Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q2L4 Society and Its Composition
Q2L4 Society and Its Composition
Uploaded by
Jennifer Raya-TalaugonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2L4 Society and Its Composition
Q2L4 Society and Its Composition
Uploaded by
Jennifer Raya-TalaugonCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
SCHOOLS DIVISION OFFICE OF BALANGA CITY
INTRODUCTION TO THE PHILOSOPHY OF THE HUMAN PERSON
2nd QUARTER
Quarter 2 || Lesson 4: The Human Person in Society
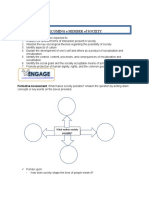
Society is an organized group of people whose members interact frequently and have a common
territory and culture. It was brought about by the human desire to relate with others. Society is
considered a product of deliberate actions by individuals who come together in pursuit of a
common goal.
Society is rooted in the concepts of the common good and general welfare, which refers to the
social conditions that enables human persons and groups to fulfill their goals and achieve well-
being.
Society is a product of a social contract. Social contract is an agreement among individuals to
sacrifice some of their wants and submit to a higher authority. There are various concepts that we
need to learn to fully grasp an understanding of the society and they are as follows;
1. Common Good – this refers to the social condition which enable persons and groups to
fulfill their goals and achieve perfection all together.
2. Social System – this is an organized and patterned set of relationship among individuals
and groups that compose a society.
3. Social Group – these are groups of individuals who have similar backgrounds and
perform similar roles in the society.
4. Social values – these are actions or things that are considered important by the society. It
is also defined as the set of moral principles defined by society dynamics, institutions,
traditions and cultural beliefs.
5. Social norms – these are set of traits and behaviors that society considers acceptable and
are encouraged and passed on others.
6. Laws – these are formal and stringent social norms that establish and define acceptable
behavior of citizens. Laws prescribe the consequences or penalties that will be imposed
on violators.
7. Folkways – these are the less formal norms that arise from tradition and does not result to
distinct punishment when violated.
PHILOSOPHICAL VIEW OF THE SOCIETY
1. Thomas Hobbes - “mankind is governed by desire which lead to conflict among individuals.”
2. John Locke - society is organized based on the “consent of the governed”.
3. John Rawls - humans naturally seek a just and fair society because of self-interest.
TYPES OF SOCIAL RELATIONS
1. PERSONAL SOCIAL RELATIONS. This refers to the interactions with others which are
based on a mutual regard for each other as persons. Hence, interactions are defined by
COOPERATION rather than COMPETITION. It emphasizes the preservation and
development of the mutual regard for each other wherein, the kind of interaction is
COMMUNICATIVE ACTION or intersubjective, which means, a manner of relating with
others as one’s equal, a fellow subject or a fellow person.
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
SCHOOLS DIVISION OFFICE OF BALANGA CITY
INTRODUCTION TO THE PHILOSOPHY OF THE HUMAN PERSON
2nd QUARTER
2. TRANSACTIONAL SOCIAL RELATIONS. This refers to the interactions which are
based on “a regard for others as a means for attaining one’s goal. In layman’s term, the
“other” is being used to attain one’s goals. It suspends the deeper reality that the “other” is a
person, not just a mere object for usage. Here, personal matters such as feelings and emotions
are put aside in the interactions and is very competitive. The kind of interaction with others is
STRATEGIC ACTION, which means, a manner of relating with others as an object or a
means for attaining one’s goal.
Activity No.
Directions: Answer the following questions concisely and correctly.
1. Differentiate and explain rationally each philosophical views of the society as given by the 3
renowned philosophers. Mention an instance or circumstance that may illustrate their
propositions.
PHILOSOPHER PHILOSOPHICAL VIEW OF THE INSTANCE OR CIRCUMSTANCE TO
SOCIETY (EXPLAIN BRIEFLY) ILLUSTRATE THE PROPOSITIONS
Thomas Hobbes
John Locke
John Rawls
2. Cite 3 circumstances or situational examples for each type of social relations.
Personal Social Relation
Situation 1:
Situation 2:
Situation 3:
Transactional Social Relation
Situation 1:
Situation 2:
Situation 3:
You might also like
- Let Review Notes in Building Bridges Across Social Science DisciplineDocument10 pagesLet Review Notes in Building Bridges Across Social Science DisciplineJerlyn Mae Sales Quiliope100% (1)
- The Role of Beliefs in Teacher Agency: A Critical AnalysisDocument9 pagesThe Role of Beliefs in Teacher Agency: A Critical AnalysisSapna Shyam JeetahNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 5 Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPDocument2 pagesQ2 Week 5 Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPTERENCE JADE BANGCONo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii - Social InteractionDocument16 pagesChapter Ii - Social InteractionPrincess Hailey BorlazaNo ratings yet
- Module-7 Philosophy Week-7Document6 pagesModule-7 Philosophy Week-7DeltaNo ratings yet
- What Is CommunityDocument7 pagesWhat Is Communityjohainabatuaan2005No ratings yet
- Group 3Document44 pagesGroup 3Shareeda RayosoNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module 6Document14 pagesUCSP Module 6reaeloisa.legiraldeNo ratings yet
- UCSP MOD 2 Lesson 2 3Document7 pagesUCSP MOD 2 Lesson 2 3Hennry WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - UCSPDocument21 pagesModule 4 - UCSPPaulo VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Social Science Theories of EducationDocument33 pagesGroup 1 Social Science Theories of EducationBernadette MirandaNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Session 7 PPT - Forms and Functions of SocializationDocument20 pagesUcsp Session 7 PPT - Forms and Functions of Socializationjohn russel p bacsa100% (1)
- Reviewer For UcspDocument6 pagesReviewer For Ucspagustizon02No ratings yet
- Three Social Theories - Dpe 102Document44 pagesThree Social Theories - Dpe 102JAYMAR BALLADARESNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Week 3 Lesson 1Document1 pageUcsp Week 3 Lesson 1Jonella PudaderaNo ratings yet
- Meaning: Definition, Scope, and Subject MatterDocument4 pagesMeaning: Definition, Scope, and Subject MatterRizwan AliNo ratings yet
- Rosemont Hills Montessori College: Lesson 1: CommunityDocument4 pagesRosemont Hills Montessori College: Lesson 1: CommunityQueenzel T. LawasNo ratings yet
- CESC and DIASS L1-L2Document8 pagesCESC and DIASS L1-L2febNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Philosophical Foundation in Social Work Unit 3 The Philosophical and Values Foundation in Social Work OutlineDocument6 pagesKnowledge and Philosophical Foundation in Social Work Unit 3 The Philosophical and Values Foundation in Social Work OutlineKendrick L. BuchanNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement Module 1 - Lesson 2Document8 pagesCommunity Engagement Module 1 - Lesson 2Jovan Salibay67% (3)
- G1 PresentationDocument20 pagesG1 PresentationLea Marie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Witsoc ReviewerDocument11 pagesWitsoc ReviewerDiana ParkerNo ratings yet
- Socialization: Quarter 1 - Module 5Document5 pagesSocialization: Quarter 1 - Module 5Johanna Gultiano100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Jimuel AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Lesson 1Document17 pagesModule 5 - Lesson 1coleni cflNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Week 2 Part 1Document59 pagesUcsp Week 2 Part 1Regor PaimanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument7 pagesModule 4 Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsJhes D. FelizarteNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledjuliannah maeryl orgasNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 St. Augustine Humanities and Social SciencesDocument28 pagesGrade 11 St. Augustine Humanities and Social SciencesJean Dhani AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Part 1 Definitions of CommunityDocument26 pagesLesson 2 Part 1 Definitions of CommunityFrance RebetaNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module 2Document28 pagesUCSP Module 2Clarissa CachoNo ratings yet
- A Level Sociology Chapter 1 NotesDocument5 pagesA Level Sociology Chapter 1 NotesMarium HasanNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document207 pagesPaper 2Bishnu Padhi100% (1)
- 6 Kingfisher and Skylark ST., Zabarte Subd., Brgy. Kaligayahan, Novaliches, Quezon CityDocument4 pages6 Kingfisher and Skylark ST., Zabarte Subd., Brgy. Kaligayahan, Novaliches, Quezon CityImyourbitchNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument7 pagesModule 2 Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsJhes D. FelizarteNo ratings yet
- Community Association Institutions SociologyDocument15 pagesCommunity Association Institutions SociologyDesi Boy0% (1)
- Soc Anthro PaperDocument5 pagesSoc Anthro PaperJanna HernandezNo ratings yet
- Social Science Theories and Their Implications To Education - 011140Document14 pagesSocial Science Theories and Their Implications To Education - 011140Janzen A. GabioNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1662297772350 6972182195761793320Document7 pagesOrca Share Media1662297772350 6972182195761793320Risavina Dorothy CondorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 The Human Person in SocietyDocument57 pagesLesson 7 The Human Person in SocietyKirl GilNo ratings yet
- Sociology Lec#4&5Document15 pagesSociology Lec#4&5Farhan MaryamNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDocument25 pagesBecoming A Member of SocietyKate KatNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 - Dominant Ideas and Approaches in The Social ScienceDocument15 pagesHandout 2 - Dominant Ideas and Approaches in The Social ScienceVictor Noel AlamisNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument33 pagesSodapdfPT MangilaNo ratings yet
- Discipline and Ideas in The Social SciencesDocument7 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in The Social SciencesAubrae Frances BannawiNo ratings yet
- Anthrop LatestDocument5 pagesAnthrop LatestangelicaaguelotanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document5 pagesModule 2balanopaulamae4No ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsAndrea IbañezNo ratings yet
- Midterms PointersDocument14 pagesMidterms PointersRhianne AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-The Human Person in SocietyDocument11 pagesChapter 7-The Human Person in SocietyElexis Castillo100% (1)
- UCSP Week 5Document6 pagesUCSP Week 5Zach BalballegoNo ratings yet
- Axr201 Lecture AxrDocument5 pagesAxr201 Lecture Axrogunshinaoluwaseun337No ratings yet
- Sociological Perspective BORROMEO AND SALVADORDocument23 pagesSociological Perspective BORROMEO AND SALVADORAlvin John SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Trust FormatDocument46 pagesTrust Formatjessicabrian7771No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4JayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Social Structure and Social InteractionDocument9 pagesChapter 4: Social Structure and Social InteractionMarc angelo LagazoNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Conceptual Fundamentals Of Political Sociology" By Robert Dowse & John Hughes: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Conceptual Fundamentals Of Political Sociology" By Robert Dowse & John Hughes: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Fundamental Problems Of The Sociological Theory" By John Rex: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Fundamental Problems Of The Sociological Theory" By John Rex: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- PR2 DLP Q1 W3Document3 pagesPR2 DLP Q1 W3Jennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Classes Suspended Due To Typhoon Classes Suspended Due To TyphoonDocument4 pagesClasses Suspended Due To Typhoon Classes Suspended Due To TyphoonJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Q2L3 IntersubjectivityDocument3 pagesQ2L3 IntersubjectivityJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Action Plan Mechanics MHPSSDocument3 pagesAction Plan Mechanics MHPSSJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Division Memorandum No. 265 2022 Submission of Data On Child Protection PolicyDocument5 pagesDivision Memorandum No. 265 2022 Submission of Data On Child Protection PolicyJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Q2L1 Week 1 - Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPDocument2 pagesQ2L1 Week 1 - Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPJennifer Raya-Talaugon100% (1)
- Q2L2 Week 2 - Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPDocument2 pagesQ2L2 Week 2 - Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- 5 Basic Facilitation SkillsDocument1 page5 Basic Facilitation SkillsJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Working As Service Crew While Studying On The Academic Performance of StudentsDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Working As Service Crew While Studying On The Academic Performance of StudentsJennifer Raya-Talaugon100% (1)
