0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pages8esm 1 27
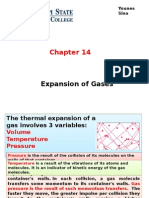
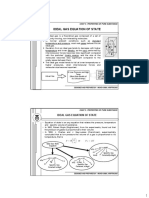
A gas undergoes a polytropic process where the relationship between pressure and specific volume is defined as pv^0.5 = constant. Starting with an initial pressure of 250 kPa and a specific volume of 0.5 m^3/kg, the final specific volume is calculated to be 3.125 m^3/kg at a pressure of 100 kPa. The process is plotted on a pressure versus specific volume graph, illustrating the decrease in pressure as the specific volume increases.
Uploaded by
alexsanderf147Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pages8esm 1 27
A gas undergoes a polytropic process where the relationship between pressure and specific volume is defined as pv^0.5 = constant. Starting with an initial pressure of 250 kPa and a specific volume of 0.5 m^3/kg, the final specific volume is calculated to be 3.125 m^3/kg at a pressure of 100 kPa. The process is plotted on a pressure versus specific volume graph, illustrating the decrease in pressure as the specific volume increases.
Uploaded by
alexsanderf147Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd