Inorganic chemistry - first stage Second semester
Some Important Carbon Compounds with Covalent Bonds
1. Methane
2. Carbon Dioxide
Carbon Dioxide has two covalent bonds between carbon and oxygen atoms and its structure can
easily be made using Lewis Dot methods. Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell
whereas oxygen has six electrons in its outermost shell, now carbon needs four electrons and
oxygen needs two electrons to complete their octet. So carbon shares two electrons with both
the oxygen atoms and hence all three atoms (One carbon atom and two oxygen atoms) achieve
their stable configuration and thus, CO2 is formed.
Properties of Covalent Bond
If sharing a single electron pair between atoms does not satisfy an atom’s normal valence, the
atoms may share more than one electron pair between them. Covalent bonds have the following
properties:
• The formation of new electrons is not the result of covalent bonding. The bond only
connects them.
• They are extremely strong chemical bonds that exist between atoms.
• Covalent bonds rarely break on their own after they are formed.
• Covalent bonds are directional in the sense that the atoms that are bonded have
distinct orientations relative to one another.
• Most covalently bonded compounds have relatively low melting and boiling points.
• Compounds with covalent bonds usually have lower enthalpies of vaporization and
fusion.
• Compounds formed by covalent bonding don’t conduct electricity due to the lack of
free electrons.
• Covalent compounds are not soluble in water.
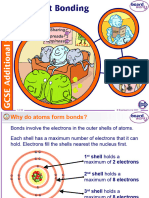
What is the Octet Rule?
Except for noble gases, all atoms have fewer than eight electrons in their valence shell which
are called valence electrons. In other words, these atoms’ valence shells do not have stable
configurations. As a result, they combine with one another or with other atoms to form stable
electronic configurations.
The tendency of atoms of different elements to achieve a stable configuration of eight electrons
in their valence shells is the cause of chemical combination, and the principle of achieving a
maximum of eight electrons in an atom’s valence shell is known as the octet rule.
|1
� Inorganic chemistry - first stage Second semester
Conditions for Writing the Lewis Dot Structures
Lewis Dot structure can easily explain the formation of the covalent bonds between two
molecules. Some points we must remember for drawing Lewis Dot Structures are,
• Covalent bonds are formed only when the electron pair is shared between two atoms.
• Two electrons or one electron pair constitute a single covalent bond in which each
atom shares one electron.
• The sharing between atoms occurs to satisfy the Octet state of the Valence Shell.
Octet rule states that an element’s stability is achieved only when it has 8 electrons in
its outermost shell (except for the hydrogen atom which achieves its stability with 2
electrons in its outermost shell)
For Example, In the formation of an H2O molecule Hydrogen atom has one electron in its
outermost shell and oxygen has six electrons in its outermost shell when two electrons of
oxygen form a bond with two hydrogen atoms its octet is completed. Similarly, the stability of
Hydrogen atoms is also achieved.
Types of Covalent Bonds:
Depending upon the number of shared electron pairs, the covalent bond can be classified
into
• Single Covalent Bonds
• Double Covalent Bonds
• Triple Covalent Bonds.
Single Bonds
When only one pair of electrons is shared by the two participating atoms, a single bond is
formed. It is denoted by a single dash (-). Despite having a lower density and being weaker than
a double or triple bond, this type of covalent bond is the most stable.
For example, an HCl molecule contains one Hydrogen atom with one valence electron and one
Chlorine atom with seven valence electrons. In this case, hydrogen and chlorine form a single
bond by sharing one electron.
|2
� Inorganic chemistry - first stage Second semester
Double Bonds
When two pairs of electrons are shared by two participating atoms, a double bond is formed.
It’s denoted by two dashes (=). Although double covalent bonds are much stronger than single
bonds, they are also less stable.
One carbon atom has six valence electrons and two oxygen atoms have four valence electrons
in a carbon dioxide molecule, for example, Carbon shares two of its valence electrons with one
oxygen atom and two with another oxygen atom to complete its octet. Because each oxygen
atom shares two electrons with carbon, CO2 contains two double bonds.;
Oxygen-Molecule: Each oxygen atom in the formation of the oxygen molecule has six
electrons in its valence shell. To complete their octet, each atom requires two more electrons.
As a result, the atoms share two electrons to form the oxygen molecule. Because two electron
pairs are shared, the two oxygen atoms form a double bond.
Triple Bond
When three pairs of electrons are shared by two participating atoms, a triple bond is formed.
Triple covalent bonds are the least stable type of covalent bond and are represented by three
dashes.
In the formation of a nitrogen molecule, for example, each nitrogen atom with five valence
electrons contributes three electrons to form three electron pairs for sharing. As a result, a triple
bond forms between the two nitrogen atoms.
|3
� Inorganic chemistry - first stage Second semester
Polarization of Covalent Bonds
Covalent (sigma) Bonds also show some properties of electrovalent bonds this is achieved as
the electron cloud between the two atoms in the sigma bond shifts towards one atom due to the
difference in their electronegativity and the atom which attracts the electron cloud attains a
partial negative charge and the other atom achieved a partial negative charge. Thus, due to these
charges polarization happens and this results in the Polarization of Covalent Bonds
For example, the sigma (covalent bond) in HCl is a polar covalent bond as Chlorine (Cl) has a
higher electronegativity than Hydrogen(H). So the electron charge shifts towards Chlorine and
it attains a partial negative charge. Similarly, Hydrogen attains a partial positive charge.
Polar Covalent Bond
This type of covalent bond exists when the electronegativity of combining atoms differs,
resulting in unequal electron sharing. Electrons will be drawn to more electronegative atoms.
The atoms’ electronegative difference is greater than zero but less than 2.
As a result, the shared electron pair will be closer to that atom. For example, consider
molecules that form hydrogen bonds due to an unbalanced electrostatic potential. The hydrogen
atom in this case interacts with electronegative fluorine, hydrogen, or oxygen.
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
This type of covalent bond is formed when two atoms share an equal number of electrons. The
difference in electronegativity between two atoms is zero.
It occurs whenever the atoms combined have a similar electron affinity. Nonpolar Covalent
Bonds, for example, can be found in gas molecules such as hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, and so
on.
Coordinate Covalent Bond
Coordinated or Dative Covalent Bond, this type of bond occurs when one of the atoms in the
bond provides electrons for sharing. This is accomplished through the reaction of ammonia and
boron trifluoride. Nitrogen has two free electrons, whereas boron lacks electrons. They
complete their last shell with eight electrons by combining nitrogen and boron.
|4
� Inorganic chemistry - first stage Second semester
Difference between Ionic and Covalent Bond
The major differences between Ionic Bonds and Covalent Bonds are discussed in the table
given below,
Covalent Bond Ionic Bond
A covalent bond is formed when two similar This type of bond is formed when a metal
electronegative nonmetals come together. and a non-metal combine.
Bonds formed by covalent bonding have a distinct shape. No definite shape
While Ionic Bond has high melting and
Covalent Bond has low melting and boiling point.
boiling point.
They have low polarity. They have high polarity.
The compounds formed by the covalent bond are more The compounds formed by the ionic bond
flammable. are less flammable.
They are in the liquid or gaseous state at room
They are in a solid state.
temperature.
e.g. HCl, etc. e.g. NaCl, etc.
|5
� Inorganic chemistry - first stage Second semester
H.W.
Q1: What are the total number of covalent bonds in CH4 (methane)?
Q2: Which molecule contains both polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
Q3: Draw the Lewis structures of the following molecules.
1. SO3
2. SF6
3. AlCl3
4. N2O
|6