- Weekly Home Learning Plan-Q2-WEEK 1-4 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan-Q2-WEEK 1-4 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Q2L4 Week 4 - Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPDocument1 pageQ2L4 Week 4 - Learning Activity Sheet in IPHPJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Perspective of Senior High School Students On K To 12 Education Program StemB G4Document31 pagesPerspective of Senior High School Students On K To 12 Education Program StemB G4Jennifer Raya-Talaugon100% (1)
- Virgen Milagrosa University FoundationDocument9 pagesVirgen Milagrosa University FoundationJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan-Q1-WEEK 5-8 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan-Q1-WEEK 5-8 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan-Q2-WEEK 5-8 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan-Q2-WEEK 5-8 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan-Q1-WEEK 5-8 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan-Q1-WEEK 5-8 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan-Q1-WEEK 1-4 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan-Q1-WEEK 1-4 - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonJennifer Raya-TalaugonNo ratings yet
- The Religion of The Ancient Celts - 9781605061979Document345 pagesThe Religion of The Ancient Celts - 9781605061979null10100% (2)
- Bsim3v3 3.3 Manual PDFDocument200 pagesBsim3v3 3.3 Manual PDFfabbNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 2 On Clause of Concession No KeyDocument4 pagesPractice Test 2 On Clause of Concession No KeyWindy LeNo ratings yet
- Neuro BrandingDocument41 pagesNeuro BrandingZia AhmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Suturing and Wound Management: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas DiponegoroDocument77 pagesBasic Suturing and Wound Management: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Diponegoropranoto jaconNo ratings yet
- CACCIATORE, Et Al v. COUNTY OF BERGEN, Et Al - Document No. 31Document26 pagesCACCIATORE, Et Al v. COUNTY OF BERGEN, Et Al - Document No. 31Justia.comNo ratings yet
- 12 ConclusionDocument50 pages12 Conclusionriyamirza36365No ratings yet
- The Five Commandments of Infectious Disease ControlDocument2 pagesThe Five Commandments of Infectious Disease ControlCarol ReedNo ratings yet
- Essay On "All My Sons" by Arthur MillerDocument4 pagesEssay On "All My Sons" by Arthur MillerAnonymous BA5UcBONo ratings yet
- 20 Useful Phrasal VerbsDocument4 pages20 Useful Phrasal VerbsCamilaNo ratings yet
- Japanese - Verb - Conjugation (From Wikipedia) PDFDocument16 pagesJapanese - Verb - Conjugation (From Wikipedia) PDFYuki MarcelinNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Short Test 2A: GrammarDocument1 pageUnit 6 Short Test 2A: GrammarGordanaNo ratings yet
- Earl Rivera-Dolera - Profile and Blurb For CIADR - July 2020Document2 pagesEarl Rivera-Dolera - Profile and Blurb For CIADR - July 2020Md. Abdullah Al MasudNo ratings yet
- Legal Writing - Case Digest - Laurel Vs MisaDocument1 pageLegal Writing - Case Digest - Laurel Vs MisaLawrenceAlteza100% (1)
- (PDF) Natural Language Processing With Tensorflow: Teach Language To Machines Using Python'S Deep Learning Library by Thushan GanegedaraDocument3 pages(PDF) Natural Language Processing With Tensorflow: Teach Language To Machines Using Python'S Deep Learning Library by Thushan GanegedaraBenit JajaNo ratings yet
- Gödel's Incompleteness TheoremsDocument6 pagesGödel's Incompleteness TheoremsLucianoNo ratings yet
- PCR Types and Its ApplicationsDocument68 pagesPCR Types and Its ApplicationsShefali Pawar100% (1)
- Yessup Compulsory Grammar ExaminationDocument18 pagesYessup Compulsory Grammar ExaminationShoun TrrNo ratings yet
- Initial Diagnosis and Management of ComaDocument17 pagesInitial Diagnosis and Management of Comaguugle gogleNo ratings yet
- Britni Freiboth's Resume 2010Document2 pagesBritni Freiboth's Resume 2010api-51238443No ratings yet
- Jasleen-Resume Dec 62020Document3 pagesJasleen-Resume Dec 62020api-534110108No ratings yet
- A Study On Buying Behaviour of Indian Consumers Regarding ShoesDocument3 pagesA Study On Buying Behaviour of Indian Consumers Regarding ShoesKavita DasNo ratings yet
- Rohan ResumeDocument2 pagesRohan ResumeRohanNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument63 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseAli100% (1)
- Text ClassificationDocument32 pagesText ClassificationSamNeil70No ratings yet
- Master Munaqasyah 15 KolomDocument17 pagesMaster Munaqasyah 15 KolomAch. Fikri FausiNo ratings yet
- Uploading Catalogs For Iproc SetupDocument7 pagesUploading Catalogs For Iproc Setuphuda_10No ratings yet
- Bagua Zhuan Huan ZhangDocument6 pagesBagua Zhuan Huan Zhangjilongfeng666No ratings yet
- Clean Edge RazorDocument14 pagesClean Edge RazorOyedele AjagbeNo ratings yet