Pressureone engNo ratings yet
- 3-Type of Retaining WallsDocument3 pages3-Type of Retaining Wallsone engNo ratings yet
- Session 02 Assignment 02Document1 pageSession 02 Assignment 02one engNo ratings yet
- Efflorescence of The Brick: Materials TechnologyDocument6 pagesEfflorescence of The Brick: Materials Technologyone engNo ratings yet
- Session 02 ClassworkDocument1 pageSession 02 Classworkone engNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Exam - ADocument2 pagesMid-Term Exam - Aone engNo ratings yet
- Traffic Engineering: University of Duhok College of Engineering Civil Department Fourth Year Students 2019-2020Document24 pagesTraffic Engineering: University of Duhok College of Engineering Civil Department Fourth Year Students 2019-2020one engNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2019-2020 - A - WDocument2 pagesFinal Exam 2019-2020 - A - Wone engNo ratings yet
- 50TJM 60Hz PDC V3.0Document32 pages50TJM 60Hz PDC V3.0Ahmed ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Engineering & Machinery Corp. v. CA, G.R. No. 52267, January 24, 1996Document7 pagesEngineering & Machinery Corp. v. CA, G.R. No. 52267, January 24, 1996jbjacildoNo ratings yet
- AGCC-02 Vol-3 Functional ECS & TVS SpecificationsDocument870 pagesAGCC-02 Vol-3 Functional ECS & TVS SpecificationsAnkit TripathiNo ratings yet
- Fire Smoke Damper - June 2018 in PDFDocument14 pagesFire Smoke Damper - June 2018 in PDFirfanNo ratings yet
- Lennox G1d91bu g1d93bc G1d93bu Installation Owners ManualDocument27 pagesLennox G1d91bu g1d93bc G1d93bu Installation Owners ManualNelson FraserNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Rac Learning ModuleDocument222 pagesK To 12 Rac Learning ModuleMark MarasiganNo ratings yet
- ICS Catalogue - Parts & Upgrade EquipmentDocument62 pagesICS Catalogue - Parts & Upgrade Equipmentmrlc2000No ratings yet
- 12HF InstallManual Ver8 WebDocument6 pages12HF InstallManual Ver8 WebUmen AryanNo ratings yet
- Honeywell TH6210U2001 Install InstructionsDocument44 pagesHoneywell TH6210U2001 Install Instructionsdarwin jose palacioNo ratings yet
- MOC63u: Moisture Analyzer Instruction ManualDocument122 pagesMOC63u: Moisture Analyzer Instruction ManualGhulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- WarmTouch User Manual Wt5200 UsDocument34 pagesWarmTouch User Manual Wt5200 Usnobel0001No ratings yet
- Passive Solar Handbook PDFDocument298 pagesPassive Solar Handbook PDFFernando RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Handbook 2000 CHDocument12 pagesAshrae Handbook 2000 CHKazuto NakazatoNo ratings yet
- Sample Productivity ChartDocument8 pagesSample Productivity ChartArwinNo ratings yet
- R19 - Mech - VI - HVACR - Sample Question BankDocument6 pagesR19 - Mech - VI - HVACR - Sample Question BankSailee AcharekarNo ratings yet
- HVAC Flow Schematic DiagramDocument6 pagesHVAC Flow Schematic DiagramAdrian IrawanNo ratings yet
- Generadores de Aire Caliente ArcothermDocument64 pagesGeneradores de Aire Caliente ArcothermEduardo Aravena PulsarNo ratings yet
- ДСТУ EN 12101-8 2014 Системи протидимного захисту. Частина 8. Димові клапани (EN 12101-8 2011, IDT)Document41 pagesДСТУ EN 12101-8 2014 Системи протидимного захисту. Частина 8. Димові клапани (EN 12101-8 2011, IDT)РоманNo ratings yet
- Aiipl Brochure 1221Document12 pagesAiipl Brochure 1221SidhuRamNo ratings yet
- Car Key Memory Options PDFDocument12 pagesCar Key Memory Options PDFcork_ieNo ratings yet
- Ingersoll Rand Compressor Manual SS3L3Document36 pagesIngersoll Rand Compressor Manual SS3L3Castoriadis100% (2)
- Water-Cooled Screw Chiller - WZY SeriesDocument11 pagesWater-Cooled Screw Chiller - WZY SeriesAbdulSattar100% (1)
- 9 Gerbur Vinyl Click Herringbone BrochureDocument17 pages9 Gerbur Vinyl Click Herringbone BrochureLeyjan JacobNo ratings yet
- LG gr-g267tv SMDocument130 pagesLG gr-g267tv SMWILMARNo ratings yet
- Cooling Heating HandbookDocument170 pagesCooling Heating Handbookhmz_engineering87100% (2)
- Chapter V Overview of HVAC SystemsDocument21 pagesChapter V Overview of HVAC SystemsMiruts MeseleNo ratings yet
- Preservation Program Works For Outages From One Month To Several YearsDocument4 pagesPreservation Program Works For Outages From One Month To Several Yearse.vicente.caballeroNo ratings yet