0% found this document useful (0 votes)
358 views10 pagesMethod Statement Crane Track Installation
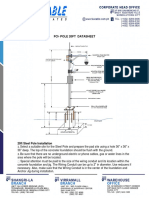
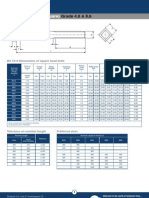
The document provides guidelines for installing crane rail tracks, including preparing the concrete foundation, installing soleplates, selecting the proper clips and holding down bolts based on load ratings, and ensuring safety during the process.
Uploaded by
munawarsyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
358 views10 pagesMethod Statement Crane Track Installation
The document provides guidelines for installing crane rail tracks, including preparing the concrete foundation, installing soleplates, selecting the proper clips and holding down bolts based on load ratings, and ensuring safety during the process.
Uploaded by
munawarsyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd